Misfires - what is it?
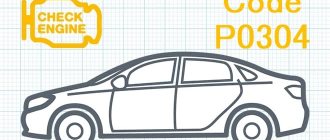
Let's start with what is a cylinder misfire? This phrase means a situation where in one of the cylinders the ignition of the fuel mixture occurs late or slow. Simply put, the “acceleration” of the piston in some of the cylinders is slower than in the others. As a result, there is a violation of the synchronization of the engine, the engine runs unevenly, jerking occurs, fuel consumption increases, and the dynamics of the car decreases so much that even a small hill becomes a big test. In addition, in cars equipped with an ECU, a corresponding error appears on the display in the form of a code, for example “P0304” - misfire in the fourth cylinder. The last digit in the code corresponds to a specific cylinder.
Consequences of incorrectly setting timing marks
If the ignition is set incorrectly, the following negative aspects are possible:
- If the engine has 16 valves, then they become deformed or bent during operation, accumulating damage.
- The previous problem causes damage to the cylinder head.
- The guide bushings may also become unusable.
- Cracks may appear in other engine components.
Crack in the cylinder block
- The motor overheats.
- The engine piston mechanism can burn out.
- Oil residue may appear on the spark plugs.
Oil deposits on spark plugs
The fuel mixture loses its ignition moment.
After repairs, the following factors most often indicate an incorrectly set ignition:
- The car accelerates worse.
- Frequent overheating of the motor.
- The craving became much worse.
Misfires - causes
First, you should perform a visual check of those parts that most often cause misfires in the cylinders. We are talking about spark plugs, explosive wires, and the ignition coil.
- High voltage wires (HV wires). These should be checked first. To begin with, as I said, it is necessary to carry out a visual inspection for the presence of breaks, cracks and other damage. After inspection, if everything is in order, it is recommended to ring the explosive wires and replace them if necessary.
- Spark plug. After the explosive wires, the spark plugs should be checked secondly, since quite often they are the cause of leaks. The spark plugs may have too much gap, they may be worn or punctured, causing the spark plug to flow intermittently or not at all.
- Ignition coil modules. If this part fails, misfires may occur in the cylinders.
Next about more global problems.
- TVS. The air-fuel mixture, or rather its quality, can often cause misfires in the cylinders. Due to low-quality fuel, contamination of injectors and fuel equipment occurs. Also, if the proportions are violated, for example, when the mixture is too rich or lean, components such as the fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator may fail, and the filter may very soon become clogged. Also, if the mixture is too “lean,” that is, it consists more of air (due to air leaks), ignition may occur intermittently, since a regular spark will simply not be enough to ignite this fuel assembly.
- Compression in cylinders. Poor and uneven compression can lead to insufficient compression of the fuel assembly, resulting in uneven and intermittent ignition.
- Timing belt malfunctions. In case of increased or excessive wear in the parts of the gas distribution mechanism or the presence of leaks in the hydraulic compensators, leaks may occur in the engine cylinders.
- Air leak. If an air leak occurs between the head and the intake manifold, it is quite possible that an error will appear indicating that misfire occurs in one of the cylinders.
Diagnostics should be comprehensive and continue until the engine runs smoothly without interruptions or misfires. As you can see, the topic is quite extensive and the reasons for misfires in the cylinders can be very different. If symptoms indicating omissions appear, it is recommended to carry out a visual inspection and, if any malfunction is detected, eliminate it. However, if the cause of the misfire has not been established independently, you should seek help from specialists who, using special equipment, will quickly and accurately determine what is wrong and why misfire occurs in the cylinder of your engine.
That’s all I have, thank you for your attention, I would be grateful if you complement me in the comments, and also if you share this article with your friends on social media. networks using the buttons below.
Checking the set ignition
To check the ignition on an 8-valve engine, one injector should be prepared:
- Multimeter.
- Set of wrenches and screwdrivers.
- Pliers (always with insulated handles).
The process looks like this:
- Remove the unit from the module, connect a multimeter (control mode should be low AC) to pins C and B, make sure there is voltage. Check the coil (2nd and 4th pin).
- With the ignition off, check how tight the high-voltage wires are and what contact is in the module.
