A hot top and cold bottom of a car radiator is a normal condition only for cold engine after launch. If the engine has been running for several minutes, during which the coolant temperature has already reached 80–90 degrees (depending on the model), and the upper radiator pipe is hot and the lower one is cold, this is sign of trouble in the cooling system. However, there are exceptions to this rule.
The main reasons why the lower radiator hose is cold after warming up are a malfunction of the thermostat or pump , or a clogged radiator . This article will tell you how to determine the specific cause of the problem and what to do in this case.
Why is the lower radiator hose cold and the upper hose hot?
- 138 6 116k
- 263 5 272k
A hot top and cold bottom of a car radiator is a normal condition only for an unheated engine after starting. If the engine has been running for several minutes, during which the coolant temperature has already reached 80–90 degrees (depending on the model), and the upper radiator pipe is hot and the lower one is cold, this is a sign of a problem in the cooling system.
However, there are exceptions to this rule. The main reasons why the lower radiator hose is cold after warming up are a malfunction of the thermostat or pump , or a clogged radiator . This article will tell you how to determine the specific cause of the problem and what to do in this case.
The engine does not reach operating temperature
You can monitor the temperature readings of the power unit directly from inside the car. The dashboard of all modern cars has a small information field, usually round or semicircular in shape, showing the driver the coolant temperature readings. This is the device that gives an idea of the temperature conditions in which the engine is operating at a given time.
If the temperature gauge does not reach 90 degrees during a long trip, you should seriously think about finding the cause of the deviation from the normal operation of the power unit. It is not recommended to delay its diagnosis, because prolonged operation of the motor in this mode will lead to wear of its internal components.
The fact is that the electronic control unit, which is popularly called the “brains” of the car, recognizes an engine that has not reached the nominal temperature as cold, and therefore the fuel system injects an over-enriched mixture.
Working in this mode leads to heavy carbon deposits on the spark plugs and, accordingly, on the internal elements of the engine, which in the future will lead to the need for a major engine overhaul.
How does the engine warm up?
Each serviceable unit has a different warm-up time. It is influenced by:
- degree of forcing;
- engine type: diesel or gasoline;
- cooling system condition;
- stove operation;
- quality of antifreeze or antifreeze;
- outside air temperature;
- type and viscosity of engine oil.
The characteristics of the oil are rarely taken into account, but experts believe that this is necessary. Various friction reducing additives and the base stock, synthetic or semi-synthetic, affect the performance in the range of 5–7 degrees. Thus, the engine will heat up faster with thinner synthetic oil.
The engine temperature gauge does not rise often due to a malfunction of the thermostat.
It is with this unit that the system check always begins if the engine takes a long time to warm up to operating temperature.
Principle of operation
Coolant enters the radiator through the thermostat. This is a large circle of fluid circulation. The thermostat usually opens at a temperature of 100 degrees Celsius. If the temperature has not reached this limit, then the liquid moves in a small circle. A thermostat malfunction is manifested by improper opening of the valves.
When the thermostat is closed, the engine overheats, and a constantly open one leads to low temperatures, since the liquid will only flow in a large circle.
Due to irregular changes of antifreeze or antifreeze, use of running water or mixing of coolants, various deposits in the form of scale may accumulate in the system. In this case, the thermostat will inevitably jam in one of its positions.
It is important to know
Beginners often make the mistake of believing that the lower pipe should never be cold, and they begin to sound the alarm.
(especially useful during winter): Drive the car into the garage. Let the engine run for 10-20 minutes so that this same pipe has time to heat up, and only then draw your conclusions. The fact is that due to the lack of heat in the cooling system (cold season), the thermostat keeps a large circulation circle closed. If the heater is on, it will prevent the thermostat from opening. Therefore, it must be turned off while the engine is warming up. If after this the lower pipe is cold, there is a problem.
Dirty radiator
The main reason for this, according to most experts, is a clogged radiator
. Over time, this important element of the cooling system becomes clogged with rust residue, dust, leaves and other debris. The location of the radiator is in front of the car. So, no matter what happens, it gets inside. Ultimately, all this leads to problems.
Since this reason is the most important, below is a method on how to clean a radiator. In addition, proper care of the radiator and its regular maintenance ensures the normal operation of the entire cooling system.
Coolant replacement
: Often, when replacing the coolant, beginners make a mistake and then complain about a cold pipe. This concerns a situation where the radiator itself is freed from old fluid, but the tank is forgotten. As a result, this affects the entire cooling system. It starts to act up and diagnostics give no clue.
Causes of poor coolant circulation
According to the above diagram, the reason that the lower radiator pipe in the VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115 remains cold is the lack of fluid circulation in a large circle of the system. Note that the radiator is the main cooling element. Therefore, the upper pipe through which the liquid enters the heat exchanger will be hotter than the lower one, even if the liquid circulates correctly.
Possible causes of stagnation in the cooling system:
- radiator clogged;
- non-working thermostat;
- airlock;
- pump breakdown.
Any intervention in the engine cooling system requires subsequent flushing of the ODS and replacement of the coolant. Poor quality coolant cannot cope with cooling the engine and can cause a blockage in the system.
Operating principle of a car heater
Why the radiator fan on the VAZ-2114 does not turn off: signs, causes and solutions
If the car heater “refuses” to blow warm air, then, of course, the interior will be uncomfortable and unpleasant, especially in inclement, cool weather. Having understood the principle of operation of the heater for the VAZ-2109 injector or carburetor, you can set up the operation of this device quite easily. A car heater stove can be considered a very ordinary heating device called a heat exchanger. The heating system is connected through a special tap to the system that is responsible for cooling the engine. When you turn on the stove, a special tap automatically opens, which allows cooling liquid to flow into the radiator located in the heating system. The liquid entering the radiator pipes is cooled, which leads to heat entering the cabin. The car heater is equipped with a fan that can operate in three modes. By choosing one mode or another, the driver can independently control the flow of warm air.
