I did not know about the existence of this sensor until the other day when I successfully went into the smoking room to discuss the purpose of this device between the installer of additional equipment and the diagnostician. Information is presented below.
On vehicles equipped with Euro-3 standards and higher, in addition to the misfire detection system, a rough road sensor is added. It is the only sensor in the system that does not directly influence the engine control process. The DND performs a purely protective function: when driving on an uneven road, using its signals, the controller can temporarily interrupt the recognition of misfires and turn off the problem cylinders.
According to environmental standards, the on-board diagnostics of a car equipped with Euro-3 must recognize misfires, which can lead to excess harmful emissions into the atmosphere, destruction of the catalyst and oxygen sensor. Such an excess occurs if, on average, per hundred operating cycles of the engine there are three to four cycles of non-ignition of the working mixture. It follows that the on-board diagnostics must be very sensitive to detect every misfire. In modern engine control systems, misfire detection is based on calculating the uneven rotation of the crankshaft using the DPKV signal. In the absence of combustion in the cylinder, the time the piston moves from TDC to BDC increases (compared to the previous half-turn of the crankshaft). If the controller detects significant piston deceleration in one of the cylinders, it classifies this as a misfire. The causes of such malfunctions may be: fuel quality, malfunctions in the ignition system, too lean or rich mixture, insufficient compression, etc. You can read more about the causes of misfires here. But this is not our case. Since the crankshaft is rigidly connected to the wheel through the transmission, all wheel beats (deceleration - acceleration of rotation) when moving over bumps are transmitted to the crankshaft. Because of this, on rough roads the likelihood of a false misfire detection increases sharply. So, when driving over bumps and potholes, the rough road sensor sends a corresponding signal to the ECU to prevent false detection of misfires. Everything is logical and not so complicated. There are much more complex systems.
The DND is an accelerometer; its operating principle is based on the piezoelectric effect and is similar to the operating principle of a knock sensor. The sensor is installed in the engine compartment on the car body and records body vibrations in the vertical plane. More precisely, the sensor converts accelerations that occur when driving on uneven roads into a proportional DC voltage signal. Based on the amplitude of the DND signal, the controller determines the moments when the car is moving on an uneven road, and during this time it prohibits recognition of misfires. As mentioned above, the DND is rigidly fixed to the body or to a special bracket in the engine compartment, usually in the area of the right front pillar. It is not difficult to detect it, it is in plain sight. It is connected to the engine management system via a 3-pin connector. Removing and installing the sensor is not difficult at all. It is more difficult to diagnose. DND is a fairly reliable product. But if suddenly problems arise, the controller will light up the malfunction light if the following error codes are present:
P1606
- rough road sensor circuit, signal out of acceptable range
P1616
- rough road sensor circuit, low signal level
P1617
- rough road sensor circuit, high signal level
Naturally, you will first need to check the connector and circuit (wiring) of the sensor, the reliability of the connection and the integrity of the elements. Next, check specifically for each wire. Using a multimeter, check the continuity of the circuit and the absence of a short to ground. If a defect is not detected here and the error appears again after “erasing” it with the scanner, then it is possible that the sensor itself is faulty. First you need to try replacing the sensor with the same one, which is known to be good, for example, from another car. It should be taken into account that the error may not appear immediately; It is advisable to take a test drive. The sensor can be disassembled, but only with a hammer. DND is a non-repairable product. A new sensor costs about $25.
Operating principle of the device
With the introduction by a special commission of the European Union of the mandatory characteristics of Euro-2 and Euro-3 in vehicle electronics, the misfire (ignition) system became mandatory for use as a function when programming the ECU. Methods for its diagnostics were also integrated into the “brains” of the on-board vehicle. With its help, to prevent unnecessary toxicity of unused fuel, a program was installed to turn off cylinders with deficiencies in the injection system. This occurs by blocking the fuel supply through the injector system.
With the help of preventive blocking of this function, the release of unburned fuel into the environment is stopped, and the functionality of the rather expensive complex of catalyst parts is not affected. On vehicles equipped with a set of additional electrical devices included in Euro-3 and subsequent generations, a VAZ rough road sensor is added to the ignition system interval control complex.
This indicator is positioned as the only device in the vehicle electronics that does not directly influence the management function of the Priora from the electrical on-board complex. When the question is posed this way, Russian car owners often ask why a rough road sensor is needed in a car.
Such a device has the function of protection when moving along sections of the roadway with obvious unevenness (bumps, ruts, etc.). Based on the pulses emitted by the device, the controller can temporarily stop the process of identifying intervals and turning off idle cylinders.
Where are they located?
