A little history
The first to create such a model of brakes (disc type) was Frederick Lanchester (Great Britain). It was in its design that a caliper was used that pressed the pads. However, technology at that time did not allow the creation of reliable disc brake systems.
Disc brakes were revived in aviation, and in the 50s they began to be installed on cars - first on sports models, and then on production ones. The first car with serial front disc brakes was the Chrysler Crown Imperial (in 1949).
The importance of this component is difficult to overestimate, because the brake disc and pads are passive components, while the caliper plays an active role. Due to this, the pads are pressed. Therefore, the brake caliper is the most important component.
Front brake caliper - design types
The development of these mechanisms is reflected in their division into 2 categories, depending on the layout:
- Fixed design - it consists of a body made of metal, and there are working cylinders on both sides of the brake disc. Their arrangement is symmetrical. In this case, the body itself is fixed on the steering knuckle. At rest, the pads are held in place by special springs, and during braking they are compressed, causing them to be pressed against the surface of the disc. To ensure the operation of such a design, it is required that brake fluid be supplied simultaneously to all cylinders, which is achieved through a whole system of hoses, pipes and various tubes. Such brakes are highly efficient, making them ideal for cars with powerful engines and large weight - racing and executive models. World famous brands - Brembo and others - specialize in such calipers.
- A floating caliper is the fundamental difference between such a caliper and a fixed one in that one of the pads is in a constant position. Its design involves the presence of a bracket, as well as a cylinder, which is fixed on the inside. Typically, such calipers are single- or double-piston. The braking process is as follows - the piston presses the pad and presses it against the disc, and at the end of this phase, the bracket (floating type) begins to move towards the piston, sliding along the guides. Due to this, another pad is pressed against the surface of the disc.
This design is usually found on cars in budget segments, as it is cheaper to manufacture and simpler.
Types of auto parts
Brake calipers are classified into types according to different criteria: location, presence of a handbrake mechanism, design, number of pistons, etc.
According to the type of design, the caliper on the Lada Kalina can be taken:
- Fixed.
- With floating bracket.
The latter variety is easy to produce and costs less.
Based on the number of pistons in the design, the following types of calipers are distinguished:
- Single piston.
- Double piston.
- Three-piston.
- Four-piston.
- Six-piston.
- Eight-piston
- Twelve-piston.
Depending on the location of the part, it can be:
- Right.
- Left.
- Front.
- Rear.
Depending on the condition, the auto part may be:
- New.
- Used.
Depending on the manufacturer, you can take a caliper for the Lada Kalina:
- Original.
- Non-original (analogue).
At the place of purchase, the caliper can be:
- Taken from a private person based on an advertisement.
- Bought at a car market.
- Ordered from the online store.
- Picked up from a car wrecker.
- Purchased from an auto parts store.
You can purchase a caliper for Lada Kalina from the following manufacturer:
- STELLOX.
- FENOX.
- AvtoVAZ.
FENOX caliper
According to the payment method, the purchase can be made:
- On credit.
- Through personal savings.
- In installments.
Working principle of brake caliper
The brake caliper performs its main task - it provides the necessary braking force required to slow down or stop the car.
Pressing the brake pedal causes pressure to build up in the brake line. It is transmitted to the caliper pistons, which at this time strictly parallel fixes the pads relative to the disc. When braking, the calipers compress the pads on both sides of the disc, causing it to slow down. But there is another effect. It involves heating, as friction energy is transformed into heat. This significantly heats up both the disc and the pads and calipers. The temperature of the brake fluid also increases.
This effect places certain demands on manufacturers. So the front brake caliper must have the following characteristics:
- high heat transfer rates;
- strength;
- high resistance to heat (so that increased temperature does not deform the caliper components).