Check the power supply to the ignition module
Check the condition of high-voltage cables. Install a working spark plug into each cap in turn, attach one end to the block and start the engine with the starter. The presence of a spark signals that everything is normal. Its absence on each wire means that the module is faulty.
Checking high voltage cables
If you were able to set the ignition correctly on the VAZ model and this was confirmed by the test, but you still observe problems, then you need to check the fuel system.
Important nuances
If misfires occur on a VAZ 2114, this is a fairly serious problem that can develop into more serious consequences. At first the car jerks, then misfires occur, and full power is not used.
Swimming revs
It will be difficult to start the car, and over and over again the detonation noise of the air-fuel mixture will occur in the idle cylinder.
- Cylinders can be checked using computer diagnostics. This method produces the corresponding errors in the form of codes. Using them it is already easy to determine which cylinder has problems. For example, if there is a misfire in cylinder 2 on a VAZ 2114, then the error code will look like P0302.
- The electronic control unit, that is, the ECU, regularly monitors the operation of the power unit using the appropriate sensors installed on the VAZ 2114. In the case of misfires, the ECU estimates the rotation speed using the crankshaft sensor. If there is a misfire in cylinder 4 on a VAZ 2114, at a certain moment the crankshaft will rotate more slowly, which will be determined by the computer.
- Modern electronics make it possible to automatically turn off a cylinder that has problems. In other words, the fuel supply to it stops.
- The cylinder may return to operation after some time, or after the engine is restarted.
- No more than two cylinders can be switched off at the same time. For your “fourteenth” model, two cylinders are enough to get to the garage or the nearest service station, thereby keeping the catalyst intact.
- In early versions of the VAZ 2114, the electronics generated errors about omissions if the car was moving on bad roads. On updated versions, this problem was eliminated by installing a road surface quality sensor.
- Misfires are not always easy to determine, since this phenomenon is not constant and can occur periodically on the VAZ 2114.
- Car owners often make mistakes in winter, when the engine starts to throttle when warming up, and then, when warmed up, it works normally. This phenomenon occurs due to wear on the cylinders, since when warmed up the metal elements expand and the system returns to normal operation.
- If the VAZ 2114 engine runs normally at idle, but when the load increases, it starts to stall or operate unstably, the cause should be sought in a burnt gasket. Because of this, pressure increases inside the combustion chamber and a leak occurs.
- When the engine coughs a little, but soon returns to normal operation, it becomes difficult to determine the cause. This will require a full diagnosis.
How to fix the problem?
The way to eliminate problems that arise is to replace damaged or worn parts.
It is better to correct such defects in a specialized service, where they will first find out the cause of the problem.
Some causes of misfires in the VAZ 2114 can be found and eliminated yourself:
- If gaps and error 300 appear on the computer screen, you need to unscrew all the spark plugs, check the gap between the electrodes and see how much carbon is present on their surface. In case of module errors 0301, 0302, etc., you must carefully monitor the condition of the spark plug in this cylinder.
- It is necessary to visually inspect the wires going to the spark plugs; if cracks are found on the surface, they should be replaced with new ones.
- Check the condition of the camshaft drive belt and the alignment of the marks on it. If the phases are violated, it is necessary to adjust the gas distribution system.
- Check the compression, which should not be lower than 10 and not higher than 14 bar and should not have a spread across the cylinders higher than 1 bar. If the pressure is low, it is necessary to check the valve clearance adjustment.
- View games with valves. Sometimes when adjusting, the gaps are set incorrectly and the drain valves do not close completely. Check and adjust distances every 20 thousand km, and when using gas as fuel - after 10 thousand km.
- If misfires occur in different cylinders under different operating conditions of the unit, the ignition module must be replaced.
Sources
- https://AlanSpb.ru/tehservis/propuski-v-cilindrah-vaz-2114-prichina.html
- https://AccBook.ru/to-avto/propuski-zazhiganiya-vaz-2114-inzhektor-8.html
- https://avtonomnaya-gazifikaciya.ru/obsluzhivanie/propuski-v-cilindrah-vaz-2114-prichina.html
- https://carfrance.ru/mnozhestvennye-propuski-zazhiganiya-vaz-2114/
- https://TrueScooters.ru/tehservis/propuski-zazhiganiya-vaz.html
- https://provaz2114.ru/elektrika/pochemu-byvayut-mnozhestvennye-propuski-zazhiganiya-na-vaz-2114.html
- https://auto-nix.ru/snyatie-i-zamena/propuski-zazhiganiya-na-vaz-2114-prichiny-diagnostika-sposob-vystavit-zazhiganie.html
- https://pilot-avto77.ru/remont/propuski-zazhiganiya-v-1-cilindre-vaz-2114.html
Troubleshooting
The task of diagnostics for misfires is to determine which cylinder on your VAZ 2114 has problems.
