Technical description and interpretation of error P0422
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic powertrain code. The P0422 code is considered a common code because it applies to all makes and models of vehicles. Although the specific repair steps may vary slightly depending on the model.
A car's catalytic converter (catalyst) helps reduce exhaust emissions by saturating them with oxygen. It helps convert hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) into water vapor (H₂O), carbon dioxide (CO₂) and nitrogen (N).
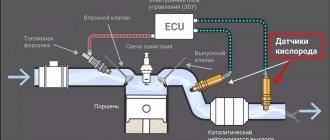
The PCM (powertrain control module) monitors catalyst efficiency using a post-catalyst oxygen sensor. This sensor is primarily used for this purpose. It should shift much slower than the front oxygen sensors.
If at any time the PCM detects that the downstream O₂ sensor is switching too quickly (indicating there is no change between the catalytic converter input and output). It recognizes this as a catalytic converter that is not working properly and displays a P0422 OBD2 error code.
Conditions for generating DTC P0420
The ECM, in the process of monitoring, compares the signals of the 1st and 2nd sensors during a given time interval, calculating the duration of the voltage signal, and if it goes beyond a given threshold, the “brain” of the car interprets this as a malfunction of the neutralizer. The threshold value of the difference between the amplitudes of the front S1 (taken as the standard) and rear S2 oxygen sensors is more than 0.7 times per minute. But the check light, indicating that an error has been recorded in the memory of the ECM unit, does not light up instantly, but only when a decrease in the performance characteristics of the catalytic converter occurs for 100 seconds, and the engine load should be from 21 to 63% when the crankshaft rotates 1,720 - 2,800 rpm, and the catalyst temperature exceeds 500 degrees.
Signal from oxygen sensor
During normal operation of the catalytic converter, the downstream heated oxygen sensor signal switches slowly between rich and lean conditions. Frequent switching of the lambda probe between these states indicates a decrease in the efficiency of the converter. As a result, its ability to accumulate oxygen is reduced.
The task of the catalyst is to oxidize carbon monoxide and neutralize CO2 hydrocarbon emissions in order to reduce the concentration of harmful substances. This process, starting with the Euro 3 standard, is monitored by two oxygen sensors. There is a constant comparison of the signals of the first and second lambda in order to register the convergence of their readings. Therefore, error code P0420, in due time, will bother all owners of cars, including VAZ, Nissan, Toyota, Chevrolet, Ford, Honda or others produced after 1996 and having 2 lambda probes in the exhaust system.
Trouble code P0420 appears when oxygen and unburnt fuel residues are detected in the exhaust gases.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0422 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light) illumination. It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in the ECM memory as a malfunction).
- The engine stalls or has trouble starting.
- Decrease in engine power.
- Increased emissions of harmful substances from the exhaust pipe.
Reasons for the error
A P0422 code may mean that one or more of the following problems have occurred:
- Bad or non-functional catalyst.
- Oxygen sensor malfunction.
- The engine is running without the optimal air/fuel ratio.
- The engine coolant temperature sensor has failed.
- Leak in the engine before the catalytic converter.
- Misfires in engine cylinders.
- Damage to wires and connectors.
- Problems with the manifold air pressure sensor.
- Contamination of the engine oil due to non-regular replacement.
- The air flow sensor has failed.
- Malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator.
