Where are the fuses on Kalina and why are they needed?
Every vehicle is equipped with a fuse box. The first generation “Kalina” is equipped with 3 such devices: installation, control and additional. The second generation model, or as it is also called “Kalina 2”, is equipped with 2 blocks.
These elements are necessary not only to protect all vehicle electronics from combustion, but also prevent the occurrence of fire, because In the event of a short circuit, they take on the entire load. In this case, the fuse itself fails, thereby stopping the flow of current to the electrical appliance.
Conclusion
If your battery has lost its charge, in 80% of cases the fault lies in the brush assembly (tablet). Changing it is no more difficult than removing the generator. If you have basic skills in working with a multimeter and a desire to solve the problem with charging a car yourself, I can say with confidence that you will be able to do this. Don't be afraid to look for the cause of the problem yourself. With every attempt to repair something or figure something out, it will be more difficult for you to be deceived by the service.
We are on YandexZen
7 910
Fuse types
Fuses are classified into cylindrical and blade. The first ones were used in the operation of old-style Russian cars. Knife-type elements are considered safer, more convenient and are used in all Lada Kalina cars.
Fuses also differ in the rated current indicated on the housing and in size. In addition, each value of the maximum permissible current has its own color, which also makes it possible to distinguish fuses without much difficulty.
Reasons for the battery not charging
Now we know how to check the charging on a car, the next step is to find the fault. The main reasons for lack of charging:
- Poor contact of battery terminals;
- Broken generator belt;
- Battery charging fuse blown;
- Failed battery;
- Broken wiring or short circuit;
- A broken car generator.
Poor terminal contact and broken generator belt. First of all, you need to open the hood of the car and check the condition of the alternator belt and terminals . The belt should be in tension and not loose. Pay attention to its condition, if it is a rivulet, then are all the rivulets intact? The battery terminals must be screwed in place; no oxide (white or light green deposits) around them is allowed. You should also check the integrity of the contact of the power wires with the terminals themselves, usually these are the places where they are bent. Wires don’t like this very much and it happens that they simply break off from the terminals.
Blown battery charging fuse . Not all cars have it, of course, but there are some. A car most often has two safety blocks, each should be checked: one under the hood, the other under the steering column. Their location depends on the car brand. You should open the cover of the fuse block; on its back side the fuse numbers and their purpose are indicated. If you find a fuse responsible for charging in the car, you should check its integrity.
Defective battery. This reason is the easiest to determine. Because if the reason is in the battery, then you will have charging, but the car will not “want” to start again after stopping the engine. Usually the battery fails due to lack of proper care or deep discharge. You can try to revive such a battery by fully charging and checking the density of the electrolyte, unless, of course, the banks in it are short-circuited.
Charging the battery
Broken wiring or short circuit. A wiring break can occur due to poor wire insulation or chafing. At the contact points, the wiring is very weak and often oxidizes, and after some time a break occurs. This is most often observed in cars over 20 years old. First of all, check the integrity of the wiring at the generator terminals.
A broken wire is often accompanied by a short circuit . As a rule, in places of short circuit there are always melted wires and a burning smell . You will find such a reason without much difficulty, but eliminating the consequences of this disaster can already be problematic. Usually, during a short circuit, all the car’s instruments go out and it shows no signs of life. If you find a short circuit, you should immediately turn off the power to the car by removing the battery terminal. Do this carefully. In the event of a short circuit, the car terminals heat up and you can get burned .
How to determine the lack of battery charging due to a break? Check the voltage at the generator with the engine running. This should be done between the car body and the power wire on the generator (thick, most often red wire). If the voltage there does not correspond to the required one, do not rush to get upset, the next step will be to check the supply of excitation voltage to the generator .
To do this, you should remove the small chip from the generator. There are usually two wires connected to it: one is the power wire through which the charging current flows, the other is the generator excitation wire, which goes to the control lamp on the dashboard. So, the polarity on the small wire should change when the ignition is turned on. To check the voltage on the excitation wire you will need an assistant. If the polarity on the excitation wire does not change , look for a wire break . Of course, this is a rare case, but it does happen.
