Motor oil and coolant have different purposes and should not be mixed. However, sometimes antifreeze gets into the oil (and vice versa). Because of this, the motor begins to malfunction.
To prevent the negative consequences of antifreeze getting into the oil by identifying the problem in a timely manner, you need to understand what the signs of the presence of coolant in the lubricant are.
The most common factors by which you can understand that antifreeze has got into the oil
There are some signs of antifreeze getting into the lubricant. How to determine and detect antifreeze in oil:
- Reducing the amount of antifreeze, provided that it does not leak out of the car.
- The engine is shaking, the motor is running unevenly.
- Whitish traces of antifreeze on the dipstick.
- When you open the valve cover, you can see that it is white on the inside. There are also white spots inside the flask.
- Air bubbles are visually observed in the expansion tank at high engine speeds. There are grease leaks on the surface.
- Antifreeze is visible on the crankcase, spark plugs, under the head, in the pan.
- High concentration of exhaust carbon monoxide. The exhaust color is white, more like steam.
- The grease darkens quickly.
Connecting pipes and clamps.
To connect all elements of the cooling system, rubber or silicone pipes are used, which are secured with metal clamps. Insufficient tightening of clamps, cracking and wear of pipes lead to antifreeze leaks. Some tips on how to avoid this:
- When performing routine vehicle maintenance, inspect the cooling system pipes for leaks, cracks and swelling;
- use hoses from trusted manufacturers (of rubber hoses, Balakovo hoses (BRT) are known, opinions vary on silicone hoses, but the main thing is not to take China);
- It is recommended to use clamps from NORMA. They provide reliable fixation, do not cut the hoses with their edges, and can also be tightened not only with a screwdriver, but also with a wrench, which is convenient for final crimping. Also, some car owners successfully use self-tightening (spring) clamps from foreign cars, selecting a set according to the diameters of the pipes.
- measure the force so as not to break off the fitting of the expansion tank or radiator, especially thin ones - steam exhaust ones;
- After replacing the pipes, you need to warm up the car, and then carefully tighten the clamps again to ensure a tight seal.
The cooling system of domestic cars requires constant monitoring and regular maintenance. If a minor malfunction of the cooling system is not corrected in time, it can ultimately lead to expensive engine repairs, so do not be lazy to periodically look under the hood.
Why does antifreeze get into the lubricant?
If antifreeze or its traces are found, you need to understand the path through which it gets into the lubricant and fix the problem.
Some possible reasons:
- The cylinder head gasket is worn, punctured, or deformed. There is no barrier for antifreeze to leak into the lubricant. This will clearly be observed on the spark plugs. They will be covered in whitish streaks of antifreeze.
- Poor installation of the cylinder head gasket. The head bolts are not tightened sufficiently or, conversely, they are overtightened.
- Lack of tightness of the heat exchanger.
- Head deformation due to harsh operating conditions, overheating.
- Poor quality antifreeze. Could freeze at low sub-zero temperatures. After thawing, such liquid leads to deformation of the block head. And also the use of low-quality fluid leads to the fact that the cylinder liners rust and collapse.
- The fluid pump is clogged or incorrectly installed.
Reasons for getting there
If you study the structure of a car engine, it becomes clear that the coolant circulates through the so-called jacket, removing excess heat. These channels do not normally communicate with the internal cavities, but at the junctions of different parts (especially where the cylinder head is connected to the block itself) there are weak spots and breaks. A special gasket is installed in this place, which becomes a connecting link and prevents antifreeze leakage. However, it often burns out as it wears out and the coolant leaks out or into the cylinders, sometimes in both directions.
Through such damage to the gasket, coolant enters the cylinders.
Often the problem occurs due to the fact that the cylinder head has defects along the plane that is pressed against the block. The slightest deviation creates microscopic cracks through which antifreeze is released under pressure. Well, the third reason is a crack in the channels on the block.
What to do if antifreeze gets into the oil
Depending on how the antifreeze got into the oil, there are certain ways to troubleshoot problems specific to each case.
| Why does antifreeze get into the oil? | Method for eliminating the cause of antifreeze penetration into the oil |
| Worn cylinder head gasket | Remove and install the block head. Replace seal gasket. |
| The cylinder head gasket is broken. The antifreeze oil partition is cracked. | Crack repair. |
| The gasket is deformed. | Replacement of the internal part of the deformed head adjacent to the motor. |
| The gasket is poorly installed. | Reinstallation, high-quality tightening of bolts. |
| Low quality antifreeze. | Replacing the fluid with a high-quality one. Repair, replacement of gaskets and cylinders. |
| The fluid pump is not installed correctly. | Reinstalling the pump. |
How to change the gasket?
