The internal combustion engine cooling system contains a number of devices that remove excess heat from the metal elements of the engine, as well as transfer this heat to the vehicle interior (as needed). The main material is coolant - water or antifreeze. Water has not been used for a long time due to its instability to sub-zero temperatures and oxidation of cooling system parts. Antifreeze, on the contrary, protects the pump and other metal elements from corrosion, and the temperature range is suitable for operation in any climatic conditions.
Failure of the cooling system can lead to a number of serious consequences. For example, engine overheating can lead to major repairs or even complete replacement of the internal combustion engine. But all this can be avoided if you have an understanding of the operation of the engine cooling system. In this article we will talk about how the VAZ 2110 cooling system works.
What does the engine cooling system consist of?
Let's consider the main elements of the internal combustion engine cooling system:
- A pump is a pump that pumps coolant.
- Closed channels through which antifreeze “walks,” leveling the temperature of heated engine elements to operating temperature. The system is divided into large and small circuits, through which the liquid is distributed using a thermostat.
- Thermostat is a mechanism that separates the antifreeze flows along the two circuits indicated above. When the engine heats up to a certain temperature, the thermostat valve opens and the liquid enters a large circuit, where cooling occurs due to the fan and radiator.
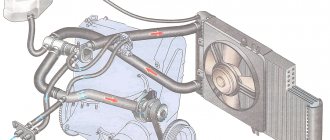
- The radiator is located at the front of the engine and is the main heat exchanger. The counter-flow of air cools the liquid passing through the radiator.
- Cooling Fan. The fan turns on if the oncoming air flow is not enough to cool the liquid in the radiator.
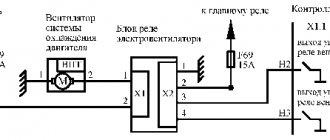
Electric fan
It is assembled on three rubber bushings and secured with nuts on the casing studs 5. The four-blade impeller 3 is made of plastic and is secured to the electric motor shaft 4 with a nut. For better operating efficiency, the impeller is placed in a casing 5, which is mounted on the radiator brackets at four points. The impeller blades have a variable radius installation angle and, to reduce noise, a variable pitch along the hub.
The electric fan is turned on and off depending on the coolant temperature by sensor 6 of type TM-108, screwed into the lower radiator tank 1 on the left side.
On motors in variant versions, mechanical fans can be installed, the impeller of which is attached to the hub 4 of the pump drive pulley 3.
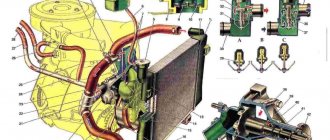
Radiator and expansion tank.
Radiator 1 is installed on two rubber supports (pillows) and secured to the front of the body with four bolts. It consists of upper and lower stamped brass tanks, two rows of brass tubes and cooling plates. The tanks have inlet and outlet pipes, the lower tank has a drain plug 7. The filler neck is closed with a radiator plug 2. The filler neck pipe is connected via a hose to a plastic expansion tank through the inlet and outlet valves of the radiator cap. The inlet valve is not pressed against the gasket (gap 0.5-1.1 mm) and allows the inlet and outlet of coolant.
With the engine running, when the temperature rises sharply or the liquid boils, the flow through the intake valve becomes insufficient and, under the influence of an increased pressure difference, the intake valve closes, disconnecting the cooling system from the expansion tank. The pressure in the system increases, providing better heat transfer through the radiator. When the pressure increases to 0.05 MPa, the exhaust valve opens and the coolant is released into the expansion tank. The temperature of the liquid will be 118-120°C. Excess steam escapes to the atmosphere through the rubber valve of the expansion tank plug, which operates at a pressure close to atmospheric pressure. The pressure at which the exhaust valve opens has been increased since 1983 to 0.08 MPa (0.8 kgf/cm2).
Engine cooling system VAZ 2110
The design of the cooling system of the VAZ 2110 is not fundamentally different from other cars - the main components are a pump, a cooling radiator and a thermostat. The thermostat is located on the battery side under the air filter. The aluminum pump is driven by a timing belt. When the thermostat opens and coolant flows through the radiator, the temperature sensor detects the heating and turns on the fan if necessary. This occurs at a temperature of 99C⁰. If the speed of movement is sufficient, the liquid is cooled by oncoming air.
