Trouble code P0123 indicates a problem with the throttle/pedal position sensor. When the engine control module (ECM) detects that the rated output voltage of the throttle position sensor exceeds the manufacturer's specification, it generates trouble code P0123.
The throttle position sensor (TPS) is another name for a potentiometer. It is located on the throttle body while the pedal position sensor is connected to the accelerator pedal.
The throttle position sensor monitors the movement of the accelerator pedal and determines how much power the engine requires. Code P0123 is triggered when the TPS voltage value is outside the specified range.
What does it mean?
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic transmission code, which means it applies to OBD-II equipped vehicles. Although general, specific repair steps may vary depending on the make/model.
The TPS (Throttle Position Sensor) is a potentiometer mounted on the throttle body. It determines the throttle angle. When the throttle body moves, the TPS sends a signal to the PCM (powertrain control module), which is the main computer that controls the vehicle. Typically a three wire sensor: 5V reference from PCM to TPS, ground from PCM to TPS, and signal return from TPS to PCM.
The TPS sends throttle position information back to the PCM via this signal wire. When the throttle is closed, the signal is about 45 volts. At WOT (Wide Open Throttle), the TPS signal voltage approaches the full 5 volts. When the PCM sees voltage above the normal upper limit, P0123 is set.
Why do you need a damper with a sensor and how does it work?
In injection cars, the air and fuel supply is controlled using an electronic unit, into which information from numerous sensors and systems flows. Thus, the angle of the damper is controlled by its position sensor. The choice of the deflection angle is necessary for the formation of an optimal air-fuel mixture and normal engine operation (without jerking and loss of power). Throttle valves on older cars were driven by a cable that was connected to the accelerator pedal. Modern dampers are deflected using a drive motor.
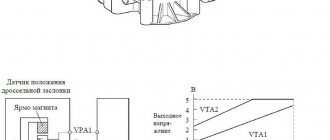
Please note that some remote sensing devices have not one, but two sensors. Accordingly, they will have more possible errors. There are two types of sensors - contact, they are also called potentiometers or film-resistive and non-contact, another definition is magnetoresistive.
Regardless of the type of TPS, they perform the same function - they transmit information about the damper deflection angle to the electronic control unit. In practice, this is realized by converting the damper deflection angle into a constant voltage value, which is a signal to the ECU. When the throttle is completely closed (idling), the voltage is at least 0.7 Volts (may vary for different cars), and when fully open - 4 Volts (may also differ). The sensors have three terminals - positive (connected to the car battery), negative (connected to ground) and signal, through which variable voltage is transmitted to the computer.
Possible solutions
A good starting point is always to check the technical service bulletins (TSB) for your specific vehicle. Your problem may be a known problem with a known fix released by the manufacturer and could save you time and money during diagnosis.