The DPKV or crankshaft sensor for the Lada Granta is one of the most important measuring units in the entire car. Its purpose is to measure the rotation speed of the crankshaft, as well as its position. While reading the parameters, the sensor sends signals to the controller, which processes this data and issues the necessary impulses to the injectors.
The unit itself is quite reliable in operation and rarely fails. However, if its performance is impaired, this causes significant problems for the further operation of the engine. In addition, the product itself is non-repairable and therefore must be replaced with a new one.
What is DPKV?
DPKV is an electromagnetic device that determines the synchronization of the functioning of fuel injectors and the injection system. In a fuel injection system, this device is one of the most basic, since without it the system would be impossible to operate.
Failed DPKV
Failure of this sensor will eventually cause engine malfunctions. And although such breakdowns are not very common in practice, if you decide to go on a long journey, it is better to have a working device in stock. After all, if it breaks down, driving the car will be impossible.
The DPKV is located near the generator drive shaft using special fasteners. It should be installed with a small gap between the device itself and the gear shaft. Ideally, this gap should not exceed 1 mm, and it is set by selecting certain washers. The principle of operation of the regulator is to transmit certain readings, by which the controller will determine which specific cylinder the combustible mixture should be supplied to and at what interval.
This regulator is of the inductive type. DPKV reacts to the passage of shaft teeth.
Summarize
Taking into account the above, we can conclude that the crankshaft sensor is one of the most important elements in the overall electronic control circuit of the power unit. Failure of the DPKV will lead to a complete stop of the engine; malfunctions in its operation greatly complicate the operation of the vehicle or make driving a car almost impossible.
For this reason, it is recommended to have a spare crankshaft sensor in vehicles where owners regularly drive significant distances on the highway. It should also be added that the cost of a crankshaft sensor for most domestic and foreign cars is quite affordable.
As for checking and replacement, at the very beginning you should make sure that there are no foreign objects in the gap between the sensor and the synchronization disk, and that the gap itself is within acceptable limits. At the same time, it should be taken into account that the device may be serviceable and operational, but the cause of failure is dirt on the DPKV core.
How to identify faults?
Next, let's talk about signs of breakdown. What are the main symptoms of a bad crankshaft sensor? This question is relevant. The main signs of failure of the crank pulley position regulator are:
- Engine knocking (knocking of hydraulic compensators) under heavy loads or driving uphill at low speeds.
- The motor began to work less steadily. Particularly at idle, you will notice a drop and a sharp increase in rpm. Additionally, your vehicle may stall at idle, either while driving or when stopped at a traffic light.
- The engine cannot operate at full power, and you can notice this drop in speed without instrument readings. Engine power may periodically fall and rise, regardless of any factors.
- Significant reduction in the dynamic characteristics of the vehicle.
- There may be problems starting the internal combustion engine.
- In addition, one of the most noticeable signs of a breakdown of this regulator, as stated earlier, is the inability to start the engine.
- Another sign of a malfunctioning crankshaft position sensor is that the spark disappears, not completely absent, but does not appear periodically.
Of course, such malfunctions may indicate other problems with the engine. For example, a drop in power and speed may indicate a clogged fuel pump or a broken fuel filter. But the information below will help you diagnose the device.
Electronic engine control unit (ECU)
The ECU is responsible for the entire operation of the engine; it is in this block that the processes of calculating the fuel mixture, supplying a spark to the desired cylinder, and much more take place. Sensors installed in the car are directly connected to the ECU. Each sensor reads the readings and transmits them to the internal combustion engine control unit. Failure of the ECU makes it impossible to operate the vehicle.
How to check functionality?
To do this, you can use several methods. We will not consider all of them, but will devote time to only two, the most basic and most accurate methods. In any case, to perform diagnostics you need to dismantle the element to check its functionality. When dismantling the crank pulley position regulator, you should visually inspect it - perhaps the malfunctions will speak for themselves.
Often, a visual inspection makes it possible to identify certain damage to the element body, as well as the condition of the block itself and the contacts themselves. If the regulator is too dirty, it must be washed with alcohol, since its contacts must always be clean. If this diagnostic method does not help detect a breakdown, then you should check the sensor more carefully.