Video: General principle of operation of the rear caliper
replacing brake discs 13″ to 14″
To upgrade from 13" to 14" brake discs you will need:
- brake disc 260mm (14” in people)
- caliper bracket from VAZ 2112 (officially “brake pad guide”)
- some tools
- Straight arms
This article is especially for those who want to have a minimum of hemorrhoids during this process.
| Loosen the wheel mounting bolts. Raise the car with a jack. Unscrew the wheel nuts. We remove the wheel and put it under the front suspension (just in case, otherwise you never know. It’s better to lay a board between the wheel and the suspension). |
| Next, take the head (or socket wrench) and unscrew the two caliper mounting bolts (located on the back side). |
| The second bolt is not indicated in the photo; it can be easily seen by bending down or feeling it with your hand. On the left is a photo with the caliper already removed for clarity. |
| Next you need to unscrew the two guide pins. Do not under any circumstances try to unscrew them with just a 7mm spanner! Take and put on two keys at once, or even better if you find a long head on “7”. |
These pins are screwed into the hub; they simply pass through the brake disc and press it against the hub, helping to put on the wheel when replacing it. It wouldn’t hurt to shed these pins a couple of times on both sides with a WD tool and at the same time shed the mounting diameter of the brake disc on the hub.
If you were able to unscrew the pins, consider half the job already done (on a car with a mileage of less than 20,000 km, the pins can be unscrewed quite simply, but if the car, like mine, has a mileage of around 55,000 km, and is also somehow adjusted by AvtoVAZ, you will be able to unscrew them It’s not easy.
Now we begin to knock on the brake disc from the inside with a heavier hammer through a piece of wood. The main thing is not the force of the blow, but the symmetry of the blows on opposite edges of the disc. The disc has a very tight fit (a normal brake disc has a groove for the hub of 58.6 mm, the hub has a groove of 58.5 mm + corrosion). We knock on the hub from the inside, turn it 180° (if you prefer, you can knock at least every 30° turn). In the holes of the wheel bolts you can clearly see how tightly the disk is pressed to the hub, and you need to knock on the side where the pressure is stronger.
Having removed the disc, we can say that the hardest part is over.
Use a metal brush to clean the mounting hole on the hub and put on a new disc.
In my case, the original 240 mm brake disc was a miserable sight; in just two sets of pads, it managed to burn blue several times, which was facilitated by the idiotic setting of the brake force regulator at the factory. As a result, the small 240 mm brake disc took on the majority (more than 80% of the car’s kinetic energy).
Visually, the difference between a 240mm (popularly 13”) disc and a 260mm (popularly 14”) disc is this:
Symptoms of a problem
There are several common signs of a failing brake caliper:
- increased force - this is what needs to be applied to completely stop the machine;
- the car pulls to the side during braking;
- the pedal becomes “soft” - pressing it requires a fairly weak force;
- brake pedal pulsation;
- slight resistance in moving the pedal to the floor;
- brake sticking;
- blocking the rear brakes with great force, etc.
Brief description of the part
A car caliper is a disc brake element that is responsible for the normal operation of the brake pads. It presses the brake pads against the disc, thereby ensuring smooth braking of the car.
In order for a part to work properly for a long time, it must be regularly maintained : cleaned, lubricated. The following signs of malfunction indicate that it is time to change the spare part:
- If the force is too high, the rear brakes are blocked.
- The brake pedal “falls” and vibrates.
- When braking, the car pulls to the side.
- Brake sticking.
- Overheating of brakes.
- It takes a lot of force to stop the car completely.
Caliper repair methods
Caliper malfunctions can be different. However, we can highlight the most common cases, as well as recommendations for eliminating them.
Brake pads jam in caliper
This is noticeable when, with the caliper removed, the pads do not move freely. Usually the reason is rust on the stationary caliper pads, which prevents the pads from moving.
To eliminate the problem, you should arm yourself with sandpaper, a metal brush and a file (but only a small one). Then you need to clean off the corrosion from the metal, and then lubricate the surface with a high-temperature type lubricant. However, there should be no wear on the caliper - pits from corrosion. If they are present, cleaning will not help - the pad will not be pressed tightly enough or will not move away from the surface of the brake disc quickly enough.
Sometimes such a defect can be eliminated with a file (subject to insignificant wear), but usually you have to buy a new part of the caliper (fixed).
