Exceeded leakage current in a car will cause the battery to discharge while parked. The causes and verification of leakage should be dealt with separately. At the initial stage, the main thing is to understand what permissible leakage and how many milliamps are the norm for a particular car, since losses will depend on the number and name of energy consumption sources. Online calculator, using the formula - Battery capacity (A) * number k, will help you quickly calculate the permissible leakage current.
Current leakage should be checked as often as possible, especially in wet weather!
What is leakage current and how does it happen?
Let's start with a specific example. Let's say we have a battery, a light bulb and a switch. Let's assemble a simple electrical circuit from all this, so that the light bulb can be controlled using a switch. Now consider two situations - in one the light bulb will be on, and in the other it will be off.
When the light bulb is turned on, an electric current naturally flows through the circuit. Question: can this current be called leakage current? Don't rush to answer. In fact, not everything is as simple as it seems. On the one hand, there is no leakage in this situation, since the current flowing through the circuit seems to be used to perform useful work. What kind of leakage is there if the current flows profitably?
Nevertheless, there is always a current leak in this case. That is, not all the energy that is taken from the battery is spent on useful work. And this is exactly what is not spent on useful work - this is, in essence, a leak. Leakage current. Where is she? Where does the current flow without use? And current leakage in this case occurs in the wires that connect the circuit elements. Since they have some resistance, part of the current flowing through them is wasted on heating them. This is, in principle, also work. But for us it is not useful (and even harmful).
The second situation is when the light bulb is turned off using the switch. Is it possible to detect leakage current in this situation? Of course not, if the system is working properly. What if the switch is faulty? For example, salt water got into it, and even in the off position it does not completely break the circuit. The light bulb may glow with a weak glow or not glow at all, but the battery will waste energy. In such a situation, we are dealing with a real leakage current. Under the conditions described, it flows in our circuit.
Now let's complicate things a little. Instead of a light bulb, let's connect some electronics to our circuit that operate in two modes - main and standby. In a car, such a device is, for example, a radio. When we turn off a consumer of this kind, it goes into the so-called sleep or standby mode. In this mode, the device consumes energy from the battery, that is, current flows in our circuit.
Now the question is: is this leakage current? On the one hand, it seems, yes. Indeed, in the case of a radio tape recorder, we are not listening to music at this moment, which means that work useful to us is not being performed. On the other hand, the current, which many call leakage, is spent by the radio on not so useless work - storing settings, clock movements, and so on.
So what then is leakage current in a car? And this is the current that flows in the circuit, but is not spent on doing useful work.
In the case of household electrical networks, the boundary in this matter is clearer. In properly organized systems, there is even a special automatic circuit breaker that, in the event of a current leak, completely cuts off the power supply.
However, when considering the issue of current leakage in machines, the line is not so clear. In the case of cars, leakage current is generally considered to be any current that is drained from the battery while parked. And this despite the fact that not all energy is wasted in this mode.
Leakage from battery when ignition is off
If the ignition is turned off, the engine does not work and the battery does not recharge. All energy accumulated during movement is spent on powering consumers - heating windows, operating the media center, lighting. The more consumers that are not turned off, the faster the battery discharges. Therefore, all devices must be turned off during long periods of inactivity.
However, if the circuit of a TV, sound system, or air conditioner is incorrectly assembled, there may be a leakage current. Often the mistake that leads to a drop in battery voltage is putting these devices into sleep mode rather than turning them off completely. Checking for leaks with a multimeter will reveal the problem.
Oxidized wiring contacts lead to the occurrence of parasitic currents. The reason is resistance, which contributes to heating of the wires. In this case, stray currents are not the main thing - you can get a fire. Worn electrical wiring with twists and poor insulation has the same consequences.
However, the battery itself loses capacity over time and the rate of self-discharge increases. If there is no large current leakage, but the battery is discharged, then you need to check its suitability.
How to check current leakage in a car
Checking the total current leakage along the 12 V line of the car is very simple: you need to turn on the multimeter in ammeter mode in the gap between the battery and the rest of the car's network. In this case, the engine must be turned off and no manipulations with the ignition must be performed. Huge starting currents of the starter will definitely lead to damage to the multimeter and burns.
It is important! Before starting to work with a multimeter, it is recommended that you read the training article on working with the device.
Let's look at the process in more detail:
- Turn off the ignition and all additional consumers.
- We get to the battery and, using a suitable wrench, unscrew its negative terminal.