Also included in the cooling system is a heater radiator through which hot coolant passes. The heater fan turns on during the process, transferring heat into the car interior. The cooling system of the VAZ 2110 8-valve injector differs from the 16-valve engine in the thermostat and the size of the expansion tank.
How the VAZ-2112 stove works
Driver comfort is largely determined by the normal operation of the stove. In VAZs, it is this system that most often fails, and in order to quickly fix the problem, you need to know about the structure of the stove, understand its circuit and have a good understanding of the principle of operation. This article will be devoted to the heating system of the VAZ-2112.
Comfort when driving in winter depends on proper operation of the stove
Causes of malfunction of the VAZ 2110 cooling system
There are a number of reasons why the system may overheat or depressurize:
- Coolant quality. If the coolant is diluted or replaced with water, this can lead to corrosion of internal components. Corrosion can damage the pump and thermostat, as well as clog channels and block flow.
- Quality of parts. Poor quality parts (pipes, radiator, thermostat) can contribute to system depressurization or overheating.
- Malfunction of the engine temperature sensor, as well as wires and relays.
- Cooling fan malfunction.
If a fan or electrical system fails, you can safely get to the repair site in the absence of traffic jams and traffic lights, but while driving, it is imperative to monitor the engine temperature. In other cases, it is extremely undesirable to operate the car, otherwise it can lead to serious engine malfunctions.
Thanks for subscribing!
Repair of main components
Repair of parts and the entire engine cooling system can be found in the ZMZ 405 repair manuals. The most common system breakdowns are the water pump and thermostat. Replacing the pump is quite simple:
- Drain the coolant.
- The drive belt is dismantled.
- The water pump mounting bolts are unscrewed.
- The old pump is removed and a new pump is installed. It is important not to forget to install the gasket.
- Install the belt into place.
- Fill the system with coolant.
Replacing the thermostat is carried out in the same way as a pump, only the element itself is located in a housing that consists of two elements. To change it, you just need to drain the liquid and disconnect the pipe. Then remove the cover and change the thermostat directly.
Recently, radiators have become a common malfunction; they become punctured by pebbles on the highways when the speed is high enough. Typically, motorists try to solder this element, but it does not always work.
Signs of a malfunction of the VAZ 2110 cooling system
Knowing the signs of a cooling system malfunction, you can always prevent the tragic consequences of such breakdowns in a timely manner. The following are the main warning signs:
- Thermometer. The temperature arrow should not exceed the permissible values.
- Engine critical temperature lamp.
- Steam coming from under the front of the car.
- A noticeable increase in air temperature from the interior heater
- A sharp drop in air temperature from the heater.
The cooling system of the VAZ 2110 16-valve injector is almost no different from the 8-valve engine system, so the characteristics of the two versions of the power unit are the same. The same applies to a carburetor engine. If such symptoms appear, you must immediately stop operating until the cause of the malfunction is eliminated.
Coolant pump
Engine advantages of Lada Granta
Centrifugal pump. Housing 1 and cover 6 are made of aluminum alloy. In the double-row ball bearing 2, locked with a screw 5, a pump roller 7 is installed, which acts as the inner race of the bearing. The bearing is filled with lubricant only during assembly and is not subsequently lubricated. The hub 4 of the pump drive pulley 3 is pressed onto the front end of the roller 7, and the pump impeller 9 is pressed onto the rear end. The seal ring 8, made of a graphite composition, is pressed against the end of the impeller, hardened by high-frequency currents to a depth of 2-3 mm. The non-separable oil seal 8 is pressed into the pump cover.
Radiator replacement
Radiator VAZ 2114
- Initially, the plug from the expansion tank is unscrewed, and the radiator plug and cylinder are also removed.
- The cooling mixture is poured into a clean container.
- The radiator ventilation system is disconnected from the power supply.
- We disconnect the rubber tubes from the radiator system and expansion tank.
- All bolts are disconnected from the surface of the casing.
- Carefully holding the radiator, we take out the casing along with the fan.
- At the end of the work, the radiator is completely free and can be removed.
Before you begin, remember that when removing and subsequently installing the radiator, the engine must be in a cold state.
After replacing the radiator or repair work, it is installed in place and secured in the same way, but in reverse order. After installation, be sure to start the engine and check the result.
Flushing
Flushing the engine cooling system is a process that many drivers often neglect, which sooner or later can cause fatal consequences.
