The VAZ 2107 clutch is designed to connect the engine crankshaft and the gearbox input shaft with the possibility of briefly stopping the transmission of torque. The reasons for its failure can be very diverse. However, all of them can be easily diagnosed and eliminated on their own.
- Reasons for replacing and adjusting the VAZ 2107 clutch
Replacing the clutch - Clutch adjustment
- Clutch slipping
- Tools and materials
Video: do-it-yourself adjustment of the VAZ 2107 hydraulic clutch
Clutch mechanism of VAZ 2107
The VAZ 2107 clutch is a rather complex mechanism consisting of several dozen elements. The reasons for its malfunction can be very different. However, they can all be divided into two groups:
- Defects in the clutch mechanism itself. These include malfunctions of the driven part of the clutch, pressure device, basket, flywheel, and clutch fork.
- Defects in the hydraulic drive of the clutch mechanism. They can be caused by leakage of the working fluid, the formation of an air lock in it, as well as malfunctions of the main or working cylinders (MCC and RCC) and the pedal mechanism.
The clutch, like any other car part, has a limited service life. First of all, it depends on the skill of the driver, and therefore is not regulated by the manufacturer. To increase the service life of the clutch, it is necessary to adjust it in time, monitor the level of working fluid, avoid off-road driving, and learn the skills of using the clutch correctly.
It must be remembered that in addition, the clutch is a safety device that protects the transmission from serious damage when the rear wheels are blocked by various obstacles. The car is stuck in a quagmire, the drive wheels are stuck, the engine power is enough to turn the stuck tires. In this case, the clutch will begin to slip, protecting the gearbox, cardan and rear axle from damage. Yes, the driven disc linings will burn out. Yes, the clutch will overheat, which can cause the steel flats to warp or weaken the spring plates. But more expensive units will be protected from breakdowns.
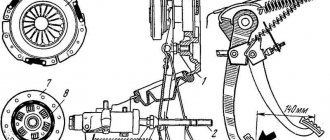
Classic VAZ models have a dry, permanently closed single-plate clutch . It includes two main elements:
- Leading part. It consists of a driven disk, the splined part of which transmits rotation to the gearbox due to friction between the friction linings and the surfaces of the flywheel and pressure plate.
- Non-removable drive unit (basket). The basket is attached to the flywheel and consists of a pressure plate and a diaphragm pressure spring.
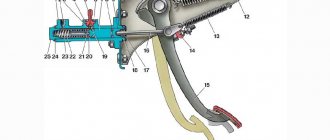
Classic VAZ models use a single-disc dry, permanently closed clutch: 1 - flywheel; 2 — clutch driven disc; 3 — clutch basket; 4 — release bearing with clutch; 5 — hydraulic clutch reservoir; 6 - hose; 7 — master cylinder of the hydraulic clutch release; 8 — servo spring of the clutch pedal; 9 — clutch pedal return spring; 10 — clutch pedal travel limit screw; 11 — clutch pedal; 12 — hydraulic clutch release pipeline; 13 — ball joint fork; 14 — clutch release fork; 15 — release spring for clutch release fork; 16 - hose; 17 — working cylinder of the hydraulic clutch release; 18 — clutch bleeder fitting
The clutch mechanism must be reliable, durable, and capable of dampening fluctuations in engine torque. The clutch has a hydraulic drive consisting of:
- clutch master cylinder;
- clutch slave cylinder;
- clutch on/off forks;
- release bearing;
- foot pedal.
Complete disassembly with gearbox removal
The work must be done on a lift or in a pit. First of all, remove the battery
We continue disassembly by removing the rod from the gear shift lever. Then you will have to use a screwdriver to unscrew the screws securing the cover that covers the hole in the car body. This completes the manipulations inside the car dealership. What needs to be done next:
- Remove the exhaust pipe (exhaust system) and resonators;
- Then remove the starter from the flywheel housing and move it to the side;
- Disconnect the cardan from the rear axle and gearbox.
To be able to remove the box, remove the cross member of the rear engine mount and the speedometer drive cable. You also need to disconnect the hydraulic drive cylinder from the gearbox and move it to the side.