- Set the multimeter to DC ammeter mode. We set the maximum measurement limit. On most typical meters this is either 10 or 20 A. We connect the probes to the appropriately marked sockets. Please note that in ammeter mode the resistance of the “tester” is zero, so if you touch the two battery terminals with the probes out of habit, you will get a short circuit.
To measure leakage current, you must turn the multimeter into DC measurement mode
It is important! Do not use a jack marked “FUSED”. This multimeter input is protected by a fuse, usually 200 or 500 mA. The leakage current is unknown to us in advance and can be much greater, which will lead to failure of the fuse. The inscription “UNFUSED” indicates that there is no fuse in this line.
- Now we connect the probes into the gap: black to the minus on the battery, red to ground. For some older meters, polarity may be important, but on a digital meter it doesn't matter.
- We look at the instrument readings. In the picture above we can see a result of 70 mA, which is quite normal. But here it’s worth thinking about, 230 mA is a lot.
If all electronic equipment is truly turned off, then a current value of 230 mA indicates serious problems
An important subtlety: after closing the on-board circuit with a multimeter, in the first couple of minutes the leakage current can be quite large. This is explained by the fact that de-energized devices have just received power and have not yet entered energy saving mode.
Hold the probes firmly on the contacts and wait up to five minutes (you can use alligator clip probes to ensure a reliable connection for such a long time). Most likely, the current will gradually drop. If high values remain, there is definitely a problem with the electrical equipment.
Normal leakage current values vary for different vehicles. Approximately this is 20-70 mA, but for older cars they can be significantly higher, as well as for domestically produced cars. Modern foreign cars can generally consume only a few milliamps when parked. It's best to use the Internet and find out what values are acceptable for your model.
What should you keep in mind?
When carrying out preventive maintenance on the battery, we recommend checking the leakage current of the car battery. On a modern car, the norm is a value of 15─75 mA with the on-board network consumers turned off.
If the leakage current value significantly exceeds the norm, then at a minimum you should consult an automobile electrician. If you have a tester and the skills to handle it, then you can find the problematic device or faulty wiring yourself. We also recommend reading about how to check battery capacity. In any case, leakage current exceeding the norm cannot be ignored. After all, this can end not just with a dead battery, but also with a fire in worn-out wiring. Be careful and good luck on the roads! If you have additions or feedback to the article, write them in the comments below.
What leakage current is normal?
In any car there is a minimum leakage current of the order of 50-80 mA. This indicator depends on many factors. In particular: the condition of the wiring, the age of the battery and the cleanliness of its terminals, as well as air temperature. Self-discharge of the battery in an open circuit is allowed no more than 1% per day, but given that it is constantly connected to the on-board network, this figure can reach up to 4 percent. Thus, the permissible leakage will be equal to the capacity multiplied by a factor of 0.4.
Since, in addition to the permissible leakage of current from the battery in a car, even at rest the following consumers can consume current: alarm and immobilizer (20-25 mA), audio system (3 mA), central locking unit and ECU controller (5 mA each), then The quiescent current will be significantly higher. In total, the provoked leakage current rate is considered to be 50-70 mA, and the maximum permissible value is 80-90 mA.
Increased current can occur due to: rotten old wiring (in most cases), a short circuit in the circuit through oxides, damaged wire insulation and an incorrectly connected alarm or radio. Although a small current consumption by the alarm is acceptable, since it is an active device and requires power to the radio module, volume/shock sensors and LED.
Our online calculator will help you calculate the leakage current depending on the self-discharge of the battery (for a new battery the rate of loss is 0.5–1.0% and for a used battery 1–1.7%) and the number of consumers who consume energy even in standby mode normal (natural) leakage of quiescent current from a car battery.
Calculator for calculating leakage current in a car
Excessive leakage current in the car will cause the battery to discharge while parked. The causes and verification of leakage should be dealt with separately. At the initial stage, the main thing is to understand what permissible leakage and how many milliamps are the norm for a particular car, since losses will depend on the number and name of energy consumption sources. An online calculator, using the formula - Battery capacity (A) * number k, will help you quickly calculate the permissible leakage current.
Current leakage should be checked as often as possible, especially in wet weather!
FAQ
What is the normal leakage current in a car?
There is a current leak in almost every car, and the rate will depend on the amount of additionally installed electronics, which can consume energy even in standby mode, as well as the power supply characteristics of the on-board network. Therefore 0.05 Ampere
– this is the norm for a modern car. And in some cases, even 70 mA is also acceptable.
What is the leakage current through the alarm?