Main causes of misfires
First of all, your light comes on, signaling the need to check the engine. During diagnostics, an error lights up - P0300 .
The table provides information regarding which error code corresponds to problems in a particular cylinder.
| Cylinder number | Error code | Where is the pass |
| №1 | P0301 | Problems with the first cylinder |
| №2 | P0302 | Problems with the second cylinder |
| №3 | P0303 | Problems with the third cylinder |
| №4 | P0304 | Problems with the fourth cylinder |
Common faults
Let us immediately note that the problem with omissions that arise should only be solved at specialized service stations. You can identify the problem cylinder yourself. But after this, you should go to a car service center and, using computer diagnostics and appropriate measures, fix the breakdown.
Diagnostic program
There are several reasons why such a phenomenon as misfires in the ignition system occurs on the VAZ 2114.
- Problem candles. If carbon deposits appear on them, the gap decreases or increases, they will not be able to work properly. As a result, there are misfires in the cylinders. Quite often, spark plugs do not work for the simple reason that the car owner decided to save money and buy spark plugs of dubious quality. You should not count on their long service life and reliable operation.
- Wiring problems. Here you most often have to deal with wire wear, chafing, and mechanical damage. Sometimes the problem is solved by replacing the wiring. But in some cases, wiring can negatively affect the functionality of the devices it goes to. As a result, both the wiring and the device must be replaced.
- Contacts. Contacts may burn out, become covered in oil, or rust. Cleaning them or completely replacing them may help. The second option is preferable in order to reduce the risk of omissions occurring after a short period of time.
- Damage to the ignition coil or module. If you have a VAZ 2114 with a 1.6-liter engine, you are dealing with a coil. Owners of the newer version with a 1.5-liter engine are already solving problems with the ignition module. Regardless of this, units often fail and cause leaks. There is no point in repairing them, so it is better to immediately replace them with new ones.
- Use of low-grade fuel. The problem for many owners of domestic cars is that they, sometimes unknowingly, doom themselves to constant repair work. A trivial example is the use of cheap gas stations. Low-quality gasoline produces a poor air-fuel mixture, clogs filters, and clogs injectors. This often causes misfires in the cylinders. The right solution is to fix the problem and start using good gas stations. Their gasoline is more expensive, but you will spend many times more money on repairs if you don’t stop refueling with God knows what.
- Omissions. They also often occur due to impaired compression in the cylinders. This fault should be checked almost first.
- The gas distribution mechanism is not adjusted correctly. Its adjustment will not take much time; the work can be done with your own hands.
- Excess air enters the fuel system. This may occur due to damage to the intake manifold, wear of the rings on the injectors and other defects. Therefore, you should check the system for leaks and find sources of air intake.
- The gap between the piston and cylinder has decreased. There may be many reasons for this, but you will definitely have to check them if this is the reason.
Diagnostics using a computer
If your car is equipped with a modern control unit, then this greatly simplifies troubleshooting; otherwise, you will have to use time-tested old-fashioned methods.
By connecting the computer to the car, you can find out in which cylinder, 1, 2, 3 or 4, and for what reason there are misfires, for example, the ignition coil or one of the injectors has failed.
But in any case, before going to a car service center, you need to check the condition of the spark plugs, injectors, high-voltage wires, how the exhaust system works, and whether there is smoke from the exhaust pipe.
Many car owners cannot afford instruments for car diagnostics, these include scanners (software and portable), motor testers, oscilloscopes, gas analyzers and other devices, and you need to be able to use them, read error codes, and so on. Although if you look into it, there is nothing complicated there.
The scanner is connected to a special connector, which can be located in different places in each car model, but it has one function: diagnostics.