Failed generator. This problem is the most common. the voltage regulator or brush assembly fails . Usually all this is combined in a so-called “ tablet ”, to which there is open access. Changing it is not difficult, and it is not that expensive. First, you should remove the brush assembly to assess its condition . This can most often be done without removing the generator ; before starting work, be sure to remove the negative terminal of the battery. If the brushes are worn out, then of course there will be no charging. The next thing to do is check the voltage regulator . The easiest way to find a diagram specifically for your generator is on the Internet and use it to check the condition of the regulator with a multimeter.
Voltage regulator
If the problem is not in the tablet, then you will have to remove the generator from the car and disassemble it .
Mounting block
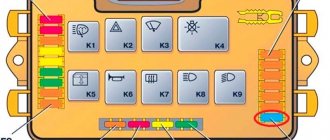
Located under the instrument panel for controlling dimensions and headlights, on the driver's side to the left of the steering wheel. In this block, Kalina fuses are responsible for the safety of almost all installed electrical appliances. The location of the mounting block for car fuses of generations 1 and 2 is the same, but its diagram is different.
A breakdown of the Kalina fuses of the 1st and 2nd generations is presented below.
General understanding of the cooling fan
The design is presented in the form of an ordinary electric motor, which is powered by 12V from the on-board network. The shaft has a special impeller, through which an air flow is formed, directed to the surface of the radiator. The fan is attached to the front of the frame, and is covered with a radiator grille on the reverse side.
Using the VAZ as an example, it is worth noting that most often there is only one fan in the system, but there are exceptions among the domestic auto industry, as well as foreign cars. For example, NIVA is equipped with an impeller with two independent electric motors. This design helps to increase the cooling rate of the liquid, which is an additional guarantee of engine safety.
Control block
On the 1st generation Kalina it is installed under a cover in the center console. The fuses in this unit protect the most basic electronics. There is also a connector for injector diagnostics. On a 2nd generation car the unit is located under the hood, in the engine compartment.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
A fan is a device that allows you to increase the efficiency of a cooling radiator. The radiator takes heat from the engine and releases it into the air. This process is accelerated by blowing through the blades of an electric fan.
The coolant flows through a closed, sealed system. Its task is to remove excess heat from overheated engine parts. Hot antifreeze flows into the radiator, is cooled here and returns back. While in the radiator, the coolant passes through a system of thin tubes. The incoming air flow while the car is moving helps to quickly remove excess heat from the engine compartment.
But when the car is stuck in traffic or idling, the air flow stops cooling it. In this case, the cooling system may not cope with its task. An electric radiator fan is designed to create air flow artificially. The temperature for turning on the fan on a VAZ 2114 is 85 degrees Celsius.
Having received a signal that the permissible temperature value has been exceeded, the sensor starts the device’s operating mechanism. An artificial air flow is created that removes heat from the radiator. The mechanism operates until the temperature level drops to an optimal state.
The thermal switch then receives a signal that the normal temperature has been reached and turns off the fan.
The device consists of four plastic blades that are mounted on the EDF shaft. A special controller regulates the automatic operating mode. The thermostat is equipped with a solid filler that is sensitive to temperature changes.
There are main and additional valves. When the temperature reaches 85 degrees Celsius, the main valve opens.
Decoding the fuses on Kalina 1
Mounting block fuses
| Marking on the diagram | Current strength, A | Protected elements of the electrical network |
| F-1 | 10 | Turn signals, reverse signal, immobilizer, instrument panel |
| F-2 | 30 | Electric door windows |
| F-3 | 10 | Emergency Signal |
| F-4 | 20 | Windshield wipers and washer, turning off heated rear view glass |
| F-5 | 25 | Interior heater engine (heater) |
| F-6 | 20 | Sound signal (beep) |
| F-7 | 10 | Car interior lights, brake lights |
| F-8 | 20 | Heated rear view glass |
| F-9 | 5 | Right dimensions, glove compartment lamp |
| F-10 | 5 | Left dimensions, external rear license plate illumination |
| F-11 | 7,5 | Rear fog lights |
