Caliper - we repair it at home
The safety of the driver and passengers of the vehicle directly depends on the performance of the braking system.
After a certain mileage, its components wear out, one of which is the caliper. Nevertheless, it is quite possible to repair the brake caliper, although most often it fails due to the process of souring of the guides or pistons. Why is this dangerous in practice? If this unit malfunctions, the brake pads begin to wear unevenly. The same goes for brake disc wear. As for the pads, increased wear may be observed, for example, on the outside compared to the inside. Uneven wear indicates that the pistons are putting too much pressure on only one of the pads, while the other does not take part in the process. Urgent repair or replacement of the caliper is required, without waiting for it to completely jam.
Types of installed calipers and their prices
The same caliper is installed on a given family of cars, with the exception of the index in its marking, indicating the model of the vehicle body. Otherwise, these are identical brake devices that have a single-piston design independent of the fixed caliper. A similar modernization took place after 2001, and the last half calipers with 4 pistons were installed on the VAZ 2108.
The cost of a caliper for a VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115 can be as follows, based on its condition:
- New – 1,610-4,270 rub .
- Used – 700-1,980 rub .
- Refurbished (restoration using original components) – 1,420-2,190 rubles .
About the reasons for caliper failure
This brake system component can break down due to improper maintenance or due to insufficient quality. The main reasons why caliper repair may be required are as follows:
- improper operation, which is associated with filling the guides with poor-quality lubricant - because of this, the boot swells and later “sours”;
- in the future, repair of the brake calipers may be necessary due to moisture getting on the guide, which leads to a breakthrough of the boot;
- Another reason is the piston itself, the body of which is also vulnerable to moisture getting inside;
- low-quality working fluid (brake) can corrode the piston from the inside if the concentration of water in it exceeds the norm.
Video tip for DIY caliper repair:
How to determine the moment of replacement?
The operation of the brake system as a whole can be affected by many different components that have a malfunction. But each element has its own individual characteristics, by which one can “calculate” this or that problematic detail. It is quite easy to track problems that are specific to the brake cylinder system; here are some of them: 1. Soured piston. This is a fairly common phenomenon on cars with high mileage and service life. Indirect signs indicating this problem are stalling of the drive wheels (the piston is jammed and it constantly presses on the block) or the brake does not work when the pedal is pressed. 2. Damage to the seal or breakage of the fitting or boot (brake fluid may leak out in various volumes).
How does a brake caliper work?
In ideal condition, the brake caliper should operate as follows:
- The driver inside the car presses the brake pedal;
- At this moment, pressure is built up inside the brake line and it is transmitted to the piston group of all calipers;
- The calipers, under the influence of pressure, bring the brake pads to the disc mounted directly on the rotating wheel;
- Due to the frictional force that arises, the rotation of the disk, and at the same time the wheel, slows down.
Important: for proper operation of the brake system, the pads must be positioned strictly parallel to the brake disc.
Because friction occurs when a vehicle brakes, it also generates heat, which warms the brake pads, fluid, and calipers. Accordingly, a working brake caliper must consist of a material whose properties do not change when heated. Also, the caliper material must be strong to withstand heavy loads.
Replacing the front brake cylinder on a VAZ 2114
- To gain access to the work area, first remove the wheel on the side where you want to replace it.
- After removing the wheel, use a hexagon to loosen the brake caliper cylinder. To do this, you need to slightly unscrew two bolts, one on top, the other on bottom.
Unscrew and disconnect the brake hose. To prevent liquid from leaking out of it, lift it vertically, or insert a sealed plug into the passage hole.
Next, using a flat-head screwdriver, pry up the fastening washers and use an adjustable wrench to unscrew the next 2 bolts.
- Now the cylinder body can be easily detached along with the bracket.
- Fully unscrew the previously loosened hexagon bolts. We disconnect the bracket from the body of our product.
- Reinstallation is done in the same order, except that the brakes will need to be bled. This must be done in order to remove accumulated air from the system.
What does the price depend on?
In addition to the brand, the following product parameters are involved in determining the consumer price:
- Total area of the brake wheel cylinder.
- Fixed caliper dimensions with fixed mounting holes (standard caliper fits 13″ stamped wheel rim).
- Dimensions of the movable bracket.
- Material of guide pins for movable bracket.
- Locking plate material.
The caliper for VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115 has a single-piston design , therefore it is the cheapest in its class. Among the additional pricing factors it is worth noting:
- Availability of a brake hose (reinforced, regular).
