Purpose and design of the front independent suspension of the VAZ 2121 Niva passenger car
A suspension is a set of devices that provide an elastic connection between the wheels and the vehicle’s supporting system (frame or body). The suspension serves to ensure a smooth ride of the car and increase the safety of its movement.
The suspension divides all the masses of the car into two parts:
sprung
- resting on the suspension - body, frame and mechanisms attached to them;
unsprung
- resting on the road - bridges, wheels, brake mechanisms.
Guide device
determines the nature of the movement of the wheel relative to the body and the road, transmits longitudinal and transverse forces and moments arising between the wheel and the car body.
Elastic device
softens shocks and impacts transmitted from the wheel to the car body when hitting road irregularities, prevents the body from copying road irregularities and improves the smoothness of the car.
Extinguishing device
reduces vibrations of the car body and wheels when driving over uneven roads and leads to their attenuation, converts the mechanical energy of vibrations into thermal energy with its subsequent dissipation into the environment.
Stabilizing device
reduces lateral roll and lateral angular vibrations of the car body.
Depending on their class and purpose, different types of suspensions are used on cars.
Schemes of dependent (a) and independent (b) suspensions:
1 and 3 — wheels; 2 - beam
Dependent
is called a suspension, in which the wheels of one axle are connected to each other by a rigid beam, as a result of which the movement of one of the wheels causes the movement of the other wheel. On passenger cars, dependent suspensions are usually used for the rear wheels. They are simple in design and maintenance, and have low cost.
Independent
is called a suspension, in which the wheels of one axle do not have a direct connection with each other, are suspended independently of each other, and the movement of one wheel does not cause the movement of the other. In the direction of movement of the wheels relative to the road and the car body, independent suspensions can be with the wheels moving in the transverse, longitudinal and simultaneously in the longitudinal and transverse planes. Independent suspensions in passenger cars are used for the front and rear wheels. They provide a smoother ride than dependent suspensions, but are more complex in design and require greater costs to manufacture and operate.
Depending on the type of elastic device, suspensions are called spring, spring, torsion and pneumatic.
Elastic suspension devices:
a - spring; b - spring; c — torsion bar; g — air cylinder; 1—root leaf; 2 - coupling bolt; 3 - clamp; 4 - gasket; 5 - bolt; 6 and 7 - rings; 8 - shell
Front suspension of a VAZ 2121 all-terrain vehicle
independent, spring, with hydraulic shock absorbers and anti-roll bar.
Front suspension of the VAZ 2121 Niva all-terrain vehicle:
1 - shield; 2 — brake disc; 3 - hub; 4 — hairpin; 5 - bushing; 6 — cap; 7— shank; 8 — bearings; 9 — cuff; 10 - fist; 11 — stretch, 12, 18, 25 and 39 — hinges, 13 — pillows; 14, 15, 28 and 34 - brackets; 16 and 31 - buffers; 17 and 27— levers; 19 and 26—axles, 20—adjusting washers; 21, 32 and 37—supports; 22 and 29—support cups; 23— gasket; 24 — cross member; 30—spring; 33 — stop, 35 — shock absorber; 36 — clip; 38— stabilizer
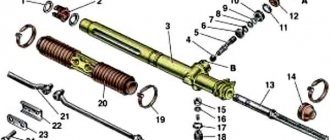
Front suspension of a front-wheel drive VAZ passenger car
independent, telescopic, with shock absorbers and anti-roll bar.
Front suspension of a front-wheel drive passenger car VAZ 2121 Niva.
1, 2, 4, 6 and 25 - supports, 3 - buffer; 5 - spring, 7 and 21 - levers; 8 and 23 - racks; 9 — washer, 10 — adjusting bolt; 11, 26 and 28 — brackets; 12 - fist; 13 — brake disc, 14 — ring; 15 — hub; 16 and 31 — caps; 17 — shank; 18— pin; 19 and 30—bearings; 20— hinge, 22— adjusting washers; 24 — stabilizer; 27 - stretching; 29 — casing
COMMITTEE OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE OF THE VOLGOGRAD REGION
GBPOU "VOLGOGRAD PROFESSIONAL TECHNIQUE OF HUMAN RESOURCES"
| Allow for protection |
| Deputy Director |
| on educational and industrial |
| work |
| _______________HE. Levina |
| "_____"_________20__ g |
WRITTEN EXAMINATION PAPER
Profession _____________________________________________________________
Approved by order of the director of the State Budgetary Educational Institution “VPTKR” No. dated_______
(Full Name)
(full name, degree, title, position)
Volgograd 2016
Features of the front suspension device of the VAZ 2121
One of the advantages of the VAZ 21213 car is its high cross-country ability. To a large extent, the Niva owes this to the successful design of its suspension, which, with a not too powerful engine, allows you to confidently overcome off-road conditions and various potholes. The compact arrangement of all components provides the vehicle with high ground clearance and makes it possible to move freely over rough terrain.
Features of the front suspension of Niva 2121
The front suspension of the VAZ 2121 is independent, on steel wishbones, with coil springs, double-acting telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers and a stabilizer bar.
