The engine of a modern car is a complex device. In such a unit, the power supply system is very complicated, consisting of a large number of elements. Various electrical circuit sensors are the main products that ensure timely injection and ignition of the working mixture. The camshaft sensor of the Niva Chevrolet belongs to this type of device.
How DPRV malfunctions manifest themselves, as well as methods for eliminating them, will be discussed in detail below.
Characteristics of the camshaft sensor
Before moving on to the question of checking the camshaft position sensor, you need to find out what kind of device it is, what it is needed for and on what principle it works.
This will help clarify the details of the audit in the future. A camshaft sensor is a device that records the angular position of a specified shaft at a specific point in time. The information obtained with its help is transmitted to the electronic engine control unit (ECU), and on its basis this control element issues commands for fuel injection and ignition of the air-fuel mixture in each cylinder at a specific point in time.
The operation of the camshaft position sensor is based on the Hall effect. So, directly on the camshaft there is a metal tooth, which, when the shaft rotates, changes the magnetic field in a nearby sensor. This tooth is called rapper. The sensor detects a change in the magnetic field, which is converted into a low voltage electrical signal. This signal is sent to the electronic control unit.
In fact, the camshaft position sensor only registers one position, corresponding to the position of the piston of the first cylinder at top dead center. Next, phased fuel injection is performed in the firing sequence of the cylinders. Typically this is a 1-3-4-2 system.
If the camshaft sensor fails (the electronic control unit receives incorrect information from it or does not receive it at all), then it is programmed to switch to emergency mode. It involves the use of pairwise-parallel (group) fuel supply to the engine. This leads to two negative consequences:
- A slight loss of engine power, especially when driving in critical modes (acceleration, driving under load).
- Increase in fuel consumption by approximately 10...20% (depending on engine power, its design features, as well as operating conditions).
As for diesel engines, camshaft position sensors are designed similarly, but there is one difference. It lies in the fact that the sensor records the position of not only the first cylinder, but all of them. This is done due to the fact that the drive disk has a separate tooth for each cylinder.
Thus, if a sensor fails, it makes sense to diagnose it as quickly as possible and, if necessary, replace it.
The operating mechanism of this part is based on the Hall effect. What does this device do? The Chevrolet Niva camshaft sensor controls the gas distribution device, its inclination according to the crankshaft. The signal is received by a system that controls the flow of gasoline and the operation of spark plugs.
The operation of the camshaft sensor is based on monitoring the potential difference between the carriers of the amount of electricity, and its work is associated with another crankshaft position analyzer. The camshaft sensor operates under the influence of the Ampere force acting on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. Using a magnet, it creates a magnetic field that changes under the action of a special iron tooth on the camshaft wheel.
Thus, the part tells where the piston of the internal combustion engine cylinder is located, and the strokes of the cylinder cycle are performed one by one.
Description of the camshaft sensor on Niva Chevrolet
Where is it located: in engines with a gasoline power system, the DPRV is installed on the camshaft pulley. In an engine with a diesel power system, the control system is somewhat different. Where the upper and lower position of the piston in each cylinder is fixed.
On engines with a carburetor fuel system, the role of the DPRV is played by the distributor. The design of the injector is different, the system was parallelized, injection and ignition were done in pairs.
During systematic operation, the household equipment wears out and becomes unusable. The process of self-replacement is not at all difficult. The task is feasible for a car enthusiast without technical equipment maintenance skills.
Repeated restart of the engine is the first sign of a malfunction of the DH (DPRV).
To determine which cylinder is on stroke, the electronic engine control unit controls the position of the camshaft using DPRV (SMR)
Data from the sensor is extremely important for setting and dosing fuel, sparks in the combustion chamber, and injectors. The camshaft sensor directly affects fuel consumption, acceleration dynamics, and the amount of emissions in the exhaust gases.
In cars, including Niva Chevrolet, magnetic and Hall effect sensors are preinstalled. Both types are designed to read and transmit data to the electronic engine control unit.
The latter, based on the analysis of indicators, adjusts the fuel supply, ignition timing, and spark frequency.
- The magnetic controller produces its own alternating current. The design has two contacts;
- The Hall effect controller has one contact, powered from a third-party source.
