And so it happened, 2 days ago I purchased a 3-level regulator, because... the generator under load did not produce the desired result. With a heavy load, the headlights + stove + heated glass + wipers + cooling fan produced 10.9-11 V. Without a load, 13.6 V was normal, after consulting with experts, everything pointed to the voltage regulator, because if the diode bridge was faulty, charging would not hold and at idle. The difference between a regular regulator and a 3-level regulator is not big in price, so I chose it.
the box is simple.
the wire is quite long.
The brushes themselves are without tablets.
actually the board itself is under the cover.
Last night I rushed to a friend's garage and started installing it. I will say one thing, the installation turned out to be easier than I thought. I removed the first protection and voila, access to the generator is free.
standard regulator.
As I read in various topics, all the regulators are mounted on bolts with a screwdriver, but in my case it turned out to be on turnkey bolts, as it later turned out to be 6 (too non-standard). I removed the terminal from the regulator and unscrewed it, and this is the result.
one is shorter than the other.
such a pill.
One brush turned out to be shorter than the other, and compared to the new brushes, these looked much shorter. I don’t know for sure, is this too critical wear?
comparison of brushes.
Next I installed new brushes on the generator. It’s easy to install; you can crawl on top of the generator with your left hand and hold the brushes from the top while you screw in the bolts.
New brushes.
The regulator body itself was screwed onto the body ground to the gas valve.
sat down like clockwork.
I put the toggle switch in the middle position, and the gene outputs 13.7-14 V. During the trip, the voltage remained steady, sometimes dropping to 12.8. In general, I'm happy, compared to what it was like. Next, we’ll travel and see how the regulator behaves.
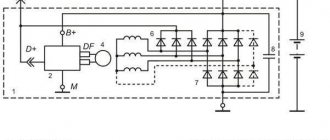
Purpose of the voltage regulator
The purpose of the voltage regulator is easy to guess from the name of this device. The regulator's task is to maintain the current coming from the generator at such a level that the voltage generated by the same generator is always kept within specified limits.
Moreover, it should not depend on the rotation speed of the generator. And the current consumed by the car should also not affect the voltage created by the car generator. The generator voltage regulator is responsible for performing all these tasks on a VAZ 2107 car.
Types and location of voltage regulators
As you know, the VAZ 2107 car began to be produced a very long time ago. And over the years, not only different motors were installed on it, but also different voltage regulators. On the earliest models, the relay regulators were external. On later “sevens” the regulators were internal three-level. Let's take a closer look at these devices.
External voltage regulator VAZ 2107
It is the external voltage regulator that many motorists in the old fashioned way call a “relay-regulator”. Today, external voltage regulators can only be seen on very old “Sevens” produced before 1995. These cars were equipped with an old generator model 37.3701, which was equipped with external relays.
The external regulator was located under the hood of the car; it was mounted on the left front wheel arch of the car. As a rule, external relays were made on the basis of a single semiconductor, although after 1998 on some VAZ 2107 there were external regulators made on a common printed circuit board.
External relays had certain advantages:
- Replacing the external regulator was fairly easy. It was held on by only two bolts, which were not difficult to reach. The only mistake that a beginner could make when replacing this device is to mix up terminals 15 and 67 (they are located next to each other on the regulator);
- the cost of the external regulator was quite affordable, and they were sold in almost all car stores.
Of course, the device also had disadvantages:
- bulky design. Compared to later electronic regulators, the external relay seems very large and takes up too much engine compartment space;
- low reliability. External VAZ regulators have never been of high quality. It is difficult to say what is causing this: the low quality of individual components or the poor build quality of the device itself. But the fact remains a fact.
Internal three-level voltage regulator
Internal three-level voltage regulators began to be installed on the VAZ 2107 starting in 1999.
These compact electronic devices were built directly into car generators.
