How does TPD stand for? This is a throttle position sensor, which is necessary to indicate accurate dosing of fuel into the system, as well as for the controller to detect the location of the throttle shield. Where is the throttle sensor located on the VAZ 2114? The mechanism is located on the same body as the throttle valve, near the idle air control.
Location of TPS on VAZ 2114
Why is TPS needed?
Most often the sensor is a potentiometer that produces a variable resistance depending on the throttle position (and therefore the throttle position sensor).
The TPS signal is used by the engine control unit (ECM) as one of the input signals of the control system. Ignition timing and fuel injection timing (and possibly other parameters) vary depending on the throttle position, and also depending on the rate of change of this position.
Some throttle valve modifications have built-in limit switches. They are full open and fully closed throttle sensors.
Types of TPS
There are several Russian manufacturers of this mechanism.
TPDZ Omega
- DPDZ "Omega" (Moscow);
- "Schetmash" (Kursk);
- non-contact TPD (Kaluga).
Often motorists install sensor number 1 – Omega – on the VAZ 2114. But the TPS from the VAZ manufacturer is film-resistor, sometimes they do not last very long and repeatedly cause problems for car owners.
Contactless units operate on the magnetic resistor effect, they are an order of magnitude more expensive than all previous options, and are famous for many years of uninterrupted service and high labor efficiency. Equipped with a rotor and starter inside. The first part is made of anti-magnetic material, and the second part is made of a sensitive magnetic field, which allows the mechanism to work for a long time without interruption.
What types of throttle position sensors are there?
The throttle position sensor is mounted on the throttle body. By design, throttle position sensors are:
- Contact type - with potentiometer.
- Non-contact type - magnetic with Hall effect and inductive (coil).
By installation method:
- Separately installed sensor.
- Built into the damper drive housing.
Communication of the throttle valve with other automotive systems of the VAZ-2110
The throttle valve of a VAZ-2110 car is a component of the engine intake system and is directly connected to a large number of other vehicle systems. These include the following systems:
- directional stability;
- anti-blocking;
- anti-slip;
- anti-slip;
- cruise control.
In addition, there are those systems that are controlled by the electronics of the gearbox. After all, it is this throttle valve that regulates the flow of air into the car system and is responsible for the quality composition of the fuel-air mixture.
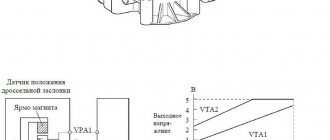
The principle of operation of TPS with a potentiometer
The TPS sends information to the controller about idle speed, deceleration, acceleration rate and wide open throttle (WOT) status.
The TPS is a three-wire potentiometer. The first wire supplies a voltage of + 5 V to the resistive layer of the sensor, the second wire is ground. The third wire is connected to the potentiometer slider, which changes the resistance and therefore the voltage of the signal returned to the ECU.
Based on the received voltage, the control unit can calculate idle speed (below 0.7 V), full load (about 4.5 V) and throttle opening speed.
At full load, the ECU ensures that the fuel mixture is enriched. In deceleration mode (closed throttle and engine speed above certain rpm), the controller disables fuel injection. Fuel delivery is resumed when the engine speed reaches its idle speed or when the throttle valve opens. On some vehicles these values can be adjusted.
TPS problems and their diagnosis
As you know, eternal parts for cars have not yet been invented. And the breakdown of the TPS can be foreseen; for this you need to inquire about the possible reasons for the failure of this part. Here are the main ones:
- Abrasion of the sprayed base layer, which serves to move the slider (the result is incorrect TPS readings).
- Failure of the movable type core (the result is deterioration of the contacts between the slider and the resistive layer).
How can you figure out problems with this sensor yourself? To do this, you can independently diagnose the operation of your diagnostics:
- Listen to the VAZ-2110 engine idling:
- the breakdown is obvious if you notice that its speed is in a “floating” state;
- Quickly release the gas pedal:
- a malfunction is present if the engine stops after this action.
- Pick up speed:
- There is a problem with the TPS if the car starts to move jerkily, which indicates an incorrect supply of fuel to the system.
Experts say that most often the sensor fails when the resistive track is heavily contaminated or is completely broken. To verify the opposite, you need to check the working condition of the TPS.
Non-contact TPS
Non-contact throttle position sensors can be of two types - with a Hall sensor and inductive.
Hall effect sensor
TPS with a Hall sensor allows you to receive a signal about the throttle position without physical contact. This makes such sensors more reliable and wear-resistant.
The Hall effect TPS consists of Hall sensors and permanent magnets that rotate around them. There is an air gap between the magnet and the Hall sensor.
The magnet is attached to the throttle shaft, whose angular movement is monitored by Hall sensors. When the damper turns, the magnets change their position.
Hall sensors detect changes in magnetic flux caused by the movement of magnets. The signal is transmitted to the circuit board, which is located in the electronic throttle body, and then to the engine control unit.
The signal sent to the ECU can be analog or digital.
Inductive sensor
Another way to measure rotational position non-contact is with a non-contact inductive type throttle position sensor. Such a TPS consists of a stator and a rotor.
The conductive rotor is a rotating part and is mounted on the throttle shaft. The rotor consists of one or more closed loops with a specific geometry, made of electrically conductive material. May be a round printed circuit board.
The sensor and board with signal processing chip are installed inside the electronic throttle body and are stationary. The stator consists of a standard printed circuit board and an application-specific integrated circuit.
The board contains the receiving excitation coils, as well as electronics for converting the input signal. When the rotor turns, a voltage is induced in the stator, which is transmitted to the ECU to determine the throttle position.