Removing the air lock
Signs of the formation of an air lock in the cooling system are rapid warming up of the car to high temperatures and poor performance of the interior heater. This can be especially easy to notice in winter. The reasons for the appearance of an air lock are different:
- incorrect filling of coolant;
- engine overheating;
- depressurization of the system;
- damage to some parts, etc.
If, during the inspection, leakage of antifreeze (antifreeze) is detected in the system, traces of coolant on the engine or other places, the causes of the leak should be eliminated. Often depressurization occurs due to poor tightening of clamps on pipes and hoses. They need to be tightened up. Any deformed or faulty parts found should be replaced.
There are several ways to remove air pockets. The easiest one is to drive up a steep hill with your face up. Unscrew the radiator and expansion tank caps. Let the car warm up for 10-15 minutes. Then release the gas a little and fill the system with coolant to the required level. Continue until bubbles stop appearing.
In VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115 cars, airing is rare. The cause of similar symptoms may be clogged hoses or radiator.
Filling with new coolant Kalina
The installation of new pipes is complete. Now the most interesting part is that you need to fill in new antifreeze. Don't forget to tighten the bolts from the drain holes back. I use Felix Green G11. To avoid the occurrence of a large number of air pockets, before filling in the coolant, I removed one hose from the throttle heating - the highest point of the cooling system. During the process of filling the system, air could be heard escaping. Out of 10 kg of antifreeze, about 2 liters remain in the canister.
I filled it up to the MAX mark on the expansion tank and put the hose from the throttle back in place. Now you can try to start the engine and see what happens. Before this, of course, you need to put in place the ignition module and the air filter along with the mass air flow sensor and the adsorber valve.
After the first start, the engine heated up to 120 degrees, but the radiator remained cold. I waited about 10 minutes until the engine cooled down and SLOWLY unscrewed the cap from the expansion tank, releasing the pressure, and then unscrewed it completely. At that moment I heard a gurgling sound - excess air was coming out. Some fluid has leaked into the system. I added new fluid to the reservoir and started the engine again. This time everything worked as it should - the radiator warmed up, the fan turned on, the stove was heating, the temperature stayed around 90º.
And on this positive note, the procedure for replacing the pipes on Kalina, as well as the thermostat and antifreeze, can be considered completed.
Cooling system hoses are inflated
First things first: Passat car 1995, ADZ engine - 1.8l. How it started: antifreeze began to leak from the gap between the tee (which has a temperature sensor) and the engine. Because it was minus 30-40 outside and there was no desire to climb, I just added antifreeze as needed. I didn’t pay attention to the pipes and others (if there is a leak, you first need to seal it, and only then look further) Now it’s warmer and on Sunday I fixed all the leaks (I found 2 more).
The problem is this: the hoses on the radiator inflate and antifreeze is forced from the expansion tank into. I think the cooling system. What I have already done (except for eliminating the leak): - I made sure that the fan on the radiator is working and it seems that the thermostat in the engine is also alive. I checked it this way: I started the cold engine and checked the temperature of the radiator with my hand. At the beginning, only the top became warmer (the bottom was cold, that is, there was a temperature difference and that meant the thermostat was closed). Using the temperature sensor on the dashboard, I waited for the temperature to be approximately 90 degrees and touched the radiator - it was equally hot from the top and bottom and on the sides - in general, it was hot everywhere. So the thermostat opened. I sat down again and pressed the gas, like warming it up (it’s like minus 10 outside) for about . (but less than 95) degrees the fan turned on and quickly cooled everything down to less than 90. - I tried to expel the air from the stove. I don’t know the technology for passats, so I did it as I once did on the figure eight - I sharply squeezed the lower pipe with my hand (like creating pressure). I tried to drive it out by starting the engine with the cap on the expansion tank open. In general, I don’t know if I kicked it out or not, but the stove heats up like crazy. At the same time I noticed this thing - antifreeze is constantly being released into the reservoir through the upper pipe (thin). I called my mechanic and outlined the problem, but there were no ideas. I read the forum - I really didn’t find anything (except maybe change the cylinder head gasket - maybe gases are breaking into the cooling system. But there is no oil or foreign smell in the coolant.) I’ll take off the spark plugs at lunchtime and see what kind of carbon deposits are on them.) A month ago the changers were black, like rich mixture, but this is understandable - it’s still minus 40, idling for 6-8 hours, starting cold, etc.) In general, I don’t know what to do next :-(((Help with advice.
Thermostat
The problem may also be related to the thermostat. This device is small in size and has the ability to block coolant. As a result, problems occur, including those related to the cold pipe.
By the way, the problem with the thermostat also affects the upper pipe. It can also be cold, but the bottom one, on the contrary, can be hot. All this taken together cannot in any way indicate the normal operation of the entire cooling system.
Drain the liquid from the thermostat, loosen its bolts and remove the device.
As a result, we gave three main reasons why this happens. Thus, having found out why the lower radiator pipe is cold, we draw the appropriate conclusions and act according to the situation.
Greetings to all readers on the RtiIvaz.ru blog. The article examines all VAZ radiator pipes that exist today and are used in Lada cars ever produced by the plant.