This technical solution had its advantages:
- compact sizes. Semiconductors were replaced by electronics, so now the voltage regulator fits in the palm of your hand;
- reliability. It’s simple: there’s nothing special about electronic devices that breaks. The only reason why a three-level regulator could burn out is a short circuit in the on-board network.
There are also disadvantages:
- difficulty of replacement. If there were no particular problems with external regulators, then to replace the internal relay the car owner first needs to get to the generator. To do this, he will have to remove the air filter and a couple of air ducts, which requires patience and time;
- difficulty of acquisition. As you know, the VAZ 2107 has long been out of production. So getting new components for the “seven” is becoming more and more difficult every year. Of course, this rule does not apply to all details. But internal three-level voltage regulators for the VAZ 2107 are among the parts that are not so easy to find today.
Dismantling and checking voltage regulators on a VAZ 2107
First, let's decide on the tools and devices that will be needed for the job. Here they are:
- household multimeter;
- open-end wrench 10;
- flat screwdriver;
- Phillips screwdriver.
Sequence of work
If the driver suspects that the voltage regulator is broken, then the first thing he should do is check the voltage supplied by the battery.
- The car engine turns off and the hood opens. Using a multimeter, the voltage between the battery terminals is measured. If it drops below 13 volts (or, conversely, rises above 14 volts), then this indicates a breakdown of the regulator.
Video: checking the voltage regulator on a VAZ 2107
Like any other device, the voltage regulator can break down suddenly. And it’s especially difficult for the driver if the breakdown occurs far from home. There is nothing surprising here: drivers who constantly carry spare regulators with them need to look further. But even in such a difficult situation, there is still a way to get home (or to the nearest service center). But you won’t be able to get there quickly, because every hour you’ll have to crawl under the hood and remove the terminals from the voltage regulator. And then, using a suitable piece of insulated wire, connect the positive terminal of the battery and contact “Ш” on the regulator. This is done so that the charging current does not exceed 25 amperes. After this, the regulator terminals return to their place, and the car starts. You can drive it for about 30 minutes, and you should turn on the maximum number of energy consumers - from the headlights to the radio. And after 30 minutes you should stop again and do the entire above procedure again, since without this the battery will simply recharge and boil.
Purpose of the three-level voltage regulator VAZ-2107
Problems with a car battery are not uncommon for domestic cars.
Rapid discharge and insufficient charge for the functioning of individual systems are common. Drivers' indignation is completely justified. Every car enthusiast strives to maximize the service life of his car’s battery, because a new one is a fairly expensive consumable. Lack of proper battery care can cause a fairly rapid failure of this element.
Even correct and careful use will not affect the battery life. Frequent changes in vehicle operating modes have a greater impact on this parameter.
The voltage regulator installed at the factory on the VAZ-2107 is designed to maintain constant voltage in the vehicle network. However, standard equipment does not take into account vehicle speed, ambient temperature, and so on. To solve this problem, engineers from domestic and foreign companies developed and began producing three-level voltage regulators.
Numerous reviews from car owners who have already tested the new equipment only confirm the effectiveness of this solution. In this article we will understand how the device works and how good performance is achieved.
Car alternator output voltage problem
The list of functions of the generator necessarily includes recharging the on-board battery, which is carried out with a certain current to ensure a long service life. The simplest way to set its value is to slightly exceed the voltage taken from the output of the relay-regulator over the current value of the battery voltage. In this case, a serious problem immediately arises, which is due to the fact that, depending on the ambient temperature, the value of this excess should be different.
An obvious and fairly easily implemented solution to obtain a given output voltage using temperature correction of the regulator response threshold by installing an appropriate sensor is of low efficiency. The reason for this is that the temperature in the engine compartment, due to its proximity to a heated engine, differs from the air temperature, and it is not possible to determine the degree of this difference by simple means.
The main functionality of a three-level voltage regulator for the VAZ-2107
The equipment in question interacts with a car generator, which produces electrical energy by converting mechanical energy.
After starting the engine, the generator, powered by the excitation winding, transmits current to the load.
