The engine cooling system is an important structural element of a car. Its malfunction leads to poor heating of the engine to the required temperature, which causes poor operation of the stove, loss of power and reduced service life of the power unit. On the other hand, the engine system may overheat, which causes breakdown of the cylinder-piston group.
cooling system vaz 21099 carburetor diagram
VAZ 2199 cooling system injector
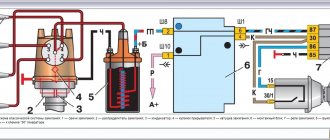
1 – element in the form of a plug for the expansion tank; 2 – expansion tank; 3 – hose for draining liquid from the pipe; 4 – hose passing between the radiator and the expansion tank; 5 – hose leading from the radiator; 6 – tank to the left of the radiator; 7 – aluminum tube; 8 – plug systems; 9 – tank to the right of the radiator; 10 – drain plug; 11 – middle of the radiator; 12 – casing for electric fan; 13 – plastic wings of the electric fan; 14 – electric motor; 15 – toothed pump pulley; 16 – pump impeller; 17 – camshaft drive belt; 18 – engine block; 19 – pump pipe; 20 – radiator hose with supply function; 21 – heater radiator hose with drain function; 22 – hose supplying coolant to the throttle pipe; 23 – exhaust pipe; 24 – hose for refilling; 25 – heater radiator hose with supply function; 26 – thermostat; 27 – coolant temperature sensor; 28 – coolant level indicator sensor.
The cooling system of VAZ 21093,2109,21099 removes heat from engine parts subject to heating through forced circulation. And the injector doses the flow of fuel. Structurally, the VAZ injector cooling system consists of:
- coolant pump,
- monoblock thermostat,
- electric radiator fan,
- radiator with expansion tank,
- pipelines, pipes, drain plugs.
How it works
The operating principle of the cooling system (CO) is as follows:
- The pump drive operates from the timing belt;
- The system has a volume of 7.8 liters, if you take into account the stove;
- The temperature is controlled by a sensor installed in the cylinder block jacket. Temperature readings are displayed on the instrument panel;
- When the engine is running, liquid from the jacket passes into the radiator (heat is removed there) or into the thermostat (work on a small circuit necessary to warm up the engine);
- Then the cooling liquid, using a pump, passes into the cooling jacket of the engine (injection);
- Due to the pipelines, coolant circulates through the system;
- CO uses a centrifugal pump;
- The radiator is a tubular-plate, dismountable, equipped with a plastic expansion tank;
- Inside, the radiator has aluminum tubes and cooling fins, but there is no filler hole;
- An expansion tank is used to fill and top up coolant. The fan switch sensor is also located there;
- The tank is equipped with a filler neck, inlet and outlet valve;
- To drain coolant from the system, you need to unscrew the drain plugs on the tank, radiator and cylinder block.
If you understand in detail the components of the cooling system and their functions and features, you will be able to carry out repair and maintenance work without outside help, change the radiator or individual components of the coolant.
Blade options
https://youtu.be/https://youtu.be/EK7_GSpECNo
_
System operation
The VAZ engine cooling system injector is required to maintain normal operating conditions inside the unit. When the motor and parts located next to it overheat, there is a risk of their partial destruction; cooling prevents this. Of course, the system does not guarantee a strong decrease in the temperature inside the unit, but its resource is quite enough to maintain the operation of the “nine”. The VAZ 2109 cooling system circuit works by distilling a special liquid through tubes placed between the car parts. As the liquid passes through hot areas, it partially reduces the temperature of the parts and heats up itself. The heated liquid is then cooled, after which the operating cycle is repeated. Now in more detail about the structure of the cooling system. It looks like this:
- pipes of the VAZ 2109 cooling system, connecting the cooling fluid (coolant) storage tank, engine and radiator;
- radiator - a device in which the coolant is cooled;
- liquid storage tank;
- pump - ensures the movement of coolant inside the system;
- a thermostat that divides the system into 2 separate circuits.
In addition, there are several small tubes that connect some parts to each other, operation sensors and various valves. Here's how it all works:
- Engine cooling begins when the temperature of the unit reaches 93ºС. A sensor inside the cylinder block measures the ambient temperature and gives a signal when the indicator reaches the limit values.
- The pump starts working, forcing the liquid to move along the lines. First, the liquid leaves the cylinder block jacket and, already heated, is directed to the radiator.
- Reaching the radiator, the coolant is distributed into several flows, filling the thin radiator tubes (thanks to this design, cooling occurs faster).
- The fan turns on, and air flows cool the coolant, after which it leaves the system through another channel and again goes to the cylinder block jacket.
- The cycle repeats.
- When warming up the engine, a small circuit is used, in which a thermostat is built-in, the principle is the same, but everything happens much faster.
The volume of the system tank is 7.8 liters; if repair of any cooling element is required, the tank is emptied. Regular maintenance and fluid replacement should be carried out regularly - every 3 months. It is recommended to use antifreeze or other brands of antifreeze as a coolant.
Pipes and clamps
Even the pipes of the VAZ 2109 cooling system, which have a simple design, play an important role in the functioning of the entire car. With their help, liquid is supplied to the required points. Several pipes can be distinguished (during repairs, they should all be replaced, not one at a time):
- Stove thermostat tap.
- Thermostat-radiator.
- Thermostat-expansion tank.
- Saxophone choke assembly.
- Saxophone-stove tap.
- Stove radiator tap (two pipes).
- Radiator-engine block.
- Engine-thermostat block (“shorty”).
- Thermostat saxophone (“shorty”).
The last two received this name because they are small in size. Don’t think that you can use scraps from other pipes. They will not be able to ensure tightness, unfortunately. Saxophone is the name of the metal pipe that connects the thermostat to the pump. It is located behind the engine, next to the exhaust manifold. When replacing pipes, be sure to change all clamps. It is advisable to use ones that have a larger contact area with the pipe.