First way
Using an ohmmeter, you can measure the resistance of the winding of the synchronization device. If your car's regulator is in working condition, then the ohmmeter readings should vary around 550 - 750 ohms.
Voltmeter for diagnostics
But before you start diagnosing the pulley position regulator, check the manual for your machine for the exact range of indicators for DPKV. The manufacturer indicates this nuance most accurately and you will need to navigate according to it. If the results obtained differ from those indicated in the instructions, then the DPKV must be replaced because it is faulty.
Second way
This method will allow you to more accurately determine the state of the component. To test your device you will need:
- digital voltmeter;
- megohmmeter;
- inductance measuring device;
- network transformer.
Megaohmmeter for device diagnostics
To make the indicators more accurate, it is recommended to carry out diagnostics at an air temperature of at least 20 and no more than 22 degrees.
First you should measure the inductance of the regulator winding. To do this, use an inductance meter. Normal readings should vary between 200 and 400 megahertz.
Using a megohmmeter, you should diagnose the insulation indicator. If the voltage level is about 500 volts, then the insulation value should not exceed 20 megaohms.
Inductance meter for diagnostics
A network transformer will be required in cases where, during diagnostics of the device, accidental magnetization of the synchronization pulley occurs. After analyzing the results obtained, you can draw a conclusion about the performance of the DPKV or its failure. As you can see, this method of checking the pulley position adjuster requires certain knowledge.
Recommendations for selecting sensors
In order not to delay the repair time due to the purchase of low-quality spare parts, service station technicians recommend purchasing only original parts.
When choosing a component manufacturer, always give preference to factory parts. Check the index matches carefully. An exhaustive list is provided in the operating instructions.
Buy analogues less often, even if they are more expensive than the “originals”. Do not use the services of dubious suppliers who sell spare parts at unusually low prices.
If you do not have personal experience in servicing a technical device, install the components at a service center, where they provide a quality guarantee for the work performed.
Video from Ramil Abdullin “Self-diagnosis of DPCV”
You will learn how to diagnose the regulator at home on your own from the video.
Technological progress in the automotive industry is displacing outdated carburetor engines, replacing them with injection ones. This leads to the need to know the design and operating principle of modern engines, in terms of the synchronization of spark formation and the supply of gasoline to the cylinders. DPKV is not provided on cars that do not have an on-board computer, and on carburetor engines.
The sensor is available in the design of only injection and diesel internal combustion engines. The stable functioning of a modern car depends on the ECU, which is its “brain”. The unit receives information about the condition of the vehicle from the installed sensors, which is processed, and based on the results obtained, the operation of all systems is adjusted. One of the main sensors responsible for engine operation is the crankshaft position sensor.
Coolant temperature sensor
The DTOZH in Grant is located in the thermostat block and serves to read the coolant temperature. The sensor is also responsible for the operation of the engine cooling fan and for the presence of warm-up engine speed. When starting the engine, you will notice that if the DTO is in good working order, the speed is slightly higher than the working idle speed; as soon as the internal combustion engine warms up, the speed returns to normal.
Symptoms of malfunction:
- There are no increased speeds to warm up the internal combustion engine;
- The engine cooling fan does not work;
Why do you need a timing sensor?
DPKV records and transmits the following indicators to the ECU:
- the moment the pistons pass TDC and BDC in the first and last cylinders;
- crankshaft position measurement.
The received data is transmitted to the ECU. As a result of processing information about the position of the crankshaft in relation to the dead points and its rotation frequency, the synchronization sensor corrects the following indicators of the internal combustion engine:
- the volume of gasoline entering the cylinders;
- fuel supply time;
- ignition timing;
- camshaft rotation angle;
- moment and duration of operation of the adsorber valve.
The tasks of the electronic unit may vary depending on the complexity of the internal combustion engine device, but not a single ECU operates without a crankshaft position sensor.
As a result of a malfunction of the DPKV, sparking is either delayed or ahead of the engine's power stroke, which leads to improper operation of the internal combustion engine or to the engine not starting. This contributes to incomplete combustion of the working mixture and, as a result, excessive fuel consumption and a decrease in the dynamic performance of the car.