The winding current is controlled by a voltage regulator. Usually this is a separate unit or built-in element in the brush section of the generator.
The regulator operates from a special section of the rectifier, and the rotor is driven from the crankshaft using a pulley.
The electromagnetic field created by the field winding induces an electric current in the stator phase windings. The consequence of this is that the motor speeds are unstable and load changes are abrupt. Accordingly, stabilization of the output voltage is simply necessary.
Just at this moment, the voltage regulator begins its work, which changes the strength of the current coming from the generator.
If the voltage regulator is working properly, the voltage in the on-board network ranges from 13.8 to 14.2 volts. Only under such conditions will the battery be charged.
On the market today you can find a large number of models of three-level regulators. Such equipment can provide the best conditions for charging the battery, taking into account its condition, air temperature and other important parameters.
Therefore, the use of such devices significantly extends the battery life and minimizes the likelihood of most possible problems occurring during battery operation.
Often on the VAZ-2107 a regulator is installed directly in the voltage generator, and this device has thermal compensation with a negative value. In other words, when the air temperature decreases, the regulated voltage increases, otherwise it decreases. But, as practice shows, he is not able to study the temperature outside the generator housing. And inside this indicator can reach +100 degrees. In addition to this, the operation of the stove, headlights or car radio causes accelerated battery discharge even when the engine is running and the regulator is working properly.
To get rid of all these troubles, it is enough to install a three-level voltage regulator on the VAZ-2107.
Purpose of the regulator relay VAZ 2107 injector and carburetor
The main purpose of the voltage regulator relay on the VAZ 2107, and any other car, is to maintain a stable and sufficient charging current for the on-board network and the car battery, as well as to level out voltage surges in the generator. Variations in the generated voltage would occur as the generator rotates at different frequencies. When the power drops below 12V, the battery stops charging, and the entire bot network no longer functions at 100%. If the voltage exceeds 16 Volts, this can lead to boiling of the battery, as well as failure of on-board devices.
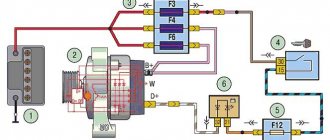
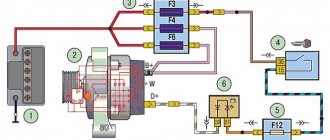
On early production VAZ cars of the carburetor type, the voltage regulator is located on the left arch of the engine compartment. Such devices are also called external, since they were installed outside the generator structure. To be more precise, a brush mechanism was installed in the generator, and control was carried out via a printed circuit board, which was installed outside the product.
Most VAZ 2107 cars of the carburetor and injection type are equipped with generators with built-in charging relays. The charging relay on such VAZ 2107 vehicles is located directly on the side of the generator opposite the pulley.
Location on generator
To maintain an acceptable battery charge, the alternator requires 13.6 to 14.6 volts of power. The voltage regulation circuit is carried out using an electrical circuit, which is located on a printed circuit board (chocolate board) or in the form of a single semiconductor module (tablet) with brushes. The switch located inside the generator is usually not able to adequately respond to the ambient temperature due to its location close to the running engine. The built-in relay is sometimes replaced with a three-level voltage regulator, which is due to the greater efficiency of the product due to manual adjustment of the output voltage.
How to check the charging relay on a VAZ 2107
If you suspect a faulty operation of the voltage regulator relay, then you must first check the voltage at the battery terminals with the car running. The power supply must be no lower than 13 and no higher than 14.6 Volts. The reasons for such increased or decreased voltage can be caused by the following factors:
- charging regulator malfunction;
- failure of the generator itself;
- lack of contact in the electrical connections of the battery or generator.
Benefits of installing a three-level regulator
This equipment is in great demand among owners of VAZ-2107 cars and other models of the same manufacturer. The average age of cars exceeds 10 years. This list also includes “eights”, “sixes”, “nines” and so on.