Signs of DPRV malfunction:
- Unstable engine operation at idle speed;
- After stopping, the engine starts again;
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Power reduction;
- Passive acceleration dynamics;
- On the dashboard there are system error indicators (see photo);
- The gearbox can be locked in one position until it comes to a complete stop and the ignition is turned off. Single or cyclic action;
- The car moves jerkily;
- The maximum speed of the car is limited to 65 – 85 km/h;
- Periodically the engine stalls;
- Misfires when turning on the ignition;
- Inability to restart the engine.
Speeds
The Chevrolet Niva speed sensor helps to determine exactly how fast the car is moving. The received information is transmitted to the speedometer. In addition to this, it also performs such functions as:
- Controls fuel consumption
- Displays information on the dashboard
- In cars with automatic transmission, it is part of the system that is responsible for engine control.
If for some reason it fails, then further movement becomes difficult. The causes of failure may be contamination or oxidation. If the device stops working, first of all you need to check for the following problems:
- Contacts have oxidized
- There was a break in the electrical wiring
- Wire insulation is damaged
- There are mechanical damages
Diagnostics can be done both visually and using a multimeter. To do this, the sensor is removed, after which you need to connect the plus to the contacts, and the minus to the ground of the car. We switch the multimeter to power measurement mode and if it shows that the voltage has increased, then the element can be considered faulty.
To change it you need to disconnect the battery. When the car is de-energized, we find the sensor which is located on the rear cover of the transfer case. Disconnect the terminal from it and unscrew it with a wrench.
Diagnostics can be done both visually and using a multimeter. To do this, the sensor is removed, after which you need to connect the plus to the contacts, and the minus to the ground of the car. We switch the multimeter to power measurement mode and if it shows that the voltage has increased, then the element can be considered faulty.
Tools:
There may be several sensors in a car. Main symptoms of malfunction Sooner or later, this element becomes unusable. The design of any camshaft position sensor is extremely simple: To find it, you need to look in the vehicle operating book. Some vehicles have multiple Hall sensors.
VAZ replacement of phase sensor, symptoms of malfunction.
You can also often hear another name for it: Signs of malfunction The electronic engine control unit monitors sensor readings. It is difficult to independently detect a breakdown in an electronic device, but there are several signs that indicate the sensor is not working properly or is broken. A sharp increase in fuel consumption is a sign of a malfunction of the camshaft position sensor. The first sign is a sharp increase in fuel consumption.
Every driver knows how much gasoline or diesel fuel his car consumes per kilometers driven. Look at the multimeter display.
Check the indicator with the specification specified in the car repair manual. In most cases you will see a fluctuating signal between 0.3 and 1 volt. To do this, set the multimeter to “constant current” mode. Connect the other wire of the multimeter to the power wire of the sensor.
Compare the multimeter readings with the specifications specified in the machine's repair manual. Compare the multimeter readings to the specifications found in your vehicle's repair manual. If the reading on the multimeter is lower than indicated in the repair manual or the data is completely missing, then most likely the camshaft sensor has failed.
If, after self-diagnosis of the camshaft position sensor, you determine that it is fully operational, then there may be a breakdown or malfunction in the vehicle components associated with the sensor. This allows you to accurately inject fuel, form an air-fuel mixture and ignite it at the required moment when starting the engine.
But it happens that devices for some reason begin to act up.
But the fact that the sensor has failed or is starting to fail can be determined independently by certain signs. One of them is a sudden increase in fuel consumption.
That is, you are already accustomed to the fact that your car consumes a certain amount of fuel per hundred kilometers in certain city or highway modes.
And if the flow rate unexpectedly, for no reason, exceeds the norm, then perhaps the Hall sensor begins to fail.
In order to drive a car comfortably and safely, you need the engine to work properly. Sometimes the effectiveness of the braking system may deteriorate, or the power steering will turn off, or the engine will simply stall while driving. The reason that the engine stops running abruptly may be that the camshaft sensor has stopped working. The Chevrolet Niva is no exception.
Removing the phase sensor
The Niva Chevrolet phase sensor operates on the Hall effect principle. It works as follows: there is a special pin on the camshaft and when it runs parallel to the end of the sensor, the sensor begins to transmit a voltage pulse to the existing controller, which should have the same position as the piston of the first cylinder in the compression position. That is, it is needed so that fuel injection and the order of operation of the engine’s cylinders correspond to each other.
In the event of a failure, it or its chain controller writes a special code into its memory and activates the alarm. And to remove it you need:
- Disconnect the battery
- Remove the decorative casing from the engine
- Disconnect the connector from the sensor
- We unscrew the bolt that secures it to the cylinder block.