In operating mode, the security device consumes up to 200 mA of current, depending on its complexity, the number of sensors and the connection method. current through the alarm – 20-30 mA
this is normal, the main thing is that consumption decreases to this level 5-10 minutes after turning it on. The problem areas are considered to be the limit switches of the hood and trunk doors, as well as the communication module (oxides appear on the board).
What is the leakage current through the radio?
On a car with a properly connected 1 din radio, the leakage does not exceed 0.01A
or
0.02A
if it is 2 din. The main problem is connecting the power wire (red) and the wire responsible for saving the settings (yellow in one twist) and directly to the battery. Only the yellow “memory” wire should receive constant power. Also, the leakage current through the radio, as in the case of the alarm system, when the ignition is completely turned off, should decrease after 10 minutes of rest.How to measure leakage current?
You can measure the leakage current with a multimeter or a current clamp (allows you to measure the leakage current without contact) by first setting the car alarm and waiting 10-15 minutes since there are ECUs that do not go into sleep mode immediately.
To measure leakage current with a multimeter
It is necessary to connect in series to the power supply circuit of the on-board network, before the negative terminal on the battery. First, you need to set the DC current measurement mode to 10A when the tester is turned on. Then, having removed the negative terminal from the negative terminal on the battery, connect one of its probes to the negative terminal of the car, and the second (red) to the negative terminal of the battery. Current leakage will be displayed on the dial.
When measuring leakage current with clamps
On the device you need to set the DC current measurement, and the measured conductor, maybe the entire twist going to the negative terminal of the battery, or from individual consumers, is placed in the ring of pliers after turning off the ignition completely. On the display you can immediately see the current consumption of the car’s electronics at rest.
Causes of leakage
Leaks occur for two main reasons: unplanned operation of car equipment, short circuits of positive contacts to ground. The vehicle equipment may remain switched on if:
- this is provided by the manufacturer (for example, the alarm and some other security systems are always on);
- mistakes were made when installing additional devices;
- individual components or parts of electrical equipment are faulty;
- the driver forgot to turn off the lights, heating or other systems;
- electrical equipment was turned on by third parties (often children who like to play with buttons).
Short circuits can occur due to wear of insulation, breakdowns of some mechanical parts of electrical equipment, and errors when connecting new devices to the system. In addition to very rapid discharge, short circuits create a fire hazard, which requires immediate localization and elimination of such faults.
Battery self-discharge
A leak is both the cause and consequence of battery self-discharge - the process can be like:
- Provoked self-discharge. Caused by current loss due to a short circuit, incorrect connection of equipment or its malfunction.
- Operational. It is caused by an external short circuit of the battery terminals through layers of contaminants on the case (dust, dirt, technical fluids).
- Electrolytic. It is caused by an internal short circuit of the battery terminals through the products of chemical reactions that have settled to the bottom (“sludge” - particles of oxidized lead).
- Natural. Degradation of battery plates and electrolyte during prolonged inactivity or during operation.
The critical value of self-discharge is the loss of more than 2.5% of capacity per day of inactivity. Normally, the battery should lose no more than 0.5-1% during this period.
Through the radio
Electrical leakage through the radio usually does not occur due to a malfunction of the tape recorder itself (although sometimes this also happens), but due to a malfunction of the wiring connected to the device. In this case, the appearance of wiring defects can occur both for natural reasons and due to violation of the rules for connecting the tape recorder.
Car alarm
The car security device must operate when all other units are resting. Alarms are also often the cause of this phenomenon. Even in normal condition, it can consume up to 200 milliamps of current, this is also included in the leak.
Good alarm systems with feedback have a transceiver that can periodically communicate with the key fob, there are geopositioning systems, GSM, etc. Now manufacturers of car alarms (for example, PANDORA) aim to minimize the current consumption of car alarms in security mode. There are models where this current is less than 20 milliamps.
Starter
A working starter does not consume current while parked, although it is also constantly supplied with supply voltage.
Leakage currents associated with humidity, contact contamination
In real operating conditions of a car, especially in the cold season, moisture with various impurities gets on current-carrying conductors, contacts, and connectors. Electrolysis currents appear.
The presence of this parasitic process is evidenced by a greenish and white coating on the contacts, wires, terminals, connectors, in a word, where salt, acid, alkali and moisture have reached.
Electrolysis is not possible without current. Sometimes leakage currents for this reason reach 0.5 Amperes (500 milliamps) or more. If the electrical wiring is well maintained and treated with special compounds, then the leakage for this reason usually does not exceed 5 milliamps.
