The great invention of the 17th century is still the basis of any modern car. Aren't the driving characteristics of an iron horse, fuel consumption and power the main source of pride for a motorist? And in this regard, the 16 valve engine of the VAZ 2110 pleases with truly excellent technical indicators. However, everywhere there is a “but” that is worth mentioning.
Despite the fact that the 16-valve system is today the most popular not only for VAZ 2110-2112 cars, but also for the automotive industry in general, everything has its downside. Ignorance of the operating features of internal combustion engines can cause unreasonably expensive repairs and unexpected failure of the machine at the most inopportune moment. It’s really worth talking about how to avoid such an unpleasant situation.
Engine VAZ 2110 16 valve
Or maybe you’re just wondering what the rhythmic growl under the hood of your VAZ 2110 (2112) can tell you. For many people, buying a car is a significant investment for the rest of their lives. The ability to understand your iron friend is worth a lot, because you have to travel considerable distances with him on your life’s journey. And in life, as you know, anything can happen. And everyone needs to be prepared for this.
Of course, it is difficult to cover such a broad topic in one article. Therefore, it is very important to convey to motorists the most key details regarding the operation of their specific engine and the main differences between the internal combustion engines for VAZ-2110 (2112) cars. If you want to know really useful things regarding the operation of your car, then don’t stop reading, it will only get more interesting.
VAZ 2110 injector 16 valves, engine characteristics, timing device
The VAZ 2110 16-valve injector became another design breakthrough for AvtoVAZ. Finally, the 4-cylinder power units of the domestic manufacturer received a modern timing system with two camshafts and 4 valves per cylinder. In total, two main 16-valve injectors were installed on the “ten”. This is a 1.5 liter engine of the 2112 and 21124 1.6 liter models.
The most interesting thing is that the 1.5-liter injection engine is more powerful than its larger brother. The VAZ-2112 engine develops 93.5 horsepower, while the VAZ-21124 has only 89 hp. The compression in the 1.5 liter 16-valve engine is slightly higher. However, the 2112 motor has one drawback. If the belt breaks, the valves bend, which leads to very expensive repairs. For the VAZ-21124 engine, this problem was solved by making special recesses for the valves in the piston bottoms; this, of course, reduces compression, but the valves do not bend if the timing belt breaks.
89888zhzh
The surface of the toothed part of the belt should not have folds, cracks, undercuts of teeth and detachments of rubber from the fabric frame. The reverse side of the belt should not have wear, exposing the cord threads, or signs of burning. There should be no delamination or fraying on the end surfaces of the belt. If defects are detected or there is a significant discrepancy between the belt tension control elements (see below), the belt must be replaced. You should also change the belt if traces of engine oil are found on it (before installing a new belt, you need to eliminate the cause of oil getting on the belt), when replacing one of the rollers or the coolant pump.
Attention! If the timing belt fails (if the teeth are broken or cut off), contact of the valves with the pistons may occur due to a mismatch in the relative angular position of the crankshaft and camshafts. As a result, this leads to expensive engine repairs.
Check the belt tension. To do this, turn the crankshaft (see above) clockwise...
Characteristics of VAZ 2110 injector 16 valves
In technical terms, the 16-valve engines of the VAZ 2110 are almost the same, however, due to the difference in working volumes, there are some differences. So the 21124 engine has an increased piston stroke, so the height of the cast-iron cylinder block is several millimeters larger. The cylinder diameter of both engines is the same - 82 mm. Below are more detailed technical characteristics of the “tens” injection engines with 16 valves.
