RANGE Gearbox 05 (KPP 2108) (I - 2.92; II - 1.81; III - 1.27; IV - 0.96; V - 0.78; VI - 0.69)
Requires 1 washer 2 mm for 4th gear
Belongs to the category of sports rows. 4 gears changed. 1st, 2nd and 3rd gears are lengthened (as in 6th), 4th gear is shortened (as in 8th by 5%), 5th is standard. Usually GP 4.1 is installed. On forced engines - with GP 3.7, 3.9.
RANGE Gearbox 06 (KPP 2108) (I - 2.92; II - 1.81; III - 1.27; IV - 1.06; V - 0.94; VI - 0.78)
Requires 1 washer 2 mm for 4th gear
Sports row. Classic installation - with 6th gear and 4.1 (4.3) gearbox. 1st, 2nd and 3rd gears are lengthened (1st significantly), 4th and 5th are shortened. 5th gear of the 6th row is 4th from the standard row.
RANGE Gearbox 07 (KPP 2108) (I — 2.92; II — 2.05; III — 1.56; IV — 1.31; V — 1.13; VI — 0.94)
Requires 1 washer 2 mm for 4th gear and 1 for 5th gear
Very short - sports (rally, motocross) series. Without 6th gear, it is impossible to achieve a high maximum speed. With 3.7 GP in 5th gear at 5000 rpm. – 128 km/h. When installed with GP 4.1, 4.23 can be used, for example, for short distance competitions such as drag racing.
RANGE Gearbox 08 (KPP 2108) (I — 3.42; II — 2.11; III — 1.35; IV — 0.96; V — 0.78; VI — 0.69)
It is also called “commercial”, since for many years it was the most popular and best-selling product. However, it remains relevant today. 1st gear extended, 2nd and 4th shortened. All changes are minimal (5%), but this is quite enough to correct the shortcomings of the standard series. Most often installed with GPU 4.1. Inexpensive, which is nice. Provides improved acceleration dynamics.
Table of rows and main pairs of gearbox VAZ 2108-2110-1118-2170
Calculation table for rows and main pairs in the gearbox of a front-wheel drive VAZ.
Allows you to select the row and main pair to suit the operating conditions of the vehicle, which will significantly reduce the load on the engine and extend its service life until major repairs. Having selected the desired configuration, use the program to convert the numbers into visual graphs.
Table of the main pairs of gearbox 2108.
Vehicle speed at 5000 rpm.
(Wheels: width 185, profile 60, R rim 14)
Sixth gear of nine types:
The main pair 4.1 - unloads the engine, it is easier for the motor to spin the wheels, the dynamics of the car increase, the gears are shortened, the maximum speed drops
at 20 km/h (at 160 km/h, tachometer revolutions are 5 thousand), fuel consumption + 1 liter. (due to changes in driving).
The main pair 4.3 is the same as 4.1 + 5 km/h in all gears.
Ch. pair 4.1 or 4.3 + sports series (06, 07 or 08): dynamics (fast acceleration due to the main pair) + long gears, mainly 1st and 2nd are spun to the maximum.
Ch. pairs 4.5 and 4.7: gears are even shorter than 4.1 and 4.3 (maximum speed at 5 thousand tachometer revolutions 140 km/h), recommended use: when towing and transporting heavy trailers.
Ch. pairs 4.9, 5.1, 5.3 and 5.07: used only on steep slopes and climbs (maximum speed 110-120 km/h)
Rows: 011, 012, 018 - installed with standard ch. a pair of 3.9 for forced engines 1.7, 1.8 and 2.0l.
Did you like the material? Share the link with your friends.
Source
Gearbox torque
Features of installing the camshaft on the engine 2108, 21081, 21083 of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Output shaft torque – torque on the output shaft. The rated power, safety factor, estimated service life (10 thousand hours), and gearbox efficiency are taken into account.
Rated torque is the maximum torque that ensures safe transmission. Its value is calculated taking into account the safety factor - 1 and the service life - 10 thousand hours.