Comparison table of different types of TPS
| Resistive | Inductive | Magnetic | |
| Reliability | Contact principle, prone to wear | Contactless, good | Contactless, good |
| Price | Low | Average | High |
| Size | Big | Big | Average |
| Interface | Analogue only | Analog and digital | Analog and digital |
| Linearity | Very good | Very good | good |
| Reservation | Additional tracks but parallel wear | Additional tracks, sensors | Easy to install two redundant sensors |
Purpose of the sensor
The sensor is designed to determine the angle at which the throttle valve has opened. The sensor transmits the received data to the engine control unit, which processes this signal.
Resistor TPS
Resistor TPS
The principle of operation of the sensor is based on a conventional electrical resistor, which, when rotated around its axis, changes the resistance. The data sent to the ECU is based on resistance. This operating principle reduces the cost of producing the sensor, but affects its durability. With this design, the working part of the sensor, namely its tracks, frays quite quickly, which leads to loss of conductivity and, consequently, to sensor malfunction.
The advantage of this sensor is its low price, but due to its rapid breakdown it is not justified.
Non-contact TPS
Non-contact TPS
There is another type of sensor - non-contact. As a rule, such a sensor costs much more, but its durability is several times higher than that of a standard sensor.
It is recommended to purchase a non-contact sensor, as it has more advantages and is more durable in comparison with a resistor TPS.
Signs of a malfunction of the TPS
Acceleration problems
The vehicle lacks power when accelerating or accelerates spontaneously. It may seem like the car just isn't accelerating as well as it should.
The car jerks when it picks up speed. Acceleration may be smooth, but it lacks power.
It may happen that the car suddenly accelerates on its own, even if you have not pressed the gas pedal. If these symptoms occur, there is a good chance that you have a TSD problem.
Floating idle
If you experience engine misfire, floating idle, or stalling, this could also be a sign of a faulty TPS.
This means that the control unit cannot detect a completely closed throttle, i.e. the idle mode is disabled. The TPS may also send incorrect data, causing the engine to stop at any time.
Reduced maximum speed
The car accelerates, but does not exceed a relatively low speed. This is another throttle position sensor failure mode that indicates that it is falsely limiting the power requested by the accelerator pedal.
You may find that your car will accelerate, but not more than 30-50 km per hour. This symptom is often accompanied by a decrease in power.
Check Engine
Check to see if the Check Engine Light comes on, accompanied by any of the following symptoms.
The check engine light may come on if you are having problems with the TPS. However, this is not always the case, so don't wait for the CE light to come on if you notice any of the above symptoms.
Check the vehicle for trouble codes to determine the cause of the problem. This can be done using a diagnostic scanner or an ELM327 adapter with Torque software.
TPS design
The throttle position sensor can be of two types:
- film;
- magnetic or contactless.
In its design, it resembles an air valve - in the open position the pressure corresponds to atmospheric pressure, in the closed position it drops to a vacuum state. The TPS includes DC and AC resistors (each resistance is 8 ohms). The process of opening and closing the damper is monitored by the controller, with subsequent adjustment of the fuel supply.
If at least one symptom of a malfunction occurs in the functioning system of this sensor, then fuel may be supplied to the engine either in excess or in deficiency. Such malfunctions in engine operation are reflected in the engine of the VAZ-2110 car and on its gearbox.
How to check TPS
Here we will talk about how to test throttle sensors, what malfunctions may occur and how to identify them.
Voltage check
- Connect the black lead (negative) of the digital multimeter to the case or negative of the battery.
- Locate the reference voltage (+5 volts), ground, and signal voltage terminals.
Most throttle potentiometers have three terminals, but some may have additional terminals that function as throttle ends.
- Connect the multimeter's red lead (positive) to the signal voltage terminal.
- Turn on the ignition, but do not start the engine. In most vehicles the voltage reading should be less than 0.7V.
- Open and close the throttle valve several times, checking that the voltage changes smoothly.
Checking the sensor resistance
- Disconnect the sensor connector.
- Connect a multimeter in resistance measurement mode (Ohms) between the potentiometer slider terminal and the reference voltage terminal. Or between the runner and the ground.
- Open and close the throttle valve several times and check for a smooth change in resistance. If the potentiometer resistance is infinite or zero, this indicates a malfunction.
- We do not indicate the exact resistance values of the potentiometer. One reason is that many manufacturers do not publish benchmark data. The fact that the resistance of the potentiometer is within certain limits is less important than the correct operation of the potentiometer, that is, a smooth change in resistance when the throttle valve is moved.
- Connect the multimeter between ground and the reference voltage pin. The resistance must be constant.
- If the resistance is infinite or small, the potentiometer must be replaced.
Troubleshooting throttle position sensor
Chaotic output signal
The signal voltage changes sharply and may drop to zero. When the throttle sensor output is erratic, it is usually caused by a faulty potentiometer. In this case, the sensor must be replaced.
No voltage signal
- Check the presence of reference voltage (+5.0 V) on the connector.
- Check the condition of the potentiometer ground contact.
- Check the signal wire connecting the sensor to the control unit.
- If problems are found with the reference voltage and grounding, check the continuity of the wires between the TPS and the ECU.
- If the sensor wires are OK, check all power and ground connections to the controller. If everything is fine with them, the most likely cause is the control unit itself.
Removing the throttle assembly
Dismantling the remote control will be necessary in any case. If there are malfunctions, the unit is replaced with a new one, but if there are no problems other than contamination, then the gasket on the damper is changed, and then a thorough cleaning is performed. For dismantling you will need a set of screwdrivers and a 13mm socket wrench. You also need to purchase a special cleaning fluid, which can be found at any car store. An excellent option would be a product for carburetors - Arbo. Dismantling is carried out only on a “cold” motor.