Next, error codes are read from the control unit and decrypted.
For example, VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115, Lada Kalina, Priora, Granta cars have the following error codes that are characteristic of misfire:
- P0300 - a large number of misfires;
- P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – misfires in cylinders 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- P0300 - a large number of misfires in a random order;
- P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – misfires were detected in 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
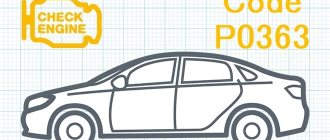
- P0363 – see point 4 + fuel supply to problem cylinders is stopped;
- P1301, P1302, P1303, P1304 – respectively, misfires dangerous for the catalytic converter were detected in cylinders 1, 2, 3, 4;
- P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – detection of misfires affecting the toxicity of exhaust gases;
- P0363, P1301, P1302, P1303, P1304 – the same as in point 7, but affecting the catalyst;
- P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354 – open circuit in the ignition coil in the control circuit 1 (1-4), 2 (2-3), 3, 4;
- P2301 P2303 P2305 P2307 - short to on-board network in the coil in the control circuit of cylinders 1 (1-4), 2 (2-3), 3, 4;
- P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204 – respectively, open circuit for controlling injectors 1,2,3,4;
- P0261, P0264, P0267, P0270 - short circuit of the injector control wires to the body, respectively, in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th center;
- P0262, P0265, P0268, P0271 – the same as point 12, but only to the on-board network;
- P1500 – electric fuel pump relay, wire break.
Diagnostics of VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115, Kalina, Priora, Granta
Let's look at misfires using the example of the VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115, Kalina, Priora, Granta models.
The computer generated error P0303 (misfire in 3rd crank).
First you need to understand how the ignition coil works. It consists of two small coils, pins 1 and 4 are connected to the first, and pins 2 and 3 to the second.
Those. during operation, voltage is simultaneously supplied to the first and fourth cylinders or to the second and third.
We have misfires in cylinder 3. Remove the wires from 2 and 3 and swap them.
Start the engine and see if the error has moved to cylinder 2, then the problem is most likely in the high-voltage wires or in the coil itself, and they need to be checked first.
High-voltage wires are tested by checking their resistance. To do this you need a regular multimeter.
Set the resistance measurement mode to 20 kOhm.
In our case, we check the third wire. If the device shows numbers within the range of 3.5 - 10 kOhm, then the wire resistance is considered normal, otherwise it changes.
Next we check the coil. For this you will also need a multimeter.
We measure the resistance between 1 and 4 and 2 and 3 coil terminals. Readings of 10 kOhm, or around this figure, are considered standard.
Important. During testing, the tester should not show 1. This means that there is an open circuit in the circuit and the coil is faulty.
Next we check the resistance between each terminal and ground. In this case, on the contrary, the multimeter should show 1 (infinity).
If resistance is shown at one of the terminals, it means that its insulation is damaged and it is connecting to ground. Accordingly, the required voltage will not be supplied to form a spark.
Next, we check the resistance between the central terminal of the ignition coil and the housing (ground). It should also be equal to infinity, i.e. 1.
Now it remains to check the resistance between the extreme terminals. To do this, set a different measurement limit on the device - 200 Ohms.
A resistance of 2 ohms is considered normal (+-). There should be no break between the extreme terminals.
Next, check the condition of the contacts on the coil itself and on the wires; they tend to oxidize over time, especially if your region of residence has a humid climate.
If the error remains in cylinder 3, but the coil and high-voltage wires are in good condition, we check the spark plug.
The easiest option is to remove the spark plug from the working cylinder and swap them.
If the error then transferred to another cylinder, then most likely the issue is in the spark plug.
If nothing has changed and the error remains, then check the injectors.
In this case, you also need a multimeter. Disconnect the wires from the injector, in our case from cylinder 3, and measure the resistance, it should be about 13 ohms.
Next, check the injector power supply circuit. Also, the injector may become clogged and not supply the required amount of fuel, which can cause misfires. Therefore, you will have to clean the injectors.
If after all the above checks the misfires have not disappeared, you need to check the valve clearances.
The valves should not be tightly clamped, as this will lead to their incomplete closing, and this, in turn, will lead to a decrease in compression and compression ratio in the cylinders and this will cause misfires. Also, if you press too hard, the valve may burn out.