This device increases the performance of the on-board network. Many drivers note positive changes in the operation of the stove and lighting.
In winter, the car requires additional heating, and this is where the regulators perform at their best.
Most car enthusiasts note the following improvements after installing the TRN:
- The problems with the alarm have disappeared. Previously, I had to use a ruler, especially in cold weather.
- Far and near lighting has been improved. The brightness of all lamps inside the cabin has increased.
- When the heating system was turned to the first position, the air flow noticeably increased.
- The operation of power windows (if available) has been improved.
- The battery always has the required charge level, and in the morning the car starts very easily.
Review of TRN for VAZ-2107 from Energomash
The equipment has proven itself very well among the majority of VAZ-2107 car owners and others. The regulator has three 25C series diodes. The nominally supported current is 6 A. The device has a high voltage barrier. There is a cooling radiator on the regulator body.
Excellent wire insulation, alligator clips and a high-quality housing - all this copes well with increased loads. Even vibration from the generator is not harmful to this equipment.
The output to the battery terminal is a red wire. While the engine is warming up, the Energomash regulator is capable of maintaining the voltage at 13 volts. At idle the value reaches 14 volts.
As we mentioned above, three-level controls improve the brightness of low and high beams, the operation of the stove and fog lights.
The Energomash TRN for the VAZ-2107 will cost the owner approximately 340 rubles.
To summarize, we note that three-level regulators are capable of solving a large number of problems associated with domestic cars. The main advantage is the extension of the battery life, which is important for the VAZ-2107 and other brands of this manufacturer. Installation of the equipment is simple, and even a novice driver can do it. Therefore, buy a TRN for your car, install it and forget about premature battery replacement.
Three-level voltage regulator for VAZ-2107
On VAZ 2107 cars, in fact, like on other models of the domestic automobile industry, there is one serious problem, which is associated with the rapid discharge of the battery. As a result, problems arise with starting the engine, and the headlights begin to shine dimly. You have to purchase a new battery almost once every 2-3 years, although during normal operation of the generator its service life is at least 5 years. To solve the current problem of undercharging, you can install a three-level voltage regulator for the VAZ 2107 car. In the design of the car, a standard regulator is installed from the factory, which has a simple design, which makes it ineffective.
Three-level voltage regulator of ZAO Energomash instead of the standard relay. Is there an effect on the VAZ-2107
As we remember from last time, the reason for the loss of charging of the generator was a breakdown of the standard voltage regulator, which was successfully resolved by replacing it.
However, after working for a couple of days, this spare part also successfully failed: the voltage ceased to remain within the normal range of 14 V and began to recharge to 16.8-17 V, which threatened the failure of all on-board equipment.
To avoid a repetition of such a situation, it was decided to replace the standard regulator with an external one for ease of repair and replacement.
Thus, a three-level voltage regulator was purchased under the brand “Council of Auto Electricians” from ZAO Energomash from the same Kaluga.
Packaged in a small square box, inside of which there is the regulator itself and the brush assembly, connected by wires, and there is also a small instruction manual.
On the bottom of the regulator itself there is a toggle switch for switching operating modes, of which there are only three: Maximum ("max") - 14.7 V, Normal - 14.2 V, and Minimum ("min") - 13.6 V. For each mode +-0.25V deviation is allowed, according to specification.
The modes are set depending on the ambient temperature, the state of charge of the battery and the additional equipment used in the car. The device comes with a 1 year warranty.
Each type of generator has its own types of regulators, differing in brush assembly and “filling”. The brush assemblies of the standard regulator and the Energomashevsky one, as we see, are identical.
So, we install the regulator brush assembly on the generator. If necessary, we make a slot in the back cover to lead the wires out.
We cut off the plastic partition.
Only the corrugation sticks out.
We connect the corrugation with wires with ties to the wiring harness coming from the generator so that nothing melts from contact with the engine.
We attach the black box of the regulator securely to the body not far from the battery, since the plate is its “ground” (can be connected with a wire directly to the “-” terminal).