Reviews
| № | Positive |
| 1. | Vladimir: for a year and a half of Grant’s operation, there were no problems with the performance of the sensors. Everything is in good condition. |
| 2. | Kirill: I corrected the contact on the mass air flow sensor once. The reason is not the meter, I just caught the block with the wires with my hand while replacing the air filter. No complaints, the quality is good. |
| 3. | Vasily: in two years of using Granta, I replaced the antifreeze temperature meter once. In all other respects, no comments, satisfied with the quality. |
| 4. | Gregory: after buying the car from the dealership, I checked all the terminals and wires myself. Some tightened up, now the machine works like a watch. |
| 5. | Vyacheslav: I have no complaints, the car is three years old, I haven’t made any investments. I believe that systematic inspection helps prevent large-scale breakdowns. |
| 6. | Vladimir: The electronic control unit is working properly, there are no comments. Digital sensors transmit information in a timely and complete manner. |
| Negative | |
| 1. | Alexander: I can’t speak positively about the factory devices, since I replaced three of them in two years. They fly like air. |
| 2. | Ignat: no matter what I do, the fuel sensor incorrectly displays information about the amount of gasoline. I'll buy another one. |
| 3. | Ivan: the manufacturing quality of digital equipment is poor, it breaks down every six months. |
Conclusion Despite the negative reviews about the digital sensors on the Lada Granta Liftback, their manufacturing quality is decent. Subject to systematic technical inspection and careful handling of the machine, the service life exceeds the warranty period.
DPKV device
The part is a steel core with a copper wire winding, placed in a plastic case and filled with compound resin.
There are 3 types of synchronization sensors available:
- Induction. The operating principle is based on the use of a magnetized core with copper wire wound on it, at the ends of which the change in voltage is measured. In addition to fixing the position of the crankshaft, it measures its rotation speed, which is also necessary for high-quality operation of the internal combustion engine. Induction sensors are the most common and frequently used in automobile devices.
- Optical. Their design is based on an LED, which emits a luminous flux, and a receiver, which captures the light on the other side. When a light beam hits a control tooth, it is interrupted, the receiver records its absence, and the information is transmitted to the computer.
- Hall Sensor. It works based on the physical effect of the same name. A magnet is placed on the crankshaft; when it passes the sensor, a direct current appears in the latter, fixed by a synchronizing disk.
The versatility of an induction-type device and a Hall sensor make them the most popular in the design of modern motors.
Sensor location
The stable operation of the engine depends on the serviceability of the crankshaft sensor, so automakers place it in an easily accessible place to quickly troubleshoot the problem. Despite the dense arrangement of parts under the hood, it is quite easy to determine where the synchronization sensor is located.
Reference disk. Other names are master or synchronizer.
Most often it is located on a bracket between the generator pulley and the flywheel.
Among other electronic sensors, it stands out because of its wire (70 cm long) with a special connector for connecting to the vehicle’s on-board network.
To replace and install the DPKV, you only need to correctly set the gap between the rod and the synchronizing disk. The gap size varies from 0.5 to 1.5 mm and depends on the make and model of a particular car. The distance is adjusted using special washers located between the device and the installation site.
Something else useful for you:
Video: Crankshaft position sensor DPKV
Catalog numbers and cost of sensors on Lada Granta Liftback
| № | Name | vendor code | Price, rub.) |
| 1. | DTOZH | 21911-3858452-05 | from 250 |
| 2. | DD | 21911-385506981 | from 350 |
| 3. | DPKV | 21911-169834-00 | from 600 |
| 4. | DF | 21911-1164010-00 | from 400 |
| 5. | Lambda probe | 28165997 | from 1000 |
| 6. | Mass air flow sensor | 280216349 | —/— |
| 7. | DS | 21911-3846491 | from 300 |
| 8. | DDM | 21911-1165402-00 | from 550 |
| 9. | DNDC | 21911-1196715-00 | from 650 |
| 10. | DST | 21911-1168234-11 | from 350 |
*prices are current as of October 10, 2018.