Next, you will need to remove the bolts that hold the clutch housing cover in place (key 10) and proceed to dismantling the box, and since it weighs a lot, it is worth putting a good support under it.
Read, it may come in handy: How to remove an axle shaft, replacing the oil seal, size, drawing, instructions with photos and videos
After this, use a socket wrench to unscrew the bolts from the flywheel housing. Now, in order to remove the box, you will have to carefully move it back, slowly removing the primary shaft from the hub of the clutch driven disc. This must be done carefully so as not to drop the box and injure yourself. That's it, the box is removed.
Video about disassembling the clutch using the example of a VAZ 2106, suitable for the “Seven”, a small difference only in the interior
Reasons for replacing and adjusting the VAZ 2107 clutch
Replacing a VAZ 2107 clutch is a rather labor-intensive and expensive process. Therefore, before replacing, you should consider adjusting the mechanism.
Clutch replacement
To install a new clutch, you will need an inspection hole, overpass or lift. It is important to detect in time the signs indicating the need to replace the clutch (it is impossible to replace it on the road), and take the car to a garage or car service center. Driving with a faulty clutch is very dangerous - you can get into an accident when crossing a railway crossing or a main road.
The VAZ 2107 clutch cannot be repaired, but is replaced as a kit, which includes a basket, driven disc and release bearing
The entire VAZ 2107 clutch is replaced, so auto shops sell a kit consisting of a driven disc, a basket and a release bearing. You should consider replacing the clutch in the following cases:
- the car climbs heavily uphill when the accelerator pedal is pressed all the way down, and you can smell a burning smell - these are signs of slipping of the driven part of the clutch;
- when the clutch is disengaged, noises appear in the area of the flywheel housing - this indicates a malfunction of the release bearing;
- when starting the car, it is difficult to engage first gear (the gearbox “growls”) - this is a sign that the clutch is not completely disengaged (the clutch is moving);
- when accelerating, the car begins to twitch, rattling sounds are heard - the reason for this is usually broken damper springs or loose sockets for them on the driven disk, deformation of segments or loose rivets on the hub.
Any noise, vibration, or whistle in the clutch area requires more detailed diagnostics and diagnosis.
Clutch adjustment
If the clutch pedal becomes too soft, falls down, and does not return to its original position, then most likely air has entered the system or the hydraulic drive adjustments have been disrupted. Clutch slipping after prolonged use usually indicates a failure of the clutch. It will probably have to be changed.
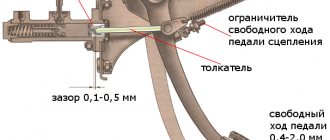
When adjusting the hydraulic clutch of a VAZ 2107, the regulated values of the gaps and the pedal stroke are set
If the clutch drives, that is, shifts gears with difficulty, in about half of the cases the reason is a discrepancy with the required values:
- play between the rod and the piston in the working cylinder;
- clearance between the release bearing and the fifth basket;
- free and working travel of the foot pedal.
What's the result?
If the clutch becomes soft without special adjustments, you need to look for the reasons and carry out repairs as soon as possible. Remember, driving with a faulty clutch is unsafe and also leads to increased wear of various parts, elements and assemblies.
We also recommend reading the article about why gears do not engage when the engine is running. From this article you will learn about the reasons why shifting gears is impossible or very difficult after starting the internal combustion engine.
Finally, we note that a complete replacement of the entire drive is required only in certain cases. As a rule, it is possible to limit oneself to replacing some individual parts and subsequent adjustment/adjustment of the clutch drive.
How to change gears without a clutch: driving a manual car without a clutch in case of malfunction. Tips and tricks.
Gears are difficult to engage or speeds on a manual transmission do not engage: the main causes of the malfunction and possible problems.
Correct gear shifting in a car with a manual transmission: when to engage a particular gear on a manual transmission, working with the clutch pedal, errors.
Car clutch: purpose, types, design, principle of operation. Frequent clutch malfunctions in the vehicle transmission system, signs of problems.
Reasons for difficulty shifting gears with the engine running. Transmission oil and level in the gearbox, wear of synchronizers and gearbox gears, clutch.