- We remove the part from its seat
- Install the new one in reverse order
The part is removed from the engine to finally verify that there is a specific problem. On the cylinder head this structure is inserted into a special hole. Next, everything is screwed on with one bolt. It is enough to unscrew this connecting element, and then pull out the part and wipe it off with engine oil. The main thing is not to disconnect the block to which the additional wires are connected.
The ignition can be turned on after the multimeter is connected - to the middle contact, the ground of the car. The steel element is brought close to the end part of the part. For example, a regular key is perfect for this. All that remains is to monitor the readings that appear on the display. If everything is normal with the sensor, it reacts to the approach of any metal whose voltage is 02.-0.4 V. A high indicator is not taken into account.
If there are no changes in the tester’s performance, the device definitely needs to be changed. The main thing is to remember about the possibility of missing an o-ring even with new original spare parts. This part of the structure must be purchased separately, or an old one must be used.
- Disconnect the negative terminal from the battery
- We remove the decorative casing to gain access to the element we need
- We press the block and disconnect it from the sensor
- Unscrew the bolt that secures the part to the cylinder block
- We remove the part from the existing hole in the block head
- We change to a new element, doing all the steps in reverse order.
Also interesting: Generator Niva 2121, 21213, 21214: which one is installed, replacement
It is recommended to replace it every five years, even if it is working properly. The replacement job takes about twenty minutes, everything will depend on what technical skills you have.
How to make sure the DPRV is working?
The easiest way to check the camshaft sensor is to connect a car scanner or a computer with an installed program corresponding to the make of the car to the diagnostic connector of the car. If the element is faulty, then after starting the engine the device will display the following error codes:
- P0340 – there is no signal from the camshaft position detector;
- P0341 – valve timing does not coincide with the compression/intake strokes of the cylinder-piston group;
- P0342 – the signal level in the electrical circuit of the DPRV is too low;
- P0343 – the signal level from the meter exceeds the norm;
- P0339 – an intermittent signal is received from the sensor.
Since the vast majority of car enthusiasts do not have scanners and laptops with software at their disposal, a more affordable method is practiced - checking with a digital multimeter. Diagnostics is carried out in 3 stages:
- Visual inspection of the wiring and continuity of the circuit for breaks.
- Measuring the outgoing current at the control contact of the DPRV.
- Testing functionality by approaching a metal object.
Location of fuse and relay blocks Lada 4×4
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zPTu4cmH_3g
There are several typical signs that indicate that the camshaft position sensor has failed. It is immediately necessary to clarify that the symptoms listed below may indicate completely different malfunctions. Therefore, it makes sense to perform additional diagnostics.
- Problems with starting the engine, under any conditions - “cold”, “hot” and in other modes. This usually results in having to crank the starter longer.
- Unstable engine operation, “floating” operating and idle engine speeds.
- “Dips” in the movement of the car; when you press the accelerator pedal, it does not respond immediately, the dynamic characteristics of the car are lost (it accelerates poorly, does not pull, especially when loaded and when moving uphill).
- When the accelerator pedal is released, the engine stalls.
- Increased fuel consumption (by 10...20%).
- The Check Engine warning light on the instrument panel activates. It is necessary to perform additional diagnostics using an electronic scanner (for example, an ELM 327 device or its equivalent). In this case, typical errors regarding the operation of the sensor are numbers P0340, P0342, P0343.
In fact, the camshaft position sensor is a fairly simple and reliable device, so it rarely fails. More often, its wiring is damaged - the wires fray, the insulation on them is damaged, the so-called “chip”, the place where the sensor is connected to the car circuit, fails.
However, for cars that run on gasoline, the problems described above are not so clearly expressed. But a failed camshaft position sensor will cause many problems for owners of cars equipped with gas equipment, in particular the fourth generation. The malfunctions and problems described above can appear on such machines “in all their glory.”
To check the camshaft position sensor, you need to know where it is located. As a rule, on eight-valve engines the DPRV is usually mounted at the end of the cylinder head. On sixteen-valve engines it is also mounted on the cylinder head, usually in close proximity to the first cylinder.
As for popular domestic VAZ cars, their owners call such units phase sensors. Their location in these motors is similar. So, on eight-valve engines, the sensor is located on the left side of the cylinder head (when viewed in the direction of travel of the car). On sixteen-valve engines - on the right front part of the engine.