- Implementation of a casing-channel for laying hoses.
- Availability of spare bolts securing the working cylinder to the movable bracket.
Do-it-yourself caliper repair - preliminary inspection
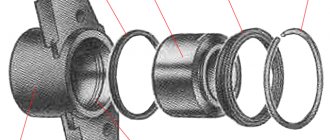
The return movement of the piston in this unit is ensured by a cuff. Firstly, it creates a tightness, and, secondly, it acts as a kind of spring. When the piston moves, it undergoes a slight deformation, but then returns to its previous state, slightly pressing it into the body. Determining the malfunction is quite simple - if you hang the wheel, it should rotate freely as soon as you press or release the brake pedal. There should be no signs of overheating on the discs themselves, otherwise you will need to repair the caliper yourself.
When conducting a visual inspection, we must make sure that there is no noticeable difference in the thickness of the outer and inner pads. The piston should move so that when pressed it easily sinks into its body. Its surface should not have noticeable traces of dirt or corrosion particles. You also need to conduct a superficial inspection of the boot and ensure its integrity.
Save the brakes: everything about caliper maintenance
They don’t brake, they jam, they get hot... At some point, the brakes, which previously pleased with the precise operation, begin to throw up unpleasant surprises. This is due to the fact that most motorists begin to deal with this unit only when problems arise, although this should be done much more often, our expert today is convinced. For obvious reasons, he asked not to give his first and last name, but he promised to clearly demonstrate what brake maintenance is in his understanding.
The main enemy is corrosion
— Let's not forget that brakes, in principle, work in very harsh conditions. During active braking, the discs can heat up to 600 degrees! The rest of the caliper parts get less, but they also constantly experience heating/cooling, and besides, disc brakes are exposed to water, dirt, salt, sand...
It is clear that the caliper working cylinder is initially protected by a boot plus an O-ring (cuff). But over time, corrosion may appear on both the cylinder itself and the piston. Yes, one of the reasons is water and dirt that enter through a damaged boot (we don’t check the rubber bands often). But due to constant heating/cooling, condensation may occur, and the protruding edges of the cylinder and piston may also begin to corrode. Like here - do you see this “fungus”? In general, for one reason or another, corrosion occurs and the surface of the cylinder is damaged.
At first, the piston begins to move with noticeable effort; over time, this problem progresses, which affects the quality of operation of the entire system. You press the brake pedal, but it is tight, you press harder, but “there are no brakes,” or they work normally every other time. The cylinder here is in very good condition, so in this case I will limit myself to running rust remover in there, then apply a special lubricant, and everything will be fine. But it is not always possible to resolve the issue this way, with little bloodshed.
Replacement or restoration?
If the problem starts, the piston generally gets stuck in the cylinder, and here you won’t get away with replacing the repair kit, which essentially consists only of rubber bands (boots and cuffs) - you need to somehow restore the surface of the cylinder, change the piston. The solution to the problem depends on the design features of the caliper, the car model, and the neglect of the issue. At a minimum, you will have to get (buy or grind) a new piston; at maximum, you will have to restore or buy a used or new caliper.
The last option is the most expensive. As a rule, people prefer to look for a used one or turn to workshops to repair or restore their parts - this turns out to be much cheaper. This is understandable: a new original or good licensed caliper for an inexpensive mass-produced model like the Opel Astra H will cost 3-4 million rubles, a used one will cost about 0.5 million, but will still require a rebuild and installation of a repair kit, so restoration is all it will still be cheaper.
By restoring a caliper, you get a new part. Pistons, guides, boots and cuffs are changed, and only the body remains old, which has been thoroughly cleaned (as a rule, they prefer to sandblast) and a new protective coating has been applied.
There are nuances...
Everything can look beautiful: pads, discs, and calipers - but the brakes “stick”! You start to figure it out and you find the reason.
If the mechanic at the station, when replacing the pads, did not carry out a complete cleaning procedure (on both sides!) of these “guides,” then it turns out that the pad simply jams in a certain position and does not brake. In order for the pad to press against the disc, you need to create additional force on the pedal - much higher than what was initially required.
I use a screwdriver so confidently now, because I have to change the disks anyway. Why? They are warped and hit when braking. And I suspect why.
There is an interesting point with some cars: the right disk is different from the left, and accordingly they have different numbers. Whoever knows this orders one right disk and one left one. Well, those who don’t know, choose any of them and order two identical (right or left) disks.