How is the clutch implemented in the transmission device on cars with automatic transmission compared to a manual or robotic transmission. Features and differences.
Several of the most common faults in the operation of the clutch of a VAZ 2107 (seven).
List of malfunctions in the clutch operation of a VAZ 2107 car
The driver disengages the clutch by pressing the pedal to change gears. In this case, the pressure bearing acts on the petals of the damper (pressure) spring of the clutch “basket”. As a result, the drive (pressure) disk stops pressing the driven disk against the flywheel. The transmission of torque from the engine flywheel to the transmission input shaft is interrupted. In this case, the gears should be switched on easily, clearly, without difficulty. Otherwise (the forward gears are engaged with difficulty, the rear with a crunch and crackling sound), the clutch does not completely disengage (“drives”), the driven disk remains slightly clamped between the pressure plate and the flywheel. The causes of this malfunction in most cases are:
When the pedal is released, the clutch will be engaged. That is, the pressure plate presses the driven one against the flywheel and torque is transmitted from the flywheel to the input shaft of the gearbox. The clutch is constantly engaged at idle, while driving with the gear engaged, and when coasting. If for some reason the driving disk does not fully press the driven disk against the flywheel, the clutch will slip (“slip”) and the driven disk will slip relative to the flywheel. Torque transmission will be intermittent and insufficient. This is especially noticeable when driving uphill, when the driver presses the gas, the engine roars and gains speed, but the acceleration of the car is weak or with some delay. The reasons for this malfunction are as follows:
Jerks and shocks when the clutch operates
The main reasons for clutch-related jerking and knocking in a car transmission when starting off are:
Noise when engaging clutch
Noise in the area of the gearbox when releasing the clutch pedal most often indicates wear or breakage of the driven disc (wear, deformation, loosening of its linings, breakage of damper springs) or loosening of the gearbox to the engine.
Noise when disengaging the clutch
If you hear a slight noise or rustling sound when you press the clutch pedal, most likely the release bearing has failed or is nearing the end of its service life. It is advisable to immediately change the release lever, since if it jams, shifting gears will be very difficult, and the wear of the clutch “basket” pressure spring petals at the point of contact with the bearing will be very rapid. It is cheaper to change the bearing right away than to replace both the bearing and the “basket” later.
In addition to a faulty clutch release bearing, extraneous noise may come from the input shaft bearing in the gearbox. It can be heard at idle (the clutch pedal is not pressed).
What to do if signs of a clutch malfunction are detected on a VAZ 2107?
If the clutch parts are worn, you will have to replace at least the driven disc with the release bearing.
Notes and additions
The clutch on VAZ 2104, 2105, 2107 cars is of a constantly closed type, that is, constantly engaged: when the pedal is released, the driven disk is pressed by the drive to the flywheel and rotates with it, as well as the release bearing and the input shaft of the gearbox. There is a gap of 1.5 - 2.0 mm between the release bearing and the lining of the thrust flange of the clutch basket pressure leaf spring. This gap is selected when the driver begins to press the pedal.
The full travel of the clutch pedal on VAZ 2104, 2105, 2107 cars is 140 mm.
The above clutch malfunctions occur not only on the VAZ 2107, but also on all cars of the classic VAZ family (2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106).
TWOKARBURATORS VK -More information on the topic in our VKontakte group
The hydraulic drive of the clutch release system has been used in the automotive industry since time immemorial, about a hundred years ago. The design has remained virtually unchanged for half a century. And yet, sooner or later the drive fails, late - if you are a fan of a quiet ride, early - if you like to light up. The clutch pedal is the first indicator of the operation of the basket and master cylinder. The clutch pedal has become soft, which means it’s time to restore the hydraulics, which are often the ones that have exhausted their service life.
A soft clutch pedal means a whole bunch of accompanying troubles:
- Speeds change poorly, hum and ringing in the gearbox, synchronizers work at their limit;
- delayed return to normal;
- An under-depressed clutch loses its performance and service life many times faster.