The easiest way to check the camshaft sensor is to connect a car scanner or a computer with an installed program corresponding to the make of the car to the diagnostic connector of the car. If the element is faulty, then after starting the engine the device will display the following error codes:
- P0340 – there is no signal from the camshaft position detector;
- P0341 – valve timing does not coincide with the compression/intake strokes of the cylinder-piston group;
- P0342 – the signal level in the electrical circuit of the DPRV is too low;
- P0343 – the signal level from the meter exceeds the norm;
- P0339 – an intermittent signal is received from the sensor.
Since the vast majority of car enthusiasts do not have scanners and laptops with software at their disposal, a more affordable method is practiced - checking with a digital multimeter. Diagnostics is carried out in 3 stages:
- Visual inspection of the wiring and continuity of the circuit for breaks.
- Measuring the outgoing current at the control contact of the DPRV.
- Testing functionality by approaching a metal object.
In practice, engine failure and immobilization of the vehicle are consequences that owners rarely encounter. The engine continues to operate, but small deviations occur that make normal operation impossible.
There are several important symptoms, although they may also indicate problems in other mechanisms:
- Natural increase in fuel consumption.
- Check Engine is an indicator that does not always light up when there are problems. But drivers notice flashes in this part of the system if the crankshaft speed increases to 3000 rpm or more.
- Reduced power of the power unit. When the load is increased, the effect becomes especially noticeable. This applies to trailer towing, sudden acceleration and lifting.
- After pressing the gas pedal, there is not dynamic acceleration, but a series of short jerks. The speed gain occurs at a slow pace.
- While driving, the engine cannot operate stably at idle speed. This problem occurs in cars of any year of manufacture - 2011, 2012.
The air-fuel mixture will be enriched if there is a malfunction in the device. Because of this, gasoline consumption is higher, and engine operation is no longer stable.
For other car models, additional symptoms of malfunction are acceptable:
- failure of the power plant due to lack of sparking;
- the appearance of additional noise;
- difficulties with automated gear shifting if an automatic transmission is used;
- difficulties when starting the engine cold;
- The engine starts without problems, but stalls while driving - this is what the 2123 model most often encounters.
At the same time, the part has a long service life. 80-100 thousand kilometers is a standard resource for domestic cars. In the case of imported ones, the figures reach 150 thousand km. You can focus on the indicated periods when faults are only being looked for.
Driving with a faulty sensor is acceptable, but not for long. Wear on spark plugs and other components increases due to the following factors:
- Electronic errors.
- Enrichment of the fuel mixture.
- Engine jerking.
They look for problems on their own, or decide to send the vehicle for diagnostics. It's easy to choose the right option.
1 — engine control system fuse box; 2 — windshield wiper relay; 3 — fuse blocks; 4 — relay block of the engine control system.
The fourth relay block is located above the gas pedal.
| F1 (30A) | Right electric fan relay contacts |
| F2 (30A) | Left electric fan relay contacts |
| F3 (15A) | Relay windings of the right and left electric fans, controller, injectors, ignition coil |
| F4 (15A) | Heating elements for control and diagnostic oxygen concentration sensors, phase sensor, mass air flow sensor, canister purge valve |
| №1 | Ignition relay |
| №2 | Main relay |
| №3 | Right cooling fan relay |
| №4 | Left cooling fan relay |
| №5 | Fuel pump relay (fuel) |
| №6 | Fuel pump fuse F5, 15A |
On some vehicle versions, a starter relay may be located under the additional unit next to the ignition relay.
Location of the DPRV on the engine
To check the camshaft position sensor, you need to know where it is located. As a rule, on eight-valve engines the DPRV is usually mounted at the end of the cylinder head. On sixteen-valve engines it is also mounted on the cylinder head, usually in close proximity to the first cylinder.
As for popular domestic VAZ cars, their owners call such units phase sensors. Their location in these motors is similar. So, on eight-valve engines, the sensor is located on the left side of the cylinder head (when viewed in the direction of travel of the car). On sixteen-valve engines - on the right front part of the engine. In the latter case, the sensor is not directly visible visually; its location can only be assessed by the signal and power wires suitable for it. The VAZ 2114 phase sensor is fixed in close proximity to the air filter, near the cylinder head.
More information about testing and troubleshooting
The Niva Chevrolet camshaft sensor creates stable engine operation. The work is based on the Hall effect. Thanks to it, the tilt of the gas distribution device is controlled according to the crankshaft. The system that controls the operation of the spark plugs and the flow of gasoline receives a corresponding signal.
