For those blog readers who follow my YouTube channel, the information will not be new, but for the rest I will describe everything here. So over the past few days my Kalina has started having problems. And they were as follows:
- After a long period of inactivity, the engine began to start poorly, often even on the second try.
- the car became very “dull”, and it felt like the loss of power was about 20%
- fuel consumption increased by 10% when the engine was idling, and when driving too
In general, based on all the signs described above, it looked like a dying gas pump. Of course, I checked the mass air flow sensor first, since its operating voltage is also already close to critical. But when it was turned off, nothing changed for the better.
As a result, I began to deal with the fuel system. I’ll say right away so that there are no unnecessary questions:
Result after replacing the fuel pump
So, after replacing the fuel pump, a pressure gauge was immediately connected and when starting the engine, excellent readings of 4 kg/cm² could be observed, and when the speed was set to almost maximum, the pressure did not decrease.
Here you can see information on replacing the fuel pump, which was done in this case. As for the result specifically in terms of the operation of the motor and its power characteristics, everything is excellent here too. Now the car drives very quickly, there are no dips or slowdowns when pressing the gas pedal. As surprising as it may sound, fuel consumption also returned to normal both at idle and when driving.
Advantages and disadvantages of a fuel pump
Despite its apparent simplicity, understanding the purpose of the fuel pump requires some explanation. The fact is that in most cases, this also applies to cars of the Lada Kalina family, the gas tank is located on the opposite side of the car from the engine. Therefore, efficient operation of the fuel pump is required to ensure that the fuel travels a significant distance at the required pressure.
The design of the Lada Kalina uses an electric fuel pump as a more modern and efficient device.
Among the main advantages of a fuel pump are several:
- ensuring the supply of the required amount of fuel taking into account the needs of the engine;
- high reliability and simplicity of design;
- high level of safety, since the pump stops working immediately after the engine stops.
At the same time, the electric fuel pump has a number of disadvantages that can affect its operation:
- noise during operation;
- need for cooling;
- demands on fuel quality.
It is the use of low-quality gasoline and untimely replacement of fuel filters that lead to a decrease in performance or failure of the gasoline pump.
What should be the pressure in the fuel rail of the Lada Kalina?
So, having bought a fuel pressure gauge, which, by the way, cost me as much as 1,500 rubles, I decided to measure the pressure, which as a result was around 3.4-3.5 kg/cm². From the data obtained we can conclude that this was not enough for normal engine operation.
Moreover, when the speed increased to certain values, the pressure in the ramp dropped to 3 kg/cm², which also should not happen in a working fuel system.
The normal pressure in the system is from 3.8 to 4 kg/cm². Of course, if you are a fan of the “retirement” driving style up to 2000 rpm, then you may not feel any difference in power loss. But when the speed increases to at least 3000, you immediately feel a failure, and overtaking is difficult with such a “stupid” ride.
Video review of a dying fuel pump on Kalina
If you don’t want to read everything written above, then you can watch this video, in which everything was clearly demonstrated.
If you have any questions, ask them below in the comments or discuss them on the channel under the video.
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm valve. Fuel presses against it at one end, and the intake manifold spring presses against it at the other. At lower speeds, the valve opens, accompanied by the draining of residual fuel from the engine into the tank. The next time fuel is supplied, the pump starts, drawing the liquid through the filter. There is a special stabilizer on the fuel rail, whose task is to maintain optimal pressure in the system.
If this component breaks down, the engine power of the machine drops and uneven operation of the engine is felt. To protect yourself from this, you need to systematically check the regulator and promptly respond to symptoms of damage to the device.
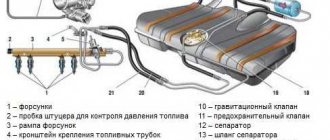
Lada Kalina fuel system design
Fuel is supplied from a tank installed under the bottom in the rear seat area
The fuel tank consists of two stamped steel parts welded together.
The filling pipe is connected to the tank with a gas-resistant rubber hose.
A ventilation tube is welded into the upper part of the filling pipe, connected to the tank with a plastic hose.
The ventilation tube is used to remove air displaced from the tank when it is filled with fuel.
The fuel tank ventilation inlet and outlet valves are built into the filler plug.
Fuel module , including a fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator and fuel level sensor, is installed in the fuel tank.