Mounting block
If all fuses are checked, but the tester still detects a current leak, the cause is in an area not protected by fuses: the generator, starter or ignition system. To do this, you need to disconnect the wires from these systems and carry out a thorough check. Also, do not forget that the car can be equipped with self-installed devices that are connected to the ignition switch circuit without using fuses.
Next, you need to check all the wiring: if a suspicious part of it is discovered, you need to “ring” the wires for integrity and look for a short circuit. These actions must be performed using the same multimeter, only set to a different mode - an ohmmeter. This mode will allow you to observe the wire resistance.
Check the generator. To do this, you need to set the multimeter to voltmeter mode, connecting it in parallel with the devices. Voltage measurements should only be made when the engine is running and the sidelights and headlights are on. Normally, the voltage is 13.5–14 V.
ABS, body control, climate control and other units
The total consumption of these units (serviceable) is no more than 10 milliamps.
High battery leakage current - problems
A large leakage current, at which it is imperative to find the problem point, is considered to be 0.5 A. A loss of half an ampere in ten hours will absorb 5 A/h, and a car left for 4 days will be discharged to zero. Therefore, when parked for a long time, the car is left with an open circuit.
If there is a problem unit in the car in which a leakage current is created, heating will definitely begin in the transistor or microcircuit. The block will fail. If current leaks through the conductor, a fire will not occur, but the insulation may be damaged. This will lead to a short circuit, intense heating at the contact point and a fire.
How to find current leakage on a battery without a device? In the dark, stop the car, open the hood, close the door, but do not activate the security system. Remove the wire from the positive terminal and wait 5 minutes. Reconnect the battery terminal. If there is a strong spark, there is a leak. A small spark is a natural process. Next, you should measure the indicators and determine the problem area.
An absolutely accurate sign of current leakage without measurement - after a week of parking, a fresh battery is completely discharged.
How does discharge affect the battery?
If now many people thought - “Whatever, morning discharges don’t scare me, I’ll charge my battery and continue riding! Well, if it runs out of charge, what’s the big deal?”
But there is a terrible thing - this is called a deep discharge of the battery; even a new battery will simply fail after several such discharges. This is because ordinary acid batteries have an electrolyte made of distilled water and sulfuric acid, and when discharged, sulfuric acid settles as salts on the plates, covering the working surface. The salts crystallize so strongly that they no longer dissolve - the operation of the battery will be impaired! The capacity will drop by two to three times and you will no longer be able to start the engine, because the starting current will also decrease.
In general, deep discharges should not be allowed, especially with acid versions of the battery (there are also AGM and GEL technologies, but they are a little different)! This is a kind of axiom.
Now let's start talking about current leakage, for starters, the normal value.
Additional signs
If you don’t have a multimeter at hand, the presence of current leakage can be assessed visually at night. To do this, you need to turn off the ignition and all electrical equipment, open the hood, close the car, without arming the car alarm.
Next, you need to disconnect the positive terminal of the battery and wait about five minutes. After this, you need to connect the battery terminal. If a large spark is generated when the terminal is connected, there is most likely a leak.
Note: there will be a spark in any case, since during the connection of the terminal the emergency lighting and alarm may temporarily turn on.
Such a check can be done if there is a main sign of current leakage: battery discharge after a short stay. It is considered critical if a fairly fresh battery is discharged after one week of parking. It is not always possible to check this, since the car is in constant use.
Video - how to measure leakage current in a car with a multimeter:
Another sign is the presence of extraneous noise, crackling, buzzing, or sparking in the car when the electrical equipment is turned off.
The presence of foreign odors with a taste of smoke when getting into the car in the morning after parking is a serious sign of a malfunction. If there is a large current leak in a car, then, according to the laws of conservation of energy, it can manifest itself in the form of mechanical, thermal or light energy.
Unfortunately, using these methods is almost impossible to find the true cause. You need to use a multimeter. Auto electricians identify the causes and eliminate current leakage in a car as complex repair work.
Reasons for battery drain
During a long period of inactivity, the charge in the unit must be maintained. The battery discharges quickly when a large number of different devices are connected to the network. Often in such situations, the current loss in the machine is much higher than the permissible values.
Among the standard reasons for such problems are:
- Low quality old wiring.
- Incorrect electrical connection.
- Dirty and oxidized contacts.