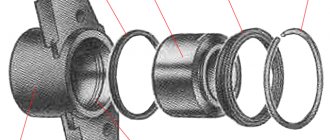
Design and principle of operation of brake calipers
A brake caliper consists of two main parts - a hydraulic cylinder with a piston that creates the stopping force on your car, and a caliper that holds the brake pads in place.
The brake piston is inserted into the brake cylinder through a system of seals to prevent leaks. When you press the brake pedal, excess brake fluid pressure is created in the vehicle's braking system. A piping system distributes this pressure to each brake caliper. Excessive fluid pressure begins to push the brake piston out of the cylinder. In turn, the piston moves the brake pads, which compress the brake disc and create braking force.
The purpose of the brake caliper is to keep the brake pads from turning during braking and to hold them against the surface of the brake rotor.
The brake cylinder is attached to a bracket on the brake caliper guides. The brake cylinder can move freely on the guides in the transverse direction (relative to the axis of movement of the vehicle). This is necessary in order to create an even braking force on both brake pads and use both sides of the brake disc for braking.
As you can see, there is nothing complicated about the brake caliper design, but the devil is in the details.
Design, principle of operation and main reasons for replacing a brake caliper in Kalina
In Kalina, the front braking mechanism is based on a floating front caliper. This means that the cylinder and piston in each of them are in one copy. The latter, when pressing the brake pedal, presses the pad against the disc from the inside, and the impact from the outside is achieved due to the displacement of the caliper relative to the disc along the guides. When the pedal is released, the piston returns to its original position and the pads move away from the discs.
The main malfunction that may lead to replacement of the brake caliper is souring of the piston in the cylinder. In this case, it either does not act on the pad when you press the brake pedal, or does not return back, constantly pressing the pad against the disc. Sometimes incorrect operation of the caliper is associated with souring or severe contamination of the guides. In this case, there is no need to change the caliper itself, but the symptoms may be similar.
Signs of faulty brake calipers
It is very easy to determine whether brake calipers are faulty; you do not need any special tools, just a quick glance at the assembly.
The lion's share of brake caliper malfunctions is associated with loss of mobility of the mating units, which in turn can cause the following malfunctions:
- Uneven wear of brake discs;
- Uneven wear of brake pads;
- Uneven fit of the brake pad to the brake disc;
- Wedging of the brake disc between the brake pads.
To eliminate the above malfunctions, it is necessary to disassemble, lubricate and develop the moving parts of the caliper. After this, it is recommended to replace the brake pads and discs.
The second most common brake caliper malfunction is a leaky brake caliper. If the caliper is not sealed, you may notice brake fluid leaks on the outer surface of the caliper. Leaks appear in the following places:
- Fluid leaks from under the brake cylinder boot;
- Liquid leaks from the bleeder fitting.
To eliminate a leaky brake caliper, it is necessary to completely disassemble the caliper and replace all rubber seals. After this, it is necessary to clean the brake disc and pads from any brake fluid that has got on them. To do this, you need to use a special degreaser, which is sold in car dealerships under the name “brake cleaner”.
Replacing caliper pins and boots
I think there is no need to explain once again that due to poor lubrication of the caliper fingers, certain problems can arise, for example:
- uneven brake pad wear
- tight movement of the bracket and even wedging it
- wear of the fingers, which will lead to rattling and knocking of the caliper
If there is enough factory lubricant in the guide pins, it can last up to 100,000 km. But there are times when practically new cars find themselves without lubrication in these parts. That is why it is better to check everything yourself. Also, lubricant can “leave” through a torn finger boot, so their integrity must be constantly monitored.
If you decide to replace the guide pins, as well as the caliper boots on your Kalina, then for this small repair you will need the following tool:
- 13 and 17 mm wrench
- Flat blade screwdriver
- Lubricant for caliper pins
- Brake cleaner (if equipped)
Replacing guides and their lubrication
So, the first thing you need to do is remove the wheel bolts. Then lift the car with a jack, and finally unscrew the bolts and remove the front wheel. Then, using a flat-head screwdriver, bend the locking washers of the caliper bolts and unscrew the top bolt, as shown in the photo below.