Online consultation
A three-way catalytic converter is used to control the exhaust emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxide (NOx). The catalyst in the converter accelerates the chemical reaction of oxidation of HC and CO in the exhaust gas, turning them into harmless vapors of water and carbon dioxide. It also reduces NOx by converting it to nitrogen. The catalytic converter can also store oxygen. The ECM can monitor this process using the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S2), located in the exhaust stream after the catalytic converter. The HO2S2 sensor produces a signal that indicates the amount of oxygen catalyst, which in turn indicates the ability to effectively neutralize exhaust emissions. The ECM monitors the performance of the converter by allowing it to warm up first, allowing it to cool down while the engine is idling, and then increasing or eliminating excess fuel by monitoring the response of the HO2S2 sensor. During normal operation of the converter, the response of the HO2S2 sensor to an excessive fuel content is sequentially compared with the HO2S1 sensor. If the response of the HO2S2 sensor is similar in level to the response of the HO2S1 sensor, then the amount of oxygen catalyst or the performance of the converter is perceived as insufficient and the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) lights up. Conditions for Setting the DTC The vehicle is operating in closed loop mode. Engine coolant temperature (ECT) is above 78°C (172.4°F). Mass air flow ranges from 15 to 30 kg/hour. Engine speed ranges from 1792 to 2304 rpm. Vehicle speed ranges from 45 km/h to 56 km/h. The deviation in air flow is less than 10 kg/hour. Predicted catalytic converter temperatures range from 300°C (572°F) to 800°C (1472°F). The engine runs for more than 60 seconds. There are no DTCs related to the HO2S sensor, misfire, coolant temperature sensor, crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, vehicle speed sensor, manifold air temperature sensor, throttle position sensor, IAC actuator, EGR valve, fuel trim or CAN bus communication. Conditions for setting the DTC. The HO2S2 filter signal value is greater than 101. Action Taken When the DTC Sets The malfunction indicator lamp illuminates. The controller records the operating conditions at the time the fault is detected. This information is stored in a status record buffer and fault logs. An archive of diagnostic trouble codes is saved. Conditions for Clearing the DTC/Malfunction Indicator The DIL turns off after three consecutive test cycles have completed without failure. The historical DTC clears after 40 heat cycles without failure. The DTC can be cleared by a scan tool. Diagnostic Aids The converter test may stop due to changes in engine load. While checking the converter, do not change the engine load (ie battery, cooling fan, heater motor). An intermittent malfunction can be caused by a weak connection, frayed insulation, or broken wiring in the insulation. Any circuit that may be causing an intermittent fault should be carefully inspected for the following: Removed terminals Terminal connections Faulty locks Warped Damaged terminals Loose connections between terminals and wires.
How to Troubleshoot or Reset Trouble Code P0422
Some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P0422:
- Inspect the sensor wires located near the catalyst.
- Check the oxygen sensors.
- Repair engine leaks.
- Test the air flow sensor as well as the manifold air pressure.
- Check the fuel pressure regulator.
- Test the engine coolant temperature sensor.
- If no problems are found, check the catalytic converter and replace it if necessary.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Error P0422 can be diagnosed using a standard OBD-II scanner. Use the scanner to view data and collect information about the code. And also to check for other error codes that may be present.
Next, clear the error codes from the PCM memory and retest the system to see if P0422 appears again. If the code disappears, it may indicate an intermittent error or that the code appeared in error.
If the P0422 code occurs again, inspect the wires and connectors near the catalytic converter. Repair or replace any damaged items. After this, inspect the catalytic converter and also perform a thorough check of the exhaust system for leaks.
If the problem is the catalytic converter, replace it. Also inspect other vehicle components to determine the cause of the catalytic converter damage.
Test methods and problem solving
In some cases, it is necessary to check the serviceability of the oxygen sensor or the exhaust system and manifold for leaks. Leaks and leaks can affect the operation of the O2 sensors and cause the P0420 error code to appear, but still, more often this problem is directly related only to the condition of the catalyst.
Some tips for a troubleshooting plan
Before starting diagnostics, in order to save time on finding out the cause and fixing the problem, we advise you to carry out a few simple checks, and then proceed to further, complex solutions to the problem. So:
Checking the operation of the catalytic converter and its parameters
To assess the efficiency of the catalyst, it is necessary to compare the output voltage graphs between the “upper” and “lower” oxygen sensors, as well as look at the fuel supply adjustment data.
Oxygen sensor readings on an oscilloscope
The output voltage of the oxygen sensor, read by the car's computer, will decrease when the mixture is lean and increase when it is rich. A normal reading for an oxygen sensor will fluctuate between 900 millivolts (rich condition) and 100 millivolts (lean condition).
Short-term adjustment, ideally, should tend to “0”, but on an engine with mileage, deviations from the norm of up to 10% are acceptable. And when the fuel adjustment exceeds 25%, then a long-term adjustment also occurs, so if both values are present, this indicates a problem in preparing the fuel-air mixture. Therefore, pay attention to the presence of additional fault codes.
How to troubleshoot P0420
Some car owners, unaware of the origin of the P0420 error, may begin to eliminate the problem by cleaning the damper or replacing sensors that affect air and fuel consumption. While, if you need to try to replace something, it’s this:
Firstly, swap lambda probes , upper and lower, since they are the same and can replace each other. Therefore, if the problem is precisely the non-working second oxygen sensor, then the error code will change (alternatively, error P0134 may appear).