When parts need to be replaced
When is it necessary to replace the VAZ 2109 coolant and cooling system elements? The fluid must be changed regularly after a certain period of use. Parts are not changed periodically, but only after a breakdown. One of the causes of breakdowns is overheating due to a malfunction of some element in the cooling system. The following signs of engine overheating can be observed:
- the coolant temperature is higher than normal and can exceed 120ºС, this is indicated by a special sensor;
- there is a sharp drop in engine power;
- the sound of the engine changes, a ringing metallic knock appears;
- oil consumption increases;
- Coolant consumption increases significantly.
As a result of overheating, after you open the hood, you will see deformed parts - bent cylinder head, gasket edging, burnout of some parts. Repairing deformed parts does not make sense; they need to be replaced.
DIY technology for replacing antifreeze on injection VAZ 2109
The replacement concept involves draining the used compound through special holes and filling the system with new antifreeze. The designers provide two drain holes in the cooling system of VAZ engines:
- on the left side of the main radiator;
- on the front wall of the cylinder block.
Replacing antifreeze on VAZ 2109 engines is not possible without first dismantling the ignition module located on the front surface of the cylinder block:
- remove the negative terminal from the battery;
- disconnect the wires from the spark plugs;
- remove the ignition module power supply block;
- unscrew the bolts securing the module relative to the cylinder block and clutch housing;
- loosen the upper left bolt of the front engine mount;
- remove the module bracket from under the bolt;
- remove the module with wires from the engine compartment.
Replacing coolant: antifreeze or antifreeze on VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115 injector
The procedure for replacing coolant on all injection 8-valve VAZs: 2108, 2109
, 2110, 2111, 2112, 2113, .
GROUP https://vk.com/avto_tochka LIVE.
Draining of used antifreeze is carried out according to the following method:
Main parts of the cooling system
The main function of the cooling unit is to remove excess heat from overheated engine parts. This is ensured by forced circulation of the cooling system of the VAZ 2109.
The VAZ 2109 engine cooling unit is a sealed closed-type system with forced fluid circulation. The presence of inlet/outlet valves ensures that pressure is maintained while the vehicle is moving. The VAZ 2109 cooling system diagram consists of the following main elements:
- expansion tank;
- liquid pump;
- radiator;
- electric fans;
- sensors;
- thermostat.
The operation of the VAZ 2109 cooling system begins with the expansion tank. The expansion tank is the main element in this scheme: the working fluid is poured into it. The tank contains a kind of reservoir into which excess boiled (expanded) antifreeze is supplied. After cooling, the liquid returns to the system. The total volume of the VAZ 2109 cooling system is 7.8 liters.
The expansion tank is equipped with valves whose function is to maintain a certain pressure. When the pressure increases, the exhaust valve operates, and when the pressure decreases, the inlet valve operates. The synchronized operation of the valves maintains the pressure in working condition. The expansion tank is made of a translucent substance (polyethylene), thanks to which you can observe the liquid level.
To connect the tank to the thermostat, hoses from the VAZ 2109 cooling system are used.
Description of design
The cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation. The tightness of the system is ensured by the inlet and outlet valves in the expansion tank plug. The exhaust valve maintains pressure in the system when the engine is hot (due to this, the boiling point of the liquid increases and steam losses are reduced), it opens at a pressure of about 1.1 kgf/cm2. The intake valve opens when the pressure in the system decreases relative to atmospheric pressure by 0.03–0.13 kgf/cm2 (on a cooling engine). The thermal operating conditions of the engine are maintained by a thermostat and an electric radiator fan.
The coolant pump is a vane, centrifugal type, driven from the crankshaft pulley by a camshaft drive timing belt. The pump housing is aluminum. The roller rotates in a double-row bearing with a “lifetime” supply of lubricant. The outer ring of the bearing is locked with a screw. A toothed pulley is pressed onto the front end of the roller, and an impeller is pressed onto the rear end. The distance from the mating surface of the pump cover to the outer end of the pulley should be 52±0.5 mm, and to the outer (facing the block) end of the impeller - 39.8±0.1 mm. A thrust ring made of a graphite-containing composition is pressed to the opposite end of the impeller, under which there is an oil seal. If the pump fails, it is recommended to replace it as an assembly.
The redistribution of liquid flows is controlled by a thermostat with a solid heat-sensitive element. On a cold engine, the thermostat valve closes the pipe leading to the radiator, and the liquid circulates only in a small circle (through the thermostat bypass pipe), bypassing the radiator. On VAZ-2108, -21081, -21083 engines, the small circle includes the heater radiator, intake manifold, carburetor throttle assembly heating unit (on engines with semi-automatic starting - and the liquid chamber of the semi-automatic starting device). On the -2111 engine, fluid is supplied to the heater and the throttle assembly heating unit.
Main elements of the VAZ 2109 cooling scheme
So, it’s worth starting with a general description. It should be noted right away that the system is completely sealed and some pressure is maintained in it. It allows the liquid to circulate (of course, this factor is more influenced by the pump). Either pure antifreeze or diluted antifreeze (antifreeze) is used as a coolant. It is highly not recommended to use water, as it leaves a lot of scale on the walls of the system. Let's take a closer look at the VAZ 2109 cooling scheme (together with the heating system).
Expansion tank
This is exactly where our scheme begins. After all, it is the expansion tank of the VAZ 2109 that allows you to fill the liquid. It stores a kind of “reserve”. When antifreeze boils, it expands and any excess goes into the reservoir. When they cool, they go into the system. With the help of the VAZ 2109 expansion tank you can get rid of air jams. One important element is the cork. A truly interesting detail as it has two valves built into it. The first one works for release (at a pressure above 1.3 Atmospheres, excess air is released through it). The second one sucks in air from outside when the pressure drops to 0.2 Atm. Thanks to the synchronous operation of these elements, almost stable pressure is maintained.