In any modern car that has a liquid cooling system, all kinds of pipes are used to connect the elements of the system. When operating a car, special attention should be paid to them, since if not noticed in time, a defect that appears can lead to serious consequences for the engine of your car.
From my many years of experience, I can conclude that attention should be paid not only to the pipes themselves, but also to the clamps that serve as a guarantor of the connection. There are cases when a clamp that is not tightened or has come loose ultimately leads to a major overhaul of the engine.
To make it easier for you to navigate the vast “sea” of today’s spare parts, I offer you this review article, which shows everything in detail. For a more complete overview, all presented materials have design numbers and visual photographs.
We start the review with classic models and present the radiator pipes of the VAZ 2101-2105 cooling system, used with a copper radiator, which have a number of advantages over the aluminum radiators used today, namely: the possibility of subsequent repairs, higher heat capacity, longer service life.
The pipes for Lada 2101-2105 cars are presented in the amount of 4 pieces. The upper supply pipe (on the right in the photograph, see further at the end of the article) has a design number: VAZ 2105-1303025 1-one; outlet sleeve (left) 2101-1303010 1-one; thermostat bypass pipe (corner in the middle) 2101-1303090 1-one also coupling connecting the thermostat and water pump (short in the middle) 2105-1303092 1-one piece.
The pipes of the copper radiator of the VAZ differ from the aluminum ones in their size; they have lower “discharge” hoses that are different in shape.
I advise you to pay special attention to the lower outlet pipe during installation. The lower fastening clamp is made technologically in a very inaccessible place and it is very difficult to make a high-quality tightening, which very often causes leakage. In this case, I advise you to completely remove the radiator and assemble the unit separately.
Removal takes no more than 10-15 minutes and will guarantee a reliable tightening. In this case, assemble all the pipes together with the thermostat in place except the upper one and install it in this form on the car. Since they are made of rubber and bend easily, installing the assembled unit is not difficult.
Next, we will consider a set of aluminum radiator pipes for the VAZ classic 2101-2107, also consisting of 4 hoses. The longest one on the far right in the photo is the top one (inlet), with a small angle of inclination the bottom one (outlet), the smallest one (the short one) goes to the thermostat, with an angle of ninety degrees (corner) the one on the far left in the photo goes to the pump.
Design numbers: VAZ 2105—1303025-10 (aluminum upper inlet pipe) 1 piece. 2105-1303010-10 (aluminum bottom outlet pipe) 1 piece. 2105-1303092 (coupling for connecting thermostat and water pump) 1 piece. 2101-1303090 thermostat bypass pipe (angle) 1 piece.
Next comes a set of radiator pipes for VAZ front-wheel drive models and we begin the review from the most common of them, Lada 2109, to the main radiator of the carburetor engine cooling system.
The set of pipes consists of four pieces: the upper inlet (wave) in the middle, see photos, the bottom outlet on the left, see photo, also two short ones (short ones), located on the right, see photos, connecting pipes for the thermostat and the water pump.
Design numbers of the upper supply pipes 2108-1303025 1-one; lower outlet 2108-1303010 1-one; connecting couplings for thermostat and water pump 2108-1303092 2 pieces. The pipes of a carburetor engine differ from the pipes of an injection engine and will be considered separately.
The Lada 2110 car has an injection engine. The set consists of four hoses, and have the following design numbers: upper radiator inlet pipe (in the middle of the photo) VAZ-2110-130302525 1-one and lower radiator outlet pipe (from the left in the photo) 2110-130302510 1-one, and two short thermostat and water pump couplings (on the right in the photo) 2110-1303092 2 pieces.
The upper inlet brings cooled liquid to the radiator at the top, and the lower outlet takes the heated coolant to the bottom of the radiator engine, as happens on most Lada cars.
The VAZ -2115 radiator kit includes three pipes. Design numbers: inlet pipe (on the left in the photo); 21082-1303025 1-one, outlet (in the middle of the photo) 21082-1303010 1-one, connecting pipes for the thermostat and water pump (on the right in the photo) 2109-1303093-01 1-one.
The smallest representative of the VAZ Oka family - 1111 has not been forgotten. The set of small car pipes consists of four hoses: design numbers of the outlet (from the left in the photo) 1111-1303010 1-one; supply (in the middle of the photo) 1111-1303090 1-one; coupling (short) 1111-1303092 1 piece; 2101-1303090 thermostat bypass pipe (angle) one.
And we complete the selection by showing the radiator cooling system pipes for modern classics equipped with an injector. Equipment: VAZ-21073 injection engine.
The upper supply hose (on the left in the photo) has design number VAZ-21073-1303025 1-one; lower outlet pipe 2105-1303010-10 1-one; 2101-1303090 thermostat bypass pipe (angle) one and 2105-1303092 coupling connecting thermostat also water pump 1 piece.
Additionally presented at the end of the article are the filler necks of the VAZ 2110 tank, which is compatible with the entire family of tens, and is slightly different in size from the tank neck of the Lada 2108, we are mutually interchangeable and then we see a picture of the long tank neck of the car 21099 of the family of nines and fourteens.
Copper radiator cooling hoses 2101-2107
Copper radiator cooling system pipes:
The radiator pipe of the VAZ 2101-2105 cooling system of the copper radiator consists of four pipes.
They have design numbers:
- Outlet pipe (number 1 on the left) 2101-1303010 1 piece.
- Thermostat bypass pipe (in the middle is corner number 2) 2101-1303090 1 piece.
- Connecting coupling for the thermostat and water pump (short one in the middle, number 3) 2105-1303092 1 piece.
- Upper pipe supplying VAZ 2105-1303025 1 piece (on the right in the photo under number 4).