Secondly, fill up with other gasoline , of better quality, and drive a little (if it’s because of the fuel, then a couple of days will change the situation).
The third step towards troubleshooting can be checking the catalyst , or rather, its throughput (there are several methods). Internal catalyst failure usually occurs due to abnormal operation of the engine systems upstream of the catalyst. An increased operating temperature of the converter is usually the cause of both the appearance of this code and its failure. For example, misfires can lead to elevated catalyst operating temperatures.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0422 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi
- Chevrolet
- Chrysler
- Dodge (Dodge Caravan)
- Ford
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Elantra)
- Kia (Kia Spectra, Sportage)
- Mercedes
- Mitsubishi
- Peugeot (Peugeot 206)
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Beatle, Jetta)
- Volvo
- VAZ 2104, 2105, 2107, 2110, 2111, 2112, 2113, 2114, 2115
- Volga Chrysler, 31105
- Gazelle Business, Next
- Lada Vesta, Granta, Kalina, Niva, Priora
- UAZ
With fault code P0422, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common are the following: P0304, P0326, P0420, P0441, P0455.
Buy a minibus and drop it off. The error only appears on the highway. When the error pops up that the second dk is dead, then replace it with a bosch.
According to readings on the forums, the problem often occurs not in the first gases. There seems to be a firmware update out now, but it’s lazy to go crazy over such a trifle.
The action plan is approximately this: You can try to swap the DCs and see what happens. VAZ supplies Delphi cultural centers, which are not of high quality.
In general, there are certain instructions in this regard:
Error 0422 – Neutralizer efficiency below threshold The error is entered under the following conditions: 1. there are no errors 0102, 0112, 0113, 0116, 0117, 0118, 0122, 0123, 0130, 0132, 0134, 0136, 0137, 0138, 0140, 0171, 0172 , 0300, 03**, 0441, 0444, 0445, 0562, 0563. 2. The ECU controls the fuel supply in a closed loop Parameter (B_LR= “YES”). 3. The conditions for the ECU to carry out the catalyst diagnostic cycle have been met. 4. The ECU has determined that the oxygen content after the neutralizer is above the threshold. The error is entered into the ECU memory on the third drive cycle. The efficiency of the neutralizer can be assessed using the ANKAT parameter (neutralizer efficiency factor). If the ANKAT value tends to zero, the neutralizer is working effectively. The larger the ANKAT value, the more the neutralizer degrades. Check procedure: 1. Turn off the ignition, connect the diagnostic tool, turn on the ignition, check for errors. If there are other errors in the ECU memory, we eliminate them first. 2. If there is an error, inspect the catalytic collector for damage, check the condition of the “filling”. 3. If malfunctions are found, replace the catalytic collector; if there are no comments, check the exhaust system between the neutralizer and the main muffler for leaks, incompleteness, or damage. Make sure that there is no damage to the DDC and that the wiring harness is not damaged. If no faults are found, replace the neutralizer. 4. If faults are found, fix them. Start the engine, warm it up to a coolant temperature of 70 degrees. Set the rotation speed of the HF to 2000 - 3000 rpm for at least 4 minutes. The load on the engine should have a stable value of 15 - 50%. If the error does not appear, the malfunction has been eliminated; if the error appears again, replace the neutralizer.
2 years ago AutoTime 0
Trouble code P0422 is a standard OBD-II trouble code. Code P0422 indicates that the efficiency of the main catalyst is below acceptable levels. Catalyst efficiency is determined by the engine control module, which uses exhaust gas and temperature data from both the upstream and downstream oxygen sensors to determine catalyst efficiency. If the sensor readings at the input and output are too similar, then the efficiency of the catalyst will most likely be below the acceptable level and the control unit will record error P0422.