VAZ 2110 injector 16 valves 1.5 liters
- Working volume - 1499 cm3
- Number of cylinders - 4
- Number of valves - 16
- Cylinder diameter - 82 mm
- Piston stroke - 71 mm
- Power - 93 hp (68 kW) at 5600 rpm
- Torque - 128 Nm at 3800 rpm
- Compression ratio - 10.5
- Power system - distributed injection
- Acceleration to 100 km/h - 12.5 seconds
- Maximum speed - 180 kilometers per hour
- Average fuel consumption - 7.2 liters
VAZ 2110 injector 16 valves 1.6 liters
- Working volume - 1596 cm3
- Number of cylinders - 4
- Number of valves - 16
- Cylinder diameter - 82 mm
- Piston stroke - 75.6 mm
- Power 16 cl. - 89 hp (65.5 kW) at 5600 rpm
- Torque 16 cl. — 131 Nm at 3800 rpm
- Compression ratio - 10.3
- Power system - distributed injection
- Acceleration to 100 km/h - 12 seconds
- Maximum speed - 185 kilometers per hour
- Average fuel consumption - 7.2 liters
With all the advantages of the 16-valve petrol engine of the VAZ-2110, this power unit is technologically more complex than its 8-valve counterparts. The cylinder head is made of aluminum alloy and has quite impressive dimensions. Banal valve adjustment takes quite a long time, and major repairs of the cylinder head of a 16-valve engine are quite a labor-intensive undertaking.
Most often, almost all owners of 16-valve injection engines “tens” are faced with replacing the timing belt, which also requires increased attention. After all, there are already two camshaft pulleys, plus a timing belt idler pulley is added. When installing a new belt, you must align three marks on the camshaft pulleys and the crankshaft pulley. In theory, it looks something like this, as in the image below.
This is a detailed timing diagram of a 16-valve VAZ-2110 injector . And this is what it looks like in a real photograph of an installed timing belt.
The timing device of the VAZ 2110 injector 16 valves is, in principle, little different from the design of DOHC engines of foreign cars. So if you have experience replacing a belt on a “ten”, then this operation will not cause problems on other cars with the same engine. It is worth recalling once again that incorrect installation of the belt on a 16-valve 1.5-liter engine can lead to bent valves. So be sure to double-check that all marks match clearly. Also, the belt must be sufficiently tensioned, otherwise the timing belt may jump, which will cause inevitable problems.
Maintenance
Engine maintenance is carried out every 10-12 thousand kilometers. The schematic map is available from official representatives of the manufacturer. But, as practice shows, it all comes down to changing the oil and oil filter.
Many car enthusiasts ask the question - what is the best engine oil to pour into the VAZ 2110 8-valve power unit? The best option remains semi-synthetic motor oil of domestic or foreign production labeled 10W-30 or 10W-40.
Schematic sketch of the VAZ-2112 engine
Detailed diagram of the VAZ-2112 engine.
1 – engine sump. 2 – front crankshaft oil seal. 3 – crankshaft. 4 – crankshaft pulley. 5 – oil pump. 6 – generator drive pulley. 7 – timing belt. 8 – front cover of the timing mechanism drive. 9 – coolant pump pulley (pump). 10 – tension roller. 11 – camshaft toothed pulley. 12 – rear cover of the timing mechanism drive. 13 – camshaft oil seal. 14 – exhaust camshaft. 15 – hydraulic pusher. 16 – valve spring. 17 – valve guide sleeve. 18 – exhaust valve. 19 – receiver. 20 – camshaft bearing cover. 21 – guide pipe. 22 – cylinder head cover. 23 – plastic cover. 24 – spark plug. 25 – intake camshaft. 26 – inlet valve. 27 – cylinder head. 28 – coupling. 29 – fuel rail. 30 – crankcase ventilation hose. 31 – nozzle. 32 – intake manifold. 33 – flywheel. 34 – crankshaft rear oil seal holder. 35 – rear crankshaft oil seal. 36 – cylinder block. 37 – oil dipstick. 38 – piston. 39 – connecting rod. 40 – connecting rod cover. 41 – crankshaft main bearing cover.
Engine chip tuning circuit
Not many car enthusiasts can boast of a powerful 2110 engine. Thus, to improve the power characteristics of the engine, it is necessary to carry out chip tuning of the VAZ 2110. To do this, they usually turn to specialists, but more and more vehicle owners are doing the process themselves.
The chip tuning scheme is quite simple. To perform the operation yourself, you will need an OBD II cable (USB-Auto), a laptop computer and software. It is worth remembering that there are three options for modifying the power unit: for power (but this will increase consumption), for reducing consumption (leading to a loss of power) and balanced (balance between the optimal indicators of consumption and power).
Typically, chip tuning of a VAZ 2110 is done with the aim of reducing fuel consumption, therefore, if the owner of the car decides to do it himself, then it is necessary to select the appropriate software. But, it is recommended not to take risks and turn to professionals for help.