The pipes of a copper radiator differ from those of an aluminum radiator in their sizes and the lower “discharge” sleeves are different in shape.
Auto 2101-2107 top view
Side view of the aluminum radiator VAZ 2101-2107
Let's look at the aluminum radiator pipes of the Lada 2101-2107. They are installed on Lada 2101-2107 cars, which have an aluminum radiator. The kit consists of four pipes. The longest one on the far right, see photos, is called the top “supply”, with a small angle of inclination, the bottom “discharge”, the smallest (short) goes to the thermostat and the pipe with an angle of ninety degrees (corner) on the far left, see photos, goes to the pump.
- 2101-1303090 thermostat bypass pipe (angle number 1) 1 piece.
- 2105-1303092 (coupling of the connecting thermostat and water pump number 2) 1 piece.
- 2105-1303010-10 (aluminum radiator outlet pipe, lower number 3) 1 piece.
- VAZ 2105—1303025-10 (supply pipe of the upper aluminum radiator, number 4) 1 piece.
All about the cooling system pipe of the Lada VAZ 2105 aluminum radiator.
Next time we will get acquainted with the hoses of the cooling system of VAZ 2108-21099 carburetor engines.
Top view of VAZ 2109, carburetor engine
Let's look today at the radiator pipes of the Lada VAZ 2109 main radiator of the carburetor engine cooling system.
The set of pipes consists of four pipes of the upper “inlet” (wave) in the middle, see the photo, the lower “outlet” on the left in the photo and two short ones (short) on the right, see the photo, connecting hoses for the thermostat and the water pump.
- Radiator pipe VAZ lower outlet 2108-1303010 1 piece. (number 1).
- Radiator pipe VAZ upper inlet 2108-1303025 1 piece. (wave number 2, see figure).
- Connecting couplings for thermostat and water pump 2108-1303092 2 pieces. (short ones numbered 3 and 4).
I’ll also add that the radiator pipe of a VAZ carburetor engine differs from the pipe of an injection engine.
Next in the photo we will look at the pipe of the Lada 2110 car:
View of the pipe from the side of a VAZ 2110
Let's look at a set of pipes for the cooling system of a Lada 2110 injection engine. The kit consists of four hoses.
- Lower outlet pipe (from the left in the photo under number 1) 2110-130302510 1 piece.
- Upper supply pipe (in the middle of the photo, number 2) VAZ-2110-130302525 1 piece.
- Two short couplings connecting the thermostat and water pump (numbers 3 and 4 on the right in the photo) 2110-1303092 2 pieces.
The upper inlet hose supplies cooled liquid from the radiator from above, and the lower outlet hose removes heated coolant to the bottom of the engine, this happens in most VAZ cars.
Side view of car 2115
The VAZ-2115 radiator kit consists of three pieces.
Radiator hose design numbers:
- “Leading” (on the left of the photo under number 1) 21082-1303025 1 piece.
- “Discharge” (in the middle of photo no. 2) 21082-1303010 1 piece.
- Connecting pipe between thermostat and water pump (on the right, see photo number 3) 2109-1303093-01 1 piece.
Cooling system pipe of the small car Oka VAZ-1111. Consist of four radiator pipes.
- Outlet (from the left, see photo number 1) 1111-1303010 1 piece.
- Leading (see photo number 2 in the middle) 1111-1303090 1 piece.
- Connecting couplings (short number 3) 1111-1303092 1 piece.
- 2101-1303090 thermostat bypass pipe (angle number 4) 1 piece.
Nowadays, cars with carburetor engines are becoming history. In front of you is a photo of a VAZ-21073 injection engine pipe with an aluminum radiator.
VAZ 21073 injection
- Upper supply pipe (on the left, see photo number 1) VAZ-21073-1303025 1 piece.
- 2105-1303092 coupling connecting thermostat and water pump (number 2) 1 piece.
- Outlet pipe of the lower aluminum radiator (number 3): VAZ-2105-1303010-10 1 piece.
- VAZ-2101-1303090 thermostat bypass pipe (angle number 4) 1 piece.
Tank filler neck 2110
The filler neck of the tank of a VAZ 2110 car of the tenth family, it is similar to the tank neck pipe of the 2108, differs slightly in size and is interchangeable.
Filler neck of the tank VAZ 21099
Filler neck of the VAZ 21099 tank for cars of the nines and fourteeners family.
Heater hoses VAZ 2101 inlet hoses number 1 - 2101-8101200 and outlet “L-shaped” number 2 - 2101-8101204
Heater hoses VAZ 1111 Oka large inlet number 3 - 1111-8101202, middle outlet 2 - 2101-8101204 and small inlet number 1 - 1111-8101206
Heater hoses VAZ 2108 inlet “big goose” rear number 1 - 2108-8101206, heater outlet hose rear “small goose” 2 - 2108-8101208, heater outlet hose front “small inside the car” 3 - 2108-8101204, heater hose front inlet “large in the cabin” 4 - 2108-8101200
Heater hoses VAZ 2108 inlet “big goose” rear number 4 - 2114-8101206, heater outlet hose rear “small goose” 3 - 2114-8101208, front heater inlet hose “small in the cabin” 1 - 2114-8101200, heater outlet hose front “large inside the car” 2 - 2114-8101204
Heater inlet hoses “large” number 1 - 2111-8101200 and outlet “small” 2 - 2111-8101208
Heater hoses: outlet "Chevy Niva" number 1 - 2123-8101204 and supply 2 - 2123-8101200
Throttle carburetor heating hose 48 cm - 2112-1148038
Radiator steam exhaust pipe “antifreeze tenth” - 2110-1303095
Filling hose for the expansion tank cooling system - 21082-1303080
Cooling system filling hose “stick” - 2111-1303080
Lower crankcase exhaust ventilation hose “large breather” 2108-1014056-10
Lower crankcase exhaust ventilation hose “large breather” - 2112-1014056
Crankcase exhaust ventilation hose “breather Niva” - 2121-1014056
Exhaust pipe hose “snail 8 cells” - 2111-1148035-10
Exhaust pipe hose “snail 16 cl” - 2112-1148035-10
You can also check out other materials:
Sometimes, even experienced motorists wonder: why is the lower pipe on the VAZ 2114 cold? It is impossible to answer this question unequivocally; there are many reasons that lead to disturbances in the engine cooling system. One thing is clear: it is necessary to find out the cause of the breakdown and restore the system to avoid problems with the engine. Let's try to thoroughly understand everything.