For rough fuel cleaning, there is a strainer at the module inlet.
To access the fuel module, there is a hatch under the rear seat cushion in the bottom of the car.
The fuel level indicator sensor controls the operation of the dial gauge and signaling device located in the instrument cluster.
The fuel pump is electrically submersible, rotary.
The fuel pump is turned on by a command from the electronic control unit (controller) when the ignition is turned on, through a relay.
The pump creates a pressure in the system that exceeds the operating pressure in the fuel rail.
Fuel filter
From the pump, fuel is supplied under pressure to the fuel filter. The fine fuel filter is non-separable, with a paper filter element.
After the filter, a tee is built into the fuel delivery line, through which fuel is supplied to the fuel rail and the fuel pressure regulator located in the fuel module.
The fuel pressure regulator is a valve that opens when the fuel pressure in the line exceeds, releasing part of the fuel into the tank.
The pressure regulator is non-separable and must be replaced if it fails.
The fuel pressure in the fuel rail with the ignition on and the engine not running should be between 3.6 and 4.0 bar.
The fuel pump is a tube with injectors installed on it.
The ramp is attached to the inlet pipe with two screws.
Fuel under pressure is supplied to the internal cavity of the ramp, and from there through nozzles into the intake pipe.
The injector is an electromagnetic valve that allows fuel to pass through when voltage is applied to it and closes under the action of a return spring when there is no power.
At the injector outlet there is a sprayer through which fuel is injected into the intake tract.
The controller controls the operation of the injectors. The injectors are sealed in the ramp and inlet pipe with rubber rings and fixed to the ramp with metal clips.
If the winding is broken or shorted, the injector should be replaced. If the injectors are clogged, they can be washed without dismantling on a special stand
Air is supplied to the engine throttle body through an air intake, an air filter and a corrugated rubber hose.
The air filter is installed in the front left part of the engine compartment on three rubber holders (supports).
The filter element is paper. After the filter, the air passes through the mass air flow sensor.
The throttle assembly is a throttle body (with channels made in it), on which the idle speed regulator and throttle position sensor are installed.
The throttle assembly is mounted on the intake pipe.
To avoid freezing of the throttle assembly at low temperatures and high ambient humidity, a heating unit is built into the assembly, through which the cooling system fluid circulates.
When you press the gas pedal, the throttle valve opens, changing the amount of air entering the engine (the fuel supply is calculated by the controller depending on the air flow).
When the engine is idling (throttle valve closed), the controller controls the air supply using the idle air control (IAC).
The idle air control valve is a stepper motor that moves the valve.
The valve shut-off element (needle) changes the flow area of the channel and provides regulation of air flow bypassing the throttle valve.
To increase the crankshaft rotation speed at idle, the controller sends a control signal to open the valve, increasing the air supply bypassing the throttle valve, and, conversely, to reduce the rotation speed, a command is sent to close the valve.
In addition to controlling the crankshaft speed at idle, the controller controls the IAC, reducing the toxicity of exhaust gases:
— when braking the engine, the throttle valve closes sharply.
In this case, the IAC increases the air supply bypassing the throttle valve, resulting in a leaner fuel mixture. This helps reduce hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide emissions.
The idle air control is non-separable and must be replaced if it fails.
The fuel vapor recovery system used in the power system includes a separator, an adsorber, an adsorber purge solenoid valve, connecting tubes and hoses.
The separator is installed in the right rear wheel arch.
Fuel vapor from the tank is partially condensed in a separator, from which the condensate is drained back into the tank through a hose and filling pipe.
The separator is equipped with a gravity valve that prevents fuel from leaking out of the tank when the vehicle rolls over.
Adsorber
From the separator, fuel vapors enter the adsorber (installed on the top of the fuel tank, on the left side) through a fitting labeled “TANK”, where they are absorbed by activated carbon.
The second canister fitting with the inscription “PURGE” is connected through the solenoid valve for purge of the canister with the throttle assembly, and the third with the inscription “AIR” is connected to the atmosphere.
The canister purge solenoid valve is installed on a bracket attached to the air filter housing.
When the engine is stopped, the purge solenoid valve is closed, and in this case the adsorber does not communicate with the throttle assembly.
