The light SUV VAZ 2121 Niva is one of the most popular modifications of the Volzhsky Automobile Plant. The most popular of the engines on Niva were modifications 21213 and 21214. The difference between these power units is the presence of an injection system and a modified combustion chamber. The Niva gasoline engine has proven itself to be a fairly reliable power unit, which, with proper maintenance, can run about 300 thousand kilometers without major repairs.
Specifications
Motor specifications:
| PARAMETER | MEANING |
| Years of manufacture | 1194 – present |
| Weight, | 117 kg |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Supply system | injector |
| Type | in-line |
| Engine displacement | 1.7 |
| Power | 81 horsepower at 5200 rpm |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Number of valves | 2 |
| Piston stroke | 80 |
| Cylinder diameter | 82 |
| Compression ratio | 9.4 |
| Torque, Nm/rpm | 125Nm / 3000 |
| Environmental standards | EURO 4 |
| Fuel | AI 93 |
| Fuel consumption | 8.3 /100 km combined cycle |
| Oil | 5W-30 |
| Oil volume | 3.75 |
| When replacing, pour | 3.5 liters |
| The oil change is carried out | 15 thousand km |
| Engine life - according to factory data | 200+ |
VAZ 21213 engine is installed on VAZ 21213, 21214, Chevrolet Niva.
VAZ 21214 engine modifications and their differences
| Motor modification | Availability of power steering | An exhaust manifold | EURO environmental class |
| 21214-41 | + | welded from stainless steel become | 3 |
| 21214-34 | _ | cast iron | |
| 21214-33 | + | ||
| 21214-32* | |||
| 21214-31 | welded from stainless steel become | 4 | |
| 21214-30 | — |
*21214-32 – has fuel pipes with quick connectors, a flywheel for the clutch of 215 mm (200 mm on other models).
The geometry of the cylinder block 21214 and 21213 is the same. There are no liners in the cylinders. Due to the use of an ejector, the configuration of the front engine cover has been changed to accommodate the installation of a crankshaft position sensor. To mount the power steering, a hole is made on the block for installing a bracket; in addition, there is a threaded hole for installing a knock sensor, as well as threaded holes with studs for mounting the ignition module bracket.
The ShPG came from 21213. Crankshaft 21213-1005015 sets the piston stroke to 80mm. The crankshaft pulley is distinguished by the presence of teeth along the outer diameter for the operation of the crankshaft position sensor. The latest internal combustion engine models are equipped with a damping pulley (21214-1005058-10). The presence of a damper made it possible to reduce the load on the crankshaft to prevent cutting of the key, and also make the operation less noisy.
Cylinder head 21214-1003011-30 (36) was modified from the head from 21213. For modification, it was necessary to introduce holes for installing a phase sensor and studs for mounting the intake receiver. To install hydraulic compensators, bosses are cast in the head and have threaded holes in them. With the introduction of hydraulic thermal gap compensators, adjusting bolts were eliminated from the head design. Oil under pressure is supplied to the hydraulic compensators through separate pipes. There are two types of heads: Russian 21214-1003015 and Canadian 21214-1003015-30. The differences between the heads are as follows: in the first, the diameter of the threads in the holes for hydraulic compensators is M18/1.5, the wells for hydraulic compensators do not have drainage holes; the second ones have M24x1.5 holes, and the wells have drainage holes (the markings are made in the casting). Interchangeability of heads, as well as hydraulic supports of old and new designs, is not possible. A new oil rail 21214-1007180-30 made of stainless steel was used, supplying oil to the hydraulic compensators. Interchangeability with ramp 21214-1007180 is maintained.
Valve levers 21214-1007116-30, in contrast to the previous 2101-1007116, have a smaller radius (11 mm) of the platform support interacting with the camshaft cam, as well as an additional groove on the side of the hydraulic compensator. Both lever options are interchangeable.