How to avoid current leaks in a car's electrical network
Car electrical problems are very complex, so it is best to minimize the likelihood of their occurrence. To do this, it is recommended to follow a few simple rules:
Keep cleanliness both in the car itself and in the electrical connections. It is especially important that the terminals and contacts remain clean;
- To minimize the likelihood of oxides occurring on wires and connections, it is recommended to lubricate the chips and connections with grease 1-2 times a year, and it is also recommended to lubricate the battery terminals;
- Install new devices into the vehicle's electrical network only at trusted service centers. If the work is carried out independently, pay attention to the electrical wiring of the car, which can be found in the car operating book;
- If one of the fuses has blown, be sure to diagnose the circuit for which it was responsible. The most common cause of blown fuses is a short circuit in the circuit;
- Keep an eye on the wires. Do not allow them to “dangle” around the cabin or under the hood. Pay attention to sufficient insulation of wires, especially those that touch metal elements of the car body;
- When performing repair work, do not forget about the wires. Make sure that after work they are not pinched or placed on heating elements.
By following these simple rules, you can avoid problems with wiring, the search and solution of which can require a lot of effort and money.
How to measure leakage current with a multimeter?
Multimeter connection diagram for measuring leakage current
To measure current leakage from your car's battery, you will need three things - a multimeter, a 10mm wrench and rubber gloves. The procedure is as follows:
- turn off the car, turn off all electronics in the cabin (all light bulbs in the cabin, trunk, glove compartment, cigarette lighter, radio);
- remove the keys from the ignition, lower the windows (to allow access to the interior without a key);
- close all doors.
- wait 10-15 minutes until all static voltage in the electrical network is reset.
- open the hood and use the key to remove the negative terminal from the battery.
- set the multimeter to current measurement mode and connect one probe to the battery negative, and the second to the terminal, the device should show you a certain value - this will be the battery leakage current.
Important: do not connect the multimeter to the positive with both probes. This may cause a short circuit and blow the multimeter's fuse.
Life hack: how to check current leakage in a car with a multimeter
In the morning, when you tried to start the car, instead of the usual rumbling of the starter, you heard lonely clicks of the solenoid relay and a faint hum of the windings? Or maybe they didn’t hear anything at all? If the starter and battery are working properly, then the cause is current leakage.
Unfortunately, the leak is most often discovered quite late, by which time the residual charge of the battery is no longer enough to start the engine. We invite you to learn more about this problem, how to diagnose and fix it.
How to find and fix a defect
Unfortunately, finding and repairing electrical leaks is not as easy as it seems. There are several difficulties here:
- The only reliable “symptom” indicating the presence of a defect is the rapid discharge of the batteries. However, in the case of a small leak, the battery may discharge quite slowly, which greatly complicates diagnostics.
- It should also be noted that if this defect is present, the car does not always give an electric shock, since the current strength can be quite low (that is, a person will not feel it when touching the car).
- The source of the malfunction can be many network elements - wiring, the battery itself, the generator, and so on. Additional devices connected to the network (for example, an alarm system) can also “take away” the current.
- However, there is no single repair algorithm. After identifying the source of the malfunction, you will have to look for yourself why this device is not working correctly. In some cases this may not be easy to do.
How to test a battery with a multimeter
To diagnose a machine, a small compact device, a multimeter, is usually used. A capacitance meter allows you to determine the parameters of the electric current in a given section of the circuit. Before taking measurements, be sure to turn off power to all electronic equipment (alarm system, tape recorder + hidden equipment in the glove compartment and under the hood).
After this, open the hood and secure it. Do not forget to close the car doors (it is recommended to leave the windows open, since the central locking sometimes works when taking measurements).
Now you can start taking measurements:
- Remove the wire from the negative pole of the battery and place it nearby (you will need it soon). Set the multimeter to “10 amperes”. Using one alligator probe, connect the multimeter to the battery, and using another probe, connect the multimeter to the wire from the battery (do not reverse the polarity).
- Pay attention to the multimeter dial - a number should appear there (this is the strength of the current passing through this section of the circuit). Normally, this number should be in the range from 0.01 to 0.03 - if the indicator deviates greatly from these values, this means that there is a leak in the network (usually this indicates a breakdown of the battery itself or damage to the wiring).
- After testing the system, be sure to check all electronic devices. To do this, connect the devices one at a time to the power supply and measure the current with a multimeter according to the instructions above. If, after connecting a device, the current suddenly increases sharply, this means that this device is operating with a leak.
- Finally, it is also recommended to measure the current on the generator. To do this, set the multimeter to the mode that is used to measure voltage. Then connect the multimeter to the battery, start the car engine, turn on the headlights and heater - normally you should get a value from 12 to 14 volts . Abnormality indicates a leak.
The method of eliminating a leak directly depends on the causes of this defect. For example, in the event of a faulty battery, it is recommended to purchase and install a new battery. If the wiring fails, you need to find the damaged area and repair it.