Also interesting: Chevrolet Niva chip tuning: owner reviews, recommendations, pros and cons
It works based on monitoring the potential difference of the required electricity, and is associated with the operation of the crankshaft position analyzer. Simply put, it informs the location of the piston of the internal combustion engine cylinder, while all cylinder stroke cycles occur sequentially. If it stops working, the device and indicator turn on, thanks to which a mixture of air and fuel occurs, dosing is suspended and the reserve mode is activated. Replacement is recommended every five years. If it is faulty, the on-board computer will display the following errors, PO343, PO342, PO340.
Connecting scanners or computers equipped with special software is the best option for identifying most faults. The main thing is to choose software that matches the current car brand.
If the camshaft sensor is faulty, the following error options appear:
- P0339. In this case, intermittent signals are received from the sensors.
- P0343. The signal is at a high level, but it exceeds the norm.
- P0342. The signal level for the electrical circuit is too low.
- P0341. The compression/intake strokes of the cylinder-piston group differ from the current valve timing.
- P0340. There is no position locator signal.
Most buyers do not have scanners or laptops with software. Therefore, a simpler method is to check with a multimeter.
In total, there are no more than 3 stages in such diagnostics:
- The wiring is subjected to visual inspection. Next, the circuit is rung to check for a break.
- The outgoing current is measured at the control contact of the sensor. There is definitely a malfunction if there is something wrong with it.
- Check functionality by approaching a metal object.
During the first stage, the most important thing is to make sure that the wiring remains intact and that the contact of the connecting block is reliable enough. Conducting cables should be inspected additionally to ensure that there is no melting of the insulation or cracks or kinks. Using a multimeter it is easy to make calls and search for a break. An additional responsibility is cleansing from oxidation. This is the first sign of problems.
After diagnosing the entire system, you can move on to the sensor itself. Standard alligator clips are easily replaced with wires with needles. The main thing is to correctly determine the location of the two power contacts and the third wire going to the controller. The voltage between the bus ground and the contact is checked by turning on the power. The signal should remain at normal level.
If the values obtained are higher or lower than normal, the sensor must be replaced.
The part is completely removed from the engine in order to perform final diagnostics and make a final decision.
Before testing the sensor using a multimeter or other electronic tools, you must check its mechanical integrity. In particular, it is installed in a housing with an O-ring, ensuring its secure fastening. We need to check its condition. It would also be useful to check the integrity of the sensor body, whether there are cracks or other damage on it. It is advisable to check the drive disk to see if the teeth are damaged or if there are metal shavings on the sensor body or nearby.
On the Internet you can find information that supposedly the DPRV can be determined to work by simply checking its magnetic properties. In particular, bring a small metal part to its end (the working sensitive part), which should “stick” to the sensor. In fact, this is not the case, and a non-working DPRV may or may not have magnetic properties. Accordingly, verification must be performed using other methods.
There are two main ways to test the camshaft position sensor - using an electronic multimeter and using an oscilloscope. The first method is simpler and faster, but the second is more accurate and provides more diagnostic information.
Symptoms of a problem
Symptoms of a DPRV malfunction may be as follows:
- The Check Engine lights up after the engine starts.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Increased engine noise.
- More toxic exhaust.
- Reduced throttle response of the internal combustion engine.
- The engine does not start well.
Many of the symptoms listed may also occur with other problems, so the product should be inspected to determine whether it needs to be replaced.
Air flow
The air flow of the Niva Chevrolet is controlled using a hot-wire sensor, which is located between the hose of the intake pipe and the air filter. The magnitude of the direct current depends on the direction and amount of moving air that passes through it. In the event of a system malfunction, a code is stored in memory and the alarm is activated.
To replace, you need to prepare a 10mm wrench and a screwdriver and do the following:
- Disconnect the connector from the sensor
- Loosen the air pipe clamp
- We unscrew the bolts that secure the sensor and the o-ring
- Installing a new one
How to check
There are two ways.
- Multimeter.
- An oscilloscope.
Both technologies have pros and cons.
Niva Chevrolet: how to check the phase sensor with a multimeter
The procedure is as follows.
- Open the hood and find the DPRV.
- Using the car's electrical diagram, determine the power and signal terminals.
- Connect a multimeter to body ground and signal terminal.
- Turn on the car ignition.
- If the sensor is working properly, the tester display will show a figure between 10 and 10.5 Volts. Otherwise, the part must be replaced.