Causes of poor coolant circulation
According to the above diagram, the reason that the lower radiator pipe in the VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115 remains cold is the lack of fluid circulation in a large circle of the system. Note that the radiator is the main cooling element. Therefore, the upper pipe through which the liquid enters the heat exchanger will be hotter than the lower one, even if the liquid circulates correctly.
Possible causes of stagnation in the cooling system:
- radiator clogged;
- non-working thermostat;
- airlock;
- pump breakdown.
Any intervention in the engine cooling system requires subsequent flushing of the ODS and replacement of the coolant. Poor quality coolant cannot cope with cooling the engine and can cause a blockage in the system.
Cleaning or replacing the radiator
The radiator, located in the front of the car, absorbs the main flow of dust and dirt. For its effective operation, timely prevention and cleaning is necessary. The radiator can become dirty both inside and outside.
An indicator of internal cleanliness is the condition of the coolant. Manufacturers recommend changing antifreeze every 75,000 km or every 5 years. However, a change in the color of the liquid, severe darkening, discoloration, or the presence of rust requires urgent replacement of the coolant. It is recommended to change antifreeze at least every 40,000 km.
To carry out internal cleaning of the cooling system of VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115, it is necessary to drain the liquid. Sequencing:
- open the expansion tank cap;
- place a container to drain the antifreeze;
- Unscrew the drain plug from the cylinder block;
- drain the refrigerant;
- unscrew the radiator drain plug (located at the lowest point);
- drain the remaining antifreeze (antifreeze);
- tighten all the plugs.
To clean, pour distilled water into the system and start the engine for about 20 minutes. Ordinary water contains many impurities and forms scale, so its use is undesirable. The liquid is drained several times until clean water flows out. This method is ineffective as it removes a small amount of deposits.
For more effective washing, it is advisable to use special chemical additives. The detergent components included in their composition allow you to dissolve deposits and remove various types of contaminants. The mixture of water and vinegar used by many motorists is less effective. It does not remove all deposits. After using chemicals, the cooling system is washed with distillate.
After cleaning the entire SOD of the VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115, an additional internal flushing of the radiator is carried out. To do this, you need to detach the hoses from the base and the upper and upper tank. Liquid is poured into the radiator through the upper pipe using a garden hose. Flushing is carried out until clean water flows from the lower pipe.
The removed radiator can be externally cleaned to remove dirt, insects, and sand from the cooler honeycomb. Cleaning is carried out with a soap solution or special devices that create a strong flow of water or air, for example a Karcher vacuum cleaner. The procedure should be carried out carefully so as not to bend the radiator honeycombs.
If damaged or heavily soiled, the radiator should be replaced.
Replacing the thermostat
If the thermostat valve does not operate correctly, the coolant does not circulate throughout the large circle of the ODS. The lower pipe remains cold even after the refrigerant is heated to 90°C. The top pipe may be hot due to steam escaping. The thermostat can also get stuck in the open position; in this case, the engine does not warm up to the required temperature or takes too long to warm up.
In preparation for replacing the device, it is necessary to drain the fluid from the system and remove the air filter. Then the radiator and fluid pump hoses are disconnected from the thermostat housing. After this, loosen the mounting bolts and remove the thermostat cover. The device is replaced with a working one. Attaching the thermostat is done in the reverse order.
These are the main reasons for the malfunction of the cooling system and the cold lower pipe of VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115 cars.
Many motorists ask us why the lower radiator pipe is cold? It is impossible to answer this question in one or more sentences. I had to write a whole article where everything was described in detail. You will find out what is the main reason for this, because with a heated engine this same pipe should not be cold. This situation indicates problems.
Why is the lower radiator pipe cold - a question that is asked not only by beginners, but sometimes also by experienced motorists. Let's try to give complete information.
The lower radiator hose is cold and the upper hose is hot, what is the reason?
, 05 Dec 2013 17:23
- Page 1 of 7
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Further
- »
- To reply, please log in to the forum first.
#1
- Omega waters
- 72 Posts:
- Gender: Man
- Vehicle characteristics: Opel Omega, 1992, gearbox-5, C20NE (without lambda)
- Name: Alexander
- Donetsk city
Hello everyone, OOA C20NE, my lower radiator pipe is always cold, while the top of the radiator and the pipe itself are hot, what could be the reason? Of course, I understand that this could be a plug or the thermostat is sticking, the lower radiator hose is cold, while on the tidy it’s 100-105 degrees, and when I turn on the heater (it’s blowing hot), the temperature in the cabin drops by 90 degrees throughout) so as not to boil the upper part The radiator is hot, air is expelled. What could this be? I replaced the thermostat, it didn't help! and one more thing I noticed is that there is no pressure in the system! The pipes are all soft, and when you try to unscrew the cap from the expansion tank with the engine turned off, no hissing occurs!