Engine device
16-valve 124 engine under the hood of a “two-wheeler”
- The engine is a sixteen-valve, in-line, four-stroke gasoline engine, consisting of four cylinders. The operating order of the cylinders is: 1-3-4-2 – starting from the crankshaft pulley. With a power supply system – distributed injection, controlled via a Bosch, “January” or GM controller.
- The engine is secured in the engine compartment using four elastic supports, of which the front and rear are rods that are fixed from the engine to the body, and the left and right are identical to the VAZ-2110(11).
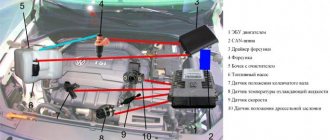
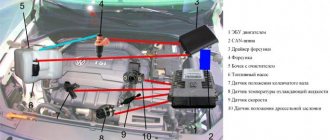
- On the engine, on one side there are camshaft and crankshaft drives, a coolant pump (about checking the pump and choosing a pump - note), a generator, as well as a timing belt (about replacing it here), on the other side there are sensors: coolant temperature, pressure oil, starter, thermostat, front: ramp with injectors, intake manifold, oil dipstick, knock sensor, crankcase ventilation hose, phase sensor. On the reverse side: oil filter, crankshaft position sensor, exhaust manifold. Top: spark plugs, high-voltage wires. More details about all sensors are written here.
- The cast-iron cylinder block has the same index “21083” with engines from the VAZ-2110 (11), however, they have different screws for the cylinder heads M10x1.25 in contrast to M12x1.25, as well as their smallest entry depth.
- Each engine has its own serial number.
Cylinders
This is what the cylinder block looks like with the engine removed.
The engine cylinders are bored directly into the block. The initial diameter is 82 mm and during repairs can be increased by 0.4 or 0.8 mm. The class of the cylinder is marked on the bottom plane of the block in Latin letters.
Crankshaft
This element practically does not fail.
The crankshaft is made of high-strength cast iron, and is equipped with five main journals, four connecting rod journals, and eight counterweights cast together with the shaft. The difference between this crankshaft and its analogues with the VAZ-2112 is due to its increased strength and wear resistance, so installation from younger models is completely excluded. The flywheel is secured to the back of the crankshaft using six self-locking bolts.
Pistons
These pistons apparently already have grooves for the valves. They won't be driven down anymore.
The piston in the engine is made of aluminum alloy, the piston skirt is conical in the longitudinal section, and oval in the transverse section. A distinctive feature of the pistons for the VAZ-2112 is that they have four recesses for the valves to avoid bending and subsequent replacement of the valves, whereas on younger models they are flat. For one engine, pistons should be selected based on weight, not allowing a difference of more than 5 grams, to reduce the imbalance of the crank mechanism (approx.). There are three rings mounted on the piston: the upper ones are compression rings that prevent gases from breaking through into the engine crankcase; they also help remove heat from the piston to the cylinder. The lower ring is an oil scraper ring (about replacing it here).
Connecting rods
As a rule, they are changed along with the pistons.
The connecting rods are made of steel and are divided into weight classes - they are marked with paint or a letter on the cover. On the covers, as well as on the connecting rods, the cylinder number is stamped (it should be on one side of the connecting rod and the cover).
Piston pins
This is what a piston pin looks like.
The piston pin is steel, tubular in section. It is secured from falling out by two retaining spring rings, which are located in the grooves of the piston bosses. Based on their diameter, they can be divided into three different classes: 1 – 21.978-21.982 ; 2 – 21.982-21.986 ; 3 – 21,986-21,990 . The piston class is also stamped on its bottom. The piston and pin must be of the same class.
View of the cylinder head on a dismantled engine.
Cylinder head - made of aluminum alloy, common to all four cylinders, centered on the block with two bushings and secured with ten screws. On the top of the cylinder head there are camshaft supports, five on each side.
Camshafts
Camshafts and their pulleys
The camshafts are cast, cast iron, five-bearing, each with eight cams. The camshafts are driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft. Due to increased loads on the timing belt, its width in the VAZ-2112 engine, compared to analogues 2110(11), has been increased from 19.0 to 25.4 mm (accordingly, the width of the toothed pulleys and rollers has been increased). Therefore, the timing belt tension has also changed. There is a support roller under the intake camshaft pulley, and a tension roller under the exhaust camshaft.