But knowing about their presence in your VAZ 2114 car is not enough. In case of problems, when the electronic control unit receives incorrect data from signaling devices, they have to be changed.
Whatever one may say, every sensor that has ceased to function properly and transmit correct data on the state of the systems to the electronic control unit must be replaced. Almost all sensors cost no more than a few hundred rubles. But even low cost and small size do not indicate the uselessness of these devices. Change devices promptly.
To do this, you need to understand how to get to this or that sensor. Therefore, we invite you to familiarize yourself with the location of key alarm and measurement devices.
Sensor
Location
On 8 valve engines it is located at the bottom of the valve cover in the cylinder head, and on 16 valve engines it is located on the left end of the camshaft bearing housing
Coolant temperature (engine temperature sensor)
Look for it near the tasty cylinder head cooling jacket pipe
Coolant level
It is located directly on the tank, inside of which there is coolant (antifreeze or antifreeze). Looks like a simple plastic cover that connects to an electrical connector
Brake fluid level
This is a float device located inside the brake fluid reservoir.
Idle speed (IAC)
Look near the throttle valve on the throttle body
Mass air flow
You will find it near the large intake pipe, directly on the air filter housing
Throttle Positions
Located on the throttle body
Crankshaft position (timing sensor)
Its location is near the electric generator drive pulley
Camshaft position (phase sensor)
Near the cylinder head cover, viewed from the air filter side
Oxygen (lambda probe)
Installed in front of the resonator in the intake manifold of the exhaust system
Located between cylinders 2 and 3 near the fan
It should be looked for inside the intake chamber of the fuel tank
Located directly on the gearbox
Look near the cup on the side of the right mudguard. You can get there through the engine compartment
Ambient temperatures
It is installed directly behind the front bumper, exactly in the middle
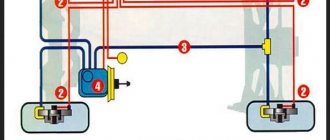
Each sensor has its own strictly designated place. Having studied their locations, you can easily replace devices in the event of breakdowns or malfunctions.
Some measuring and signaling devices are located literally on the surface, so there is no need to carry out additional dismantling work. To get to others, you will have to seriously dig into your VAZ 2114 and remove quite a few parts.
The integrity of your car, the safety of the driver, passengers and all other road users depend on their performance. Therefore, treat the sensors with appropriate respect, monitor their condition and change them in a timely manner if the need arises.
Source
Replacing the device
Technical properties of the sensor:
- device voltage 5 V (nominal);
- network current no more than 20 mA;
- operating temperature range from -40 to 105 degrees Celsius;
- working pressure from 630 to 800 mm Hg. St;
- resistance at the output connector is no more than 0.3 Kom;
- acceleration limits from -5 to 5g.
Checking the ADC pulse of the VAZ rough road sensor can be carried out using the DST-2M device or its analogues. The BSMW indicator is analyzed and diagnosed in the form of acceleration configuration g. If the sensor is subjected to a slight impact with a click or knock, then there is a change in acceleration values with a different spectrum, from instantaneous to small values. In principle, this device is very sensitive, changes are observed even by the body's rocking.
Error codes VAZ rough road sensor
- P1606 – the pulse has left the limited interval;
- P1616 – reduced pulse value;
- P1617 – pulse value too high.
To dismantle the rough road you will need a Phillips head screwdriver:
- Disconnect the power wire from the negative terminal of the battery.
- We compress the spring-type clamp.
- Disconnect the wire block from the contacts of the product.
- We dismantle the fastening of the device to the mount.
- We remove the sensor from the landing site.
- Install the device in reverse order.
At this point the function can be considered complete.
Many car owners are wondering what a rough road sensor is for and what functions it performs. This newfangled device appeared relatively recently, so it is not surprising that many motorists simply have not heard of its existence. Today, this cunning device is found on almost all modern domestically produced cars and on some foreign cars. So, what is a rough road sensor for and how does it work? This is what we will talk about today.
Idle speed control
Where is the oil pressure sensor on a Kamaz? As in engines with a carburetor, an injection engine keeps idle speed with the throttle valve fully closed. This is possible only under one condition - if the design of the throttle provides for a bypass channel, and it must have a variable throughput. To do this, a conical valve was installed in the bypass air channel of the throttle body, regulating the air supply when the throttle valve is closed, and called it IAC, idle air regulator. It consists of a conical valve, a stem and a stepper motor. Depending on which winding the impulse is applied to, the motor rotates in one direction or the other, thereby changing the throughput of the bypass air channel. The idle either rises or falls as a result of the movement of the cone valve. The idle speed sensor on the VAZ 2115 has catalog number 1148300 02.