Maximum torque – the maximum torque that the gearbox can withstand under constant or changing loads, operation with frequent starts/stops. This value can be interpreted as the instantaneous peak load in the operating mode of the equipment.
Required torque – torque that meets customer criteria. Its value is less than or equal to the rated torque.
Design torque – the value required to select a gearbox. The estimated value is calculated using the following formula:
Mc2 = Mr2 x Sf ≤ Mn2
where Mr2 is the required torque; Sf – service factor (operational coefficient); Mn2 – rated torque.
Gear ratios tuning VAZ gearbox rows
Table of gear ratios of gearbox rows. A very useful thing, and very complete, share with friends, it will be useful to almost everyone who is interested in modifying cars!
You can read about how easy it is to choose a row on my channel and in the VK group.
The gear
ratios
of the gearbox rows are front-wheel drive. Standard (I - 3.63; II - 1.95; III - 1.35; IV - 0.94; V - 0.78; VI - 0.69) CAT RANGE 05 (I - 2.92; II - 1.81; III - 1.27; IV - 0.96; V - 0.78; VI - 0.69) GEARBOX RANGE 06 (I - 2.92; II - 1.81; III - 1.27; IV - 1.06; V - 0.94; VI - 0.78) GEARBOX RANGE 07 (I - 2.92; II — 2.05; III — 1.56; IV — 1.31; V — 1.13; VI — 0.94) Gearbox RANGE 08 (I — 3.42; II — 2.11; III — 1.35; IV — 0.96; V — 0.78; VI — 0.69) Gearbox RANGE 011 (I — 3.64; II — 2.22; III — 1.54; IV — 1.17; V — 0.87; VI — 0.78) Gearbox RANGE 012 (I — 3.17; II — 1.95; III — 1.35; IV — 1.03; V — 0.78; VI - 0.69) CAT RANGE 015 (I - 3.17; II - 1.81; III - 1.27; IV - 0.94; V - 0.73) CAT RANGE 018 (I - 3.17; II - 2.11; III - 1.48; IV - 1.13; V - 0.88; VI - 0.78) CAT RANGE 020 (I - 3.17; II - 1.90; III - 1.26; IV - 0.94; V - 0, 73) Gearbox ROW 026 (I - 3.41; II - 2.53; III - 2.05; IV - 1.73; V - 1.47; VI - 1.26) Gearbox ROW 074 (I - 2, 67; II - 1.93; III - 1.58; IV - 1.37) CAT RANGE 102 (I - 3.17; II - 1.95; III - 1.35; IV - 0.94; V - 0.73) CAT RANGE 103 (I - 2.92; II - 1.95; III - 1.35; IV - 0.94; V - 0.69) Gearbox ROW 104 (I - 2.92; II - 1.95; III - 1.35; IV - 1.03; V - 0.73) Gearbox ROW 111 (I - 3.17; II - 2.22; III - 1.53; IV - 1.16; V - 0.88) Gearbox ROW 112 (I - 3.17; II - 2.05; III - 1.35; IV - 1.03; V - 0.78) Gearbox ROW 200 ( I - 2.92; II - 2.22; III - 1.76; IV - 1.39; V - 1.17) CAT RANGE 719 (I - 2.66; II - 1.93; III - 1, 58; IV - 1.31; V - 1.14; VI - 0.9) Gearbox RANGE 745 (I - 2.66; II - 1.93; III - 1.56; IV - 1.36; V - 1.20) Gearbox ROW 777 (I - 2.91; II - 2.00; III - 1.58; IV - 1.31; V - 1.14; VI - 0.9) Gearbox ROW 779 (I - 2.81; II - 2.18; III - 1.78; IV - 1.50; V - 1.29; VI - 1.12)
Ivanov M.N. Machine parts. Textbook. M.: Higher school, 1984, 336 p.
2. Tkachenko V.A. Design of multi-satellite planetary gears. Kh., KhSU, 1961, 132 p.
3. Poletuchy A.I. Wave gear transmissions. Kharkov, KhAI, 1979, 106 p.
4. Calculations and design of gears. Artemenko N.P., Voloshin Yu.I., Efoyan A.S., Rydchenko V.M. - Kharkov: KhAI, 1980.- 113 p.