It is recommended to carry out such work simultaneously with replacing the coolant. Taking into account the car model and its brand, this must be done from 1 time per calendar year to once every three years.
Signs that it's time to flush
- If the temperature gauge needle is not in the middle, but tends to the red zone while driving;
- It’s cold in the cabin, the heating stove does not provide sufficient temperature;
- Radiator fan turns on too often
It is impossible to flush the cooling system with plain water, since contaminants are concentrated in the system and cannot be removed even by water heated to high temperatures.
Scale is removed with the help of acid, and fats and organic compounds are removed exclusively with alkali, but both compounds cannot be poured into the radiator at the same time, since they are mutually neutralized according to the laws of chemistry. Manufacturers of cleaning products, trying to solve this problem, have created a number of products that can be divided into:
- alkaline;
- acidic;
- neutral;
- two-component.
The first two are too aggressive and are almost never used in their pure form, as they are dangerous for the cooling system and require neutralization after use. Less common are two-component types of cleaners containing both solutions - alkaline and acidic, which are poured alternately.
The greatest demand is for neutral cleaners that do not contain strong alkalis and acids. These products have varying degrees of effectiveness and can be used both for prevention and for thorough flushing of the engine cooling system from severe contamination.
Flushing the cooling system
Flushing the cooling system
- Antifreeze, antifreeze or water is drained. Before doing this, you need to start the engine for a couple of minutes.
- Fill the system with water and cleaner.
- Turn on the engine for 5-30 minutes (depending on the brand of cleaner) and turn on the interior heating.
- After the time specified in the instructions has passed, the engine must be turned off.
- Drain the used cleaner.
- Rinse with water or a special compound.
- Fill with fresh coolant.
Flushing the cooling system is simple and accessible: even inexperienced car owners can perform it. This operation significantly extends the service life of the engine and maintains its performance characteristics at a high level.
Pipes
Branch pipes are usually called thick hoses that transfer coolant from one unit to another, although in fairness it is worth noting that almost any elastic hose that transfers coolant can be called a branch pipe, regardless of its diameter and length.
The pipes can be divided into several groups: plastic, rubber, reinforced rubber, large cross-section, small cross-section, long, short. Naturally, each pipe can simultaneously belong to several groups, for example, it can be of large cross-section, reinforced with thread, and short.
But among motorists and repair specialists there is an unspoken division of pipes into hoses (tubes) and pipes. Don't be surprised if the technician tells you that you need to replace the tube (or hose) going from the radiator to the expansion tank, since such a term is quite applicable in this situation.
Types of pipes: reinforced
First, let's look at a regular reinforced pipe, which is quite easy to find in every car.
It can be of the most bizarre shape (everything greatly depends on the internal architecture of the engine compartment), the most varied lengths (from 50 centimeters to a tiny short one) and the most unexpected cross-section, from 5 mm to 15 centimeters in diameter (on trucks the cross-section can be even larger ). Also, recently there has been a tendency to make the ends of the pipes like fire hoses, that is, at the ends there is a fastening part that is attached to the radiator and engine block without a clamp; such fastening is, for example, used in Samant cars. But usually the ends of the pipes are made in the classical way, for clamping with a clamp.
A reinforced pipe is called reinforced for the reason that inside it there is a mesh made of synthetic fabric that prevents the pipe from bursting when working at high hydraulic pressure and temperature.
In the early 90s, a lot of counterfeit products appeared on the markets, which were made without fittings and were made of low-quality rubber that burst in the cold and could not withstand even a small heating-cooling cycle. It is worth mentioning here that both the duration of its service and reliability under extreme loads depend on the quality of the rubber used in the pipes. After all, rubber is a complex compound, the design of which takes into account many factors included in GOST standards, which, unfortunately, are not followed, especially by small manufacturers. That is why, for example, the pipe of a VAZ or AZLK car produced in 1970 can retain its elasticity and resilience in 2010, and the pipe of the same VAZ, replaced three years earlier, will become “wooden” by the same date.
What problems can arise if the pipes are badly worn?
- If the engine hose tube becomes leaky, oil may be lost. This will cause the engine piston to seize due to excessive friction against the cylinder walls. As a result, repairing your car will cost a lot of money.
- A worn-out hole in the air filter pipe supplies heated air. The engine is not able to operate at full power, which also causes serious problems.
- Damage to the filter causes the ingress of foreign particles and impurities, which negatively affects the condition of the car.