Caliper assembly (right or left) for VAZ-2108, 2115
Dear customers, in order to avoid errors when sending the front wheel brake mechanism of VAZ 2108-21099, 2113-2115 ... +, in the “Comment” line indicate the right or left caliper, the model of your car, the year of manufacture.
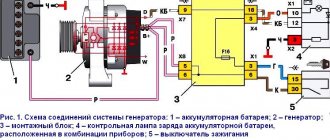
The service brake system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099, VAZ 2113, 2114, 2115 is hydraulic, dual-circuit (with diagonal separation of the circuits), with a pressure regulator 10, a vacuum booster 5 and an indicator of insufficient brake fluid level in the reservoir. If one of the brake system circuits fails, the second circuit provides braking of the vehicle, although with less efficiency.
1 – main cylinder for hydraulic brakes; 2 – pipeline of the “right front – left rear brake” circuit; 3 – flexible hose of the front brake; 4 – master cylinder reservoir; 5 – vacuum booster; 6 – pipeline of the “left front – right rear brake” circuit; 7 – rear wheel brake mechanism; 8 – elastic lever of the pressure regulator drive; 9 – flexible rear brake hose; 10 – pressure regulator; 11 – pressure regulator drive lever; 12 – brake pedal; 13 – front wheel brake mechanism.
The brake mechanisms of the front wheels 13 are disc, with a single-piston floating caliper. Currently, brake pads are available with a mechanical (acoustic) or electrical wear indicator. At the factory, cars are equipped with pads without a wear indicator or with an electric indicator (if a control unit is installed on the car).
The price is for 1 caliper assembly
Caliper VAZ-2108, 2115 right assembled, Article 2108-3501012
VAZ-2108, 2115 left caliper assembly, Article 21083501013
Pads and brake discs are not included in the delivery package.
Cars VAZ 2108, 21081, 21083, 2109, 21091, 21093, 21099, VAZ 2113, 2114, 2115 have front wheel disc brakes with a single-piston floating caliper.
Cast iron, not ventilated. Minimum thickness 10.8 mm. Attached with two guide pins to the front wheel hub flange. The back is covered with a protective cover.
They have a shaped steel base and graphite friction linings. Due to the shape of the pads, their tight fit to the guide is ensured. In addition, springs are installed on the pads, on which the caliper presses, strengthening their fixation. A wear indicator sensor (mechanical or electrical) can be installed on one of the pads.
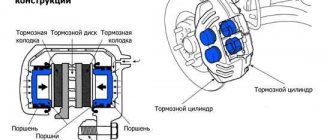
The “floating” caliper VAZ 2108-3501012 / 2108-3501013 consists of a caliper and a brake cylinder. The caliper is made of cast iron. It has a groove for the brake pads and an inspection window to visually determine their condition. It is attached with two bolts to the brake cylinder. The caliper and brake cylinder form a “floating” caliper. The “floating” caliper is connected through the pins to the brake pad guide. Due to the mobility of the fingers, the “floating” bracket floats. The pin holes are filled with grease. They themselves are bolted to the wheel brake cylinder. The fingers have protective covers called anthers.
The brake cylinder is made of aluminum alloy. A steel piston is installed inside it, sealed with a trapezoidal rubber ring. The ring is located in the annular groove inside the cylinder body. Due to the elasticity of the ring, the piston is automatically recessed into the cylinder after releasing the brake pedal. The outside of the cylinder and piston are protected by a boot.
The brake pad guide (fixed caliper bracket) is cast iron, made in the form of a bracket. Has four bosses. Two of them have threaded holes for mounting bolts to the steering knuckle. Two with blind holes-channels for the fingers of the floating caliper bracket. The pad guide has a longitudinal groove for the brake disc and openings for installing brake pads. In the openings there are shelves for the clamping springs of the pads.
The brake mechanisms of the front wheels of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars are identical to the front brakes of VAZ 2113, 2114, 2115 cars.
To improve the front brake mechanisms, you can install ventilated 2110 or 2112 instead of standard brake discs 2108. However, in this case you will have to replace the calipers with 2110 or 2112 (except for the brake cylinders) and the wheels (you will have to set them to 14 if the brake discs are 2112), since they bigger size.
The brake mechanisms of the rear wheels 7 are drums, with two-piston wheel cylinders and automatic adjustment of the gap between the shoes and the drum. The automatic clearance adjustment device is located in the wheel cylinder.