In the timing camshaft drive, instead of a double-row chain, a single-row chain 21214-1006040-03 is used on rollers and bushings. Single-row sprockets for the chain were taken from the 2123 motor. The number of teeth on the oil pump sprocket was reduced to 30 to increase the performance of the oil pump and improve the operation of the hydraulic chain tensioner and hydraulic compensators. The external difference is complemented by a solid steel tube with a diameter of 6 mm for supplying oil to the hydraulic chain tensioner. Previous engine models used a coiled-brazed tube of smaller diameter.
The camshaft 21214-1006010 is original with a modified cam profile and can be interchanged with the shaft from 21213.
The 80 amp generator is the same as the 2112, with a slight difference in the diameter of the pulley 80 mm for the drive belt 2107-1308020 (944 mm).
The exhaust manifold can be made of cast iron or stainless steel. The cast iron manifold is made by casting. The stainless steel manifold version has a welded design. A welded manifold is lighter and heats up quickly, which is good for the operation of the catalyst located in the manifold. In addition, an oxygen sensor is installed in the exhaust manifold.
The intake manifold and fuel rail (2123-1144010-11) were borrowed from the 2123 engine. The injectors of the fuel injection system are SIEMENS VAZ 20734 (yellow), injectors (0280 158 110) were installed on early engines.
Ignition module from engine 2112.
Electronic control is carried out by the BOSCH MP 7.9.7 ECU. or JANUARY 7.2 depending on the year of manufacture and modification of the internal combustion engine.
The cooling system began to be assembled using gaskets with an elastic polymer bead, which improved the tightness of the system. The water pump (pump) includes an oil seal (cuff) that is more resistant to wear and loss of properties.
Peculiarities
The VAZ 21213 four-cylinder eight-valve petrol engine has a displacement of 1.7 liters. The power of the power unit is 81 horsepower with a torque of 125 Nm.
Engines 21213 in their latest generation were equipped with an injector and ran on high-octane 93 gasoline. The cast iron cylinder block ensured maximum strength for this power unit.
The use of numerous automatic engine control systems made it possible not only to change the traction performance of this engine, but also significantly improved fuel efficiency. Niva in suburban mode consumes 8.3 liters of gasoline per 100 kilometers when driving at cruising speed.
Starting from 2014, Niva cars with a diesel engine are also offered to customers.
The Niva engine with an overhead camshaft is equipped with a chain drive, which significantly simplifies the service of this power unit. The chain drive does not require replacement of the tensioner or any adjustment during operation of the motor. We also note the presence of hydraulic compensators, which relieves the car owner of the need to carry out the procedure for adjusting the valve clearance. All maintenance work on this engine can be performed by the car owner himself, without contacting branded service stations.
Flaws
Niva engines have excellent technical characteristics and have proven themselves to be quite reliable power units. At the same time, it should be understood that, like all other VAZ power units, they are not without drawbacks.
The disadvantages of this motor include:
- increased noise;
- tendency to vibration;
- increased oil consumption.
Such problems often appear after a mileage of 100,000 kilometers. Car owners need to closely monitor the condition of the cooling system.
Often, problems with the pump and thermostat lead to overheating of the power unit. The result of such overheating can be the appearance of cracks in the cylinder head, which in turn leads to coolant entering the oil. The VAZ 21213 engine in this case requires complex and expensive repairs.
Weaknesses of the VAZ 21214 engine
In addition to the weak points of the base 21213, the motor has the following weak points:
Cylinder block. This weak point appears on various models of Nivov engines, including the previously discussed 21213. Due to insufficient quality control, the assembly unit is manufactured with a high percentage of factory defects. In short, the drilling depth of the intake manifold stud holes is not maintained, causing the holes to meet the camshaft stud holes. In this way, L-shaped through channels are obtained. After installing the studs at the factory, the connections remain sealed for some time and the problem is not identified when the quality control department employees accept engine tests. After the sale of new cars with low mileage, during sharp braking, oil begins to seep through the studs onto the hot intake manifold, so much so that smoke from the oil burning in the manifold pours out from under the hood, and accordingly, there is nothing to breathe in the cabin. It would seem that there is a manufacturing defect and it should be fixed free of charge or the cars should be recalled altogether to eliminate the defect, but that was not the case. In service centers they pretended to know nothing until the very end...