- Top
#2
- Gender: Man
- Vehicle characteristics: Opel Omega B, 1998, manual transmission, X20XEV
- Name: Vladimir
- City: Velikiye Luki
How's the pump doing? Have you tried bleeding the radiator? You can also check the opening thermostat in hot water, maybe it will.
- Top
#3
- Gender: Man
- Vehicle characteristics: Opel Omega, 1992, gearbox-5, C20NE (without lambda)
- Name: Alexander
- Donetsk city
Relays and fuses
A blown fuse is one of the most common stove malfunctions in a VAZ-2114. This reason is extremely simple, since it can be eliminated by every person who does not have the slightest idea about the structure of a car. However, this reason is also very unpleasant, since it is, firstly, necessary to establish the reason why the fuse blew, and secondly, not so easy. Typically, a blown fuse indicates a problem with the vehicle's electrical wiring.
What to do if the engine overheats
First of all, it should be remembered that if the overheating is short-term (for example, the temperature needle rises in a traffic jam), then you should observe whether the temperature will drop after you start driving (counter air flow appears) or as a result of turning on the radiator fan.
If the car was already in motion and the engine temperature reached a critical level, you should not immediately turn off the engine. Also, you should not try to cool the engine by pouring water on it from outside, pouring cold water into the radiator, etc. Such actions will lead to the need to repair the internal combustion engine, and it may be necessary to change the BC and cylinder head.
Next, you need to wait a few minutes, while simultaneously inspecting for obvious and strong signs of antifreeze/antifreeze leakage under the car or in the engine compartment. If no leaks are visible, but the temperature does not drop, the unit must be turned off.
Please note that you need to immediately turn off the engine when steam starts coming out from under the hood; traces of intense coolant leakage are clearly visible. In this case, the engine must be stopped, without expecting that turning on the stove will reduce the heating.
Stove motor failure
Of course, the stove motor, like, in fact, any other electrical part of the VAZ-2114, can burn out over time. However, before deciding to replace it, it is necessary to check the functionality of all fuses, the temperature mode switch, and the ignition relay. If all the above parts are in order, then the problem is still in the motor.
To replace it, you must first disassemble and then remove the entire dashboard, turn off the heater valve, and also drain the antifreeze or antifreeze. Next, we remove all the pipes, take out the old motor, and install a new one in its place. Once the functionality of the new heater has been verified, the system can be refilled with the fluid that was drained at the beginning of this process.
Why does the radiator pipe shrink and burst?
One of the dangerous manifestations of a malfunctioning cooling system is a violation of the geometry of the radiator pipes. Why is the situation dangerous if the inlet or outlet pipes of the radiator flatten when the engine has cooled down, and when warmed up they gradually return to their normal state? Why is this happening, can I solve the problem on my own?
About pressure in the cooling system
To effectively remove heat from the engine jacket, liquid cooling systems are hermetically sealed from the environment and can withstand pressure from 1.2 to 2 or more atmospheres. This is necessary to prevent the coolant from boiling when the temperature reaches 100°C. At elevated pressure, various brands of antifreeze and antifreeze can boil when heated to 107°C−120°C, and sometimes 150°C.
Technical means to increase pressure in the cooling system are not used. The required values are achieved due to a natural increase in the volume of heated liquid circulating in the “jacket” of a running engine. Excess pressure is released through the system expansion tank cap, equipped with special valves, in which a certain amount of air is always present.
Bends and cracks in radiator pipes
The excess air released during the expansion of antifreeze or antifreeze in the tank after stopping and cooling the engine is compensated from the atmosphere through the second check valve of the lid. If this does not happen, a vacuum is created in the tank, radiator, connecting pipes and engine jacket. The first to react to this by compression are the least durable elements of the system - the rubber radiator pipes.
The maximum possible value of negative (compared to atmospheric) coolant pressure depends on the temperature difference between the heated and cooled engine. It is no coincidence that motorists notice this problem in winter, when the temperature range is greatest. In this case, the pipes wear out quickly and, having lost their initial elasticity, can burst. The vehicle cannot be operated with such a malfunction.
Expansion tank cap: design features
In addition to the plastic body, threaded part and sealing gasket, the tank lid is equipped with two valves: inlet and outlet. Each of them is designed and must operate under certain conditions. The first opens at excess pressure - for example, 1.2 Bar. The second is needed to compensate for pressure when the antifreeze cools down. If this valve fails, a dangerous level of vacuum is created in the system.
The solution to the problem is to flush the valves or buy a new cap.
The metal parts of the valves may simply be clogged with dirt from the cooling system if it has not been flushed for a long time. In such cases, the problem can be temporarily eliminated by blowing and cleaning the lid valves. If there are repeated failures, you will have to start with a general flush of the entire cooling circuit. If the valve malfunction is due to corrosion of their metal elements, you should purchase a new cover.
How to identify a malfunction
In order to make sure that the radiator pipes are flattened precisely because of the strong vacuum in the cooling system, and the reservoir cap is to blame, it is enough to unscrew the latter a little (only on a cold engine). A characteristic whistle of incoming air will indicate a clogged or rusted check valve. If there is no whistle, you need to flush the entire system. In this case, it is better to start with the upper radiator pipe, which connects it to the expansion tank.