The efficiency of the main neutralizer block 1 is below the threshold
From the moment I bought the car, literally in the first thousand kilometers, I began to be haunted by one single error “P0422 Converter efficiency below the threshold”, it is periodically registered in the ECU and not long after that it pops up on the instrument panel “CHECK”. I’ll immediately erase the staff and continue riding, approximately between “CHECKS” the mileage is around 400 - 500 km. It looks like it still sits from the manufacturer's factory. It’s as if my upbringing tells me that this is a mistake and needs to be corrected. What has already been double-checked a hundred times:
1) The spark plugs are all new, 3 sets just for fun and nothing changes, there is no plaque on them, the gaps are clear, the insulators are intact. 2) The wires to the armor were tested for both integrity and resistance, I tried to test it from a working machine and there was no difference. 3) The coil was removed and checked, I also used Kalina 2 and the result was the same. 4) The fuel rail with injectors was removed and tested in a bench, the spray was excellent, the same, just in case I washed it, in one flask, unlike the other three, it was a fraction of a millimeter smaller than in the others, but the flask was 15 centimeters and half a millimeter, just a miracle result. 5) The filters are all new, I change them along with the oil every 6-7 thousand km. 6) The timing and timing gear marks are all clear. 7) The clearances in the gas distribution mechanism are excellent, they were recently rechecked. I’ve already forgotten the specific compression number, but this is what I remember, it’s the same in all cylinders, everything is clear and not low. 9) The pressure in the fuel rail was checked, everything seems to be normal, I checked it two years ago. I can’t say for sure now. 10) The sensors were not touched at all. 11) Gasoline is used only by G95, and by the way, I noticed a tendency that the “CHECK” usually pops up 300-400 meters after refueling.
What are the symptoms and abnormalities:
1) The non-original ECU was changed right during pre-sale preparation in the showroom with the same only blue standard Granta 2) From the sound in the video you can hear that there is a certain misfire, as if one cylinder is out of tune, a small misfire is a barely audible pop 3) Engine speed at idle are not stable and wander a little around 90-100 rpm. min. Well, something like this. I'm waiting for advice! Give up another year with this sore, or still suffer.
VAZ fuel-injected cars have a special engine control and diagnostic system called an ECU (electronic control unit). With its help, you can get acquainted with malfunctions that arose during the operation of the car. VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115 cars and the procedure for eliminating them.
Causes of error P0422
The most common cause of the P0422 code is a faulty catalytic converter. However, there are many other problems that can cause the catalytic converter to malfunction (or may cause it to fail), including the following:
- faulty oxygen sensor
- Coolant temperature sensor malfunction
- faulty fuel pressure regulator
- Malfunction of the manifold air pressure sensor
- malfunction of the mass air flow sensor
- contaminated motor oil
- leakage of the exhaust system in front of the catalyst.
- incorrect engine operation
- damaged wiring or connectors.
Diagnosis of error P0422
Diagnosis of error P0422 is carried out using an OBD-II fault code scanner. First you need to read the stored error codes. After this, clear all saved errors and start the car. If no error is returned, then most likely there is no problem.
If the error returns, you need to inspect the wiring and connectors of the oxygen sensors. If there is a problem, it must be fixed, and the error codes must be reset to make sure that there are no errors. After wiring, you need to inspect the catalyst itself and the exhaust system.
If problems are detected with the catalyst, you need to find out the cause of its damage, which is usually the result of a malfunction elsewhere in the engine.
What does P0422 mean?
Trouble P0422 is a general trouble code that indicates that the primary catalytic converter (bank 1) efficiency is below acceptable levels. Catalyst efficiency is determined by the transmission control module (PCM), which uses exhaust gas and temperature data from oxygen sensors located upstream and downstream of the catalytic converter to determine efficiency. If the readings from both sensors match or are almost identical, this indicates that the catalyst efficiency is most likely below acceptable levels. In this case, error P0422 will appear.
Catalytic converter - what is it for?
Car designers are increasingly paying attention to reducing harmful emissions.
To achieve this, the power supply systems of power plants are being modernized in order to achieve the lowest possible fuel consumption, without affecting power performance.
Also, more and more cars are equipped with catalytic converters installed in the exhaust system.
The essence of the catalyst's work comes down to the breakdown of harmful elements into harmless ones through chemical reactions.
The catalytic converter consists of a housing, inside of which active catalysts, the so-called bobbins, are placed.
Nowadays these bobbins are often made of ceramic, but some are also made of metal.
The reel contains a large number of honeycombs through which the exhaust gases pass.
But ceramics do not enter into a chemical reaction; for this purpose, the surface of the honeycomb is covered with a layer of noble metals - platinum, iridium. Thanks to these metals, a reaction occurs, which reduces the harmfulness of car emissions.