The most unpleasant of the possible options, when the clutch pedal is soft and the gears are not engaged, is the breakage or destruction of the diaphragm spring petals, as a result of which the clutch is constantly not engaged. If, when you try to quickly pick up speed, a smell of burnt linings appears, there is something wrong with the spring, and the entire basket structure may need to be replaced.
Often, drivers believe that the reason for the malfunction and the fact that the clutch pedal has become soft is simply incorrect adjustment, deformation or breakage of the fork, or non-compliance with the basic operating parameters of the device. To increase efficiency, increase the stroke of the rod, and the soft pedal will disappear.
Most often, drivers complain that the pedal has become soft after replacing the clutch. If adjustment does not help, you should bleed the hydraulic circuit, pipes and cylinders as efficiently as possible. During any repair, air enters the pipe system. If, after assembly, the pipeline fittings were not tightened thoroughly enough, the system will certainly be air-filled, and as a result, the pedal will be soft, without any hint of operation.
Sometimes a simple and effective procedure is carried out for additional verification. Perform a couple of pumps with the soft drive pedal and fix it in the depressed state. Using a 8 key, unscrew the fluid supply fitting to the working cylinder until air bubbles appear or the brake fluid leaks. After completing the procedure a couple of times, check the fluid level in the tank. In a normally operating mechanism, liquid will flow into the system, but there should be no leakage of “brake fluid” in the area of the rod and at the pipe connections.
Both cylinders – main and slave – should be checked separately. The softness of the force indicates the presence of a non-rigid element in the pedal-fork-release bearing transmission chain. As statistics show, the working cylinder is prone to jamming, and the main cylinder is prone to loss of tightness and loss of injection functions.
If these manipulations do not produce results and the pedal remains soft, remove the main drive cylinder and inspect it. Typically, the loss of the ability to pump brake fluid into the circuit is associated with destruction, crease or catastrophic abrasion of the cuffs.
Alternatively, the defect associated with the appearance of a soft pedal effect was often eliminated by selecting brake fluid with a higher viscosity.
For cable clutch drive systems, the appearance of a soft pedal means deformation and destruction of the drive tab or release bearing. To check the operation of each element, you will have to do a lot of work to disassemble the crankcase and gain access to the release bearing. If the defect appears periodically, the cause may be the destruction of one of the damping springs of the driven disk. A fragment of the spring got into the space between the discs, thereby preventing the spring from fully engaging the clutch.
Purpose
To understand where the release bearing is located, you need to understand the purpose and design of the clutch. The clutch and all its parts belong to the vehicle's transmission. It ensures the transmission of torque from the engine to the drive axle and wheels, and must be located between these parts of the machine. But an important condition for the location is accessibility in its control by the driver. Most often this is the clutch pedal, less often the lever near the steering wheel. Using the clutch mechanism, the driver periodically disconnects the engine from the transmission. This allows you to stop the car, change the gearbox, and change the driving dynamics.
Leveling up
To bleed, you will need brake fluid and a container for draining it, as well as a transparent hose with a diameter of 5mm. and an assistant who will have to press the clutch pedal until heaviness appears in it. After this, it must be clamped, and at this time a second person must unscrew the fitting and drain all the brake fluid. Air bubbles will be visible in the hose. The procedure should be repeated until these same bubbles disappear. Also, do not forget about the fluid level in the expansion tank.
VAZ 2107 clutch diagram
FakeHeader
Comments 31
this is the input shaft bearing... the same problem, but I stopped paying attention a long time ago, since you install a new one and there is an option that the same thing will happen... spare parts are crap. I advise you not to touch it yet
By the way, when you remove the box, be sure to check the plug for cracks, they often break
This is a box. When depressed, the clutch disengages and the sound disappears. In most cases this is the large input shaft bearing. If the noise is minor, it's okay. I drove 40 thousand with such a bearing, changed all the bearings when the noise really became annoying. The release mechanism makes just the opposite noise when squeezing, as described below.
the noise is not annoying, but as if delaying this problem would lead to consequences) and they seem to be there)
In the best case, if the bearing jams, it will turn, in the worst case, the bell will break, but that’s when it will make a terrible noise. If possible, you can change
And the fact that the clutch is hard and gives vibration to the pedal is already a problem for the clutch. First, check how the working cylinder rod moves. For a long time I had the problem that the pedal became hard and the gears were difficult to engage. The reason was in the hose that runs from the body to the working cylinder, for some reason it was corroded, it was all swollen and, as a result, it did not allow fluid to pass through well. I’ve never encountered anything like this before, and I’ve never heard from people about it. But I had the same problem.