Why buying a new cover may not solve the problem
Unfortunately, the simplest part costing a few rubles does not always meet the requirements. The lid may not function due to a significant difference in pressure at which the valves installed in it open or close. You can check their serviceability and response threshold using a compressor for inflating tires, and adjust it by reducing the number of turns of the corresponding spring. Or simply buy and install a cover from another manufacturer.
What can be done?
If the car is not warming up well, you can inspect the thermostat yourself.
Checking the functionality of the thermostat
The design of the device implies sensitivity to changes in temperature. The pressure in the coolant system does not affect the restriction of antifreeze circulation through the small circuit, cylinder head and block cooling space. As the temperature difference between the engine and the environment increases, the thermostat gradually opens the coolant supply from the main radiator to the engine.
The same thing happens when the difference in indicators decreases. This process helps maintain and limit the temperature limit of the engine, as well as heat the interior of the car. To determine if the thermostat is working properly, you do not need to remove it.
You can detect a breakdown manually when starting the engine. When it has warmed up for 5 minutes, you can check the device.
Starting will cause coolant to circulate through the engine's cooling passages. Heating of the coolant begins in the engine and radiator of the car. The pipe going in the opposite direction from the radiator to the engine should not be hot. If this happens, then there is a problem with the thermostat.
Removing the air tube
The main reasons for poor heating in winter include air lock. It is useful for a car driver to have the knowledge and skills to remove air from the system. Its accumulation occurs at the highest point - the throttle assembly. From there you need to remove the air plug. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- Unscrew the filling cap on the engine, remove the screen and screw the cap into place to avoid contamination of the crankcase.
- Find 2 pipes, which are located side by side in the throttle assembly, and pull out 1 of them.
- Open the coolant expansion tank and cover it with a clean cloth.
- Blow slowly into the tank until antifreeze flows out of the hose.
- Put the tube back on and tighten the clamp quickly so that no air gets into the pipe.
This scheme is suitable for the VAZ 2114. When clogging of the cooling paths occurs frequently, check the entire system, which may be depressurized. If after these steps the engine temperature does not rise, then you need to look for another source of problems.
Engine insulation
By insulating the engine, you cannot get rid of all problems with warming up. If the engine is properly insulated, it will not require prolonged warming up during the day, and the coolant temperature will be normal. To insulate domestic equipment, heat-insulating material is installed between the radiator and the front grille. The motorist can use cardboard or buy special insulation.
In a purchased product, the padding consists of synthetic insulation covered with a leather substitute. It has the advantage of special holes that open when the temperature rises. Insulation can be achieved by installing a heat insulator under the hood. Special blankets have been developed for this purpose.
You can buy them or make them yourself from felt, mineral wool or other material. This type of thermal insulation helps prevent a layer of ice from freezing on the hood, which often happens in winter when snow falls on the car, melts and freezes. The heat insulator can be glued to the lower engine protection. In the future, it will need to be cleaned of dirt so that it does not get into the engine.
Thermostat for dummies - logbook Peugeot 308 Sport Back 2009 on DRIVE2
Anyone whose car doesn't heat up well and who has a problem with the thermostat is here for everyone. All the information in one place + express test of your thermostat.
I finally figured out how the thermostat should work correctly. The cornerstone in understanding the work was one trick, but more on that below. First, a little theory. All modern thermostats work on the same principle:
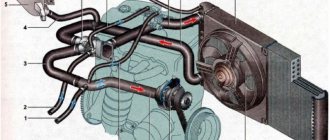
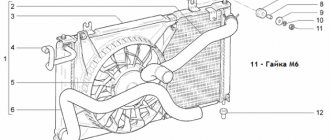
Engine cooling system diagram. top) small circle of circulation, bottom) large circle of circulation
1 - radiator; 2 — pipe for coolant circulation; 3 - expansion tank; 4 — thermostat; 5 - water pump; 6 — cylinder block cooling jacket; 7 — cooling jacket of the block head; 8 — heater radiator with electric fan; 9 — heater radiator valve; 10 — plug for draining coolant from the block; 11 — plug for draining coolant from the radiator; 12 - fan
The small circle performs the function of heating the engine. Those. After a cold start, the liquid begins to circulate in a small circle, only through the radiator of the interior heater. Each thermostat has its own large circle opening temperature. Approximately 90oC +/-. After heating to this temperature, the thermostat opens a large circle and the liquid begins to circulate in a large circle and cools in the engine radiator.
It is very simple to check the correct operation of the thermostat. Just look at how the coolant supply and outlet pipes of the engine radiator and the radiator itself heat up. Warm up the engine to approximately 70°C.
The top pipe should be warm and the bottom pipe should be cold. The radiator itself should also be cold (perhaps a little warm on top).
So, what is this cornerstone in understanding the operation of a thermostat? The large circle opening valve is located in the thermostat on the coolant outlet line from the engine radiator, and not before the supply, as one might logically assume. In theory, if you don’t need to supply coolant to the large circle, close the inlet. But no - the 308s have a closed exit))) I don’t know about other cars...
After the engine has reached a temperature of approximately 90°C, the thermostat opens (the outlet opens) and hot liquid begins to circulate through the engine radiator. Accordingly, the radiator and the lower hose from the radiator warm up. The top one will always be a little hotter than the bottom one.
Why does the upper pipe heat up after a cold start? The liquid that circulates in a small circle heats the liquid that is still standing in the radiator without moving. By regular mixing, because The entrance to the great circle is always open.
What problems could there be with the thermostat:
1. Stuck in open position. The coolant always flows in a large circle. In this case, at subzero temperatures the engine will take longer to warm up. While driving, especially at high speeds and at low engine speeds, the coolant temperature will drop. Example: We warmed up the car to 70 degrees. Go. We went out onto the highway. Engine temperature does not rise or drop. It turns out that the liquid is always cooled on the engine radiator. The thermostat cannot close the large circle when needed.