We recommend: How to flush a car’s cooling system on your own, including using a folk remedy
Liquid pump
The VAZ 2109 engine is cooled largely thanks to this simple device. It is also called a pump - it is based on only three elements. These are the housing, the drive pulley and the impeller (today plastic is more common, but in the past it was often possible to see aluminum samples). The drive is from the timing belt of the VAZ 2109 pump. The axis rotates through a bearing (but some manufacturers even use bushings to reduce costs). Of course, car owners have little confidence in bushings, even though they are durable. There is a gasket between the cylinder block and the pump housing that prevents coolant leaks. Perhaps this is all that can be said in general terms about this unit.
Radiators VAZ 2109
There are two of them in the cooling circuit - the main one and on the stove. The first one is installed exactly between the headlights, opposite the grille. Thanks to its specific design, as well as the shape of the bumper, air is taken in and the cells are uniformly blown. The heater radiator is installed in a volute heater, which is located under the panel. Connection to the cooling system is carried out using four thin pipes: two in the cabin, two in the engine compartment. Between them there is a heater tap - a plastic part installed in the body window. It has two holes with tips for pipes. Moreover, one is equipped with a simple valve, driven by a lever on the beard via a cable.
Electric fans
Both the main heater radiator and the heater radiator have forced airflow. The main radiator is equipped with a fan, which is mounted in close proximity to the cells. It is turned on using a sensor located at the bottom of the radiator. The first models of nines had a relay in the electric fan switching circuit. It reduced the load on the sensor, which helped increase its service life. But in the late 90s, they began to abandon the additional electromagnetic relay, since the production used sensors whose contacts could withstand the inclusion of power circuits. But if you suddenly decide to re-equip the VAZ 2109 cooling circuit, use a relay, it is more reliable and its use is much more efficient.
But the stove fan has a more complex connection, since it has three rotation speeds. It is installed in the engine compartment, in the center of the body. The air from it flows to the radiator through an air duct with dampers. Three rotation speeds were achieved through the use of a resistor. These are several turns made of nichrome wire, and there is also a branch from the middle. First speed (minimum rotation speed) - all turns of the resistor are included in the power circuit. Second speed - only half of the resistor is turned on. And the third is power directly from the battery. In this case, the impeller speed will be at its highest.
Sensors
The VAZ 2109 cooling circuit uses only two sensors. The first is on the radiator, designed to turn on the electric fan. And the second one is in the engine block (under the distributor). It displays information about the current temperature on an indicator in the dashboard. No maintenance is required as these devices cannot be repaired. If any malfunction occurs, the VAZ 2109 coolant sensor is replaced with a new one. This procedure is complicated only by the fact that it will be necessary to drain the antifreeze (all or partially, depending on which sensor has failed).
Thermostat
The best part was left for the end of the saga about cooling the nine. A thermostat is necessary to redirect fluid flows. Initial heating occurs when antifreeze circulates in a small circle. When it reaches a temperature of about 85 degrees, some of the liquid begins to flow into a large circle (to put it simply, circulation begins through the main radiator). So the thermostat can jam, as a result of which the antifreeze does not flow into the radiator, and the engine begins to overheat. To correct such an “error”, you can knock out all the insides from the assembly (although you will have to drain the antifreeze and pipes). But if there is a breakdown on the road, this is the only way out of the situation. Just remember to fill the liquid level afterward. Here is such a simple cooling scheme for the VAZ 2109, although at the very beginning it was even scary to look at it, because there were so many incomprehensible things in it.
CO elements
The cooling system used on the VAZ 2109 operates at low pressure. After studying the components, you will learn about their functions and features.
| Element | Peculiarities |
| Pump | It ensures efficient, stable operation of the system. The pump is used to pump cooling liquid, which facilitates its movement along a small or large circuit. The pump consists of a housing, an axle with a pulley located on it connecting to the timing belt, and a plastic impeller. The latter allows the coolant to move. A bearing lubricated with antifreeze is installed between the axle and the housing. Because of this, the presence of water in the system is unacceptable. Otherwise the bearing will collapse |
| Thermostat | Plays an important role, although in practice the CO can do without it. The system works in such a way that the engine first warms up to operating temperature (about 90 degrees Celsius), after which it is necessary to further cool the liquid. First, the coolant moves along a small circuit - through the jacket into the stove radiator, and then the excess is returned to the expansion tank. But when the operating temperature is reached, the thermostat begins to move the coolant flow into the radiator. A thermostat can be called a mechanical valve that automates the operation of the CO. Hot liquid acting on the bimetallic plate of the thermostat deforms it, which is why the coolant supply valve to the radiator can open or close |
| Radiators | The SO VAZ 2109 has a pair of radiators - a stove and a main one. Their design is the same regardless of whether you have a carburetor or an injector. At the same time, there is a noticeable difference between the main and stove radiators. The main one is larger in size, they perform different functions, plus the main one has holes for a sensor that turns off the fan. If the stove radiator can be connected to operation at any time by pressing a button, then the main radiator operates in automatic mode when certain operating parameters of the CO are achieved |
| Expansion tank with plug | A constant pressure is maintained inside the CO, which ensures efficient coolant circulation. On the VAZ 2109, the system is designed so that at high pressure the liquid does not boil when it reaches 100 degrees, but at higher parameters. This increases engine reliability. Pressure support is provided by an expansion tank with a cap and a pair of mechanical valves - inlet and outlet. The inlet valve is activated if the pressure drops to 0.13 atm. The second one comes into operation at the moment when the pressure is above 1.3 Atm. |
| Pipes, clamps | Do not underestimate the role of pipes and clamps in the CO, since it is through them that the coolant is supplied to the required points. When replacing, under no circumstances use cuttings from other pipes that do not correspond to the parameters used previously. Plus, if at least one pipe is damaged, everything will have to be replaced as a set, and not separately |
| Sensors | Looking at the radiator (main), below you will see a pair of wires and a yellow device twisted into the hole. This is the electric fan switch sensor. Another sensor is also located in the motor block - temperature. It transmits information to the electronic control unit or pointer |
| Electric fan | As a standard, the VAZ 2109 is equipped with fans equipped with 4 blades. But if you want to achieve greater efficiency, we recommend replacing it with a 6-blade electric fan. This will increase the air flow while maintaining the original power and rotation speed. Heat from the heater radiator begins to flow inside the cabin when the tap is opened. There is a fan under the hood connected via a rheostat. It regulates the rotation speed of the impeller. The switch is located under the audio system, near the heater damper control levers. |
Thermostat
When planning to replace an electric fan, work should be done through the engine compartment. No need to dismantle the snail .