5. Anuriev V.I. Handbook of mechanical engineering designer. In 3 volumes. M.: Mechanical Engineering, 1979.
6. Dunaev P.F., Lelikov O.P. Machine parts. Course design. – 3rd edition, revised. and additional – M.: Mechanical Engineering, 2002.-536 p., ill.
7. Bezruchko K.V., Gaidukov V.F., Gubin S.V., Dranovsky V.I., Karpov Y.S., Turkin I.B.. Solar batteries of automatic spacecraft. - Kharkov: National Aerospace University 'KhAI', 2001.-276 p.
8. Reshetov D.N. Machine parts: Textbook for students of mechanical engineering and mechanical specialties of universities.-4th ed., revised. and additional - M.: Mashinostroenie, 1989. - 496 p.: ill.
VAZ 2108 gearbox row table
RANGE Gearbox 05 (KPP 2108) (I - 2.92; II - 1.81; III - 1.27; IV - 0.96; V - 0.78; VI - 0.69)
Requires 1 washer 2 mm for 4th gear
Belongs to the category of sports rows. 4 gears changed. 1st, 2nd and 3rd gears are lengthened (as in 6th), 4th gear is shortened (as in 8th by 5%), 5th is standard. Usually GP 4.1 is installed. On forced engines - with GP 3.7, 3.9.
RANGE Gearbox 06 (KPP 2108) (I - 2.92; II - 1.81; III - 1.27; IV - 1.06; V - 0.94; VI - 0.78)
Requires 1 washer 2 mm for 4th gear
Sports row. Classic installation - with 6th gear and 4.1 (4.3) gearbox. 1st, 2nd and 3rd gears are lengthened (1st significantly), 4th and 5th are shortened. 5th gear of the 6th row is 4th from the standard row.
RANGE Gearbox 07 (KPP 2108) (I — 2.92; II — 2.05; III — 1.56; IV — 1.31; V — 1.13; VI — 0.94)
Requires 1 washer 2 mm for 4th gear and 1 for 5th gear
Very short - sports (rally, motocross) series. Without 6th gear, it is impossible to achieve a high maximum speed. With 3.7 GP in 5th gear at 5000 rpm. – 128 km/h. When installed with GP 4.1, 4.23 can be used, for example, for short distance competitions such as drag racing.
RANGE Gearbox 08 (KPP 2108) (I — 3.42; II — 2.11; III — 1.35; IV — 0.96; V — 0.78; VI — 0.69)
It is also called “commercial”, since for many years it was the most popular and best-selling product. However, it remains relevant today. 1st gear extended, 2nd and 4th shortened. All changes are minimal (5%), but this is quite enough to correct the shortcomings of the standard series. Most often installed with GPU 4.1. Inexpensive, which is nice. Provides improved acceleration dynamics.
RANGE Gearbox 011 (KPP 2108) (I — 3.64; II — 2.22; III — 1.54; IV — 1.17; V — 0.87; VI — 0.78)
Requires 1 washer 2 mm for 4th gear
Came from motorsport, where it is installed mainly with 6th gear and 4.1,4.3 GP. In custom versions it is usually installed with GPU 3.7, 3.9. 4 gears changed. At the same time, 1st is the standard, the rest are similar. An excellent option for those who do not want to extend the 1st speed. Smooth, dynamic acceleration.
RANGE Gearbox 012 (KPP 2108) (I — 3.17; II — 1.95; III — 1.35; IV — 1.03; V — 0.78; VI — 0.69)
The most maintainable (like the 103rd) row, because 1st (longer by 12.91%) and 4th (shorter by 10%) gears have been changed; 2nd, which, according to statistics, most often fails, is standard. Installed with almost any GPU. When installed with NP 4.1, the gear ratios are similar to the 11th row with GP 3.7.