The controller, by controlling the solenoid valve, purges the canister, after the engine has operated for a specified period of time from the moment it switches to the closed-loop fuel supply control mode, the control oxygen sensor must be warmed up to the required temperature.
The valve connects the adsorber cavity with the throttle assembly - and the sorbent is purged: fuel vapors are mixed with air and discharged through the throttle assembly into the intake tract and further into the engine cylinders.
The greater the engine's air consumption, the longer the duration of the controller's control pulses and the more intense the purge.
How does the Lada Kalina gasoline vapor recovery system work?
The EVAP system in question was created to prevent the release of harmful gasoline vapors into the surrounding atmosphere resulting from fuel evaporation; it includes:
- fuel shut-off valve;
- adsorber;
- solenoid valve for purging the absorbent element;
- connecting pipelines.
The most important component in the system is the adsorber (also called a carbon filter), the basis of which is activated non-edible carbon, enclosed in a plastic housing. The resulting gasoline vapors are absorbed by the carbon of the absorbent element, gradually accumulating in it. When the engine starts, the canister purge valve (KPA) is turned on, and due to the vacuum, all accumulated vapors enter the intake manifold and then burn out.
On the Lada Kalina, the adsorber is located in the gas tank area, and getting to it is very difficult. To dismantle this EVAP element, it is necessary to remove the fuel tank, but the control unit is located in an accessible place - the valve is located in the engine compartment, in close proximity to the battery, on the rear wall of the air filter housing. It should be noted that for turbocharged engines, a vacuum is not created in the intake manifold, and in order to force the vapors in the desired direction, an additional two-way valve is included in the circuit.
Replacing a faulty valve
The regulator to be replaced is located in the fuel block, which includes other elements: an electric fuel pump, a coarse filter and a Kalina fuel level sensor.
You will need to remove the entire unit from the tank and then change the regulator. To do this, relieve the pressure, as described above, and then remove the rear seat. The module is located under a hatch covered with a mat and sound insulation, which moves to the side. You need to unscrew the screws and remove the hatch, then disconnect the wires and fuel hoses.
The pressure ring holding the assembly is twisted to the left. You can move it from its place with light blows of a hammer on the protrusion through the adapter. Then the fuel module along with the float is carefully removed from the opening.
You need to remove the wire from the regulator installed in it and pull out the spring retainer with a Phillips screwdriver. After this, the valve can be easily removed and replaced with a new one. Before reinstalling, the O-rings of the new part must be lubricated with fresh engine oil.
When assembling the unit, it is important to monitor the condition of the gaskets and replace them if worn. When installing the fuel module into the opening, you must ensure its orientation; the arrow on the cover should point towards the trunk. At the end, it doesn’t hurt to check the pressure again, and only then you can screw in the spool and start the engine.
To be sure, the Lada Kalina should be tested in motion, making sure that the dynamic properties of the car are restored.
tweet
back The process of replacing the clutch on Kalina
Next Why doesn't the Lada Kalina ECU work?
Tags: replacement, umbrella, valve, fuel pressure regulator, installation
Signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator
If your car's engine stalls at idle or engine power drops while driving, these may be symptoms of a faulty fuel pressure regulator. Most often, a sudden increase in fuel consumption is a signal of RTD failure.
There are other signs of breakdowns:
- the engine runs unevenly;
- at idle speed the engine stops;
- the crankshaft speed suddenly increases or decreases;
- The cooling system does not work well;
- the engine noticeably loses power;
- when you press the gas pedal there is partial or complete response;
- the engine seems to choke;
- poor acceleration of the car when changing gears;
- vehicles begin to move frequently in jerks;
- rapid fuel consumption occurs.
The presence of even one of these signs requires checking the condition of this device.
How to check the fuel pressure regulator?
There are several simple ways to determine the causes of problems and defective components:
- Visual method. A simple inspection without the use of any fancy tools is fine for carburetor engines. Pinch or disconnect the valve and observe the flow of fuel. The intensity of the fuel flow will help identify the malfunction. This method of verification is effective in its own way, but one cannot count on absolute accuracy.
- Method using a pressure gauge. Place a pressure gauge between the fuel hose and the fitting. To do this, temporarily disconnect the vacuum hose. The pressure level should change from 0.3 to 0.7 Bar. If the pressure indicator has not changed, repeat the operation with another hose.