CO pump
Flushing the VAZ 2109 engine cooling system
From time to time, the eight and nine engine requires flushing the cooling system. This is mainly due to the use of low-quality coolants such as antifreeze, which contributes to the formation of plaque and deposits on the walls of the water jacket. Such liquids have an even more destructive effect on the heater radiator and on the main radiator of the cooling system. If the radiator is tightly clogged with coolant decomposition products, it is simply unable to perform its function and the engine instantly overheats even in cold weather. And this doesn’t mean anything good. This is why the cooling system should be flushed.
Coolant replacement intervals
Over the years of operation, the coolant loses its physical and chemical properties, including protection against scale and corrosion, expansion properties when cooling and boiling, and provides lubrication of the centrifugal pump.
To avoid these malfunctions, it is necessary to inspect both the fluid and all units, and, if necessary, replace them during seasonal maintenance.
Owners of cars that have experienced fluid boiling need to take special care of the system, since the protective layer of paint on the walls of the cooling jacket is damaged and the engine block is severely corroded. You need to fill it with high-quality antifreeze and rinse it first.
How to flush the cooling system of a VAZ 2109
You can rinse the cooling system with ordinary boiled (!) water. Boiled, because this way we minimize the amount of salts and minerals in the water that will remain after flushing in the system. Flushing the system is easy. The old fluid is drained, boiled water is poured in, the engine is allowed to idle for 15-20 minutes, after which the water is drained.
This method is ineffective, but very cheap, because water is practically free. If the owner does not spare 300-500 rubles for a special means for flushing the system, then the effect of the procedure will be a hundred times higher. The fact is that these flushes contain substances that carefully and carefully remove scale and coolant decomposition products. And this is a truly effective flush. For example, liquid for flushing the BBF system costs about 300 rubles per flush. After washing, even plaque is removed; the main thing is to strictly follow the instructions.
Antifreeze boils in the expansion tank: causes of the problem and ways to fix it
For proper and efficient operation of the internal combustion engine of a car, antifreeze is used, which is designed to cool the engine . Antifreeze or antifreeze, as a solution, has a higher boiling point and a lower freezing point compared to ordinary water, however, in some cases, this liquid, unable to withstand loads, is capable of boiling directly in the engine cooling system.
Every motorist sooner or later encounters this problem and immediately wants to know why the antifreeze is boiling in the expansion tank. There can be quite a lot of reasons.
Features of the VAZ injector cooling system
Cooling in cars 21093,2109,21099 is liquid, but you need to understand that the radiator is cooled by the flow of incoming air and a fan, which increases the cooling intensity. Also, part of the heat is removed by the car's interior heater radiator at low temperatures.
The expansion tank is designed to compensate for the volume of liquid when heating, to top up and control the level of antifreeze.
The thermostat system provides temperature control, preheating of the VAZ engine, initial heating of the interior in winter, and only then ensures the inclusion of a large cooling circuit.
The temperature sensor provides control of the cooling system, allows you to monitor the engine temperature and regulate the operation of the fan.
We recommend: How to transport a container from point A to point B?
The entire operating cycle of the cooling system is controlled using a power unit control system that takes into account all temperature parameters. It determines the optimal switching conditions and operating time of the structural elements of the system.
VAZ 2109 coolant circulation
The engine cooling system is an important structural element of a car. Its malfunction leads to poor heating of the engine to the required temperature, which causes poor operation of the stove, loss of power and reduced service life of the power unit. On the other hand, the engine system may overheat, which causes breakdown of the cylinder-piston group.
1 – element in the form of a plug for the expansion tank; 2 – expansion tank; 3 – hose for draining liquid from the pipe; 4 – hose passing between the radiator and the expansion tank; 5 – hose leading from the radiator; 6 – tank to the left of the radiator; 7 – aluminum tube; 8 – plug systems; 9 – tank to the right of the radiator; 10 – drain plug; 11 – middle of the radiator; 12 – casing for electric fan; 13 – plastic wings of the electric fan; 14 – electric motor; 15 – toothed pump pulley; 16 – pump impeller; 17 – camshaft drive belt; 18 – engine block; 19 – pump pipe; 20 – radiator hose with supply function; 21 – heater radiator hose with drain function; 22 – hose supplying coolant to the throttle pipe; 23 – exhaust pipe; 24 – hose for refilling; 25 – heater radiator hose with supply function; 26 – thermostat; 27 – coolant temperature sensor; 28 – coolant level indicator sensor.
The cooling system of VAZ 21093,2109,21099 removes heat from engine parts subject to heating through forced circulation. And the injector doses the flow of fuel. Structurally, the VAZ injector cooling system consists of:
- coolant pump,
- monoblock thermostat,
- electric radiator fan,
- radiator with expansion tank,
- pipelines, pipes, drain plugs.
Diagnostics of the engine cooling system of VAZ 21093, 2109, 21099 and identification of faults
If problems arise with the engine cooling system, the causes should be determined, starting with the most probable and simple ones:
- If there is a coolant leak, first check the fluid level in the system. In cars 21093,2109,21099 this is done using the level indicator or when inspecting the expansion tank.
- If the level has changed, inspect the engine compartment for leaks. As a rule, the main reasons are: worn pipes and clamps, damaged engine cooling radiator or heater.
- In case of jet changes in the tank at 3000 rpm. It is necessary to check the fluid circulation. To do this, open the cap of the expansion tank and determine the uniformity of antifreeze flow. The causes of poor circulation may be a clogged system or a malfunction of the circulation pump.