The upper and lower arms of the VAZ 2121 have a similar design: at the ends of the “fork” there are cylindrical eyes for rubber-metal hinges (silent blocks), and on the opposite side there is a platform with three holes for attaching a ball joint. On the front branch of the upper arm there is a boss into which the rebound buffer rests at maximum suspension travel, and on the lower arm there are four holes for attaching the lower spring support cup. The ball joints of the upper and lower arms are interchangeable and unified with the upper ball joints of the suspension of rear-wheel drive VAZs. The support is attached to the lever along with the boot and the pressure plate with three bolts with spring washers and nuts. The threaded ends of the pins of both the upper and lower bearings point downwards and fit into the tapered holes of the steering knuckle. The pins are secured with self-locking nuts. Thus, the steering knuckle can rotate about an axis passing through the centers of the ball joint pins.
When to change the upper arm silent blocks
The service life of the upper silent blocks of the front suspension on the Niva is quite high. However, signs of wear may appear already after a mileage of 70-80 thousand km, or even earlier if the car is operated on a dirt road. The first sign of a worn silent block is a creaking and knocking sound when driving over uneven surfaces.
In the most advanced cases, a worn silent block will affect the car's handling and ability to keep a straight line; increased uneven tire wear and yaw along the road in a straight line are possible. The easiest way to determine the condition of the silent block is visually - there should be no cracks or chips on the surface of the rubber, and there should be no delamination or play.
Rear suspension
The rear suspension is dependent, spring, with hydraulic shock absorbers. The rear wheels of the car are connected to each other by the rear axle beam, as a result of which the movement of one of the wheels in the transverse plane is transferred to the other wheel. The guiding device of the rear suspension (Fig. 38) is longitudinal 3, 17 and transverse 24 rods, the elastic device is coil springs 9, and the damping device is telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers 25.
Rice. 38. Rear suspension:
1 - spacer sleeve; 2 — rubber bushing; 3, 17 — lower and upper longitudinal rods; 4, 11 — spring gaskets; 5 — lower spring support cup; 6 - compression buffer; 7 — finger of the upper longitudinal rod; 8 — bracket for the upper longitudinal rod; 9 - spring; 10 — spring cup; 12 — upper spring support cup; 13 — rod of the brake pressure regulator lever; 14 — shock absorber finger; 15 — body cross member; 16 - additional buffer; 18 — bracket for the lower longitudinal rod; 19 — bracket for the transverse rod; 20 — brake pressure regulator; 20 — regulator lever; 22 — clip; 23 - bushing; 24 — transverse rod; 25 - shock absorber.
Which silent block is better for Niva?
There are two dozen different silent blocks on sale, ranging from factory VAZ ones to polyurethane ones of various hardnesses. It is not advisable to install polyurethane silent blocks that are too hard - all the vibration will be on the body, and in cold weather a squeak is guaranteed.
- BRT, Balakovo, article 2121-2904040 and 21210-2904040, price about $9;
SEVI, Kedr, BZAK (Belebey) at about the same price and about the same quality, the price per set is about 12 dollars;
The quality and characteristics of polyurethane silent blocks strongly depend on the rigidity of the material, so they must be installed with the expectation that vibrations on the steering wheel and body will be inevitable, and the service life is unpredictable. According to the owners' reviews, the best option for the Niva is VAZ rubber silent blocks, which have proven themselves well over many years of operation.
There are two dozen different silent blocks on sale, ranging from factory VAZ ones to polyurethane ones of various hardnesses. It is not advisable to install polyurethane silent blocks that are too hard - all the vibration will be on the body, and in cold weather a squeak is guaranteed.
Shock absorbers
Shock absorbers are designed to dampen vibrations of the car body and wheels. Hydraulic shock absorbers, as a result of the resistance they create (fluid friction), convert the mechanical energy of vibrations of the body and wheels into thermal energy, which is dissipated into the environment. The front and rear suspensions of the car are equipped with hydraulic shock absorbers of the telescopic type, double-acting, which dampen vibrations of the body and wheels of the car both during compression and recoil strokes.
The front and rear shock absorbers have the same design and differ only in length and mounting method.
The shock absorber (Fig. 39) consists of three main components: a cylinder 12 with a bottom 2, a piston 10 with a rod 13 and a guide bushing 21 with seals. The shock absorber piston has two rows of through holes located around the circumference. The holes of the outer row are closed from above by a bypass valve 24, which is under the influence of a weak plate spring 23, and the holes of the inner row from below are closed by a recoil valve 29 with a strong spring 9. At the bottom of the shock absorber cylinder there is a compression valve, the holder 6 and plate 7 of which have a number of through holes. Cylinder 12 is filled with shock-absorbing fluid, the flow of which is prevented by oil seal 18, pressed by nut 15, which is screwed into reservoir 11. The shock-absorber cavity, enclosed between cylinder 12 and reservoir 11, is a chamber that serves to compensate for changes in the volume of liquid in the cylinder on both sides of the piston, arising due to movement of the rod 13.