Especially the condition of the valves should be paid to owners of cars with LPG, since the combustion temperature of gas there is slightly higher than gasoline and therefore the thermal clearances of the valves in this case should be slightly larger, i.e. not 0.2, but 0.25 mm. And where is 0.3, then 0.35 mm (for the above models).
READ ON THE TOPIC: Other characteristic malfunctions of the VAZ 2110 and other cars in the series.
BMW x5 e53 engine m54 3.0 USA
If we talk about foreign cars, they also have special error codes indicating misfires.
Let's look at the error codes using the example of a BMW x5 e53 motor M54 3.0 USA (if the country of manufacture is different, the codes may differ).
As a rule, these errors are associated with problems with mixture formation, sparking and decreased compression:
- Problems with the ignition coil - errors 101, 202, 303, respectively, cylinders 2, 4, 6;
- Injector circuits – errors 505, 606, short circuit, open circuit;
- Injector - codes 2216, 2317, 2418, 3321, respectively, refer to cylinders 3, 6, 4, 5;
- Malfunction of the idle air control valve - 271V;
- Ignition coil - errors 291D, 301E, 311F - 1, 3, 5 ts.
- Problems with the camshaft position sensor - error code 6541;
- Fuel pump relay - error code 6945;
- Problems in the ignition system - 210D2;
- Failure of the idle air control valve as a result of its mechanical damage - 211D3;
- Poor quality fuel mixture - 227E3 for cylinders 1, 2, 3 and 228E4 for 4, 5, 6.
- Cylinder misfires - 238EE in the first, 239EF in the second, 240F0 in the third, 241F1 in the fourth, 242F2 in the fifth, 243F3 in the sixth;
- Weak flow in the air mixing system - 245F5 cylinders 1, 2 and 3. Error code 246F6 - 4, 5 and 6 cylinders.
Also, the reasons for misfire in a BMW x5 e53 M54 engine can be:
- Air leakage, for example, the throttle corrugation or other suction points are torn;
- The mass air flow sensor has failed;
- Incorrect operation of hydraulic compensators;
- Timing chain stretching and ignition timing deviation;
- The high-voltage coil of one of the cylinders has failed (rearrange it to check);
- The problem is in the flow meter, remove the terminal block from it and see how the engine works;
- If the BMW x5 e53 has misfires after 3000 rpm, then check the DIS (DISA - installed inside the intake manifold, designed to suck in the fuel mixture through separate pipelines);
- A failed membrane is responsible for the mixture of gasoline and air;
- Other reasons.
Why do misfires occur and how to fix them? 7 main causes of malfunction
The engine is the heart of the machine, which, if not properly maintained, can break down and cause failure of other systems and components. There are often situations when the car loses power, vibration appears, and the equipment stalls at idle. The cause of this phenomenon can be various engine breakdowns, including misfires, which reduce engine efficiency and can lead to failure of the fuel and exhaust systems.
Almost every motorist has encountered the problem of flammable mixture ignition. There can be many reasons for problems when igniting a combustible mixture, but they all lead to a drop in engine power and the shutdown of one or a pair of cylinders. On cars with an ECU, when the engine malfunctions, errors appear that indicate problematic parts of the unit. If misfires occur, you should urgently contact a service station to troubleshoot the problem.
How does the ECU know when misfires occur?
The ECM may detect misfires differently depending on the vehicle model and engine. The ECU uses many sensors to know when to fire the spark plug, when to inject fuel into the cylinder, and how to change the air-fuel mixture. To detect misfires, the control unit often uses a crankshaft sensor.
Engine ECU
The crankshaft sensor measures the position of the crankshaft and calculates its revolutions per minute. The crankshaft sensor uses the camshaft sensor to determine which cylinder is at top dead center and ready to ignite. Pushing the pistons down causes a slight increase in crankshaft speed. If the crankshaft sensor does not recognize this increase in speed, the engine control unit will store a fault code on the cylinder on which the misfire occurred.
Sometimes the control unit cannot determine which cylinder is misfiring and it stores the error code P0300 (random misfire).
Some ECUs use ignition coil resistance. When ignition does not occur, the control unit understands this through the electrical wiring, which leads to an error. This method is not as common as detection using the crankshaft sensor.