We disengage the brake hose from the front strut, then use a screwdriver to push the cylinder down a little so that you can then tilt the bracket up without any problems.
And we fold it back, as mentioned above.
Now we have access to the upper caliper pin. With a slight movement of your hand, you can remove it by slightly pulling it to the side, overcoming the force of the boot.
Now that the finger is removed, thoroughly rinse it with cleaner and the boot, if it is intact. If necessary, take a new finger and boot.
Now you can apply new lubricant in small quantities so that excess does not get on the active working surfaces (brake pads and discs). For this procedure, I used MC1600 lubricant, which at one time was actively advertised in videos on YouTube and on third-party Internet sites. But I took it not because of advertising, but because of the lack of more or less normal lubricants in the store at the time of purchase.
According to the stated characteristics, the operating range of this lubricant is from -50 to 1000 °C. By the way, I didn’t expect that the cost of this bag is only 80 rubles. I thought it was several times more. Although, I can’t say that it’s particularly cheap! If you are constantly servicing the brake system while on the road, then of course it is more profitable to buy a large tube. If I'm not mistaken, it costs about 600 rubles per 100 grams.
This same bag will be enough to service the calipers of your Kalina for a year for sure!
You should not be overzealous, as excess may end up on the working surfaces, which will lead to a decrease in braking efficiency, and you will have to remove the residue with a cleaner or other degreaser.
Now you can put your finger in its place.
The lower finger changes in a similar way, so you are unlikely to encounter any difficulties when carrying out this repair! The effectiveness of the lubricant used can only be judged after long-term use, so we won’t rush to conclusions!
Lubricating the brake caliper guides
If there is a loss of mobility in the caliper assemblies, the first thing you need to pay attention to is the guides. They are the ones who most often cause trouble to car owners. Soured guides can be the reason for the manifestation of all malfunctions associated with loss of mobility between the caliper assemblies.
The guides must move freely along their axis. If this is not observed, it is necessary to disassemble the caliper, remove the guides from the bracket, clean them of old grease and evaluate their condition; it is also necessary to clean the guide seat in the bracket.
The working surface of the guides must be free of corrosion and without strong signs of wear. If slight corrosion appears on the surface of the guide, it must be cleaned with very fine sandpaper, after which the guide must be lubricated with a special lubricant and installed back into the caliper bracket. After this, you need to check the free movement of the guide along its axis. You should not use any great force to move the guide. The guide should move freely in the body of the bracket when grasped with two fingers.
If this does not happen, then perhaps you have not cleaned the guide properly, or it has a lot of wear and is jammed in the mounting hole of the bracket; in this case, the guide must be replaced.
Support. Troubleshooting Lada Kalina brake calipers
While driving a car, over time, ineffectiveness in wheel braking is revealed, as well as fluid leakage through leaks in the cuffs. Provided the fault has been previously eliminated (the pads have been replaced), no changes are observed during braking. The thing is that the malfunction is hidden in the condition of the caliper itself, which can lead to serious consequences. If the braking of one of the wheels is ineffective while the car is moving, there is a real possibility of the vehicle skidding and overturning. A special feature of the front wheel brakes of the Lada Kalina is a mechanism consisting of ventilated discs with a single-piston floating caliper. The design of which includes: a caliper and a wheel cylinder, tightened together with two screws. In turn, the cylinder is attached with two bolts to the guide pins, which are installed in the holes of the shoe guide.
When installing brake pads, springs are installed that press them against the guide grooves. The design of the cylinder includes a piston sealed with a rubber ring of rectangular cross-section. Installing a rubber ring helps maintain a constant optimal gap between the brake pads and the disc, which is ensured due to its elasticity.