Let's consider the replacement procedure using the example of a VAZ-2109 car. To do this we need:
- Remove the air filter housing.
- Disconnect all fuel supply hoses and power wires.
- Drain the coolant.
- Unscrew the manifold.
- Disconnect high-voltage wires.
In this way, we free the head from everything unnecessary, so that nothing gets in the way when removing. To unscrew the head itself you need a powerful wrench and a hexagon. A total of ten bolts need to be unscrewed. The latter are removed along with the washers. Next, the head carefully rises up. It is important not to distort it. The gasket itself may remain on the head or stick to the block. You can remove it with your own hands or pry it off with a negative screwdriver. The surface of the cylinder head is inspected for corrosion. If there is rust, it will need to be milled and sanded. If all is well, you need to remove traces of the old gasket. Having cleared the surface of its residues, degrease the area.
What are the consequences for the engine when antifreeze penetrates into the oil?
Antifreeze is a liquid mixed with concentrated additives: pure water. Additives prevent water from freezing at low negative temperatures.
Antifreeze gets into the oil and causes its lubricating and protective properties to change dramatically. The additives that make the oil a unique material capable of preventing the engine from dry friction, ensuring optimal engine performance at different ambient temperatures, are destroyed.
As a result, the engine wears out quite quickly. Cooling antifreeze, being in the oil, leads to the fact that the consequences for the engine can be catastrophic. There may be a knocking sound in the crankshaft and camshaft. It appears due to abrasion of the friction layer of the liners. When viewed under microscope magnification, white balls of salt are visible on the inserts. They are the cause of abrasion and corrosion of the liners. They are formed as a result of a chemical reaction between lubricant additives and antifreeze additives. During operating mode, the oil heats up and speeds up the reaction.
Another reason for engine problems is that oil additives dissolve better in water than in oil. Antifreeze is water based. Even a small amount destroys a large percentage of additives. Thus, the oil base ceases to have the protective properties declared by the manufacturer. This is why antifreeze is dangerous for lubricating fluid.
Coolant and antifreeze getting into the oil eventually lead to a major overhaul of the engine if the cause of the penetration is not eliminated in time. Even tenths of a percent of coolant in oil are very dangerous for the engine.
In order to promptly notice and eliminate this kind of malfunction, as well as see leaks, you can coat the engine with silver paint that is not afraid of high temperatures.
Problem Definition
It can be quite difficult to determine with accuracy why oil gets into the antifreeze. Basically, this problem is identified by white smoke from the exhaust pipe. The quality of the oil is of great importance. If the oil dipstick has a white coating, this indicates the presence of this problem. The best solution for drivers is, of course, to turn to specialists
. To identify the problem, use a special luminous additive. It helps to determine the exact locations of cracks, depressurization and other deficiencies. When the problem cannot be solved in this way, the entire cooling system and some engine parts are gradually disassembled. All parts undergo diagnostics for all kinds of breakdowns and malfunctions.
After detecting oil in antifreeze, you need to determine the cause of its appearance, do testing and eliminate this deficiency. To prevent oil from getting into the antifreeze, it is necessary to regularly monitor the liquid level, color and condition. When a breakdown is detected, it allows you to save on repairs and minimize all consequences. Sometimes the situation can still be saved by replacing the gasket, crimping and grinding the cylinder head, as well as replacing the valve stem seals.
What can happen:
- reduction in filter capacity;
- formation of balls with ethylene glycol and oil;
- the formation of acids that cause chemical destruction and corrosion;
- decrease in antifriction properties;
- worn out sliding bearings.
Oil getting into the coolant is associated with the cylinder block. An experienced motorist immediately determines that this is a burnt gasket.
The consequence is a change in the color and saturation of the exhaust gases, a decrease in the level of coolant fluid in the distribution tank.