The disadvantage of this method is the low accuracy of the technique, but this is enough to check the functionality of the sensor.
Checking the sensor using an oscilloscope
A more accurate method involves the use of special equipment. Experts recommend using a physical tool, not a virtual program on a laptop, which is justified by the dubious accuracy of the readings of such a combination.
The essence of the test is to connect the device to the sensor and measure the actual pulses. Depending on the sensor model and engine characteristics, the data on the display may vary significantly.
Among the disadvantages, one can emphasize the presence of experience and knowledge of how to use an oscilloscope correctly.
Oxygen
The Chevrolet Niva oxygen sensor is also called a lambda probe; it is located in the exhaust gas system on the receiving pipe. The oxygen contained in the exhaust gas interacts with it, thereby creating a potential difference at the outlet. It varies from approximately 0.1 to 0.9 V. For it to function normally, its temperature must be at least 360 degrees.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SqqIBAU8osQ
The Chevrolet Niva oxygen sensor is also called a lambda probe; it is located in the exhaust gas system on the receiving pipe. The oxygen contained in the exhaust gas interacts with it, thereby creating a potential difference at the outlet. It varies from approximately 0.1 to 0.9 V. For it to function normally, its temperature must be at least 360 degrees.
Location of fuse and relay blocks Lada 4×4
If during the inspection it turns out that the camshaft position sensor itself has failed, then it must be replaced. As a rule, these units are non-repairable, since their body is sealed and cannot be disassembled. The sensor is inexpensive, and the replacement procedure is simple, and even a novice car enthusiast can handle it.
The sensor replacement algorithm is as follows:
- With the engine not running, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Disconnect the “chip” from the camshaft position sensor (as when checking).
- Depending on the vehicle model, it is necessary to remove parts that prevent access to the sensor. For example, on modern cars like the Lada Vesta, it is necessary to remove the bracket for auxiliary units.
- Using a wrench, unscrew one or two mounting bolts, depending on the type of fastening. The size of the wrench can be different, usually for VAZs it is a 10 mm wrench.
- After dismantling the mount, you must similarly remove the sensor from its seat.
- Installing a new sensor is performed in reverse order.
- Connect the negative terminal to the battery.
Replacing this part is relatively easy. The on-board computer registers errors such as P0340, PO342, PO343.
Error P0340 appears on the self-diagnosis system if the crankshaft rotates. Code P0342 - the camshaft electrical circuit shows a low signal and code P0343, accordingly, shows a high signal. It is necessary to check the wiring - for this purpose it is good to use an oscilloscope or other testing device.
Mechanical specialists, even if the sensor is in good working order, still recommend changing it every 4-5 years - such prevention will protect you from breakdowns and accidents, especially since the part is very cheap despite its importance. After all, the semiconductors inside the sensor react poorly to temperature fluctuations - remember your school physics course.
And also interesting: Fuel consumption on a Chevrolet Niva per 100 km: indicators "
There is a special offer on our website. You can get a free consultation with our corporate lawyer by simply submitting your question in the form below.
The preparatory stage will require the collection of certain tools:
- additional lighting, if required;
- Phillips screwdriver;
- rags;
- new controller;
- key to 10.
The sequence of actions is described as simply as possible:
- First open the hood.
- The tie from the rubber pipe of the air duct must be released.
- We remove the air duct itself.
- The controller is easy to find in the first part of the block.
- Remove the terminals and unscrew the bolt. The main thing is that the phase is maintained.
- All that remains is to remove the sensor and replace it with a new part.
- We put on the terminals and mount the air duct pipe back.
How to replace the camshaft sensor
- Key to "10";
- New controller;
- Rags;
- Phillips screwdriver;
- Additional lighting is optional.
- Open the hood;
- We release the metal clamp - the tie from the rubber pipe of the air duct. We extract it;
- At the top of the block we find the controller, remove the terminals, unscrew the bolt to “10”;
- We remove the sensor and replace it with a new one;
- We put on the terminals and install the air duct pipe.
The controller replacement is complete. We start the engine and check the serviceability of the equipment.
The most common causes of phase sensor failure in a VAZ family car with an engine injection system.
Sensors are classified as measuring instruments; they convert measured physical quantities into electrical signals and display digital data on a display.
The phase sensor is present in all 16-valve engines of the VAZ family; On 8 valves with Euro-3 toxicity standards and with phased, sequentially distributed fuel injection.