What does the generator have to do with it?
The generator is responsible for replenishing the battery charge and normally must keep the current at the same level and can itself create problems. Firstly, if there is insufficient power or a technical breakdown, due to insufficient tension of the drive belt, the generator cannot produce the required voltage. Its malfunction affects the stability of the on-board electrical system. Secondly, the excess voltage created by the generator can accelerate the wear and tear of other electrical equipment, including the battery.
If the diode bridge of the generator breaks down and its windings short-circuit, it itself can turn from a source of electricity into a consumer and contributes to even greater leaks and after the battery gives up all its charge, the car will lose its functionality.
Electrical equipment is one of the basic systems of a car, the serviceability and stable operation of which largely determines the convenience and safety of all systems.
Leaks in the on-board electrical system of cars are one of the most common problems. They cannot be ignored, because over time this can lead to serious damage.
Carry out diagnostics of electrical equipment on your car in a timely manner.
The battery died overnight. What to do?
They didn't turn it off!
The simplest causes of current leaks can be caused by the absent-mindedness of the car owner. Roughly speaking, he did not turn off the external lights at night, and the machine, in turn, did not tell him anything.
There are also cars with a bad factory idea - at least remember the heated rear window, the power circuit of which goes past the ignition switch.
And also children! Especially boys. Even in our team, several employees were already unable to leave the dacha at the first call of their wife, after the boys sat in the driver’s seat and turned various knobs, leaving the consumers on.
Connected wrong
In the era of the car music craze, many radios easily drained battery power because the installer didn't bother to connect them correctly. But it was enough to run one power wire through the ignition switch.
The second abnormal thief of electricity is the installed anti-theft device. If everything was fine before installing it, and then problems started, then there is nothing to think about - let a respected installer prove that he is not a camel. To be fair, we note that some security systems actually consume up to a hundred milliamps, but even with this current, nothing will happen to the battery during a night of parking.
Finally, do not forget about the cigarette lighter socket or socket - whoever has what. Not in all cars they are de-energized when the ignition is turned off. Therefore, an accidentally forgotten connected device - a radar detector, recorder, navigator, etc. - can suck current without bringing any benefit.
Is there a leak?
It also happens that there is no leak, but the battery is empty in the morning. This happens when there is a negative charge/discharge balance. If the car is constantly crawling in traffic jams, the mileage is short, you have to turn off and start the engine often, and it’s also cold outside, then the battery simply does not have time to charge to normal. And so one day he refuses. In addition, the same car music with kilowatt output power may be to blame - such musical monsters consume crazy currents. But, we repeat, this has nothing to do with current leaks: these are no longer leaks, but simply excessive consumption.
Dirty Deeds
The cause of a real current leakage may be something that we have a lot of - dirt, therefore. Here the leader is a chain with a thick starter wire, constantly living in unsanitary conditions - salt, water, etc. Almost the same problems can occur with the generator wiring. And not only with the wiring - the generator itself resembles a colander, through which the sand-salt mixture that is sprinkled on the roads is constantly filtered. The surface of the battery is also rarely clean: pendants like to run away along such electrically conductive areas to “nowhere”. Note that worn-out wiring with shoddy insulation can cause not only a leak, but also a fire. However, let's not talk about horror stories.
How to detect a malfunction?
Which cars are more susceptible to the problem?
Vehicles produced by VAZ are more susceptible to disruptions in power supply. The problem does not arise out of nowhere, but against the backdrop of illiterate decisions by developers.
One of them concerns the machine’s power system, which is far from ideally formed. Because of this, even without the engine running, the battery continues to lose excessive amounts of electricity. However, in new Grant-level car models, this omission was eliminated.
Another category of danger includes older foreign cars that house a large amount of electronics. The problem is the same - the lack of an adequate energy consumption system.
Multimeter
As soon as the multimeter reacts with a sharp decrease in current readings, the culprit has been found. The rest is a matter of technique. Of course, after checking the circuit, each fuse should be immediately returned to its place. They have different denominations, and therefore simply replacing one with another is unacceptable.
What if it doesn't work out?
If the fuses run out and the multimeter does not catch anything, then only power circuits remain, not protected by anything. As a rule, these are the starter, generator and ignition system.
Why does the voltage drop?