- Hose clamping method. The pressure regulator is checked by pinching the return hose. A pressure gauge connected to the fuel system should give an immediate response. If the motor does not develop normal speed, you can determine the inoperability of the RTD without the device. Start the engine and clamp the return hose. Then track the RPM and listen to the engine. If the engine starts to run smoothly, then the problem lies in a faulty control valve that needs to be replaced.
Selecting new filter elements
To purchase fuel purification system parts for VAZ 1117-19 models, you need to know what they look like:
- The coarse filter is a flat mesh bag made of chemically resistant plastic and catches large particles of 80-100 microns.
In the center of the element there is a plastic fitting that fits onto the counterpart of the gasoline pump. The mesh element is equipped with a pipe that fits onto the fuel pump fitting - The fine filter is made in the form of a cylinder with two fittings at the ends.
The body is made of metal or special plastic - polyamide, and there is filter paper inside it. It traps particles 15-50 microns in size. The pipes are equipped with clamps for fastening fuel hoses. The element is equipped with clamps for fastening fuel line connections
All modifications of the Lada Kalina, including the second generation, are equipped with absolutely identical filter elements - a “barrel” and a mesh catcher. The dimensions of the spare parts are also identical.
There are no tricks in choosing a coarse mesh - the parts are made according to a single sample and cost from 30 to 45 rubles. The only caution: in order not to purchase a low-quality product or a fake, contact well-established stores. Although the fuel pump mesh costs a penny, it plays an important role in the fuel system: it catches large debris that can quickly clog the filter paper of the next cleaning element.
How to repair an RTD?
As part of component repair, the following work must be performed:
- Look under the hood of the car where there is a fitting plug designed to control fuel pressure. Unscrew it, then using a special protective metal cap, carefully unscrew the spool inside the fitting.
- Connect the hose with the pressure gauge and secure it to the fitting using a clamp. After starting the engine, check that the pressure reading on the measuring device does not exceed 3.25 Bar.
- Disconnect the vacuum hose from the RTD. This operation should be accompanied by an increase in pressure. If nothing happens, repairing the fuel pressure regulator is useless; you will have to replace the element with a new one.
If the part cannot be repaired, we proceed to install a new device.
- Disconnect the vacuum hose. The pressure will begin to increase. Having reduced the pressure in the power system, proceed to remove the vacuum hose. You will need to unscrew the securing nut on the fuel drain pipe, where diesel or gasoline flows through the fuel filter to the RTD.
- After unscrewing the two bolts securing the device to the fuel rail, you can safely remove the regulator from the fuel discharge tube itself. The ring remaining in the ramp can be easily removed by hand and placed on the regulator before installation.
- Install a new regulator and perform all previous steps in reverse order. Make sure the new device is in working order, only then proceed with complete assembly. Upon completion of installation, perform a control check of the operation and serviceability of the device.
Mechanism of operation of the element
The regulator (RDT) is an ordinary diaphragm valve, whose task is to maintain a constant gasoline pressure in the line running from the tank to the fuel rail. No matter what mode the engine operates in, its value must be in the range from 3.7 to 3.9 bar.
When the upper pressure threshold is exceeded, the valve begins to dump excess fuel directly into the internal size of the tank. If the fuel pressure is insufficient, the regulator is not able to increase it, but if it breaks down, it can itself become a prerequisite for a decrease in pressure. How Kalina’s power system works is perfectly reflected in the diagram above.
To correctly diagnose a diaphragm valve malfunction, you need to understand how the fuel system works:
- When the ignition of the Lada Kalina car is turned on, the fuel pump (item 6) starts working, creating the required pressure in the fuel rail (item 2). If after a few seconds the starter is not started, the controller will automatically turn off the pump.
- Gasoline passes through coarse and fine filters (item 7) and enters the RTD, and from there along the line (item 4) to the ramp and injectors (item 3).
- After starting, the engine begins to consume fuel to one degree or another, depending on the driving style.
- At idle speed, the fuel pressure regulator dumps a huge part of the fuel back into the tank (item 5), since its consumption is low, and the fuel pump always operates in the same mode.
- At high speeds, the engine needs more gasoline and the valve actually does not release anything.
There are 2 types of regulator defects, characterized by a decrease in fuel pressure or, on the contrary, its excessive increase. The element cannot be repaired and must be replaced if broken.