How to check
The most common failure of the IAC is a break in the windings of the stepper motor. To check the windings, you need a multimeter turned on in resistance measurement mode. The resistance value between contacts A-B and C-D is within 45-80 Ohms. Otherwise, the regulator requires replacement. There should be infinite resistance between pins AD and B-C. This means that the windings do not short circuit each other. If there is resistance at these contacts, the sensor is replaced. Rated supply voltage is from 7.4 to 14.1 V.
brief information
You may be interested in: 2LTE engine: technical specifications
In fact, not all motorists know about the true purpose of the rough road sensor. So if you are one of them, don't be discouraged. In fact, this strange device is surrounded by many rumors and even legends with which car owners try to explain its presence in the design of their vehicle.
Most often, motorists consider the main task of this sensor to be limiting speed while driving on uneven roads. But in fact, this opinion is fundamentally wrong and is not at all related to the real purpose of the device. Remember: this device has absolutely nothing to do with the speed of movement on bumpy surfaces. To be more precise, the sensor concerns this problem only indirectly. At least it won't signal if you drive off-road at top speed.
You may be interested in: Years of production of the VAZ-2107. Car history
Then why do you need a rough road sensor? You might be surprised by the answer to this question. However, in reality it is necessary to temporarily stop the cylinder misfire diagnostic system. In simple terms, it disables certain functions of the car so that the check engine light on the dashboard stops systematically lighting up.
How does the misfire check mechanism work?
Any injection engine is equipped with a self-diagnosis system for misfires. A crankshaft position sensor is installed near the crankshaft pulley, which is an electromagnetic element that reads the speed and stability of rotation of the pulley and sends impulses to the engine control unit.
If the sensor detects unstable rotation, misfires are immediately checked, after which “Engine Error” may appear on the instrument panel, and when a diagnostic scanner is connected, a history of misfires will appear in the report.
Working principle of the rough road sensor
So, let's take a closer look at the purpose of this device and its functions. From the name of the sensor it becomes clear that it somehow reacts to the roughness of the road. This is necessary for improved operation of the knock sensor, which is installed on all engines starting from Euro 3. In other words, knowing the environmental class of the car, you can understand whether it has this device. At the moment of hitting an obstacle, the knock sensor reacts to incoming vibrations, mistaking them for dangerous manifestations. At the same time, he completely unreasonably slows down the ignition.
As a result, part of the fuel burns while in the catalyst and exhaust manifold, which negatively affects the condition of these spare parts. In addition, engine efficiency and other important indicators significantly decrease. It is to prevent such phenomena that a rough road sensor is installed. It is triggered the moment you hit a bump and transmits a signal to the controller.
Location of all sensors on the injection VAZ 2114
It cannot be said that the VAZ 2114 is a very modern car filled with electronics.
However, the list of sensors used that are connected to the electronic control unit is quite impressive on the fourteenth. Each of these devices is responsible for certain functions and collects data transmitted to the main computer of the car. This way, the ECU controls the entire process and makes appropriate changes, so that the driver does not have to look for the reasons for the failure or insufficiently efficient operation of a particular unit.
When and why did the sensor appear?
This device, unknown to many car owners, is found on most modern cars. All cars began to be equipped with a rough road sensor after stricter environmental requirements, and especially after the mass introduction of exhaust gas catalysts and the Euro 2 standard.
And all this is because unburned fuel quite quickly provokes failure of the catalyst. If the engine detects a misfire in a certain cylinder, the supply of fuel to it is stopped, and this is done to preserve the integrity of the catalyst.
If misfires are detected in different fragments, the “check engine” light on the dashboard lights up. But if the same thing happens, but with the participation of a rough road sensor, the light does not turn on.
What is an adsorber?
After the introduction of EURO-1 toxicity standards, the need arose for maximum control of exhaust gas emissions into the atmosphere, as well as control of gasoline evaporation. The adsorption system does not allow gasoline vapors to enter the atmosphere, thereby relieving the driver and passengers of the smell of gasoline, thereby increasing environmental friendliness and fire safety standards.
The adsorber itself contains activated carbon, which absorbs all harmful substances when the engine is not running. The system is called EVAP and works as follows:
- at the end of engine operation, vapors appear in the fuel tank, which rise to the fuel filler neck and tend outward, creating dangerous excess pressure in the tank;
- near the neck there is a separator that separates liquid from steam, which flows through special tubes back into the tank in the form of fuel condensate;
- the remainder of the vapor that the separator could not cope with enters the adsorber, and after starting the engine, gasoline vapor enters the intake manifold through the ventilation valve, and then into the engine cylinders.