The main brake cylinder 1 is attached to the housing of the vacuum booster 5 on two studs. A translucent polyethylene brake reservoir 4 with an insufficient fluid level sensor is inserted into the holes in the upper part of the cylinder on rubber seals. The tank has markings for maximum and minimum fluid levels. Two screws are screwed into the bottom of the cylinder to limit the movement of the pistons. The screws are sealed with copper gaskets. A plug is screwed into the front part of the cylinder (along the direction of the car), which serves as a stop for the return spring and is sealed with a copper gasket. The pistons in the master cylinder are located in series, the one closest to the vacuum booster operates the left front and right rear brake mechanisms, and the one closer to the plug operates the right front and left rear. The high-pressure rubber sealing rings (cuffs) of the master cylinder and rear wheel cylinders are interchangeable (nominal diameter 20.64 mm). The low pressure sealing ring is grooved, installed on the piston in contact with the vacuum booster rod.
Vacuum booster 5 is located between the pedal assembly and the main brake cylinder 1 and is attached to a bracket, which, in turn, is fixed to the front panel of the body on four welded studs. The amplifier is of a non-demountable design; if it fails, it is replaced. The simplest way to check the serviceability of the amplifier: on a car with the engine turned off, press the brake pedal several times and, holding it down, start the engine. If the amplifier is working properly, after starting the engine the pedal should move forward. Failure to operate or insufficient efficiency of the vacuum booster may be caused by a leak in the vacuum supply hose from the intake manifold.
The brake pedal is a suspended type, fixed on the same axis with the clutch pedal, rotates in two plastic bushings, and is equipped with a return spring. The brake light switch is located above the pedal; its contacts close when the pedal is pressed. The free play of the brake pedal when the engine is not running should be 3–5 mm; it is adjusted by moving the brake light switch with the locknuts loosened.
The pressure regulator is installed under the floor and is attached with two bolts to a bracket in the left rear part of the body. The front bolt also secures the pressure regulator actuator fork bracket. Due to the ovality of the holes for its fastening, the bracket together with the lever can be moved relative to the pressure regulator, changing the force with which the lever acts on the regulator piston (see Checking and adjusting the rear brake pressure regulator drive). As the load on the rear axle of the car increases, the elastic lever is also loaded, transmitting force to the piston. When the brake pedal is pressed, fluid pressure tends to push the piston outward, which is counteracted by the force exerted by the lever. When the system comes into balance, a valve located in the regulator isolates the rear brake cylinders from the main brake cylinder, preventing further increases in braking force on the rear axle and preventing the rear wheels from locking ahead of the front wheels. As the load on the rear axle increases, when the traction of the rear wheels with the road improves, the regulator provides more pressure in the wheel cylinders and, conversely, as the load decreases, the pressure drops. There is a hole in the regulator body that is closed with a plug. Leakage of brake fluid from this hole indicates leakage of the regulator O-rings.
The floating front brake caliper VAZ 2108-3501012 / 2108-3501013 consists of a caliper and a wheel cylinder, which are tightened together with two screws. The cylinder is attached with two bolts to the pins installed in the holes of the pad guide. Lubricant is placed in these holes. Rubber protective covers are installed between the pins and the pad guide. The brake pads are pressed against the guide grooves by springs. The cylinder contains a piston with a rectangular rubber sealing ring. Due to the elasticity of this ring, a constant optimal gap between the brake pads and the disc is maintained.
Brake discs are cast iron. The minimum disc thickness during wear is 10.8 mm, the maximum permissible runout (at the largest radius) is 0.15 mm.
The rear wheel brake cylinders are equipped with a device to automatically maintain the gap between the shoes and the drum. Its main element is a steel spring split ring mounted on the piston with an axial clearance of 1.25–1.65 mm. The thrust rings (2 per cylinder) are inserted with an interference fit, providing a shear force along the cylinder surface of at least 35 kgf, which exceeds the force of the brake pad tension springs. When the brake linings wear, the pistons move the thrust rings by the amount of wear. If the cylinder mirror is damaged due to mechanical impurities in the brake fluid or corrosion (the presence of water in the brake fluid), the rings may “sour” in the cylinder, and one piston (or even both) will lose mobility. In this case, the cylinders must be replaced at the same time (it is advisable to also replace the brake fluid).
If the rear brake drums are worn out (ovality, runout, scuffing), they can be bored. In this case, the internal diameter after boring should not exceed 201.5 mm.
The parking brake system is driven mechanically, by cable, to the rear wheels. It consists of a lever, an adjusting rod, an equalizer, two cables, a pad drive lever and a spacer bar. The stroke of the lever after adjustment should be 4-5 teeth of the sector, in operation - no more than 8.