Why do you need pressure in the cooling system and is it needed at all?
The boiling point of water at atmospheric pressure is the well-known and canonical 100 °C. Ethylene glycol antifreeze under the same conditions – 105-107 °C. But, since with increasing pressure the boiling point of the coolant becomes higher, a pressure of about 1.2-1.5 atm is purposefully created in the engine cooling system. Thanks to this, the boiling limit of antifreeze shifts to values of 120-125 °C and even higher, and “hot” engines (which have become the majority in the last 10 years) successfully maintain a stable temperature without the risk of coolant boiling under normal conditions.
Pressure exceeding atmospheric pressure is the norm for cooling systems in 99.9% of modern engines. Its main and only task is to ensure that antifreeze does not boil if the operating temperature of the engine is higher than the boiling point of the coolant at atmospheric pressure. Boiling generates abundant vaporization, which prevents the pump blades from effectively pumping liquid, and steam bubbles, which act as a barrier between the liquid and the surface washed by it, sharply impair heat dissipation. These two processes are closely related, mutually support each other and are rapidly progressing. The result is a rapid overheating of the engine, which does not stop immediately even after shutting down and for this reason is rarely completely without consequences.
Actually, the operating temperature of internal combustion engines has increased throughout their evolution, and this process continues today. Conventionally, the “stages of growth” can be defined as follows:
- “80-85 °C” (long-gone temperature characteristics characteristic of engines of the mid-twentieth century)
- “95-105 °C” (characteristics that have been the norm for the last few decades and are still relevant for relatively simple engines)
- “120-130 °C” (temperatures at which the most advanced modern engines operate, which are at the peak of fuel efficiency and environmental standards)
These figures are approximate, given simply to understand what values we are talking about. There are also exceptions where “everything is the other way around,” but they are rare and only confirm the rule.
We are now interested in the early period of development of the automobile industry - those same 80-85 ° C. As we can see, this temperature is lower than the boiling point of water at atmospheric pressure, and even more so – lower than the boiling temperature of antifreeze under the same conditions. Therefore, these engines did not need pressure in the cooling system? Absolutely right - he wasn’t there! Old clay times - the era of engines with an open cooling system! Of course, there were plugs in the radiators of cars of that period, but they did not ensure tightness, but served only to prevent splashing of water when the car shook on potholes. Everything else did not differ significantly from modern engines: the pump also rotated and with its impeller drove liquid in a circle through the engine jacket and the radiator, and the water expanding when heated was forced out into the compensation volume, which served as the upper tank of the radiator that was not completely filled.
Despite the decent overall power, these engines operated in mild conditions at low speeds and little power extracted from each liter of cubic capacity. The blocks and heads were cast iron, massive, with large volumes of oil in the crankcases, with large radiators and constantly rotating cooling impellers mounted directly on the pump or crankshaft pulley, without any temperature sensors or viscous couplings. Therefore, even at maximum load, the water temperature in the cooling system without pressure did not approach one hundred degrees, and a working engine did not boil. And even at the initial stage of malfunctions (the thermostat not fully opening, low fluid level, partially clogged radiator, etc.), the problem did not arise immediately - the engine had a large supply of “meat”, and it was not possible to bring it to the point of spewing steam it's that simple.
However, the other side of the coin and integral companions of the characteristics of such engines was fuel gluttony and low environmental friendliness. These two points subsequently required reforms in motor engineering, and engines began to shrink in size, eat less, deliver more per liter, and their operating temperature increased. Open cooling systems disappeared, giving way to sealed ones - the temperature rose, and the antifreeze pressure took on the main role in protecting it from boiling.
Accordingly, under the hood there appeared such a detail as an expansion tank plug with a calibrated valve, which was entrusted with a great responsibility - to keep the pressure at a strictly designated limit. And if it is exceeded, in the event of a malfunction in the cooling system, open and release steam and antifreeze to the outside, so that hoses and radiators do not burst.
However, despite the fact that nothing fundamentally changed in the operation of the cooling system after the introduction of pressure, except for a shift in temperature to a higher zone, many car enthusiasts began to mistakenly consider pressure a necessary condition for a variety of processes. On auto forums you can often come across statements that if, due to a malfunction or absence of the expansion tank plug, the pressure in the system disappears, the pump will not be able to work normally, the thermostat will not open, the engine will not reach operating temperature (!) and similar fantasies.
This is wrong. The pump drives fluid and does not know what pressure it is under or without it at all. The quality of circulation is affected only by the integrity of the impeller, belt tension, cleanliness of the channels in the radiator and the viscosity of the antifreeze. The thermostat opens only based on the coolant temperature and nothing else. When the antifreeze in the thermostat area reaches the opening temperature of the thermostat, the latter will open, even if the pump does not rotate at all. Yes, increasing the operating temperature of engines has become one of the inevitable measures that ensures modern requirements for environmental friendliness and efficiency. But the pressure cooling system also has two very significant disadvantages...
The first is the increased risk of antifreeze leaks. While the car is new, of course, there are no problems, but with age, weak points begin to appear in the cooling system. The spring clamps weaken, the rubber pipes lose their elasticity and become cracked. Plastic elements (adapter connectors, fittings, thermostat housings, etc.) become brittle and brittle. And where it’s thin, it breaks. The pressure of the coolant begins to force it out at the first opportunity. An “age-related” cooling system is unpredictable in its surprises, the price of which is very high - if the engine does not “crack” from overheating, then at the very least you will have to fork out for a tow truck, since without antifreeze, even after cooling, you will not go far...
The second drawback is partly a variation of the first. Modern engines have practically no reserve of “meat”, no matter where you poke them, not excluding the heat capacity of the cooling system. The increased pressure accelerates the antifreeze onto the asphalt when the slightest leak appears, and where an old engine (even with a cooling system operating under pressure, not to mention an open one!) would have held on for some time, losing liquid gradually, a modern engine is deprived of it by dangerous pace. Or rather, the pace is the same, but the result is different. The cooling system of a modern B-class car holds half as much antifreeze as even a classic Zhiguli, and if in half an hour each of the cars loses a liter, then the first will have a 10% loss, and the second will already have a 20% loss... It falls proportionally " survivability" of the machine, and the risk of overheating consequences increases proportionally.