Symptoms of a problem
A mixture misfire is a failure to ignite the fuel-air mixture or its untimely ignition. In any of the cases, the system counts the number of misses and delays, and, if necessary, turns off the idle cylinder or even a pair. On most cars, the first sign of a malfunction is the “check” symbol lighting up on the dashboard.
Also among the common signs can be noted:
- Smell of fuel from the exhaust pipe . Since the mixture did not ignite in the cylinder, it is discharged almost unchanged or partially neutralized.
- Shoots in the exhaust system . If a partial fire occurs, the catalytic converter is severely damaged, which can lead to popping noises.
- Loss of power . The engine does not work properly, causing the crankshaft to spin at a lower speed, resulting in a significant loss of power.
- Engine tripping . Failure of one or a pair of cylinders leads to the fact that the engine begins to vibrate during operation and other signs of malfunction appear.
In cars with an electronic control unit, there are several types of errors that indicate a breakdown.
- P0300 . It is a sign of multiple failures in the process of ignition of the combustible mixture in different cylinders.
- P0301 - p0304 . The last number shows which cylinder is not working properly.
SIGNS AND REASONS OF “ADJUSTMENT”
Engine trouble: what is it, and what are the signs to identify this malfunction? You can understand that the internal combustion engine is malfunctioning by the following signs:
- At idle speed, the engine operates unevenly, jerking periodically;
- The car does not develop the required power when driving;
- The car drives jerkily, when you press the gas pedal, there are gaps in operation;
- The exhaust from the muffler is uneven, with interruptions, pops and shots are possible;
- Fuel consumption increases.
Increased fuel consumption hurts your pocket Reasons: There are many reasons why the engine misfires. There are such nuances that even experienced technicians do not immediately determine the nature of the malfunction. But the most common cylinder failures are the following (starting with the elementary ones):
- The candle does not work;
- The high-voltage wire is broken;
- The ignition coil has failed;
- The control unit is faulty;
- There is an air leak in the intake manifold;
- Exhaust valve burnt out;
- The cylinder head gasket is broken;
- The compression rings on the piston are broken,
- The piston itself has burned out, or the bridge on the piston between the compression rings has burst.
This article is about the VAZ 2114 car, so carburetor malfunctions are not considered, since this device was not installed on the 2114 model. This brand of car has a fuel system with distributed injection (injector), and the answer to the question of why the engine stalls may be hidden in this system.
Causes of misfire in injection engines
Since carburetors have a lot of shortcomings and unstable operation, injectors are mainly installed on modern cars. Stable operation, efficiency, frost resistance and environmental friendliness ensure the reliability of the motors and their durability. Injection engines are equipped with an ECU that regulates the composition of the combustible mixture and its supply.
When problems arise with fuel ignition, an error appears in the control unit, which helps to identify the faulty part of the unit.
When a breakdown is detected, it is necessary to conduct in-depth diagnostics to identify all faults. The most common reasons are the following.
Combustible mixture quality
If the air-fuel mixture has incorrect proportions, it will not ignite. Sometimes simply changing the gas station is enough, but in some cases major repairs may be needed. Low-quality fuel can clog injectors and filters. The reason for supplying the mixture in the wrong proportions may be a faulty fuel pump or pressure regulator. It is better to entrust complex diagnostics to authorized service stations, since independent examination of devices does not always allow you to detect an error.
Candles
Worn spark plugs can lead to misfires at idle and the engine constantly stalling. Sometimes you come across defective spark plugs that do not produce a spark. A change in the gap can also cause the fuel-air mixture to fail to ignite.
Armored wires
Faulty high-voltage wires do not cope with the task, which leads to misfires. Damage due to the mechanical impact of the armored wires or high resistance in them does not allow the mixture to ignite and can cause engine failure.
Cylinder deformation
If the gap between the piston and cylinder has changed, then significant changes appear in the operation of the engine. Although this reason is quite rare, it must be taken into account during a full diagnosis.
Incorrect compression
Uneven or low compression of the combustible mixture prevents it from igniting. The problem arises due to a violation of the integrity of the piston rings or wear of the CPG.