Brake mechanisms 2108-3501012/2108-3501013 are standardly installed on VAZ 2108 - 2115 cars. They can be used for tuning the brake system of VAZ 2101 - 2107 cars. They are used with non-ventilated 240 mm brake discs. The minimum wheel size that can be installed with these brakes is 13".
Other articles of the product and its analogues in the catalogs: 21080350101200, 2108350101300, 21080-3501012-30, 21080-3501013-30.
VAZ 2108, VAZ 2109-21099, VAZ 2113-2115.
Any breakdown is not the end of the world, but a completely solvable problem!
How to independently replace the front caliper assembly on a Lada Samara car
With the AvtoAzbuka online store, repair costs will be minimal.
Just COMPARE and BE SURE!!!
Don't forget to share the information you find with your friends and acquaintances, because they may also need it - just click one of the social networking buttons located above.
Repair kit
To make it easier to rebuild the Lacetti caliper, there are repair kits specially designed for it. Essentially, this is a set of small and spare consumable parts. As a rule, it consists of:
Depending on the brand of the car and the manufacturer of the kit, other elements may also be included, but the listed components are a standard set of almost any repair kit.
It is worth noting that the design of the front and rear calipers of one car is different. That is, you will have to purchase two sets. In this case, you should choose the option that best suits the car according to its documentation.
Principle of operation
The main task assigned to the caliper is to provide the necessary force to slow down or stop the vehicle. Each time the driver presses the brake pedal, a certain pressure is created in the line. It is transmitted to the caliper pistons, which, in turn, engage the pads. In this case, the mechanism ensures strictly parallel movement of the pads relative to the brake disc. As a result, the parts tightly compress the disk, which leads to slower movement.
But there is one key thing to be aware of before you move on to rebuilding your front caliper and that is friction. Since the pads clamp the rotating disc, heating cannot be avoided. Moreover, this applies to both the pads themselves and the caliper. The temperature of the brake fluid also increases. This circumstance poses serious demands to many manufacturers.
First of all, calipers must be made of a material that:
- has high strength;
- has a high degree of heat transfer;
- resistant to high temperatures.
This last point is especially important because heat usually causes objects to deform.
How much does a caliper cost for a VAZ (2109, 2110, 2114, 2115)
A brake caliper for a VAZ 2109-2115 family costs on average from 1,610 to 4,270 rubles . The cost is influenced by the brand, as well as the quality of the components used, which is reflected in the mileage without fogging and the passage of brake fluid through the piston body.
Since brakes are a key vehicle system, the need for their repair and routine maintenance is constantly increasing. The efficiency of the caliper lies not only in the installation of new pads and discs, but also in the ability to optimally act on large and small cylinders with a force of 137 kg . At the same time, at the base of the beginning of the useful stroke of the piston, where the sealing ring is located, there should be no brake leaks liquids.
When buying a caliper for the front brakes, it is important to pay attention not only to the price, but also to its material support. Some manufacturers, when creating a kit, take into account the need to provide anti-squeak lubricant, spare piston boots, retaining rings, cotter pins and return springs.
Repairing a caliper whose pistons have corrosion on the top is not possible. The use of repair kits also cannot guarantee full results. It is best to buy a new caliper assembly, thereby eliminating the piston biting to the point of breaking.
What is needed to remove the caliper
- screwdriver or bit;
- keys for 17, 14 and 10;
- pliers;
- a piece of rubber tube or bolt with a diameter suitable for the inner diameter of the brake hose tip;
- marker.
It is necessary to remove and install the caliper when replacing it in case of deformation or damage. This is also a necessary action in order to repair the VAZ 2107 caliper.
To carry out the work, you must lift the car on a lift or use a jack. The latter option is somewhat more tedious, but ideal for home use.
Examples of prices for current items
When buying a caliper for a VAZ 2109-2115, you can operate with the available amount, since there are quite a lot of good quality analogues to choose from, namely:
- Caliper assembly, R13 TRIALLI – RUB 1,880 .
- ATE assembled with a ventilated moving bracket – RUB 2,480 .
- LUCAS with an extended hose (without adapter) – RUB 4,050 .
- LADA (standard set for R13 wheel) – 4,270 rubles .
The choice of calipers is represented by more than 17 analogues, 2 original brands and 3 brands operating under AvtoVAZ license. Consequently, the price may change based on the financial policy of the manufacturer, as well as the final cost of the caliper.