Valves
These valves are not afraid of bending if there are grooves on the pistons.
The valves are made of steel, while the outlet is made of heat-resistant steel with a directional chamfer, and the inlet area is larger than the outlet. If we compare in size, they are smaller than the analogues of the “tenth” model. They are arranged in two rows in a V-shape. They are driven by cams using hydraulic pushers, which in turn are very sensitive to the purity of the oil and its quality. And in the presence of mechanical impurities, premature failure of these elements is possible, which will be accompanied by increased noise during the operation of hydraulic pushers. How to replace these elements is described in detail in this article.
8988kkkk8
Use a 15mm spanner to loosen the bolt securing the tension roller...
Replacing the timing belt VAZ 2112 1.6 16 cl.
1. Remove the timing belt protection. The timing belt guard is secured with six bolts. Remove the chip from the crankshaft sensor, unscrew one bolt and remove the sensor.
2. One tooth is missing on the pulley, this is not without reason, this allows the crankshaft sensor to determine the top dead center, and also allows you to block the crankshaft in order to unscrew and tighten the pulley mounting bolt.
3. This is done like this: the pulley is aligned with the hole for the crankshaft sensor and through the hole for the sensor, a suitable size tube or other suitable object is inserted, in my case it is a hexagon, the pulley is blocked, and then unscrewed and removed.
4. Loosen the tension roller nut and remove the old timing belt.
5. Install a new belt, the belt can be installed by turning the right camshaft with a wrench, or you can remove the tension roller, whichever is more convenient for you.
6. Tighten the pulley mounting bolt back and align the timing belt drive gear according to the marks. If there are no marks on the oil pump housing, put marks on the flywheel and, using a chisel, make a mark on the oil pump, this will be more convenient.
7. Align the marks of the camshaft pulleys so that the timing belt drive gear does not go astray
8. Using a special wrench, tighten the belt with a tension roller. If there is no key, don’t be upset, you can tighten it with two nails and a screwdriver between them, or you can take a steel fork, remove the two middle teeth completely, and shorten the two outer ones in half and bend them. Be sure to remember to tighten the tension pulley nut. (To tighten the belt, turn the tension roller counterclockwise (about 10–15°); to loosen it, turn it clockwise)
9. Turn the crankshaft two full turns and check the marks; if all three marks match, put the pulley in place, do not forget about the generator belt and crankshaft sensor, then the belt protection and you can start the engine.
Timing belt tension
1. Check the belt tension. A correctly tensioned belt should rotate 90° from finger force (1.5–2 kgf) in the middle between the crankshaft and camshaft pulleys.
2. I take it with two fingers between the camshafts and up and down. 5-6 mm fluctuates back and forth, then I leave it.
3. Adjust the timing belt tension using a special device. The most correct belt tension is 2 kGs. Having achieved this result, fasten the fastening nut.
4. In the "Manual", the manual verification method is described in detail. It involves checking the tension of the toothed belt in the middle part of the branch between the camshaft pulleys. It should be such that under the action of an object 3 mm wide with a force of 10 kg, the belt deflection is 5.4 mm. Deviations in any direction are allowed no more than 0.2 mm. The engine must be at “room” temperature (+15-30°C). An overtightened belt breaks - the strength of the cord threads is limited. And the tighter the belt is, the faster the threads will break. A loose belt will also not last long, because... when entering the pulley, the belt teeth do not fall into the cavities of the pulley teeth - undercutting occurs and the subsequent separation of the teeth from the base.
Advantages of a sixteen-valve engine
We have already said that the internal combustion engines of the VAZ-2110 (2112) family discussed in the article are distinguished by greater power, lower fuel consumption, and also high technical characteristics, unlike the V8s. It's time to find out what design features make the VAZ 2112 16 valve engine such an attractive choice for motorists.
Let’s immediately make a reservation about exactly what “advantages” will be discussed in this section of the article:
- fuel economy;
- higher power;
- detonation resistance;
- advanced cooling system;
- simple tuning due to the separation of the intake and exhaust tracts.