On a free stud
We start the car while we check the operation of the regulator at idle speed and with consumers turned off in each mode.
High (“max”), nominal and low (“min”)
As we can see, the device successfully produces the declared voltage, taking into account the permissible deviation of 0.25 V.
Now we turn on consumers: rear window heating, low and high beams, fog lights, interior heater.
High (“max”), nominal and low (“min”)
The voltage immediately drops to 11.8-12 V, regardless of the mode in which the regulator operates.
Now we turn off the consumers and see that the voltage is gradually returning to normal again.
High (“max”), nominal and low (“min”)
Now let’s test the operation of the device when the car is moving in city mode. We reconnect the multimeter to the cigarette lighter, taking into account that its readings will be 0.1 V lower than at the battery terminals. Let's check only in high mode 14.7 Volts.
In neutral gear and idling without load, except for the low beams and dimensions, it shows 14.3 V, which is quite normal.
With load it drops to 12 V at idle.
Only when reaching 2-3 thousand engine revolutions in 4th gear does the charging current reach almost 14 V.
Preliminary conclusion: the regulator works, however, I am confused by such a deep voltage drop depending on the load and engine speed, which should not happen. Let's try to check the density of the electrolyte in the battery, and also apply additional “mass” to the engine.
Advantages of installing a three-level regulator
The three-level voltage regulator on the VAZ 2107 is capable of maintaining a constant voltage supplied by the generator to the vehicle network. With this product it is possible to save and increase the battery life. In addition to regulating voltage, three-position regulators are capable of maintaining current within a certain range.
Some of the main advantages of the device in question include:
- The main board of the device is located not in the generator itself, but away from it, which contributes to less heating of the product, as well as extending its service life.
- Possibility to regulate the voltage level manually thanks to a special switch. The device operates from a switch.
- The charge level is significantly higher, in contrast to standard products.
Problems with starting the engine, especially on frosty days when it is very difficult for the starter to start the engine, can be avoided by replacing the standard device with a three-position one. Large loads on the electrical circuit in a car, such as headlights, heater, heated glass, can contribute to battery discharge, even if the engine is running and the standard product is in good working order.
Types of regulator relays are simple, three-level and with temperature compensation. In the brush section of a standard seven generator, in most cases, a temperature-compensated option is installed. But, as practice shows, in terms of thermal regulation, these regulators are mostly ineffective. Recently, among drivers of the VAZ 2107 and other Lada models, the three-level type is gaining more and more popularity. Car owners who have installed such a regulator overwhelmingly recognize it as more effective than the standard one.
Characteristics of the Energomash device for VAZ 2107
The Energomash voltage regulator for the VAZ 2107 is equipped with three “25C” type diodes and a mode switch. With their help, a three-stage voltage change is carried out. A three-level balancer is also called a current injector, since the device is capable of maintaining it at a level of up to 6A. The main functionality of the three-level voltage regulator for the VAZ 2107 model "Energomash" is based on changing the current from the generator, thereby increasing the voltage of the on-board circuit to 13.6-14.7 V.
The first operating mode provides for maintaining the voltage at the generator output at 13.6 Volts. The switch should be installed in a position where the ambient temperature is +20 degrees and above. The switch in the neutral position should be set at temperature values from 0 to +20 degrees. And in the third position, the generator will produce a voltage of 14.7 V when the air temperature is from 0 to -20 degrees.
It is important to know! The Energomash model will cost about 350 rubles.
Replacing a standard product with a VAZ-2107
Connecting a three-position regulator, or rather, changing a standard product, does not present any difficulties. After purchasing the product, you must complete the following steps:
- Initially, you need to remove the protective cover of the generator. Don't forget to disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- The standard part is removed by unscrewing two bolts using a screwdriver or a “6” key, which depends on which VAZ generator is installed on the car. It is also necessary to remove the terminal.