Is it possible to fight this? It’s possible, but it’s difficult... Experienced Gazelle drivers, by the way, can recall a fairly massive story in the late 90s, when the build quality was such that even handy drivers couldn’t overcome antifreeze leaks for months. And only unscrewing the cap of the expansion tank and switching the cooling system to the “no pressure” mode made it possible to get rid of the endless blue puddles on the asphalt in the morning... But this trick only worked with ancient ZMZ engines, the ancestors of which worked calmly without water pressure.
On modern cars, in order to avoid overheating, it is unfortunately impossible to convert the sealed cooling system to an open version. Therefore, when purchasing a car that is 7-10 years old and/or with high mileage, it is highly advisable to completely replace the entire cooling system - at least all rubber hoses, clamps, most plastic parts (adapter connecting pipes between hoses, etc.), thermostat and expansion tank plug. But even with the use of a decent non-original, such a procedure turns out to be very expensive, and rare buyers of used cars decide to take such preventive measures without obvious breakdowns...
Survey
Is your cooling system ok?
Your voice
Total votes:
Causes of VAZ engine overheating
- A faulty thermostat can cause the engine to overheat. If on a warm engine the upper pipe is hot and the lower pipe is cold, the thermostat is jammed and the antifreeze flows only in a small circle. Or the thermostat will only turn on a large circle, which will not allow the VAZ engine to warm up to the required operating temperature. In this case, the thermostat should be replaced.
- Another reason for excessive engine heating may be airing of the cooling system; in this case, the system must be pressed and air removed from all cavities.
- At high temperatures, the fan does not turn on - there is a problem with the temperature sensor, fan relay or the wiring harness to it.
- Sometimes the radiator honeycombs become clogged, which sharply reduces the intensity of heat transfer. It is necessary to thoroughly clean the radiator; it must be done carefully to avoid damage to the cells.
These are the main reasons that affect the quality operation of the VAZ 21093,2109,21099 engine cooling system; with their help, you can identify and eliminate malfunctions, ensuring reliable and durable operation of the engine.
Didn't find the information you are looking for? on our forum.
How to deal with cooling system malfunctions
Repair in most cases consists of replacing parts. We find the cause of the breakdown, and then replace the faulty part.
- Constant decrease in coolant level in the tank. If antifreeze is leaking, you need to check the cooling system pipes and thermostat, some of these parts are damaged, replace the faulty one with a new one.
- The temperature sensor near the cylinder block may have failed, check its contacts and reconnect. If that doesn't help, replace the sensor.
- Sometimes an air plug forms in the radiator, which prevents coolant from moving through the channels. How to remove air from the cooling system? Warm up the radiator and feel its body with a gloved hand. If it is cold in some places, it means there is a traffic jam. We will need the upper pipe (hose) that leads to the radiator. Fill the antifreeze tank full and turn on the engine. The pipe needs to be slightly bent, the air will gradually come out on its own. In order for the air lock in the cooling system to disappear, you will need to perform this procedure very carefully. The air will come out when antifreeze flows out of the pipe and the pipe itself heats up.
- If the problem is in the cylinder head gasket, you may not be able to detect the problem right away. The amount of coolant in the tank will gradually decrease, which is almost imperceptible. One of the signs of this malfunction will be the cloudy color of the oil, which occurs after the antifreeze enters the oil pan.
This type of problem can be repaired in the following way:
- find the carburetor from which the contacts and throttle cables should be disconnected;
- the choke cable is disconnected;
- the pipes are removed;
- the distributor is removed;
- unscrew the 3 bolt fastenings of the cylinder head distributor;
- the coolant is drained;
- remove everything that prevents you from getting to the gasket;
- the cover is removed after you unscrew the 2 nuts and the head;
- the old gasket is dismantled, then a new one is installed, after which it is reassembled in the reverse order.
These are the simplest options for dealing with malfunctions that lead to overheating of the VAZ 2109 engine. More complex repairs are best carried out at a service station. If you notice while driving that the coolant temperature has risen to 120ºC, the only way to cool the engine is to pull over to the side of the road and turn off the engine as soon as possible.
Level control and required volume
Before changing the working fluid, the car owner should know what the volume of the Nine’s cooling system is and how much refrigerant it will contain in order to buy the required amount of fluid to complete the task. When changing, the plastic reservoir under the hood will hold about 8.7 liters of antifreeze. If the working substance is not completely drained from the system, then approximately 7-7.5 liters will be poured into it. As for the level control, it is carried out according to the expansion tank marks in the engine compartment. Please note that when the car engine is warm, the fluid volume may be higher. Therefore, before checking, the engine must be turned off and allowed to cool.
Ideally, the refrigerant level should be between two marks - MIN and MAX.
Serber24 user Sani4 in his video clearly demonstrated the procedure for changing antifreeze in a VAZ 2109 car.
For what reasons is coolant consumed?
There are several reasons why the volume of refrigerant will decrease in the refrigeration system:
- Low negative temperatures. In severe frost, the liquid decreases in volume. This reason cannot be called a leak, but car owners in winter often confuse this problem with a fluid leak. During the cold season, experts recommend adding refrigerant to the system.
- Formation of cracks and damage in the expansion tank or on its cover. As practice shows, if the defect on the container is insignificant, it will not be easy to detect it visually. The crack may resemble a scratch. Detailed diagnostics will be required. To identify the location of the leak, you will have to use a special dye that is added to the liquid.
- Lack of tightness in the connections of the lines or damage to the pipes. This problem can be clearly identified. In places of malfunctions, wet traces of refrigerant are visible. If the defect is minor, then it will also not be possible to detect it through visual diagnostics. You will have to add dye to the refrigerant.