Working principle of the synchronization sensor
For stable operation of the engine, the DPKV working process occurs according to the following principle:
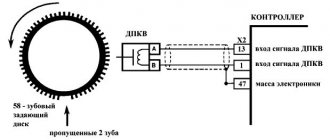
- The crankshaft has a special gear (reference disk) with two missing teeth - start and zero.
- When the crankshaft rotates, the teeth, passing through the magnetic field of the DPKV, change it - as a result, pulses are formed in the device, the data of which is transmitted to the control unit;
- When a gear with missing teeth passes past the sensor, the nature of the pulses changes, and the unit determines the initial position of the crankshaft;
- Based on counting the received pulses, the computer determines the position of the crankshaft in a certain period of time:
- After processing the information, the ECU sends signals to the appropriate vehicle systems, and their operation is adjusted.
As a result, stable operation of the car engine is ensured.
Mass air flow sensor
The mass air flow sensor is designed to count the air sucked into the engine to adjust the fuel mixture. The readings from the sensor are sent to the ECU. This sensor is one of the most expensive on Grant. It is installed on the air filter housing and secured with two 6mm bolts.
Symptoms of malfunction:
- High fuel consumption;
- Uneven engine operation;
- Floating XX;
Signs of a malfunctioning crankshaft position sensor
The first thing worth noting is that the DPKV does not act up and does not work from time to time; it either functions in a given mode or does not work at all. This is due to the simplicity of the element design. The process of part failure is irreversible. If he has lost his ability to work, he will not work again. This part is non-repairable. If the test confirms its malfunction, it is replaced with a new one.
There are several reasons for its failure. Loads at elevated temperatures, high humidity, sudden changes in temperature and mechanical stress have a negative impact. As a result, the car operates in an unknown mode or does not start.
Signs of a faulty DPKV do not depend on its type. The following symptoms will indicate a breakdown of the crankshaft position sensor:
- a decrease in the vehicle’s traction performance (this sign indicates the need to diagnose the internal combustion engine, but does not always indicate a breakdown of the DPKV);
- instability of engine operation, “swimming” of its speed at idle and when the vehicle is moving;
- engine detonation when the load increases;
- inability to start the engine.
Methods for diagnosing DPKV
When determining the serviceability of the crankshaft position sensor, we are guided by the principle - from simple to complex. In other words, first an inspection, then checking the characteristics with instruments (ohmmeter, oscilloscope or computer). The absence of moving parts and the simplicity of the design of the element make it a fairly reliable part. Therefore, the crankshaft sensor in rare cases becomes unusable on its own. Most often, it receives mechanical damage during repair work under the hood of a car or as a result of foreign objects getting between the sensor and the gear wheel.
Before you begin diagnosing an electronic component, you need to note its original position on the motor. After dismantling, the device is checked for defects in external surfaces. If the DPKV is dirty or has corrosion on the contact group, then it must be cleaned with alcohol. If the inspection shows no defects, it can be diagnosed using special instruments. It is advisable to carry out the test using a multimeter, which can be switched to different modes.
Ohmmeter test method
This method is simple and accessible, but does not guarantee detection of a breakdown. It is used to measure the resistance of the coil. To do this, it is enough to simultaneously touch the coil terminals with the probes. The polarity of the touch is not important in this case.
The resistance value depends on the characteristics of the coil and is usually in the range of 500-700 Ohms. To determine the resistance value of your sensor model, you need to look in the description of the DPKV or search on the Internet.
The multimeter is used as follows:
- We set the measured parameter (resistance) in a range close to the measured value, but not lower.
- We touch the ends of the sensor with the probes and look at the readings.
If the indicators are close to the standard values, then the coil is working properly. The disadvantage of this method is that it does not always indicate a faulty crankshaft sensor. Therefore, it is advisable to check using other methods.
Checking inductance values
When excited, all coils display an inductance indicator, including the coil located in the crankshaft sensor housing. The diagnostic method boils down to measuring this indicator.