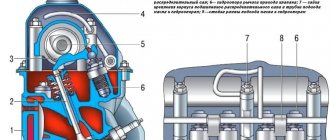
The most interesting thing is that AvtoVAZ knows about this problem and, in response to questions in correspondence with car owners, advises eliminating it according to the following technical specifications:
A sketch for the technical specifications for eliminating oil leaks from under the exhaust manifold studs.
- Remove the GC cover;
- Unscrew the two studs securing the bearing housing (see sketch) and remove oil from the threaded holes;
- Thoroughly degrease the holes and stud;
- Apply sealant UG-10 or its analogues to the lower threads of the studs;
- Place the studs in place;
- Tighten the bearing housing nuts;
- Install the cylinder head cover;
- Wait at least 30 minutes for the sealant to set.
Malfunctions
| FAULTS | CAUSES AND REPAIRS |
| The appearance of a characteristic knock at the bottom of the engine. | This indicates problems with the main bearings. The car must be towed by a tow truck to a service center and the appropriate repairs must be carried out. |
| The appearance of a pronounced knocking sound with a metallic sound. | The reason for this is problems with the bearing rods and piston pins. It should be said that operating a car with such problems may subsequently lead to the need for expensive major repairs. |
| Engine troubles at low speeds. | There may be several reasons for engine tripping: first of all, it is the use of low-quality gasoline. It is also possible that carbon deposits may appear in the combustion chamber. In rare cases, problems are observed in the operation of the injection system. Repair in this case is carried out only after a comprehensive diagnosis. |
| Loud knocking sound when the engine is not warmed up. | This may indicate the beginning of camshaft wear. This problem is typical for power units whose mileage exceeds 100,000 kilometers. It is necessary to carry out appropriate diagnostics and then replace the camshaft. |
Tuning
There are several ways to increase the power of a Niva engine. We will tell you in more detail about these methods of tuning the VAZ 21213.
- Deep engineering tuning of the Niva engine with crankshaft replacement and cylinder boring. This kind of work allows you to increase the working volume of this engine to 1.95-2.1 liters. Accordingly, when adjusting the injector, the VAZ 21213 engine receives power of about 100 horsepower.
- Chip tuning of the Niva engine allows you to get about 10 additional horsepower at minimal cost. In this case, the work does not pose any difficulty. You just need to select the appropriate chip tuning and reprogram the engine control unit. The advantage of this option is the complete preservation of engine life.
- Installation of turbines and compressors on VAZ 21213 engines. In this case, we can recommend that you use compact turbines with a pressure of no more than 0.5 bar. At the same time, the injector is reconfigured and the oil and fuel pumps are replaced. It is necessary to understand that such work should only be performed by a specialist who knows the features of the VAZ 21213 engine.
Note that installing a turbine and boring the Niva engine invariably negatively affects its service life. Therefore, the car owner needs to weigh the pros and cons, and only after that perform tuning of the Niva engine.
Repair dimensions of cylinders and pistons of the VAZ 21213 engine during major repairs
| Repair cylinder size, mm | Piston and cylinder class | Piston diameter, mm | Cylinder diameter after boring, mm | Cylinder diameter after honing, mm |
| 1 repair | ||||
| 82,4 | A | 82,34-82,35 | 82,37-82,38 | 82,40-82,41 |
| B | 82,35-82,36 | 82,38-82,39 | 82,41-82,42 | |
| C | 82,36-82,37 | 82,39-82,40 | 82,42-82,43 | |
| D | 82,37-82,38 | 82,40-82,41 | 82,43-82,44 | |
| E | 82,38-82,39 | 82,41-82,42 | 82,44-82,45 | |
| 2 repairs | ||||
| 82,8 | A | 82,74-82,75 | 82,77-82,78 | 82,80-82,81 |
| B | 82,75-82,76 | 82,78-82,79 | 82,81-82,82 | |
| C | 82,76-82,77 | 82,79-82,80 | 82,82-82,83 | |
| D | 82,77-82,78 | 82,80-82,81 | 82,83-82,84 | |
| E | 82,78-82,79 | 82,81-82,82 | 82,84-82,85 | |