Take off the gearbox and see if you buy a used clutch, then buy a centering device for the clutch disc) otherwise I’m tired without it
I already thought about this by the way) I was looking at the Schemers program on Discovery and just saw how Ed used a shaft from some machine to center the disk, you will definitely need to get a centering machine)
here it costs 50 rubles)
- there is no lubrication in the release lever - the clutch basket may have fallen apart - perhaps the damper on the clutch disc has fallen apart, that’s what happened)
The lubricant has run out and it whistles.
When the noise died down, did you press the pedal or let it go? Maybe try adjusting it first. Regarding the clutch, the Master said that now the easiest way is to take a VIS and skate 50-60 thousand freely, and then maybe the whole hundred.
6 seconds squeezed the clutch, 9 seconds released, also 15 squeezed the clutch 16 released. We regulated it a year ago, we should try to start with this
It’s not a release lever, it’s the other way around, when you squeeze it out it starts to make noise, it’s the input shaft bearing, most likely yours is noisy, when you squeeze the clutch it goes quiet, the release starts making noise. They are there for 100k mileage, it seems, they are designed taking into account spare parts, or rather their quality, they last less
I have the same crap, but the mileage is 23,000 km
At first, the bearings can howl in cold oil in the box, then you can’t hear them, the mileage after overhauling the box itself is 3k, but the primary bearings also make a little noise in cold oil. I try to ride the first 100-200 meters at XX to warm up the oil in the axle box. Everything also depends on the oil, change the oil in the axle box every 60k, but in fact the axle is 15k, the gearbox is 30, then it’s better to change it. Well, again, the quality of the spare parts, I had almost 100k mileage, the bearings were all on the verge of death, and the fork was also very worn out.
Having your own car does not require a thorough knowledge of its structure. But the baggage of technical knowledge is never a burden. Knowing the signs of a faulty clutch release bearing, you can prevent an accident or equipment failure at the most inopportune moment. Acting proactively always minimizes repair costs. It is more difficult to deceive an informed person and inflate him with an unjustified price. It’s easier for him to know how to identify a problem and what to do in trouble.
Basic faults
The slave cylinder has several rubber seals, which often become unusable or become oily, causing the car’s clutch to “slip.” Replacing old seals with new ones will require using a lift or inspection hole, since the main cylinder is located in an inconvenient place.
When replacing seals, do not forget that there is brake fluid in the system; it must first be drained.
It is advisable not to touch the flare nut, otherwise additional adjustment will be required later. In order to replace the gaskets without removing the master cylinder, certain skills and experience are required.
Another cause of clutch malfunction may be wear of the release bearing. To replace it, you will have to dismantle the gearbox. Brake disc linings wear out just as often, which is easy to notice by the characteristic noise when the pedal is released. And the most common problem with a clutch malfunction is air getting into the system. Air can be removed by bleeding.
How to get to the nearest service station or home if the clutch pedal has failed?
The task, although not easy, is still quite realistic. The main thing here is to get going and not take your foot off the gas, maintaining the speed in first gear.
You need to proceed as follows
We warm up the engine, turn on the emergency lights, then turn on first gear, and turn the key in the ignition. When the engine starts to “catch”, give the gas and start moving. With the right approach, the car will not stall, and you will be able to move away and slowly get to your destination. Don't try to change gear without a clutch - it is certainly possible, there is a technique, but without the proper skill you will most likely stall or damage your transmission.
Now you know why the clutch pedal does not return, for what reasons this happens and how to solve this problem. In addition, if this happens, you will know how to get home if the VAZ clutch pedal fails. That's all for me, write in the comments how you solved this problem and what signs of malfunction you had and the cause of the breakdown. Thank you all for your attention and see you again at VAZ Repair. Bye.