- Damage to thermostat or gasket. If there are defects in the device seal, liquid will leak out, and over time its amount in the cooling system will decrease.
- Damage to the radiator device of the heating system. During operation, the radiator wears out. If it has already reached the end of its service life, refrigerant may leak through cracks formed on it or through the hose connected to it. Adding liquid is not practical; the cooling radiator must be replaced.
- Presence of defects on the cylinder head gasket. If there is damage, a leak will form. As a result, the antifreeze will begin to mix with the engine oil, which will enter the coolant. Repairing the problem involves replacing the cylinder head gasket.
The coolant addition procedure is performed with the engine cold. In order to add antifreeze, you need to open the hood of the car and unscrew the cap of the expansion tank. The required amount of liquid is added to the reservoir, after which the lid is screwed on.
If it is not known what fluid was used previously, it is better to change it. Because mixing different types of refrigerants will cause the substance to lose its properties.
Possible consequences
A high level of heating of antifreeze or antifreeze is normal for a running internal combustion engine. The only question is how much the coolant warms up, and whether the temperature exceeds the established boiling limits.
Oil leak through the oil seal
It is impossible to say exactly at what temperature antifreeze or antifreeze will boil. It all depends on the specific manufacturer who adds certain additives to the composition.
In fact, antifreeze is purified water with special additive components. They largely determine the quality and temperature stability of the liquid. In this case, the coolant can be painted in different colors. The dye itself does not affect the properties, but allows you to divide antifreezes and antifreezes into several categories. Some of them can be mixed, while others absolutely cannot be added to one expansion tank at the same time.
If we talk about at what degrees the antifreeze will begin to boil, then we need to proceed from the physicochemical properties of the liquid and the additives used. Previously, boiling occurred as in the case of ordinary water, that is, at 100 degrees Celsius. But in modern antifreezes the boiling temperature limit is higher, as a result of which the coolant boils at approximately 101-108 degrees Celsius.
It is difficult to determine the exact boiling point to the nearest degree. This depends on the specific manufacturer and its features of manufacturing the coolant. It is recommended to start from your own coolant used in your car. This way you will find out whether the antifreeze in the tank boils at a temperature of 100 degrees Celsius or more.
Boiling is indicated by obvious signs when antifreeze literally shoots out from under the lid. This informs the motorist that the coolant is boiling. Therefore, it is necessary to take appropriate measures to avoid undesirable consequences.
Some motorists underestimate the degree of threat posed by boiling and seething antifreeze. As a result, they do not pay attention to it, continue driving and think that they will solve the problem when they get to the house, garage or the nearest car service station on their own.
We recommend: Wires for lighting - buy copper starter (starter) wires at a good price in the VseInstruments online store
But if you do this, you can provoke serious troubles and cause dangerous breakdowns of the engine and related systems. The consequences of boiling depend on how severe the engine overheating due to boiling coolant is. There are 3 stages:
- weak;
- average;
- strong.
Let's start with the safest low overheating of the internal combustion engine. If literally 10 minutes have passed since the coolant began to boil, but no more, problems are practically eliminated, that is, there is no serious threat to the integrity of the engine.
This happens quite often, since not all drivers immediately notice signs of boiling. Often, the corresponding sensor on the dashboard indicates that the engine temperature limit has been exceeded. If the sensor gives a signal, it is recommended to immediately turn off the motor. Without doing this, the engine pistons may begin to melt.
Mild overheating is nothing terrible or dangerous for modern vehicles. It is only important to stop in time so that overheating does not begin to develop into medium and strong forms.
The next level is the average level of engine overheating, caused by the boiling of antifreeze or antifreeze in the system. This is a more serious situation that can lead to the following consequences:
- formation of cracks and deformation of the cylinder head;
- occurrence of oil leakage through the seals;
- damage to the piston ring partitions;
- burnout of the cylinder head gasket.
This happens when the coolant continues to boil for more than 20 minutes.
Moderate and low levels of overheating are mainly encountered by those motorists who are negligent in servicing the cooling system, forget to add antifreeze on time and do not change the coolant according to the recommendations.
Severe overheating is rightly considered the most undesirable. If it occurs, the car owner risks losing the engine, which will require major repairs or a well-deserved send to a landfill.
If the engine temperature has been below the red line for a long time, literally all components of the internal combustion engine will suffer. But this is not the worst scenario. In practice, there have been cases when prolonged severe overheating caused the engine to explode.
But the situation reaches severe overheating extremely rarely. Even in the initial stages, most drivers manage to turn off the engine and take a number of other measures aimed at preserving the engine and ensuring their own safety.
In fact, severe overheating is followed by a wave of destructive phenomena. The pistons burn out first, then the melted metal ends up on the piston walls, the pistons themselves fail, and the cylinder block is deformed. Do not forget about the destruction of the lubrication system, crankshaft, etc. Ultimately, the piston may pierce the block wall, and the engine is unlikely to be returned to its previous state.
Useful tips
For the purposes of this article, we note that antifreeze can not only boil, but also foam. At the same time, the temperature of the antifreeze does not increase. This happens when:
- air entering the expansion tank;
- low-quality antifreeze;
- mixing antifreeze from different manufacturers;
- using coolants not recommended by the car manufacturer due to different chemical compositions;
- Damage to the cylinder head gasket. Then it allows air to pass through, and when it enters the cooling system, it forms foam.
It must be taken into account that minor foaming is acceptable, but if there is a large amount, it is necessary to flush the cooling system and replace the antifreeze with a higher quality one.
We also recommend reading an article about what consequences can occur for the engine if antifreeze gets into the engine cylinders. From this article you will learn about the reasons why antifreeze or antifreeze gets into the cylinders, as well as what this leads to.
Antifreeze has its own service life and with its long-term use the chemical composition changes and the cooling properties decrease. This fluid must be replaced with a new one; replacement is carried out with flushing.