- After this, we compare the standard device with the three-level one. The brushes and fasteners must be identical in design, otherwise the product will need to be replaced.
- A new product is installed in place of the standard “tablet”, after which it is fixed with fasteners (bolts).
- The body of the product should be secured to the ground of the car in any convenient place (pictured below). This is not difficult to do, since the wire is long enough.
Malfunctions: Tired of installing a 3-level voltage regulator
Hello! After a small problem with the generator https://avtomarket.ru/journal/VAZ/2107/35838/ and replacing the burnt-out voltage regulator with a new one, I seemed to be happy, but after a couple of days it failed again. The voltage began to jump to 16.8-17 Volts, as measured by a multimeter, and a lamp for a problem with the engine lit up on the panel, which threatened to cause the entire electrical system to fail.
I removed the generator again, but now I took it to a mechanic I know to check, he confirmed my guesses that the regulator had burned out again and needed to be changed. This company may just have been defective.
Having thought about disassembling half the machine again next time, I decided to install an external regulator or, as a last resort, remove a standard tablet. But I remembered, having scoured the Internet, people gave advice to buy a three-level regulator from Energomash, so I went to the store and bought it. It is packed in a box, by the way, each generator has its own and has a different brush assembly, as I understand it.
It comes with a 1 year warranty. It differs from the standard “pill” in that the brush assembly is sealed off from the relay, and it is located in a small black box with a switch, and they are connected through wires.
There are 3 voltages on the regulator: low 13.6 V, nominal 14.2 V, and high 14.7 V. Depending on the ambient temperature, the state of the battery and consumers, it is switched manually via a toggle switch.
Without thinking twice, I installed the brush assembly in place; in the rear plastic cover of the generator it is necessary to cut off one edge to bring the wires out.
The regulator itself was screwed to a bolt on the wing to ground.
So, a confusion arises. When I start the car, I check the voltage on the battery - in all three modes at idle with the consumers turned off, it shows the declared values with slight deviations.
But as soon as you turn on all the consumers: heated rear window, low and high beams, fog lights and the stove, the voltage immediately drops and remains around 12 V and even lower, regardless of the mode in which the regulator operates.
I didn’t notice this with the standard regulator; before it burned out, it always held 14 V. I tightened the belt a little, checked the ground, measured the voltage on the go, everything worked out the same way, when a large number of consumers were turned on, the voltage tended to 12 Volts.
Only when reaching 2-3 thousand revolutions in 4th gear was the charging current nominal 14 V.
Is tension supposed to flow like that? What could be the cause of the malfunction, or is this how this regulator works? By the way, the battery has not yet been discharged after several days of such driving.
I think I'll check the battery just in case and throw some extra ground on the engine.
Good luck on the roads!
Such an inconspicuous, inexpensive and reliable element of a car's electrical network as the VAZ 2107 voltage regulator relay is rarely remembered. Usually, attention is paid to it only after the battery stops charging and problems with starting the engine begin. To prevent this, it is necessary to monitor the operation of the relay when the voltage of the on-board network is unstable and replace it if a malfunction is detected.
Content
What is it for?
Relay regulator 2107 is necessary to provide a stable charging current for the battery and equalize voltage drops in the on-board network. Drops would inevitably occur, since the generator spins at different frequencies and the current at its terminals can differ greatly from the nominal 12 volts. If the voltage drops below that, the battery cannot charge and many electrical appliances simply do not work. Likewise, if the voltage is too high, the battery may boil and devices may fail.
If the charging current to the battery drops, first check the regulator, since the generator itself rarely fails. You can simply check the charging current at the battery terminals using a tester or multimeter. In normal mode, the system voltage should be between 13-14 volts. If the readings are lower than 12 V, then the regulator may need to be replaced.