It is worth noting that in the period from 2004 to 2005, the mass introduction of phase sensors began on such engines as 2111, 2112, 21114, 21124 with Bosch M7.9.7 and January 7.2 engine control units.
The phase sensor is designed to determine the engine operating cycle and generate a pulse signal. The phase sensor is an integral sensor, i.e. includes a sensitive element and a secondary signal-to-pulse converter. The sensor's sensitive element operates according to the Hall principle, responding to changes in the magnetic field. The secondary element of the sensor contains a bridge circuit, an operational amplifier, and an output stage. The output stage is designed as an open collector.
The operation of the phase sensor represents the selection of the stroke for the first cylinder: camshaft active link transition to basket camshaft determines which valve is open, which valve timing.
Carburetor engines do not have this sensor. The fact is that a carburetor engine supplies a spark plug at the moment of compression and at the end of the exhaust gases, and for this principle of operation the readings of the crankshaft position sensor (CPS) are sufficient. This type of engine operation is called the “ignition system”.
On injection engines, when the phase sensor (DF) dies, the check light comes on and the engine switches from phased injection to the ignition system, that is, relying only on the DPKV readings.
Fuel level
The Niva Chevrolet fuel level sensor determines the remaining fuel in the tank and transmits the readings to the dashboard. It is located in the fuel tank. Its breakdown can lead to the car stopping at the most inopportune moment, so the driver will not know how much fuel is actually in the tank. Therefore, if there are problems with it, it is better to replace it as soon as possible, this can be done like this:
- The right side of the rear seat rises
- A fluffy rag is folded back
- Unscrew two screws on the fuel pump hatch
- Removing the hatch
- Disconnect the two pipes and terminals
- Unscrew 8 screws
- Carefully remove the fuel pump and replace the required element
All work is done within 10 minutes.
Temperature
The Niva Chevrolet temperature sensor helps determine the ambient air temperature. Located on the lower part of the bumper on the driver's side. If it stops working, you can replace it, for this you need:
- Disconnecting the battery
- Find the sensor itself
- Carefully pull it out of its seat
- Let's take him outside
- By pressing the latch, disconnect the plug from it
- Install the new one in reverse order
Idle move
The Chevrolet Niva idle speed sensor ensures the supply of air to the engine during idling. When a signal is received by the ECU, the sensor moves the valve, changing the flow hole in the air valve. If it fails, it will not be possible to repair it, since it has a non-demountable design.
To replace it, you need to prepare a thirteen socket wrench, pliers and a Phillips screwdriver and do the following:
- Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove the housing from the throttle valve
- Disconnect the wiring connector of the engine regulator
- Unscrew a couple of screws on the throttle body
- Removing the regulator
- Remove the O-ring from the existing hole.
To summarize, we can conclude that the failure of any of the above elements can seriously affect the operation of the car, therefore, in the event of a malfunction, you need to replace a new part as soon as possible. All replacement work can be carried out independently.
Oil pressure sensor (OPS)
The oil pressure sensor is located on the right side of the cylinder block and is screwed into the oil line fitting. This sensor is necessary to monitor the oil pressure in the engine. As you know, operating a car with low oil pressure in the internal combustion engine can damage it. When the oil pressure in the internal combustion engine decreases, the sensor closes the contact and sends a signal to the Niva instrument panel, lighting up the oil pressure indicator in the form of a red oil can.
Signs of DDM malfunction:
- Constant lighting of the oil pressure lamp;
- Oil leak from the sensor junction;
Meter design and location
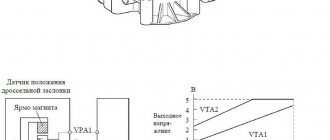
The operating principle of the DPRV is based on the Hall effect - the sensor reacts to the approach of a metal mass by changing the voltage on the signal wire. The design of the device is similar to another element - the crankshaft position detector. Inside the plastic case there is a coil where the 12 V on-board voltage is constantly supplied.
The meter is installed on the engine cylinder head in close proximity to the camshaft. The latter is equipped with a special plate or gear, whose rotation affects the DPRV. The work algorithm looks like this:
- After turning on the ignition and starting the engine, a supply voltage of 12 V is supplied to the sensor. Through the third signal wire, the element supplies the controller with a voltage of 90–95% of the original one.
- When the protrusion on the rotating part of the camshaft passes next to the DPRV housing, the voltage at the signal contact drops to 0.2–0.4 volts, depending on the design of the device and the vehicle model.