| F-12 | 7,5 | Right low beam, low beam position control for right headlight |
| F-13 | 7,5 | Left low beam, low beam lamp position corrector for left headlight |
| F-14 | 10 | Right high beam |
| F-15 | 10 | Left high beam |
| F-16 | 10 | Right front fog lights |
| F-17 | 10 | Left front fog lights |
| F-18 | 15 | Seat heating |
| F-19 | 10 | ABS brake system |
| F-20 | 15 | Cigarette lighter |
| F-21 | 10 | Reverse fuse "Kalina" (limiter on the gearbox) |
| F-22 | 15 | Security alarm |
| F-23, F-24, F-25 | Stock | |
| F-26 | 25 | ABS |
| F-27 | 50 | Electric power steering |
| F-28 | 50 | ABS |
luxury equipment
| № | Denomination | Protected Circuits |
| F1 | 50A | Heated windshield |
| F2 | 60A | Generator |
| F3 | 60A | Generator |
| F4 | 40A (in the configuration without air conditioning - 30A) | Electric radiator cooling fans |
| F5 | 50A | Electromechanical power steering |
| F6 | 40A | Anti-lock brake system (ABS) control unit |
All lamps used in Lada Granta >>>
"Kalina 2" - decoding the purpose of the fuses
Mounting block fuses on Kalina 2
| Designation on the diagram | Current strength, A | Protected elements of the electrical network |
| F-1 | 15 | Ignition coil, injectors, engine control unit (ECU, “brains”), engine cooling fan |
| F-2 | 25 | Body electrical equipment, power windows, exterior mirrors |
| F-3 | 15 | Automatic transmission |
| F-4 | 15 | Airbags |
| F-5 | 7,5 | Instrument panel, electric power steering, speed sensor, brake light, windshield wipers, heated rear and windshield, heated seats |
| F-6 | 7,5 | Reversing warning light |
| F-7 | 7,5 | Canister purge valve, mass air flow sensor (MAF), oxygen concentration sensor, phase sensor |
| F-8 | 25 | Heated rear window and exterior mirrors |
| F-9 | 5 | Right dimensions |
| F-10 | 5 | Left dimensions, rear license plate illumination |
| F-11 | 5 | Rear fog lights |
| F-12 | 10 | Right low beam |
| F-13 | 10 | Left low beam |
| F-14 | 10 | Right high beam |
| F-15 | 10 | Left high beam |
| F-16 | 10 | Front fog lamp right |
| F-17 | 10 | Front fog lamp left |
| F-18 | 20 | Cigarette lighter, heated seats |
| F-19 | 7,5 | ABS system |
| F-20 | 15 | Sound signal (beep) |
| F-21 | 10 | Fuel pump |
| F-22 | 15 | Wipers and washer for rear and windshields |
| F-23 | 5 | Diagnostic connector |
| F-24 | 7,5 | Air conditioning, climate control |
| F-25 | 7,5 | Brake lights |
| F-26 | 25 | ABS |
| F-27, F-28, F-29, F-30 | — | Reserve |
| F-31 | 30 | Body electrical equipment, windshield wiper motor |
| F-32 | 30 | Interior heater (stove), climate control |
Changing the safety valve
Another equally common problem that can lead to fan interruptions. If the above checks have been previously performed and all elements are in order, then you need to check the safety valve of the expansion tank.
The main function of the valve is to maintain the operating pressure above atmospheric pressure. Thus, the water present in the liquid does not boil when the temperature reaches 100 degrees. If the valve stops working, the pressure becomes the same as atmospheric pressure, and the liquid will begin to boil when it reaches a certain temperature.
The sensor will only work at 105-107 degrees. The liquid will begin to boil and the fan will not work. It is impossible to check the operation of this element in artisanal conditions. But it’s realistic to buy a new part and make a replacement.
If you need to replace the sensor, it is important to buy the same model with identical characteristics. Otherwise, the cooling system will start working too sooner or later. You can do the replacement yourself using the following procedure:
disconnect the battery terminal;
empty the radiator of liquid;
disconnect the two wires that are connected to the sensor. Use a 30 mm wrench;
Apply sealant to the new sensor and install it in the appropriate place;
do not tighten the sensor too much;
Fill with coolant, start the engine and wait until the temperature rises.
If all steps are done correctly, the procedure does not take much time. On average, replacing a new sensor takes no more than 30 minutes. You can contact a specialized center, but a simple procedure can be expensive.
What can you do when the battery is not charging?
If the battery does not charge while driving, you need to localize the problem. First you need to figure out whether the battery or electrical equipment of the car is to blame. If the battery is 5+ years old, then it may not be charged simply due to the exhaustion of its resource. If it is less, you need to check the level and density of the electrolyte, try charging from an external charger. It’s even better to carry out a control charge-discharge cycle by measuring the actual battery capacity, then everything will become clear. If everything is in order, the fault must be looked for in the car.