When checking inductance, you must have a megohmmeter, a network transformer, an inductance meter and a voltmeter. To determine the indicator, carry out the following steps:
- Use a multimeter to measure the inductance of the coil (standard values are in the region of 200-400 mH).
- Using a megohmmeter, measure the resistance of the insulating layer between the ends of the DPKV (the data should be above 0.5 MΩ).
- A network transformer is used to demagnetize the sensor coil (deviations indicate the need to replace the part).
Video: Checking DPKV, it couldn’t be simpler. Injector diagnostics.
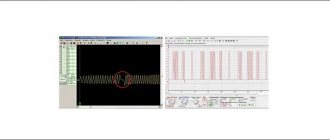
Diagnostics using an oscilloscope
The most advanced and accurate method of determining the health of a part is checking with an oscilloscope. Diagnostic work is carried out with the power plant running.
You can also use an oscilloscope to check serviceability on a dismantled crankshaft sensor. This requires an electronic oscilloscope and special software. In this case, the check is carried out according to the algorithm:
- Probes must be connected to the terminals of the crankshaft position sensor;
- Launch the software;
- Move any metal object near the part.
If the sensor is working properly, a graph is constructed on the device screen based on the DPKV readings.
If the part reacts to the movement of a metal object, then it is working. But the result of checking it on a running internal combustion engine will be more accurate.
The simplest, most reliable and fastest way to determine the performance of the DPKV is to install a known-good synchronization sensor in place of the one being tested. And if the problems with the car disappear, then the conclusion is clear - the part is faulty and needs to be replaced.
When installing, you should take into account the correct installation: maintaining the required gap between the DPKV and the flywheel. You can find out this indicator from the instructions for the sensor or from the Internet, but on average it is 0.5-1.5 mm.
In a modern car, the operation of a gasoline or diesel engine is controlled electronically. The controller prepares the fuel mixture and regulates sparking at the spark plug electrodes, relying on the readings of several meters located at key points - the air and exhaust tracts, the throttle valve, and so on. But what happens if one such element fails? In this case, it is proposed to consider the signs of a malfunction of the crankshaft position sensor (CPS) and how to check it in a garage environment.
Diagnostics using a multimeter
To check, you need to switch the device to the mode for measuring electrical resistance (ohmmeter):
- The upper limit value should be set within 2 kOhm.
- This indicator must be measured on the DPKV inductor coil by touching the multimeter probes in pairs to its terminals.
- Normally, the resistance should show a value in the range of 500-700 Ohms. If, as a result of measurements, the device shows such numbers, then everything is in order with the coil and sensor.
This method is quite simple and accessible to most car enthusiasts. On the other hand, it does not provide a 100% guarantee that it can be used to identify all faults.
Thus, the crankshaft position sensor is a very important device. If the above-described signs of its malfunction appear, it is necessary to urgently carry out diagnostics. The most common devices are suitable for these purposes, even such tools as handy for every driver, such as wrenches.
How does the sensor work?
To learn how to troubleshoot the specified device, you need to understand its design and understand the principle of operation. The sensor design is simple and includes the following elements:
- multi-turn coil;
- magnetic core;
- the coil leads are soldered to the connector contacts;
- non-separable plastic case with a hole for fastening.
The meter is installed in close proximity to the toothed pulley attached to the crankshaft on the timing gear side. Through conductors, the sensor is connected to the main electronic unit that controls the operation of the motor.
The magnetic core is brought out through the end part of the plastic case and is as close as possible to the teeth of the rotating pulley. The gap between the parts does not exceed 1 mm.
The operating principle of the device is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction . When a significant mass of metal passes in close proximity to the core, the coil generates a short-term electrical impulse. The teeth of the rotating pulley cause a series of such impulses, transmitted through the wires to the controller. Thanks to this, the electronic unit always “knows” the position of the crankshaft, determines the top dead centers of all pistons and promptly sends a command to the injectors to inject fuel.
Signs of sensor problems
The crankshaft speed meter is considered a fairly reliable device, functioning properly for 100 thousand km or more. There are often cases when an element lasts the entire service life of the car. A crankshaft sensor malfunction may occur for the following reasons:
- An internal break or short circuit of the coil winding occurs due to prolonged exposure to vibration transmitted from the engine. Such a breakdown is very rare.