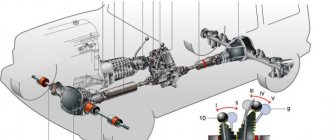
Mechanical gears
See also: Mechanical transmission
The gear ratio
of any mechanical
transmission (gear, chain, belt, wave, worm and others) is the ratio of the angular frequencies of rotation of the input and output shafts.
Thus, at a value above 1, the mechanical transmission is a reduction gear (reducer), and below 1, a step-up transmission (multiplier). The most common is the use of reduction gears, since engines usually have a higher rotation speed than the devices they drive. i12=ω1ω2{\displaystyle i_{12}={\frac {\omega _{1}}{\omega _{2}}}}
The gear ratio of mechanical gears can be constant or variable
, and in the second case it can change stepwise (change of gear pairs in machine tool gearboxes, car gearboxes, bicycle sprockets) or steplessly (V-belt variator, torque converter). Belt and hydromechanical transmissions have slippage during operation, and the gear ratio can vary depending on the transmitted torque. In mechanical transmissions, the gear ratio has a sign, and it is positive if the direction of rotation does not change. However, if the direction of rotation does not matter, the sign is omitted.
Torque ratio
mechanical transmission rotation
is equal to the ratio of the moments on the output and input shafts
.
i12=M2M1{\displaystyle i_{12}={\frac {M_{2}}{M_{1}}}},
where M1,M2{\displaystyle M_{1},M_{2}} are the input torques and output shafts. There is a difference between the gear ratios in terms of angular velocities and torques, since gears usually have an efficiency different from unity. As a result, the torque of the shafts and angular velocities will be related by the following relationship:
ω1ω2∗ηM=M2M1{\displaystyle {\frac {\omega _{1}}{\omega _{2}}}*\eta _{M}={\frac {M_{2}}{M_{1} }}},
where ηM{\displaystyle \eta _{M}} is the mechanical efficiency of the transmission.
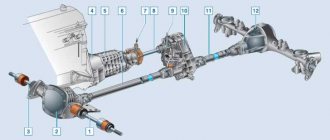
Technical characteristics of the VAZ 2108 gearbox
| R wheels |
| Wheel width |
| Profile |
| Engine speed |
| Main couple |
| 1st gear |
| 2nd gear |
| 3rd gear |
| 4th gear |
| 5th gear |
| 6th gear |
| Results: |
| Type | Mechanics |
| Number of gears | 4 |
| For drive | front |
| Engine capacity | up to 1.3 liters |
| Torque | up to 100 Nm |
| What kind of oil to pour | Gazpromneft GL-4 80W-85 |
| Lubricant volume | 3.0 liters |
| Change of oil | once every 65,000 km |
| Replacing the filter | every 65,000 km |
| Approximate resource | 170,000 km |
Classification by number of stages and type of transmission
| Gearbox type | Number of steps | Transmission type | Axes location |
| Cylindrical | 1 | One or more cylindrical | Parallel |
| 2 | Parallel/coaxial | ||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | Parallel | ||
| Conical | 1 | Conical | Intersecting |
| Conical-cylindrical | 2 | Conical Cylindrical (one or more) | Intersecting/Crossing |
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| Worm | 1 | Worm (one or two) | Crossbreeding |
| 2 | Parallel | ||
| Cylindrical-worm or worm-cylindrical | 2 | Cylindrical (one or two) Worm (one) | Crossbreeding |
| 3 | |||
| Planetary | 1 | Two central gears and satellites (for each stage) | Coaxial |
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| Cylindrical-planetary | 2 | Cylindrical (one or more) Planetary (one or more) | Parallel/coaxial |
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| Cone-planetary | 2 | Conical (single) Planetary (one or more) | Intersecting |
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| Worm-planetary | 2 | Worm (one) Planetary (one or more) | Crossbreeding |
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| Wave | 1 | Wave (one) | Coaxial |
Gearbox torque
Output shaft torque – torque on the output shaft. The rated power, safety factor, estimated service life (10 thousand hours), and gearbox efficiency are taken into account.
Rated torque is the maximum torque that ensures safe transmission. Its value is calculated taking into account the safety factor - 1 and the service life - 10 thousand hours.