It is the separation between the intake and exhaust tracts in the design of the VAZ-21120 and 21124 engines that makes it possible to achieve quite noticeable fuel savings. Thus, the supply of fuel and the intake of exhaust gases is carried out by a separate spaced valve system, due to which there is no unwanted mixing of fuel and combustion products. It is also obvious that this increases the efficiency of the engine and its power.
Sixteen-valve VAZ 2110 engine
The innovations did not ignore the combustion chamber, as well as the structure of the cylinder block. Their design is slightly modified in such a way that the risk of detonation of the fuel mixture is minimized. This is truly a significant advantage, because the quality of gasoline in our gas stations leaves much to be desired. Accordingly, this kind of internal combustion engine design remains a guarantee of its long service life.
Add a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Engine VAZ 2110 16-valve
Today, every motorist knows that the internal combustion engine is the heart of every car. Knowing the structure of the VAZ 2110 engine is not a whim for the owner of the corresponding car, but a practical necessity. The life of an engine is partly determined by its quality, and partly depends on the intensity of daily use of the car. Of course, the higher the mileage, the higher the likelihood that the engine will fail. The design of the VAZ 2110 16 valve engine is given in detail in the article below.
Tuning of the internal combustion engine cylinder block, conversion of the 8 valve VAZ-2110 (2112) engine to 16 valve.
Tell me, after reading all the above-mentioned information, are you not inspired by the idea of having a car with 16 internal combustion engine valves? In this case, you will be pleased to know that this kind of modernization is allowed. Of course, this process is thorough and cannot be completed without careful preparation. But the result will really justify itself. If you have any doubts, just read the next few paragraphs of the text.
Without going into technical details, the essence of tuning is to replace the cylinder head with a new one. Of course, now you will have two camshafts, and you will also have to rack your brains over the fastening system, because the diameters of the holes in the 16 valve head do not correspond to those on the 8 valve head.
The mounting holes of the block head should be drilled, increasing the diameter from 10 to 12 millimeters.
You can do this yourself, but it is better to contact a specialized workshop. For this kind of work they should not charge more than 3-4 hundred rubles. It should also be taken into account that the standard mounting bolt for the 16-valve cylinder block is slightly smaller than that for the “eight” and must be shortened accordingly.
It is better to study in advance what a 16-valve engine is like on a VAZ 2110 and then you will certainly be able to carry out this kind of tuning yourself. It will be necessary to change the timing belt, pump pump, rollers, wiring, spark plugs, connecting rod mechanism and other structural elements due to the peculiarity of the cylinder head. The head is assembled separately before installation on the engine. After completing the work, it is also advisable to use specialized services for setting up and calibrating the operation of the internal combustion engine.
Basic faults
The main malfunction characteristic of the VAZ 2110 is the appearance of the engine tripping effect. Malfunctions can occur for various reasons. Let's consider the factors that cause unstable engine operation, as well as methods of elimination.
Poor quality fuel
The first thing you need to check is how high-quality the fuel was poured into the vehicle. If the gasoline was of poor quality, then most likely one of the elements of the fuel system was forgotten. So, the motorist will have to find out what the fuel supply scheme is and find parts that could have failed.
So, the first element that comes under scrutiny is the spray nozzles. Malfunctions of the injectors can cause unstable operation of the engine, which will lead to tripping. A special stand is used to diagnose and clean the unit, but many motorists carry out the process themselves, using carburetor cleaning fluid.
Also, unstable engine operation may be caused by clogged fuel filters. One is located under the rear right wheel, and the second is in the fuel pump. There is a filter mesh on the fuel pump intake that needs to be replaced. The process is quite complicated, since you have to remove the rear seats and remove the fuel supply element. But the fuel filter under the wheel can be changed quickly and without any problems.
Ignition system
Damage to spark plugs or high-voltage wires can also cause tripping. So, it is necessary to check all the elements using a tester, as well as visually inspect them. If there is damage, it is recommended to replace the entire set.
Sensors and ECU
Another major reason for engine tripping is the failure of one of the engine sensors, as well as a malfunction in the electronic control unit. To carry out diagnostics you need to connect to the “brains”.
Next, based on the errors shown, find the faulty meter and replace it. If this does not help, and the error in the ECU remains, then it is recommended to reset, and in some cases, flash the control element.