Rice. 39. Shock absorber:
1 - eye; 2 - bottom; 3 — compression valve discs; 4 — throttle disk of the compression valve; 5 — compression valve spring, 6 — compression valve cage; 7 — compression valve plate; 8 — recoil valve nut; 9 — recoil valve spring 10 — piston; 11 - reservoir; 12 - cylinder; 13 - rod; 14 — casing; 15 — tank nut; 16 — protective ring; 17 — protective ring gasket; 18 — rod seal; 19 — oil seal cage; 20 - sealing ring; 21 — rod guide bushing; 22 — restrictive plate; 23 — bypass valve spring; 24 — bypass valve plate: 25 — throttle disk of the recoil valve; 26 — washer; 27 — piston ring; 28 — recoil valve discs; 29 — recoil valve plate; 30 - compensation chamber.
During the compression stroke, the piston 10 moves down and the rod 13 enters the cylinder 12. The pressure exerted by the piston on the liquid displaces it in two directions: into the space above the piston and into the compensation chamber 30. Having passed through the outer row of holes in the piston, the liquid opens the bypass valve 24 and flows from under the piston into the space above it. Part of the liquid, the volume of which is equal to the volume of the rod introduced into the cylinder, enters through the compression valve into the compensation chamber, increasing the pressure of the air located there.
During the recoil stroke, the piston moves up and the rod exits the shock absorber cylinder. Bypass valve 24 closes and the fluid pressure above the piston increases. The liquid enters the space under the piston through the inner row of holes in the piston and the recoil valve 29. At the same time, under the influence of air pressure, part of the liquid from the compensation chamber also enters the shock absorber cylinder.
With a smooth recoil, valve 29 is closed, and the liquid passes through the grooves of its throttle disk 25. With a sharp recoil, the speed of the piston increases, under the influence of increased pressure, the recoil valve 29 opens, and the liquid passes through it.
The recoil valve relieves the shock absorber and suspension from heavy loads that occur during high-speed vibrations when the vehicle is moving on an uneven road. The valve also limits the increase in shock absorber resistance if the fluid viscosity increases at low temperatures.
The resistance created by the shock absorber during the compression stroke is several times less than during the rebound stroke: 5 times for the front shock absorber and 4 times for the rear. This is necessary so that shocks and impacts from road irregularities are transferred to the car body to a minimum extent.
Kit kit for independent mounting of RPM NIVA ZSTehnology OPM-1
The decoupling of the OPM-ANK bridge reduces vibrations by decoupling the opposite phases of the sides of the front axle and the engine. It also has a positive effect on the operating angles of the drives when lifting the suspension.
“Earring” brackets are attached to the gearbox housing at the connection points of the wheel drives (CV joints) on the left and right outside the covers, which, in turn, are connected through powerful elastic silent blocks to the “ear” brackets welded to the front beam of the car.
The RPM crankcase cover is replaced with a steel one, with a powerful extension shank, which allows you to secure the RPM at the third point, on the elastic element - the front stabilizer bar.
Thus, the front axle of the car is not connected to the engine by mounts, and if the owner wishes, the engine and gearbox mounting mounts can be replaced with softer ones.
Not supplied with hardware. You will also need to purchase additional stabilizer clips and bushings.
During installation, welding work will be required.
Additionally you will need to buy:
Stabilizer cushion clip: 2123-2906052- 2 pcs. Silent block (stabilizer cushion): 2123-2906046- 2 pcs. Bolts for securing silent blocks: M12x80 - 2 pcs. Nut M12x1.25 with nylon: 2 pcs.
What you need for replacement work: keys, components, consumables
To carry out work on replacing shock absorbers, you need to purchase original struts or high-quality analogues, prepare a set of keys, a jack and wheel chocks. This part comes with all the necessary components, including washers and gaskets. The main thing is not to lose small parts during unpacking and installation work.
Attention! To make it easy to unscrew the nuts, it is recommended to treat all threaded connections with penetrating lubricant before removing the racks.
How to choose a part: average prices
When choosing spare parts for Niva, look at the article number. The part must fit exactly your car model. Don't take the bottom from a Chevrolet Niva. It has different dimensions, which means the part will have to be trimmed.
When buying a new spare part, remember that the factory bottom does not have a number of elements:
- hairpins;
- fastening elements;
- bracket for the hand brake cable.
They will have to be moved from the old flooring. If you are not sure of their safety, it is better to immediately order all the related parts. The average price of the bottom in the capital is 5,000 rubles. If you want to buy a spare part cheaper, contact a VAZ car dismantling center.
Repairing the bottom yourself requires patience and time. Spare no effort in processing the metal and cleaning it from rust. Poor preparation and careless attitude towards post-repair work will negatively affect the service life of the new body element.
Advantages and disadvantages
The car demonstrates good off-road qualities. They clearly appear after lifting to install rubber with an increased outer diameter.
However, many owners of the Chevrolet Niva note the insufficient strength of the reaction rods holding the rear axle.
And also interesting: Do-it-yourself tuning of Niva 2121 (photo video) - Self-repair of cars
Those who plan active off-road trips should take care of reinforcing the parts. Kits of reinforced reaction rods are sold for this purpose.
Also in need of attention are ball joints with silent blocks, which are not durable. To extend the service life of the hinges, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the anthers in order to change them on time.