Maximum torque – the maximum torque that the gearbox can withstand under constant or changing loads, operation with frequent starts/stops. This value can be interpreted as the instantaneous peak load in the operating mode of the equipment.
Required torque – torque that meets customer criteria. Its value is less than or equal to the rated torque.
Design torque – the value required to select a gearbox. The estimated value is calculated using the following formula:
Mc2 = Mr2 x Sf ≤ Mn2
where Mr2 is the required torque; Sf – service factor (operational coefficient); Mn2 – rated torque.
What power units were used on the VAZ-2109
This car’s own engine model, marked “2109,” never existed; power units were installed instead:
Initially, the VAZ-2109 received units 21081 and 2108, which were installed on it from 1987 to 1997. They were based on a carburetor that supplied fuel. These power plants were replaced due to a malfunction that was unpleasant for many car enthusiasts - when the timing belt broke, the valve covers were bent.
Model 21083 was also equipped with a carburetor; “nines” are most often found with it. This engine model was developed back in 1987, and began to be installed only in the nineties.
This version of the engine is a modified 2108. The main difference of the power unit is that if the timing belt breaks, the valve pistons do not bend.
Injection engine modifications were initially intended only for export. They were developed on the basis of the 21083 engine. The first version was 2111-80, which subsequently underwent a deep modernization in order to increase its power. The converted version was released under the marking 11183-20. Since 1998, cars with these engines began to be sold on the domestic market.
Manual transmission calculation - DRIVE2
Tire calculator with 3D visualization online
Hi all. After writing an article on calculating a diesel transmission for my car, I receive a bunch of personal letters asking me to also calculate manual transmissions of other designations. In general, it’s not difficult for me, but it takes time, and you don’t always have time. In my article, everything seems to be clear and transparent, but no one wants to delve into it themselves. Therefore, in this article I will try to show how to make such a calculation yourself as quickly and simply as possible, using a special TABLE.
manual transmission calculation
You only need to enter data in the green field, the rest will be calculated automatically. It’s clear that you can’t do without the ETKA catalog data, so we’ll assume that it exists and is installed. For example, I will take the calculation of a 5-speed. Manual transmission EHV, which was installed on the 1.8T. First, we look for the data of the main pair of our box:
Full size
EHV 37/10
There we see the value “37/10”, and enter it into the table in the line “main pair”. Next, we look for the values for each gear of our EHV box
Full size
EHV
and similarly enter into the table according to the transfer, we get the following calculation:
EHV calculation
Next, go to THIS site to calculate the speed in different gears, and enter the values from the red column of our table on the site:
The table shows the speed in km/h at different speeds. If this data is not enough, then you can study the orange “Total” column
This column shows the total gear ratio for each gear of a particular gearbox. This will help you understand which box is generally longer or shorter. We compare these values of two different boxes, the smaller, the longer. That's all the calculations, it seems clear. If you have any comments or additions, I will be happy to add them to the article.
www.drive2.ru
Disadvantages, breakdowns and problems of the Lada Samara box
The reliability of the manual transmission is weak, the transmission is famous for unclear shifts and howling
Gears switch off spontaneously due to wear of the locks on the couplings and gears
The box hums most often due to a lack of lubrication or when the bearings are damaged.
A strong crunch when switching hints at a quick replacement of synchronizers
The weak point of the gearbox is the rocker; it often requires repair or replacement
Another common problem is oil leaks from different seals.
You can contact the site administrator by email: [email protected]
All texts were written by me, are authored by Google, included in the original Yandex texts and notarized. For any borrowing, we immediately write an official letter on company letterhead in support of search networks, your hosting and domain registrar.
Weight and dimensions
Finally, about the load-bearing part. The Eight had a three-door hatchback body. Afterwards, the 5-door hatchback VAZ-2109 and the sedan VAZ-21099 were released on its basis.
The dimensions of the VAZ-2108 were: length - 4.006 m, width -1.75 (including one side mirror), height - 1.402 m. Ground clearance - 170 mm.
The curb weight of the car is 920 kg, and when fully loaded, the Eight weighs more - 1370 kg.