The above information suggests that the reasons for oil getting into the antifreeze are few. Although the consequences can be catastrophic for the vehicle engine
. It is necessary to carry out a visual inspection of parts every day and regular maintenance of the vehicle. Don't ignore the problem and warning signs from the inside of your vehicle. The slightest defects and breakdowns must be repaired immediately by contacting specialized service centers or service stations.
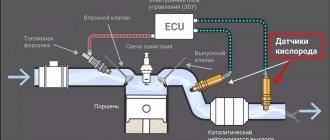
How does the engine cooling system work?
Any passenger vehicle is equipped with a cooling system. The volume of the liquid heater contained is usually within ten liters. Either antifreeze or antifreeze acts as a “coolant”. The liquid element heats up during operation.
The temperature range of normal functioning in the Northern regions is minus forty degrees, and the highest limit is plus one hundred degrees.
Despite the significant difference in temperature, the volume of antifreeze increases by five to ten percent.
This indicates the need for reserve capacity to ensure the simultaneous performance of not one, but several functions:
- Excess liquid flows into the radiator device for cooling;
- The system operates under closed conditions at appropriate pressure. When liquid coolant enters the reservoir, the layer of air is compressed, along with an increase in pressure. In this case, the plug is squeezed out. To avoid this, a compressed volume of air is expelled through the valve;
- When the liquid cools, it flows from the reservoir simultaneously with the air supply from outside. Such conditions are created so that vacuum does not occur in the pipes and an air lock does not form.
The tank is a container closed with a plastic lid. It can be any shape. The lid is equipped with a bypass valve. It ensures air or steam exchange during the boiling of antifreeze.
What conclusions can be drawn?
So, antifreeze ingress is a fairly common problem and relatively easy to diagnose. A leak can be indicated, firstly, by a constant decrease in the liquid level in the expansion tank, and secondly, by thick white smoke with a characteristic odor from the exhaust pipe. In addition, the color of the oil on the dipstick and on the filler cap changes. Well, if the spark plugs are also wet and smell of antifreeze, then this is a sure sign of antifreeze in the cylinders.
The difficulty and cost of solving the problem depends on the reason why the coolant got into the oil. In any case, you cannot delay diagnostics and repair, since even untimely replacement of an affordable gasket can lead to subsequent serious expenses for engine repairs.
Basic methods for repairing a cracked engine block. Crack detection, repair by welding, riveting or applying an epoxy layer.
What malfunctions are indicated by the emulsion on the oil dipstick and oil filler cap? Ways to independently determine the causes of this problem.
Why does the engine overheat? What should the driver expect and what damage may occur if the engine overheats. What to do if the internal combustion engine overheats.
Types of sealants for car engines: anaerobic, silicone, belt sealants. Operating principle, differences, scope of application. How to choose the best sealant.
How to fix a breakdown yourself
Repairs should always be preceded by preliminary diagnostics. First, the cause is clarified, and then the problem with antifreeze leakage is eliminated.
Problems in practice are usually resolved in one of the following ways:
- If the plug valve malfunctions, it is simply cleaned. It may even need to be replaced, which is quite expensive;
- If the tank bursts, then it is replaced with a new one or, at a minimum, soldered;
- Hoses are replaced if there is a leak in them. Only in case of bottom leakage, you can simply trim them a little;
- A hole in the pump seal requires replacing not only it, but also the water pump;
- A detected problem in the radiator allows repair work to be carried out. Service workers can check that the resulting cracks are not due to corrosion;
When a cylinder head gasket breaks, it is changed immediately, since it is impossible to use a car with such a breakdown.
If the problem is discovered during a trip, it is recommended to add water to the system. This is done in order to be able to get to the nearest service center. Except in cases of gasket burnout. Then the only way out is to call a tow truck.
How does the problem manifest itself?
You can determine that coolant has entered the cylinder block based on several signs. The main ones are considered to be the following:
- White smoke coming out of the exhaust pipe;
- Constant decrease in the level of antifreeze in the tank;
- Formation of a white emulsion when checking the oil level with a dipstick;
- The appearance of characteristic wet sediment and soot on the spark plugs.
Typically, the smoke coming from the exhaust pipe when antifreeze leaks into the cylinder block may not have any odor at first. Only later can it acquire the distinct aroma of burnt antifreeze. In addition, if coolant enters the cylinder block, the color of the oil may darken. In this case, it is quite possible that a coating in the form of a white emulsion will form on the oil filler neck.