Malfunctions of the device can cause misfires on a cold engine. Due to the incorrect size of the device gaps or leaks in the hydraulic compensators, problems may arise when the mixture ignites.
The problem may also be in modules or faulty coils (
Algorithm for checking elements to eliminate error P0300
Since there are many possible causes for error P0300, it is necessary to adhere to a certain troubleshooting algorithm. Here is a sequence of actions to quickly detect the cause of misfires:
- Diagnostics should begin by checking the high-voltage wires. To do this, you will need to get a multimeter, set it to measure resistance (Ohm) and measure the values of the wires. If the insulation of high-voltage wires is not broken, as a result of the test the resistance will be about 4-10 kOhm;
- Inspect the intake manifold gasket. If it is very worn, it will need to be replaced;
- Another possible cause of P0300 is a stuck exhaust gas recirculation valve. When diagnosing a vehicle, check the long-term fuel trim value for a specific cylinder. It should differ from the ideal value (which can be found from the literature on maintenance of a specific car model) by no more than 1-3% in any direction. If the deviation is 7% or more, then there is additional air intake.
The above are the basic steps that most often help to find the cause of the P0300 error code. When checking the above elements, pay attention to their condition - the presence of soot, traces of mechanical damage, and so on.
Other possible causes of the P0300 error must be determined depending on what other errors the scanner indicates during diagnosis. That is, if the oxygen sensor fails, then in addition to P0300, error P0134 or P0130 may occur. Try eliminating other errors that are diagnosed together with P0300, perhaps this will immediately eliminate it too.
How to detect a malfunction yourself
We also recommend reading our expert’s article, in which he talks in detail about what a contactless ignition system is.
Be sure to read our specialist’s article, which tells you how to set the ignition correctly.
In cars with ECU
In cars with an ECU, troubleshooting is a fairly easy task. To do this, you need to connect an autotester and find the error code. If among the error codes there is an indication of a specific cylinder, then you should pay special attention to the condition of the element. Perhaps the problem is hidden in the armor wires or spark plugs that go to this cylinder. The gaskets may also need to be replaced. If a complex error (p0300) is issued, then you should pay special attention to the quality of the fuel and the filter.
Even domestic cars now have electronic units installed. If the car initially has an ECU, but its performance leaves much to be desired, then you can replace the part at a certified service station. The new “brains” must be compatible with the previous model. Thanks to the new electronic control units, you can easily find misfires in the 1st and 4th cylinders of the VAZ-2114 or on any old foreign car, as well as diagnose the operation of the 2nd and 3rd cylinders without unnecessary hassle.
In cars without ECU
It is much more difficult to find a fault on machines without an ECU. Most often, misfires occur in two cylinders at once. In cars, it is necessary to manually check the operation of each device and inspect the electronic elements. First of all, you need to check the condition of the spark plugs and armored wires.
If the ohmmeter shows unacceptable values, then the high-voltage wires need to be replaced. If the inspection does not reveal any malfunctions, then the compression indicators in the cylinders are measured and the fuel pump is checked (read more about how to check the fuel pump).
The final stage of diagnosis consists of dismantling the valve covers to inspect the condition of the piston rings and the cylinders themselves.
Let's figure out how to set the ignition on a VAZ 2114 correctly
The first cars in this series were produced with a contactless ignition system, and an electronic one appeared only later. Due to the fact that throughout its history the car has been equipped in different ways, before setting the ignition on the VAZ 2114, you need to find out what it is.
Ignition systems of the 8-valve injection VAZ-2114
You can determine the type of ignition by looking under the hood:
- If you find a switch near the “heart” of your car (analogous to a distributor installed on contact systems), it means that your car belongs to the first series, and the ignition of the VAZ 2114 injector on it is non-contact, based on the switch-distributor block. The ignition in such systems is adjusted by gradually turning the distributor, and the results of the work depend on the experience of the performer and the availability of special equipment. Then, using a strobe light, you can debug the system exactly as the car owner wants.
- If this part is missing, your car belongs to the tenth family and is equipped with an electronic ignition system. It cannot be installed manually and its operation is completely controlled by the ECU. However, it is not completely unregulated, because by connecting to the on-board computer, some of its parameters can be reconfigured to your liking, but only a few specialists know how to do this correctly.