Despite the fact that the model has not been produced for a long time, it still remains popular and is in demand. Moreover, this car is an excellent field for experiments to improve its appearance and technical characteristics.
Calculation of maximum vehicle speed
Calculation of depreciation according to compulsory motor insurance yourself and using an online calculator
Hello friends! I haven’t written anything on my blog for over a year, but today something went wrong. I wandered into the wrong place, read in the wrong place, and inspiration came, the desire to move forward.
This will not be an information post as usual, but a kind of manual, a calculator, which, depending on the specified tire sizes, engine speed and the specified gear ratios, will calculate what the car's speed will be in gear.
Of course, the car speed calculator based on gear ratios and tires makes calculations under ideal (laboratory) conditions. In real conditions, the final speed of the car is influenced by many factors, ranging from climatic conditions and the state of the road surface, and ending with engine tuning. In other words, the calculator shows the potential of the gearbox, to what maximum speed it can accelerate the car.
Posts 1 page 12 of 12
Share January 114, 2011 23:27:56
Link: https://4×4.lviv.ua/?calculator=tuning Moderators, please correct me if I inserted the link incorrectly, I just didn’t understand how to do it. Thank you.
Share January 215, 2011 09:20:50
Mikha150 Thank you, the link is good, there is one thing - it is not suitable for a tractor with only rear-wheel drive (or only front-wheel drive).
Share January 315, 2011 09:55:04
I also downloaded and looked. I'm not good at programming, but I think you can change the parameters and do it for one bridge. Or contact the authors so that they themselves change it so that there are no violations
Share4 January 15, 2011 20:29:56
Everything fits, I considered all-wheel drive on it. It’s very convenient, especially all-wheel drive with different wheel diameters, in the left column you fill in the data on tire sizes and the GP gear selection method. Example: in the right column, tires in mm 20575R16 and UAZ GP value 5.125 in the left column 16580R12 we select The GP of the front axle from a standard VAZ turned out to be 4.1, while in the speed column before and after tuning I got the same values. It’s also convenient to select the speed. in general, everything is clear there; one thing is not convenient, because in most cases you have to set the gearbox to 2 gearboxes, the gear ratios have to be summed up on a calculator or using a pencil and paper, but that’s what you like.
Edited by Mikha150 (January 15, 2011 20:39:32)
Engine dismantling
You can reduce the weight of the power plant if you remove it without:
- Gearbox (its weight is about 30 kilograms);
- a head weighing approximately 10 kilograms.
As a rule, at service stations, power units are removed assembled with the gearbox, while during self-repair, dismantling is carried out without attachments.
Let's give an example of engine dismantling, which is described in the car's operating instructions. The peculiarity of the work in this case is that the engine is removed through the bottom of the car. The manufacturer recommends not to disconnect the box from it, but to install the car itself on a lift.
- Disconnect the terminals and then remove the battery.
- Drain the coolant and engine oil.
- Remove the crankcase protection.
- Disconnect the muffler and remove the air filter.
- Loosen the brake booster hose clamp that leads to the powertrain inlet pipe.
- Unhook the ground from the crankcase; to do this you will need to unscrew the fasteners.
- Remove the high-voltage wire from the central contact of the distributor cover.
- Using a screwdriver, turn the spring clip and remove the block with the wires coming from the contact socket of the distributor.
- Remove the fuel hose.
- Remove the clutch cable end from the clutch drive lever.
- Disconnect the wires from the traction relay, from the generator output and from the carburetor shut-off valve.
- Disconnect the air supply hoses to the throttle and the fuel hoses leading to the carburetor.
- Remove the spring from the throttle actuator.
- Remove the speedometer and accelerator drive cables from the valve covers.
- Unhook the block with the wire from the economizer, remove the oil pressure and liquid temperature sensors in the cooling system.
- Remove the heater outlet hose and transmission drive rod.
- Next, you will need to disconnect the remaining conductors from the box and move the drive shafts to the side.
- After the steering rod and other parts are disconnected, place a stand under the engine and unscrew the nuts of the rear mounting support, then the right front and left.