- Open circuit between the device and the controller. The reasons are the same vibration, melting of conductors from contact with hot parts of the engine, or accidental damage by a car enthusiast.
- Mechanical destruction of the body occurs during repairs carried out in the engine compartment. For example, being hit by a broken wrench.
- Loss of contact in the connector due to oxidation or loosening.
- Contamination of the working surface interacting with the toothed pulley.
The last item on the list requires a separate explanation. It is common knowledge that electromagnetic fields penetrate dielectric materials, including dust and dirt. But at the location of the sensor, small metal particles and chips flying from gears are added to traditional contaminants. When they hit the end of the core, they shield the magnetic field, causing the electrical pulse to gradually weaken.
Reference. Contamination of the core with tiny metal particles is typical for worn-out power units with leaking main oil seals. A mixture of engine oil + dirt + chips thickly coats nearby parts, including the crankshaft position meter.
How a car owner can identify the symptoms of a sensor malfunction:
- When the element completely fails, the engine stalls and does not show signs of “life” during subsequent attempts to start, since the controller does not “see” the position of the crankshaft. A broken electrical circuit gives a similar result.
- Unstable operation at idle. The engine speed “jumps” and vibration of the power unit is observed.
- Loss of power from the power unit, failures during acceleration.
- Increased consumption of gasoline or diesel fuel.
As strange as it may sound, the first sign is the most favorable. It is much easier to revive a “dead” motor - just check the circuit or change the sensor itself. In case of unreliable contact and other minor troubles, the engine does not fail, but behaves unstable. The problem is that if other sensors fail and the ignition system malfunctions, the power unit behaves in the same way and identifying the real malfunction is much more difficult.
When the air flow sensor, throttle position sensor or lambda probe is faulty, the control unit switches to emergency mode, supplying fuel according to average indicators. This results in unstable operation and increased consumption. The same symptoms are observed when there is a problem in the crankshaft speed meter circuit.
Methods of checking in garage conditions
When your car's engine suddenly "dies", you need to remove the sensor and perform the diagnostics described below. If the motor continues to operate with signs of instability, perform the following manipulations:
- Thoroughly clean the device body with a rag moistened with an organic solvent - white spirit, turpentine or other degreaser. Pay special attention to the end facing the toothed pulley.
- Make sure the fastening is secure. Due to a loose screw, the sensor may move away from the metal teeth, as a result, the gap will increase and the generated pulse will weaken.
- Clean the connector contacts from oxidation.
- Inspect the wiring for melting or breakage.
If the above actions do not produce results, the crankshaft sensor is dismantled and checked with a multimeter in 2 stages. At the first, the resistance between the terminals of the device is measured, which makes it possible to verify the integrity of the induction winding. Clean the contacts, turn on the ohmmeter and check the resistance between them. Normal readings are in the range of 500–700 Ohms; if the turns are shorted, you will get a zero or reduced value; if there is a break, you will get infinity.
At the second stage, the performance of the element is tested according to step-by-step instructions:
- Switch the multimeter to voltage measurement mode, the maximum threshold is 200 millivolts.
- Securely attach the wires to the contacts of the sensor block (for example, with alligator clips).
- Take any metal tool - a wrench, a large screwdriver or something similar. Apply and tear it sharply from the magnetic core of the element, holding the body with your hand. The voltmeter should show voltage surges.
Advice. If the crankshaft sensor is OK, check the wiring with an ohmmeter. Perhaps the reason lies there.
Further actions are as follows: the broken crankshaft speed meter is replaced with a new one; the part cannot be repaired. The working sensor is installed back, maintaining the gap, and the troubleshooting continues in another place.
A few words about how to check the crankshaft sensor on the road when you don’t have a multimeter or other diagnostic tools. You will need 2 wires and an LED light bulb from any car lamp (for example, an interior lamp). For convenience, unscrew the element and connect the lamp to the connector, then apply a wrench to the magnet, as described above. A working sensor will cause the LED to flash.