Logbook VAZ 21074 (2006)
I believe that the author of the review was in vain to fall for this craft. Anticipating the indignant cries of individual visitors to this resource that again this Bronnik is muddying the waters for nothing, I answer: I always objectively and unbiasedly express my opinion on this or that issue, even if it may sometimes be too straightforward and with a touch of ironic sarcasm, which sometimes Some comrades don't like it. But this is true, by the way. As for the issue under discussion, I propose that everyone together consider in more detail what this device actually is. So, we must pay tribute to the manufacturer, he did everything possible so that an inexperienced buyer would choose his “product”, especially since the very name “THREE-LEVEL REGULATOR” sounds downright magical, and the hand itself reflexively reaches into the pocket for money to get it. buy it soon. In addition, the manufacturer, without a twinge of conscience, recommends it instead of a standard voltage regulator, promising a bunch of benefits for the car enthusiast and an increase in battery life, a more optimal charging mode, etc.
So, according to the instructions, the lower level of the regulated voltage 13.6 V should be used at an air temperature of 20 degrees and above and when driving in traffic jams. In our city, this mode should, in theory, be the main one, since traffic jams on the roads exist around the clock and the average temperature of 20 and above lasts for about 6 months a year (by the way, today the sun was so hot that by lunchtime in the shade it was also +20 degrees and this March 1st!).
But on the other hand, a person who has at least a little understanding of auto electrics, after reading the instructions, immediately begins to understand that the manufacturer of this device has simply deceived him, since in this case there can be no talk of any increase in the battery life; on the contrary, it will greatly reduce its service life, due to chronic undercharging, especially if the battery is more than 2 years old, especially since in traffic jams, when operating at idle (when the generator output is low) and the battery is fairly discharged (see above), on the latter is still pressed by the load in the form of headlights, brake lights, engine cooling fan, etc.). which further significantly reduces its service life. It becomes obvious that the 1st mode is absolutely not working, and therefore the manufacturer needed to leave only the 2nd and 3rd. But 2-level sounds much less pompous than 3-level. But let's move on. The second level, by and large, does not differ much from the operating mode of a conventional regulator and therefore few people will use it (why change the awl for soap). The main advantage of this device, according to some, is the slightly increased regulated voltage of 14.7 V at level 3. Yes, we must admit that this really makes it possible to improve the energy balance in the vehicle’s on-board network, provide a better battery charge (especially calcium-type batteries and “aged” ones), make the headlights shine brighter, etc. There are, of course, disadvantages, for example, lamps burn out more often, but these are minor things. But, on the other hand, a person who knows at least a little about auto electrics again begins to understand that here too the manufacturer has brazenly cheated him and forced him to pay 300 rubles more. (compared to the cost of a native voltage regulator) for what he could simply do on his own by paying 100 times less (by installing a 3-ruble additional diode of a suitable type in the circuit of the native voltage regulator, or even completely free of charge, simply taking one for these purposes from additional diodes from a diode bridge that had previously failed and was lying around as junk somewhere on a shelf in the garage) and ultimately getting exactly the same result! Or rather, even better, since in this case there will be no “collective farm” of corrugated tubes with wires and a box on the mudguard. In addition, the original native voltage regulator usually has compensation (which the device under discussion does not have) for the amount of regulated voltage depending on the ambient temperature, which really has a very positive effect on the overall life of the battery.
Well, okay, since the job has already been done, it won’t disappoint the author once again and it’s better to switch to a new problem that appeared after replacing the regulator with a voltage drop below 12 V when a large number of consumers are turned on. I hasten to reassure him, since most likely the cause of this problem lies in the brushes not being ground into the slip rings of the generator rotor. In addition, the latter are probably oxidized more than normal. In this case, due to the inevitable increase in transition resistance, the current flowing through the rotor winding is slightly reduced, and accordingly the output voltage is less than it could be. After some time, the brushes will rub in and everything will return to normal.
Types of relay regulators
All regulators that were used on VAZ cars at different times can be of only two types:
- External regulator.
- Three-level internal regulator.