2. Stuck in the closed position. No liquid flows through the engine radiator. The engine will overheat. Most likely there will be an error in the bookmaker. The fan in front of the radiator will often turn on and run at the lowest speeds.
3. Stuck in the middle position. It will be something between 1 and 2.
4. It does not close completely. It is not jammed. It works, i.e. Opens a large outline. But he can’t close down completely. There are no errors in BC. This is my situation. Perhaps there are deposits in the thermostat, preventing it from closing or something else, I don’t know. But it works like this: after a cold start, the upper pipe, the radiator from top to bottom, and the lower pipe begin to gradually warm up. Those. Some of the liquid circulates in a large circle (the thermostat is slightly open), some in a small circle. By 70 degrees both pipes and the radiator are hot. Hence we have a longer engine warm-up. It's 70 degrees, let's go. If it’s cold outside and especially a headwind, the road is clear - you can drive for a very long time without warming up to 90. This part of the liquid that travels along the large circuit is cooled and merges with the rest of the liquid. Warming up faster in traffic jams. The engine radiator provides less cooling.
Now with a slight plus. The car warms up faster. It also reaches 90 faster. Perhaps there is simply a small gap in the large circle that remains when closed. If it were big, it definitely wouldn’t get warm.
Bottom line: I will change the thermostat. I already have it, I just need to choose the time. Dorestayl manual transmission 1336Z8
Dorestayl automatic transmission 1336Z6
I hope this post will help many. Especially the owners of pego-like ones. The thermostat is a known problem.
Special thanks to Gamodrilla - opened my eyes to the truth. And to everyone who took part in the discussion in the previous two parts about the thermostat))
Everyone +1 to knowledge. And thank you to me)))
The VAZ 2114 stove blows cold, what are the reasons?
Sometimes owners of VAZ-2114 cars have to deal with the problem of a non-working stove. In particular, such malfunctions cause problems in winter, since the car interior is not only unbearably cold, but also the windshield tends to become covered with a thin crust of ice, which significantly blocks the view. Therefore, if suddenly the stove in a VAZ-2114 stops working, you should immediately find the cause of the malfunction.
These problems can occur for a variety of reasons, ranging from worn-out cooling systems to electrical wiring problems. This article will discuss in detail all possible causes of stove malfunction, thanks to which it will be possible to find a solution to this problem.
It should be noted that symptoms of stove malfunction can be divided into two types:
- Cold air is blowing from the stove. Sometimes barely warm.
- The stove does not turn on at all or does not work in some individual modes.
Problem with switches
In order to check the serviceability of the stove switches, you need to acquire the simplest light bulb, 12 volts, with two wires. Next, remove the central part of the dashboard and perform the following steps:
- turn on the car ignition;
- connect the negative contact from the light bulb to ground with a wire;
- The positive contact is alternately connected to outputs 1-2-3 on an additional resistor.
If the light comes on during this procedure, this indicates that the switch is working. But if the light does not light up, most likely the fuse has blown or the circuit has broken.
Messages 11
1 Topic by Dmitriy.Bobilev 2015-07-07 21:11:34
- Dmitriy.Bobilev
- New member
- Inactive
- Registration: 2014-08-11
- Messages: 4 Thanks : 0
- Auto: 2110
Topic: All pipes are hot, but the engine is overheating
Hello everyone, in general, I have been fighting with CO for a long time, at the moment the symptoms are as follows: At idle, warming up goes as it should, it reaches about 88, the needle freezes, then it heats up like crazy, i.e. while you are driving normal, you just need to stand somewhere and let it work Carlson won’t be left behind later (that is, while you’re stuck in a traffic jam, it will turn on annoyingly every minute, maybe less! It’s worth driving 300-400 meters at speed and again in a circle) while the antifreeze on the small return circle from the larger radiator is normal, as soon as goes to a large trickle less and less, it may disappear altogether, the pump is luzar with an iron impeller, the thermostat is working, the radiator is hot evenly, the pipes are new, there is no air lock. I don’t even know what to look for, where to dig. It is advised to remove the gasket from the pump and place it on sealants in order to reduce the distance between the walls of the block and the impeller. Maybe the problem is still in the radiator? The pump is new.
By the way, the problem persists even in the rain and at an outside temperature of +10
2 Reply from Aleksandr.21124 2015-07-08 06:08:38 (2015-10-02 21:15:44 edited by Aleksandr.21124)
- Aleksandr.21124
- Brother-in-law
- Inactive
- Registration: 2014-08-11
- Messages: 392 Thanks : 169
- Car: VAZ 21124
Re: The pipes are all hot, but the engine is overheating
Dmitriy.Bobilev – Perhaps the radiator is clogged inside (if so, replacing it will help) and the radiator itself on the outside may be clogged with dirt (wash with a Karcher). And if you have a grille or mesh on the bumper below the state number (from flies and dirt), then remove it. And also turn off the two hoses that go to the throttle valve - this is a small circle of hot antifreeze (by turning off the car, it heats up less in hot weather). I switched it off myself and for a year now everything has been working fine both in winter and summer. This heating is not needed (it is removed during conversion) on the electronic throttle valve it is not present.
3 Reply from kuler_78 2015-07-08 07:53:38 (2015-07-08 08:03:29 edited by kuler_78)
- cooler_78
- Experienced
- Inactive
- Registration: 2014-10-22
- Messages: 142 Thanks : 57