The operating efficiency of this device depends on the temperature - the optimal temperature is considered to be from 300 degrees, so there is also a heat-insulating layer inside the housing, and the element itself is placed as close as possible to the exhaust manifold.
You can read more about the design features of the catalytic converter, as well as the principle of its operation, here.
One of the main disadvantages of the catalytic converter is its relatively short service life. On average, it is designed for 100-120 thousand km, after which it becomes inoperative.
Causes of error P0422
The most common cause of P0422 is a faulty catalytic converter. Other reasons are:
- Oxygen sensor malfunction
- Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunction
- Fuel pressure regulator malfunction
- Manifold air pressure sensor malfunction
- Air flow sensor malfunction
- Engine oil contamination
- Engine leak before catalytic converter
- Misfires in engine cylinders
- Damage to wires and connectors
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0422 code?
Error P0422 can be diagnosed using a standard OBD-II scanner. The mechanic uses a scanner to view data and gather information about the code, as well as check for other error codes that may be present. The mechanic will then clear the error codes from the PCM memory and retest the system to see if P0422 appears again. If the code disappears, it may indicate an intermittent error or that the code appeared in error.
If the P0422 code appears again, have a mechanic inspect the wires and connectors near the catalytic converter. He will repair or replace any damaged items. The mechanic will then inspect the catalytic converter and also perform a thorough check of the exhaust system for leaks.
If the catalytic converter is the problem, the mechanic will examine other vehicle components to determine the cause of the catalytic converter damage.
Common errors when diagnosing code P0422
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0422 code is failure to follow the diagnostic protocol, which leads to hasty replacement of the catalytic converter. Before replacing the catalyst, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of its damage, and also consider other error codes present.
It is also a mistake to hastily replace oxygen sensors. Before replacing them, it is necessary to perform a thorough diagnosis, since usually a faulty sensor is not the only cause of the P0422 error.
p0504
Also, many owners of a Lada Priora with 16 valves have questions about the appearance of error p0504. She tells the owner that there is a malfunction in the brake pedal sensor. To find out the exact reason for the appearance of p0504, you need to remove the sensor and disassemble it. Pay attention to its springs, one of them could burst - replace the damaged part.
see also
This error usually occurs on cars with a 127 engine. It is associated with the throttle valve, the quality of which in this power plant leaves much to be desired. P1558 does not interfere with normal engine operation, but you can still try to fix it. Some people solve the problem by flashing it, but we offer a simpler method.
Remove the throttle valve, and then remove the cover - this can be done using a hexagon. We find a plastic gear inside - this is the working part. Lubricate the gear thoroughly and reassemble in reverse order. Most likely, error p1558 will disappear after these manipulations.
How serious is the P0422 code?
The severity of the P0422 code depends on the cause of its occurrence. If the problem is a bad catalytic converter, the engine may stall frequently or be difficult to start. In this case, problems with the vehicle's handling may occur. However, if everything is in order with the catalyst, there should not be any serious problems. In any case, if this code is detected, it is recommended that you contact a qualified technician as soon as possible to diagnose and repair the error to avoid serious damage to the catalytic converter.
To resolve error P0422 you may need to:
- Replacing the catalytic converter
- Replacing oxygen sensors
- Repair or replacement of electrical wires and connectors
- Repairing engine leaks
- Replacing the air flow sensor
- Replacing the manifold air pressure sensor
- Replacing the fuel pressure regulator
- Replacing the engine coolant temperature sensor
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0422
If the cause of this error is a faulty oxygen sensor, other error codes related to this sensor may also appear along with the P0422 code.
Car manufacturers are required to provide a 100,000 kilometer warranty on the catalytic converter. If the catalyst is damaged or fails, you need to find out whether it can be replaced under warranty.
Need help with error code P0422?
The company - CarChek, offers a service - on-site computer diagnostics; specialists from our company will come to your home or office to diagnose and identify problems with your car. Find out the cost and sign up for on-site computer diagnostics or contact a consultant by phone
The last time this error occurred was after refueling. BUT! I've been filling up at this gas station my entire car life! The name of this gas station is Gazprom! AI-95!
Tell me, is it still because of the gasoline? Or what other common reasons are there? How did anyone deal with this problem?
In advance, very grateful for your answer!