To know how to increase the voltage in the electrical circuit of a car, you need to understand the reasons:
- Battery malfunction - as practice shows, this is one of the common causes. In order for the battery to replenish its charge after parking, you need to drive the car for about 20 minutes. But if the battery is discharged for certain reasons (for example, due to sulfation of the plates or due to a lack of electrolyte), then this method of replenishing the charge will not help. It is necessary to accurately identify the reason why the battery does not hold a charge and eliminate it - replenish the electrolyte level, and sometimes simply charge it. If you realize that the battery cannot be restored, then it is better to replace it.
- Generator. Incorrect operation of the generator can lead to problems with the on-board network. Before increasing the voltage in the wiring, you need to identify the cause of the malfunction of the generator unit.
- Leakage current. Sometimes it happens that a break in the electrical circuit leads to a current leak. To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to identify the exact location of the leak and eliminate the break.
- Using equipment that is not suitable. If the rating of the electrical appliances used does not match the one set by the manufacturer, this will lead to a voltage drop. If you use powerful lighting lamps or many different gadgets for which the battery is not designed, this will cause a voltage drop. The battery will provide the charge necessary for the normal operation of light bulbs or electronic devices, but it will not have time to be replenished.
Other reasons for battery discharge
What to do if the driver measures the current consumption and it does not exceed the norm? As mentioned above, difficult starting after a long period of parking may not be caused by leakage currents. Some of the most common causes of this problem may include:
- High battery self-discharge.
- Generator malfunction.
Testing the battery for self-discharge
To determine the condition of the battery, you need to remove it from the car and wipe it clean with a rag soaked first in a solution of baking soda, then in water.
If the battery is serviceable, you need to check the density and electrolyte level in each section (there are only 6 of them). The battery is then fully charged by the mains charger to normal voltage (12.7 V without load). We recommend: Getting started with a new car battery
All that remains is to leave the unconnected battery for several days and then measure the voltage at the terminals again. If the voltage loss is more than 0.2 V, then the problem is in the battery. You will have to buy a new battery or try to restore the damaged one, at least temporarily, by contacting the appropriate specialists. If the battery “holds”, then either the problem has been eliminated (for example, water was added to semi-dry jars), or the problem is different.
The principle of connecting current consumers to the on-board network
Electric current will flow through the conductor only if the electrical circuit is closed. Electricity consumption should be normal - battery terminal “plus” - consumer - terminal “minus”, and the circuit should not be broken. As an example, we gave the simplest scheme. In your car, consumers are connected to a circuit whose complexity is several times higher. Therefore, it will be difficult for a non-professional auto electrician to understand all the nuances.
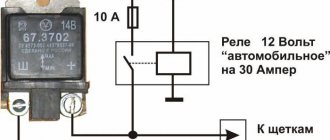
How to check for current leakage in a car? Refer to the image above. On it you can see that there is a single “minus” between the lamp and terminal 85 of the relay; it is usually connected to ground (body).
In this case, a switch is installed on the positive wire, breaking the circuit. When the switch contacts close, electricity flows through the relay coil, which is connected to pins 85 and 86. Due to the electromagnetic field, the coil begins to close the 87th and 30th contacts, and the electric current flows through the lamps.
The described scheme is standard for most vehicles. However, usually the circuit is opened by an additional switch - the ignition switch, and the fuse is embedded in the positive wire. To make it more convenient, one or two mounting blocks combine relays with fuses. Knowing this, you won't be shocked when you see a lot of wiring harnesses. You can also, by dividing a huge number of connected circuits into mini-circuits, check for current leakage in a car using clamps.
Some car devices are combined into common networks. Imagine that this is one consumer, but simply expanded in space. Is a current leak detected in the car after checking? The reason is that different circuits are connected to each other or to the “ground” of the machine due to the fact that the wiring insulation has become unusable. Leakage can also occur due to electric current “bridges” that appear due to dirt.
How to carry out in-depth diagnostics
It is worth starting a deep check of current leakage in the car after you inspect the wires. The essence of testing: we disconnect the car device, and then measure the electric current using a multimeter. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- disconnect the negative terminal from the battery to place the multimeter;
- connect the multimeter to the disconnected battery cable and the negative terminal;
- pull out the fuses to open the circuit;
- If surges in electric current are observed, we determine which device the fuse belongs to.
You can check for current leakage in a car by making an adapter, which can be used as a blown fuse. We connect the multimeter probes to the homemade adapter. Next, the steps are repeated: we check the circuits separately.
If you have identified a faulty location, you need to find out whether there will be a short circuit. To do this, you need to ring the wires using a multimeter, having previously set the resistance measurement mode.
Important!
Not every device operates with a fuse. Therefore, this method of checking current leakage in a car is not always suitable.