Identifying signs of a faulty brake caliper on a Lada Kalina car: 1. When pressing the brake pedal (to stop the car), additional effort must be made.2. When you press the brake pedal, the car pulls to the side.3. When you press the brake pedal, there is no force.4. When you press the brake pedal, the movement is transmitted by pulsating movements.5. When the brake pedal is fully pressed to the floor, a slight resistance is felt.6. When you press the brake pedal, the brake mechanisms jam. Having identified the faults, we place the vehicle on a flat surface (concrete area, inspection ditch). We carry out all the necessary basic and auxiliary operations for preparing and removing the front wheel (photo N1). Operations performed when removing the brake mechanism (caliper) of a Lada Kalina car (photo N2):
Replacing brake calipers
The operation of replacing brake calipers is quite simple. To do this, you need to remove the caliper from the car and then install a new caliper in its original place. To do this, you will need to unscrew a couple of bolts.
The most difficult part of the operation is bleeding the new brake caliper. During this operation, it is necessary to fill the new caliper with brake fluid and remove all the air from it. To carry out this procedure, you will need an assistant or a special device for bleeding the calipers. The operation of bleeding calipers is written in more detail in the relevant literature.
If you are not confident in your own abilities, then it is better to entrust the operation of bleeding calipers to service station specialists.
Important note: it is strictly forbidden to drive a car with unbleeded brake calipers.
Approximate prices
A new caliper for a Lada Kalina car can be bought in stores in Russia for 2600-4750 rubles . Approximate prices depending on the manufacturer are given below:
- STELLOX - from 2980-3000 rubles.
- FENOX - about 2600 rubles.
- AvtoVAZ - 4670-4750 rubles.
If delivery is required, you will have to pay an additional 500-600 rubles .
Used brake calipers for Lada Kalina are sold at auto wrecking yards for 500-800 rubles . According to a private advertisement, a spare part in good condition can be purchased for 1000-1200 rubles .
Replacing the caliper repair kit
The most difficult and responsible operation when repairing calipers is replacing the caliper repair kit. During this operation, all seals and rubber parts of the caliper are changed.
To begin with, you must purchase a repair kit for the caliper of your car. To do this, in a car store you will have to tell the seller the make and model of your car, the year of its manufacture and other information that the seller asks.
To carry out repairs using a repair kit, you first need to dismantle the caliper. After that, transfer it to the workbench and completely disassemble it. A very important note - the place where the caliper is disassembled must be as clean as possible. If even the smallest grain of sand gets inside the caliper, it can quickly fail.
When disassembling the caliper, it is recommended to write down or photograph the places and methods of installing certain parts.
In most cases, you will need to replace the following rubber products:
- Brake cylinder seal;
- Brake piston boot;
- Guide boots;
- Guide seals;
- O-ring of the bleeder fitting.
If there is deep corrosion on the working surface of the brake piston (with the formation of cavities), then the piston must also be replaced.
Reassemble the caliper in the reverse order of disassembly. After this, the caliper must be installed on the car, the guides lubricated and the brakes bled. As you already know, you will need an assistant or a special device for this.
Device
The unit is a cylinder with a piston running inside it. The system also includes brackets - they hold the brake pads. On passenger cars, products driven by a hydraulic system are installed; on trucks, a pneumatic system is installed.
This is what the caliper consists of:
- frame;
- caliper guides - must be coated with lubricant;
- the anthers of the fingers on which the caliper runs;
- internal and external pads;
- brackets in which the braking elements are secured;
- sealing and fastening rings;
- piston boot;
- hoses supplying brake fluid.
The main element is a piston with a cylinder. The design includes a valve that removes air. Under the influence of pressure, the air temperature increases, which is why there is a risk that the liquid will boil, and this negatively affects braking. The hole in the rear caliper is opened when bleeding the brakes. The rear brake caliper is connected to a cable, so the piston can be pressed mechanically by the parking brake.
How does it work
The operating principle of the brake caliper is based on hydraulic pressure. The force causes the piston to move in the master cylinder. The property of a fluid is that it does not compress under pressure, so the pressure is transferred to the brake unit. Since the caliper also has a piston, it moves outward under pressure. The disc is clamped on both sides by pads, they rub against it, and the speed is reduced by friction. The return of the piston to its place occurs as a result of the action of the elastic rings.