- When the voltage drops, the electronic unit clearly “sees” the valve timing, promptly supplies the fuel mixture to the engine cylinders and directs the spark discharge to the desired spark plug.
When the meter is faulty, the electronics are unable to control the operation of the gas distribution mechanism. In such cases, the control unit goes into error and is guided by the signals of other meters. Spark generation and fuel supply are adjusted according to the programmed program, which affects the operation of the power unit.
What is a sensor
In the cylinder head of each car there is one or a pair of camshafts, on which there are petals that are necessary for the normal operation of the exhaust and intake valves. The cylinder block contains a crankshaft, thanks to which torque occurs from the movement in the piston block, transmitted via gears, a belt or timing chain to the camshaft itself. And thanks to the camshaft sensor, the computer determines in the engine which cylinder is on stroke in order to correctly adjust it relative to the position of the crankshaft. This sensor affects how much gasoline consumption will be and how much emissions will be in the exhaust.
One of the most common types is:
- Magnetic sensors
- And which are based on the Hall effect
More information about testing and troubleshooting
Practice shows that a malfunction of the camshaft position sensor does not lead to engine failure and immobilization of the vehicle. The engine continues to operate with some deviations that interfere with the normal operation of the car. Symptoms of DPRV failure are quite vague and similar to problems with other measuring elements:
- Unstable engine operation at idle and while driving.
- Instead of dynamic acceleration, after pressing the gas pedal, there is a series of small jerks and a sluggish increase in speed.
- The power of the power unit decreases. The effect becomes noticeable when the load increases - on a hill, sharp acceleration, while towing a trailer.
- The Check Engine light on the dashboard does not always come on. But many drivers note that if the meter is faulty, the display flashes after the crankshaft speed increases to 3000 rpm or more.
- Fuel consumption is naturally increasing.
If the measuring element is faulty, the control unit prepares and supplies an enriched air-fuel mixture to the cylinders. This results in an increase in gasoline consumption and unstable idling. Jerks and drops in power are caused by untimely supply of a spark - the controller “does not see” the end of the compression stroke in the cylinder and cannot clearly determine the ignition timing.
On various car models, additional symptoms of a malfunctioning camshaft sensor are noted:
- the engine suddenly stalls while driving, but starts without problems;
- cold starting of the engine becomes difficult;
- on cars equipped with a robotic gearbox, difficulties arise with automatic gear shifting;
- the engine “troits” - skipping ignition cycles is heard, sometimes popping sounds are observed in the exhaust manifold;
- On some cars, the power plant fails due to lack of sparking.
Driving with a broken air pressure sensor is acceptable for a short period. Jerking, rich fuel mixture and electronic errors accelerate the wear of spark plugs and engine parts. After detecting the listed symptoms, you should send the car for diagnostics or find the source of the problem yourself.
Read news about the new Niva
- The modernized Lada Niva Legend (4x4) 2021 was shown on the Internet
- Lada 4×4 Bronto - sales stopped, new details » Lada.Online - all the most interesting and useful about LADA cars
- Description of the instrument panel Lada 4×4 (VAZ 2121, 2131) » Lada.Online - all the most interesting and useful about LADA cars
- Chevrolet Niva gasoline consumption per 100 km
- Buy LADA (VAZ) 2131 (4×4) 2022 in Rostov-on-Don, low price for Lada 2131 (4×4) 2022 on the Avto.ru website
- Fuses Niva 21214 injector «
- The new large Lada 4×4 Niva “Bigster” 2021-2022 based on the Dacia Bigster was shown for the first time. The SUV has changed beyond recognition
- New Niva Chevrolet Lux 2022 - review of GLC equipment
Niva with ECM
As you know, the first Russian SUV Niva was born back in the days of the Soviet Union. At that time, in the USSR they did not even think about an electronic engine control system; the entire process of operation of the internal combustion engine was mechanical. The engine was supplied with fuel through a carburetor. At present, the Niva still continues to be produced, but with its ancestors, the modern Niva has only the body left and it has undergone minor modifications.
The carburetor was replaced with an injector, the interior was changed and the appearance of the car was transformed, but still the Niva remained Niva. The legendary Niva cross-country ability did not deteriorate after these modifications, but became much more comfortable.
In this article we will talk about the sensors of the engine control system in the injection Niva, namely, it describes in detail each of the sensors, where it is located and what function it is responsible for, as well as the signs of sensor malfunction are described in detail.