It happens that there is no leak, but the battery dies overnight. This happens due to a negative charge/discharge balance. The battery may simply not be fully charged if you are constantly stuck in traffic jams, trips are always short distances, the car often has to be started and turned off, and the car is used in winter. As a result, the battery fails.
Additional installed music consumes a huge amount of energy. However, this is no longer a current leak in the car.
We recommend
“How often to change filters in a car: we give deadlines and tell you tricks” Read more
A couple of tips from experienced car enthusiasts
Tip 1.
It is not necessary to measure leakage using the “negative” terminal; you can test the on-board network using the “positive” terminal.
The algorithm of actions is approximately the same - the terminal block is disconnected from the “positive” terminal of the battery.
Probes are connected to them and measurements are taken. But if when measuring on the “negative” terminal the polarity of the device connection is not important, then when checking on the “plus” it is important to connect the device correctly - the “negative” probe of the device is connected only to the terminal block with a wire, and the “positive” probe to the battery terminal.
It is important here not to confuse the polarity, otherwise you can damage the device.
Tip 2.
Before taking measurements, it is better to open the car windows, and you should not leave the keys in the ignition.
The fact is that when the terminal block is disconnected from the battery, the central locking may be activated, as a result of which the car will close.
Open windows and keys in your pocket will avoid such troubles as a locked car with the keys inside.
Lada 2114 Graphite metallic › Logbook › The leak has finally leaked. From 300 mA to 40 mA.
After reading forums and watching videos from various auto electricians, I began to take out all the fuses in the mounting block one by one and look at the change in leakage.
Then I got to the alarm and its fuses - the leak changed very slightly, by about 30 mA. In general, for a long time I looked for the cause, I thought it was a short circuit in the wiring to the body or between each other. Or a leak due to the initiative of the previous owners (for example, installing an electric trunk lock, etc.). The result, the solution and what helped and pushed me on the right path.
A friend came to me to temporarily exchange the mass air flow sensor to check its survivability.
We randomly measured the voltage on the sensor with a multimeter - first his, then mine. As a result, it turned out that when the ignition is on and when the ignition is off, it shows 0.99 volts. The fact that he is a worker is, of course, wonderful, but the fact that he always works was a big surprise. At first I thought there was a short in the wiring to the sensor, but somehow it didn’t look like it. Then it became clear that all the sensors were energized, including the injectors - everything that works when turned on. ignition Verdict
: The ECU was constantly active, the main relay was always closed, regardless of the position of the key in the ignition switch.
I checked the relay, replaced it with another working one - nothing changed. By checking and measuring the voltage at the sockets under the relay, I found out that in place of 87 - 30 contacts and 85 - 86 a constant voltage is always supplied. The problem was in the wire that came from one socket under the relay and was screwed to ground. I unscrewed it, disconnected it from the body, and insulated it. I checked - the voltage began to disappear when the ignition was turned off. I measured the leak and there were approximately the following numbers:
The same applies to the alarm mode. 40mA.
Before this, I had not paid attention to this wire before and did not attach any importance to it. Perhaps this wire should not be shorted to ground due to the alarm being inserted into the ECU circuit. It’s difficult to understand what the previous owners or auto electricians chemisted there, and it’s also difficult to detect or change something.
Source
Instead of an afterword
When buying a used car, it is useful to know how to find an electrical leak and understand its cause. Take a multimeter to inspect your car - you will save yourself from unpleasant surprises, such as a suddenly dead battery, power surges or burnt wiring.
For the same purpose, check the car's history. This can be done directly during a conversation with the seller. It’s convenient to use the Autocode service - monitor information from 13 sources at once: traffic police, RSA, EAISTO, banks, tax and other services. The verification will take 5 minutes.
Afterwards you will find out the actual mileage, number of owners, history of fines, as well as information about theft, participation in an accident, restrictions on car registration and much more. Be carefull!
Having fully studied the online report, it is still worth taking a closer look at the technical nuances of the car when purchasing. And if you are not confident in your knowledge, or it is not possible to go for an inspection, order an on-site inspection service. The specialist will conduct a diagnosis for you and make a detailed conclusion from a professional point of view.
Many car owners have encountered a situation where they were unable to start their car in the morning. And everything was fine in the evening. And the battery itself is new and in good condition. The reason here may be battery leakage current. This phenomenon exists on any car, but must fit within a certain norm. If the leakage current limit is exceeded, the battery will discharge while parked. As a result, you will have problems starting the engine. It's time to figure out what causes battery leakage current and how to bring it back to normal.