Note! Since friction releases thermal energy, the discs heat up to 500-600 degrees on any type of car. The design provides constant airflow, so it does not heat up to more than 250 degrees.
The dimensions of the assembly body may vary depending on the size of the pads. Both the rear and front calipers work the same way.
- fixed;
- floating;
- enlarged floating.
The fixed system is fixed to the steering knuckle, and the pistons are located on both sides of the disc, the pads compress the disc. In the inactive position, the pistons are held in place by springs. Brake fluid is supplied through branched pipes to the cylinders from different sides. This system works efficiently and is used for vehicles where the load is especially high - trucks.
How to change the front brake cylinder
Judging by user requests, Kalina owners practically do not experience any breakdowns related to the front brake wheel cylinder. It is safe to say that the unit installed at the factory is quite reliable and must be replaced in exceptional cases. It is for such cases that I decided to write this article.
First, as usual, below is a list of the necessary tools:
- Jack
- Balloon key
- Head 13, TORX E14 with wrench
- Open-end wrench for 15 and 17
- Flat blade screwdriver
The procedure for removing and installing the front brake cylinder of the Lada Kalina
- First of all, we lift the front part of the car from the side where we will carry out the repair, after slightly loosening the wheel bolts.
- Unscrew all the wheel bolts completely and remove it.
- Now you can unscrew the brake hose and hang it upside down so that the fluid does not flow out so much:
- After which we can begin to unscrew the bolts securing the cylinder itself, where we will need a TORX E14 head with a knob. You will have to apply quite a lot of force to break these bolts, since the tightening torque is considerable. Although all Kalina repair instructions say that you first need to remove the cylinder and caliper assembly, and only then, holding it in a vice, unscrew the bolts. But judging from my practice, this does not need to be done if you have the necessary tools.
Service
The calipers get very hot and work in aggressive conditions; these are the factors that have a destructive effect on the parts. Chinese analogues are generally destroyed by high temperatures. Professionals recommend installing either spare parts from well-known brands or originals on your car. You can't skimp on brakes.
- squeaking brakes;
- brake lock;
- deviation of the car's course when braking;
- change in brake pedal hardness.
An important detail on which the service life of the parts depends is the boot. The boot protects structural elements, in particular the piston surface and the oil seal, from dust and dirt. If the boot ruptures, dirt and sand instantly gets inside, the parts rust, the lubricant is washed out or dries out, the tightness of the seal is broken and a leak occurs. Running the piston dry leads to disastrous consequences: braking efficiency is significantly reduced, or it becomes impossible, the piston is blocked and the wheel jams.
Piston souring occurs when a worn brake pad is used for a long time. Insufficient thickness of the lining leads to the fact that the piston extends too much, and deposits form on its side surface, which prevent it from returning to its original position. If you install new pads on such a caliper, the following problems will arise:
- rapid pad wear;
- disk failure;
- uneven pad wear;
- creaking caused by overheating of rubbing parts;
- steering wheel beating, which appears due to constant pressure on the rotating disk. It is especially noticeable when braking at high speeds.
Steering wheel wobble when braking
Noise in the assembly can be noticed some time after installing new parts. Causes:
- design features of the unit;
- low quality parts.
To eliminate this drawback, springs are additionally installed.
Corrosion of the inner surface of the piston occurs due to neglect of the timing of brake fluid replacement. It is capable of absorbing water even from the air. Therefore, over time, even parts that only come into contact with brake fluid are exposed to water and begin to corrode.
Important! The frequency of replacing brake fluid is every 3 years.
In order for the caliper to serve for a long time, it is necessary to change the lubricant in a timely manner. This action will ensure reliable operation of the piston and safe operation of the vehicle.
For calipers, you cannot use conventional lubricant such as graphite grease or Litol. It will dry quickly even with a whole anther. The main requirement for lubricant is resistance to temperature changes. Specialized lubricant is sold in packages of 45 g. This is enough for one-time maintenance.