Starting with the 2105 and 2107, the factory installed only internal relays on the alternator. External ones were used on older models and they were removed from the generator, since they were not particularly compact. On these machines, the relay was installed under the hood on the mudguard on the left.
If there was a need to replace the external regulator, then this was done easily and simply - it was in an accessible place, attached directly to the body with self-tapping screws, and was simply removed. The main thing that needed to be taken into account when replacing it was the correspondence of the terminals to pins 67 and 15. It was enough to simply check the correct connection of the new relay using the diagram, start the engine and take the measurement again.
Internal regulator VAZ 2107
Replacing the internal relay may be difficult, since it is installed on the back of the generator, and access to it is somewhat complicated. Despite this, replacement is carried out even without removing the generator, directly on the car. It is screwed to the body with two screws. By unscrewing these screws with a Phillips screwdriver and disconnecting the terminal, you can remove it and replace it with a new one.
Often owners of old VAZ models change the generator due to failure. In this case, you need to check the wiring diagram of the old car's generator in order to remove the old device or at least disconnect it from the system. The old and new relays have exactly the same characteristics and are therefore completely interchangeable. But at the same time, the new regulator is more stable, accurate and durable compared to the old one. In addition, the new model ensures optimal charging of batteries of any capacity, and this significantly affects the battery life.
How to install TRN on a VAZ-2107
Before installing a three-level battery on a car, you need to disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
To do this, remove the protective cover from the battery case and unscrew the fastening bolts. The winding switching relay must be removed and a contact group of new equipment installed in its place. The wire is pulled through the generator cover.
The TPH block is secured to one of the free studs with a ground contact. The terminals must face down.
Before carrying out work to replace or install the device, experienced mechanics recommend first charging the battery and taking measurements at the terminals.
Diagnostics
To check the installed relay, simply measure the voltage at the battery terminals, and it will become clear what condition it is in. To check what has been removed and is suspicious, the verification method is slightly different, but in any case it will help to identify:
- Absence or poor contact in the brush holder terminals.
- Broken brush conductors.
- The relay itself is faulty.
A multimeter or a 12-volt test lamp, the power of which does not exceed 2 W, is simply connected to the regulator brushes. It is enough to apply 10-12 V, the lamp should light up or the multimeter should show the corresponding value. After this, a voltage greater than the nominal voltage is supplied - 16-20 volts. In this case, the relay should operate, but the lamp should not light. If the lamp continues to light when the voltage increases, then the regulator is broken and does not perform its functions. In this case, it must be replaced. Also, when replacing, you should pay attention to the condition of the brushes. They should protrude beyond the brush holder by no more than 5 mm.
This way you can test your regulator and save the battery from premature wear. Keep an eye on the network voltage, and have a good trip!
Checking the removed voltage regulator
To clarify the condition of the regulator, it must be removed. It is better to test the device complete with brushes and brush holder. This will allow you to immediately detect:
- poor contact between the terminals of the brush holder and the voltage regulator;
- breaks in the output conductors of the brushes.
Electronic devices are produced already assembled with a brush holder and one-piece brushes. The relay regulator will need to be connected to the removed brushes.
A voltmeter or a 12 V lamp with a power of 1–3 W is connected to the brushes of the device removed from the generator 37.3701. For the regulator from the G-222 generator, the connection is made to terminals “B” and “W”. The “plus” of the power supply is connected to the terminals “B”, “C” (when they exist), and the “minus” to ground. First, a voltage of 12–14 V is applied, and after that – 16–22 V. A sign of the device’s serviceability will be the lamp lighting up (deviation of the voltmeter needle) in the first case and going out (zeroing the voltmeter) in the second.
When the lamp lights up in both cases, this means that there is a breakdown in the device. If in both cases the lamp does not light, then there is no contact between the regulator terminals and the brushes, or there is a break in the device. Another cause of improper voltage regulation can be worn or stuck brushes. They must protrude from the housing of the electronic device or the brush assembly of relay regulators by no less than 5 mm.