Reasons for replacing the device
If during operation the temperature of the coolant increases and the level does not decrease, then most likely there are problems with the radiator. Since the tubes of the device are aluminum and their diameter is small, they cannot be repaired. Today, auto stores offer various coolant-soluble additives and plugging fistulas. However, it should be remembered that their use is a temporary measure. During the trip, the malfunction may occur again and lead to serious consequences.
Driver actions
Having noticed that antifreeze begins to boil in the expansion tank, you need to take a number of mandatory measures. Don't wait for the coolant to start splashing out onto the hot engine. Once the liquid boils, there are corresponding reasons.
Pour antifreeze into the car
You already know at what temperature antifreeze usually boils in cars, what causes overheating and what consequences this can lead to. Therefore, no one wants to encounter something like this in their own car. It is necessary to start cooling the engine using available methods, not forgetting that the coolant is now under high pressure.
There are several useful tips and a certain algorithm of actions that allows even a beginner to figure out what to do if antifreeze suddenly boils.
- Be sure to try to quickly unload the engine. To do this, you can put the gearbox in neutral and drive until it comes to a complete stop.
- Turn on the fan and stove at the same time. Even if it’s hot outside, the heater will take away some of the heat, thereby speeding up the process of the engine temperature dropping.
- After stopping the car, turn off the engine. At the same time, leave the stove in working condition.
- Pull the handle or press the button to open the hood from the passenger compartment and access the engine compartment. There is no need to stand in front of the hood and open it, as hot steam will immediately come out.
- By opening the hood slightly, steam will come out and fresh air will begin to flow into the engine. Wait a while. Then lift the hood and lock it. It is better to have gloves or a rag with you so as not to grab possibly hot elements with your bare hands.
- Do not try to open the expansion tank cap immediately. Otherwise, you risk your own health. Liquid under pressure, even if the lid is opened slightly, can splash out and get on your skin.
- Wait about 30 minutes. At this time, you can try to find a driver who will take you to the service station, or call a towing service.
- When the engine has cooled down a little, open the expansion tank cap. Surely the coolant has become much less than the proper level. Add liquid into the reservoir in small portions. At the same time, the stove is still working.
- There is no need to immediately pour in a large volume of antifreeze if its level becomes minimal after boiling. Abrupt mixing of cold antifreeze or antifreeze with hot coolant can provoke dangerous negative consequences.
- If you can only get to the service station on your own, after adding coolant and cooling the engine, start it and set off on the road, trying not to load the engine. When the temperature again reaches above 100 degrees, stop, turn off the engine and wait for it to cool down again.
You can't sit and do nothing either. If the coolant continues the boiling process, the engine will overheat first to medium and then to high levels. You already know about the consequences of such heating.
Based on everything discussed above, we can speak with confidence about the seriousness of the problem of coolant boiling. To prevent such situations, carefully monitor the condition of the cooling system, check the functionality of the main components and try to carry out timely maintenance.
Sources
- https://luxvaz.ru/vaz-2109/322-sistema-ohlazhdeniya-2.html
- https://expertVAZ.ru/2109/sistema-ohlazhdeniya-kak-rabotaet.html
- https://ladafakt.ru/sistema-ohlazhdeniya-vaz-2109-inzhektor.html
- https://vaz-remzona.ru/sxema-oxlazhdeniya-vaz-2109/
- https://ladamaster.com/sistema-okhlazhdeniya-vaz-2109-inzhektor
- https://7road.ru/drugoe/net-cirkulyacii-v-sisteme-ohlazhdeniya-2.html
- https://www.vazzz.ru/vaz-2109-tsirkulyatsiya-ohlazhdayushhej-zhidkosti/
- https://avtomechanic.ru/vaz-2109/dvigatel-vaz-2109/konstruktsiya-sistemy-okhlazhdeniya-vaz-2109
Text version
Auto repair
You need to prepare the container in advance, you need to prepare everything, there is such a thing, it’s just like it won’t run once, of course you won’t run?
Even here the cartoon offended us, we don’t get the plug on the expansion valve, unscrew it, I broke it for you, in general, the process has begun, I’m no longer a crap antifreeze. Lost shade after parting this word radiator faucet no one unscrews the faucet product antifreeze cold day.
Replacing antifreeze
He ran, it would also be advisable to close the generator so that this salon doesn’t get caught, you can click it, it will come in handy for anyone small! This is how it turned out, then we move on to washing, so I bought such a product, I don’t know the connection. Each one is located differently, let's look further, find a watering can, cover all the plugs on the radiator with blocks, maybe it's not too tight, you need to tighten it!
They tightened the Dothrak and tightened it, oops on the radiator, too, all the liquid was running, I added an additive to the radiator, confiture, is it a sticky thing? I filled in the additive according to the instructions, the leaking stopped now when I replaced the antifreeze, okay, it’s just a matter of overcoming this additive: Usually we pour warm water if it’s cold outside.
Replacing antifreeze for VAZ 2108
Often she will pass there, you can hear the street, you can open it, or rather unwind it. The pipe that goes to heat the carburetor can be done.
Already all the child is on fire now when the upper scale is standing where it will go. Then we can add more water to the radiator and return the industrial ones to work.
You need 10 minutes to wash and I’ll take the benefits in short? How int glad with the boiling water will go let's go do it it's done cherry radiator this same hour let's let everything washed all clean and pretty. Now we’ll give one more round of water from the radiator.
21099
Screw me with hot water again, let’s fill it with water for five minutes, let’s work and pour it in directly. The antifreeze system is empty, we will fill ourselves with antifreeze, we will not tighten it too much, we have unscrewed it. Heating the carburetor so that everything would surely leak out, the air would not be held in anything by the perry, we top it up, we fill it.
The ambassador tightened the radiator, everything was twisted especially should be enough: In principle, in principle, it’s blue, then my son, if you see that you h1 on the antifreeze barrel has changed color from red to red or blue, too, to red, then that’s it. It's time for me, it loses its properties or we are the last antifreeze, eggplant bushes and almost all the last drops: