I installed a “new” (used, non-functional) camshaft. I first measured the back side of the cams for runout with a micrometer. The old camshaft had an offset of the cam axis of both the intake and exhaust cams on the first and third cylinders by up to 0.06 mm (factory tolerance from various sources is 0.02, according to ZMZ documentation a maximum of 0.035). When adjusting, the feeler gauge pinched (on the back of the cams) if you turned it and became noisy during operation. The “new” shaft was measured before purchase. For all cams, the maximum runout (not displacement) was 0.01 mm. On the seventh cam it turned out to be 0.03 mm. The rocker did not change, the wear is minimal, there are no scuffs. I threw the camshaft. First, I slowly tightened all the nuts evenly so as not to load the studs, and tightened them according to the diagram (from any old book on repairing classics) with a force of 22 Nm. I installed a split bevel gear from OKB Dinamika.
I tightened the chain and adjusted the valves. I forgot the adjustment sequence))) I adjusted by bringing each cylinder to the end of the compression stroke))) The back side is still a cylinder with a known runout))) The clearance for the intake valve according to the indicator is 50, for the exhaust valve 57. It was no more than 10 degrees outside. Valve clearances depend on temperature. I took it from this tablet.
Annotation on setting up the ignition system of the VAZ 2107 with your own hands
The Zhiguli “classic” VAZ 2107 does not belong to modern cars, manufactured with the latest technology and stuffed with sophisticated electronics. This is its beauty - there is no need to contact car service specialists for any reason; most of the car maintenance work can be done by the owner himself. This also includes the procedure for the ignition option, which anyone can perform, having previously studied the detailed instructions.
When should you turn on the ignition?
The first thing you need to know is that there are no regulations for this operation, since the ignition timing is set or adjusted only as needed. It may be caused by the following reasons:
- You recently acquired a “seven” on the secondary market and are trying to “bring it to mind.”
- After repairing the engine, which included disassembling it.
- After unscrewing or removing the head ignition distributor (distributor), regardless of the reason why it was made.
- When switching from high-octane fuel to gasoline with a lower octane number and vice versa.
- After replacing the contact group or bearing in the distributor (in cars with an old ignition system).
Note. On VAZ 2107 vehicles equipped with an electronically controlled injector, a prerequisite for checking the spark generation system can be the flashing of the Check Engine display on the instrument panel. True, it behaves in a similar way when a dozen more malfunctions occur. So ignition problems must first be diagnosed by contacting a service station.
In the vast majority of cases, set as a result of a violation of the settings after disassembling or repairing the engine. A separate issue is the transition to high-octane gasoline, which requires ignition with greater advance, for which adjustments are being made.
It is advisable to check the timely formation of a discharge on the electrodes of the spark plugs in cases where unstable engine operation is observed, popping noises are heard in the carburetor and exhaust pipe, accompanied by an increase in fuel consumption. If you have not yet discovered the “gluttony” of the car, then pay attention to the color of the smoke; with high gasoline consumption, it is black, as is the carbon deposits on the electrodes of the spark plugs.
Reasons for proper tightening
As noted above, tightening is carried out after disassembling the cylinder head, and it, in turn, is most often performed when it becomes necessary to replace the gasket in model 2107. In most cases, a malfunction of the element in question is grounds for prohibiting further operation of the vehicle.
A very common problem is wear of the gasket in the area between the lubrication channels and those responsible for the circulation of antifreeze. In this situation, mutual contamination of working fluids occurs. The characteristic symptoms are:
- oil dilution and a drop in its level;
- change in the shade of antifreeze (it begins to look like tea).
Such a breakdown requires urgent repair.
The second variant of the VAZ-2107 malfunction is loss of tightness in the area between the cylinders themselves and the coolant supply system. Typically the culprits here are:
- defective cylinder head gasket;
- insufficient tightening torque.
Regardless of this, the same thing happens - air enters the cooling system, and after that:
- coolant temperature rises;
- The distribution tank is literally boiling.
Much less often, the gasket is destroyed in the space between the cylinders. Signs of a malfunction include a drop in compression and unstable operation of the engine.
Many people look for the reasons for the failure in other places if they have recently replaced the cylinder head gasket, but this is just a waste of effort. The fact is that now such elements are often of low quality, and are sometimes produced in artisanal conditions. As a result, the seal fails in a matter of months. Take a close look to see if there are any leaks of antifreeze in the space between the cylinder block and the engine. If so, try tightening the bolts. When this measure does not help, then most likely the problem is an uneven gasket.
Types of systems
For decades, while the VAZ 2107 model was produced (from 1982 to 2012), it was equipped with three types of ignition systems:
- mechanical with contacts - breakers;
- contactless;
- controlled by an electronic unit (ECU).
Note. The first 2 varieties were installed on the “seven” with a carburetor, the latter was introduced together with an injector.
See:
In the mechanical version, the contacts opened by the cam of the distributor shaft break the low voltage circuit, initiating the formation of a powerful pulse in the secondary winding of the coil. This discharge is directed to the electrodes of the spark plug, which ignites the fuel in the cylinder where the piston has risen to top dead center (TDC) and the compression stroke is completed.
The contactless circuit operates on the same principle, only the signal to break the circuit is supplied by the Hall sensor, and it is implemented by the switch. Therefore, setting the ignition on carburetor “sevens” is done almost identically. Another thing is cars with an injector, where a new system has been introduced that does not have not only contacts, but also a distributor and any moving parts. Here, the moment of spark formation is determined by the ECU controller, which is guided by the signals of various sensors.
Self-tightening of VAZ 2108 cylinder head bolts instructions, photos and videos
In order for a car to always work correctly, all its components must function properly. This is especially true for the power unit. If you want to know how the VAZ 2108 cylinder head bolts are tightened, why is this necessary and what is needed for this? Our resource will help you understand these issues.
In what cases is tightening needed?
Most domestic drivers do not understand for what purpose this procedure needs to be performed, what order must be followed and what the tightening torque should be. However, every driver should know that incorrect actions during this process can damage the cylinder block. Accordingly, this procedure should be treated with all care and responsibility.
Just a few years ago, vehicle manufacturers were required to tighten the cylinder head bolts during the first maintenance of the vehicle. But now this need has disappeared and now it falls entirely on the shoulders of the drivers. If you are the owner of a VAZ 2108, then this procedure should be carried out from time to time. In what cases is it needed:
- If an oil stain appears in the place where the cylinder head connects to the block itself. This indicates a leakage of consumable fluid, which can be a consequence of both wear of the gasket itself and loosening of the pins.
- If you have done engine repairs. Sometimes even qualified specialists can make such mistakes. Therefore, the owner of a VAZ 2108 may find this information useful.
- For verification purposes. Experienced car enthusiasts recommend tightening the bolts at least every 2 thousand kilometers. In practice, there are cases when during the operation of the VAZ 2108 the pins loosen on their own.
Thus, if you notice a leak of engine fluid in the place where the head connects to the cylinder block, first of all you need to check the tightening torque of the pins.
Procedure and diagram
We advise you to tighten the torque of the screws if you have ever encountered such a process. The following will describe the general procedure for the Lada 2108, but it should be noted that each engine has its own operating nuances that need to be taken into account.
Necessary tools
You will need a torque wrench for this procedure. This tool is needed specifically for tightening screws and determining torque. It can be purchased at any specialized store, and its price fluctuates around 1,300 rubles (approximately 400 hryvnia).
Sometimes so-called “masters” say that it is not necessary to use a torque wrench for this procedure. They say that an ordinary wrench will work just fine, and in general, you can tighten the screws “by eye.” Naturally, it will be possible to tighten the screws, but it will be incorrect, and later this may cause other problems.
Stages
If you feel that the quality of the head screw is poor, then do not even try to tighten it. Replace it immediately to protect yourself from possible problems. In addition, before the actual procedure, you should check the quality of the thread. It is also advisable to lubricate it. Do not forget that reusing spring parts is unacceptable, since in this case you will not achieve normal tension.
The stages of tensioning the pins on the Lada 2108 are similar to those performed on classic car models. The diagram is provided below. The process itself should begin with the central bolts. It takes place in four steps.
- Using the above tool, all cylinder head bolts must first be tightened to a torque of 2.0 kgf*m. First, the two middle elements are tensioned, then the two lower and two upper ones, which are located on the sides of the middle bolts. Then you need to tighten the two leftmost and two rightmost screws, starting with the bottom ones. The order should be exactly like this. The numbers on the diagram indicate the order of the components.
- Then, in the same order, using the same tool, you need to tighten the components with a torque of 7.5 - 8.5 kgf*m.
- After this, all pins must be tightened 90 degrees.
- Then they should be turned again, again by 90 degrees.
Preparatory stage
To set the ignition on a VAZ 2107 , no special conditions are required; the operation can be done both in the garage and on the street, including in winter. For work, prepare the following set of tools:
- flat screwdriver;
- metal probe 0.35 mm thick;
- open-end wrench size 13 mm;
- a car light bulb designed for a voltage of 12 V with wires soldered to it;
- a wrench with a long handle designed to turn the crankshaft;
- key for unscrewing spark plugs.
Note. Instead of a special key to rotate the crankshaft, you can use a regular open-end wrench measuring 36 mm. If you don’t have such a key, then you will have to set the marks in the old proven way: by engaging 4th gear and raising the rear wheel, turn it manually, thereby turning the crankshaft.
Ideally, it is better to have in your arsenal a device for setting the ignition on a running engine - a strobe light. It is equipped with a lamp that flashes simultaneously with the moment of spark formation in the cylinder, which allows you to see the position of the notch on the crankshaft pulley at idle speed and clearly adjust the advance angle.
Important point. The ignition is set in order to ensure that the spark appears in a timely manner and the engine starts, after which additional adjustments will be required. But the latter will not bring you the desired result when there is no compression in the cylinders or problems with the carburetor make themselves felt. If these faults are not eliminated, the engine operation will remain unstable, no matter how you configure the spark generation system.
Hence the conclusion: you can set the ignition correctly at any time, but to set it well - only on a working engine and carburetor.
ICE theory: Motor 2103 with head 21214 with reg. star (modern)
2:17 — How to measure compression 9:55 — How to install an adjustable sprocket 10:00 — How to set up a split gear.
VAZ 2107 injector - treatment of tripping and misfires
Diagnostics revealed that the fourth gasoline injector was clogged, tripping and multiple misfires in all.
ENGINE
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, N.m (kgf.m) |
| Cylinder head bolt | M12x1.25, | See Engine section |
| Nut of the stud securing the intake and exhaust manifolds | M8 | 20,87–25,77 (2,13–2,63) |
| Tension roller nut | M10x1.25 | 33,23–41,16 (3,4–4,2) |
| Camshaft bearing housing stud nut | M8 | 18,38–22,64 (1,87–2,31) |
| Camshaft pulley bolt | M10x1.25 | 67,42–83,3 (6,88–8,5) |
| Accessory housing mounting screw | M6 | 6,66–8,23 (0,68–0,84) |
| Nuts of the studs securing the outlet pipe of the cooling jacket | M8 | 15,97–22,64 (1,63–2,31) |
| Main bearing cap bolt | M10x1.25 | 68,31–84,38 (6,97–8,61) |
| Oil sump bolt | M6 | 5,15–8,23 (0,52–0,84) |
| Connecting rod cap bolt nuts | M9x1 | 43,32–53,51 (4,42–5,46) |
| Flywheel bolt | M10x1.25 | 60,96–87,42 (6,22–8,92) |
| Coolant pump mounting bolt | M6 | 7,64–8,01 (0,78–0,82) |
| Crankshaft pulley bolt | M12x1.25 | 97,9–108,78 (9,9–11,1) |
| Coolant pump inlet pipe mounting bolt | M6 | 4,17–5,15 (0,425–0,525) |
| Muffler exhaust pipe fastening nut | M8 | 20,87–25,77 (2,13–2,63) |
| Nut securing the flange of the additional muffler | M8 | 15,97–22,64 (1,63–2,31) |
| Nut securing the clutch cable to the bracket | M12x1 | 14,7–19,6 (1,5–2,0) |
| Nut of a bolt of fastening of a forward support of the power unit | M10x1.25 | 41,65–51,45 (4,25–5,25) |
| Nut of the bolt securing the left power unit support | M10x1.25 | 41,65–51,45 (4,25–5,25) |
| Nut securing the left support bracket to the power unit | M10x1.25 | 31,85–51,45 (3,25–5,25) |
| Nut securing the rear support of the power unit | M10x1.25 | 27,44–34 (2,8–3,47) |
| Nut of the bolt securing the rear support bracket to the power unit | M12x1.25 | 60,7–98 (6,2–10) |
| Bolt securing the oil receiver to the main bearing cover | M6 | 8,33–10,29 (0,85–1,05) |
| Bolt securing the oil receiver to the pump | M6 | 6,86–8,23 (0,7–0,84) |
| Oil pump mounting bolt | M6 | 8,33–10,29 (0,85–1,05) |
| Oil pump housing bolt | M6 | 7,2–9,2 (0,735–0,94) |
| Oil pump pressure reducing valve plug | M16x1.5 | 45,5–73,5 (4,64–7,5) |
| Oil pressure warning light sensor | M14×1.5 | 24–27 (2,45–2,75) |
| Carburetor mounting nuts | M8 | 12,8–15,9 (1,3–1,6) |
| Cylinder head cover nut | M6 | 1,96–4,6 (0,2–0,47) |
Tuning on carburetor modifications of the VAZ 2107
All old textbooks on servicing classic Zhiguli models describe a method for setting the moment of spark formation using a light bulb, although experienced motorists can easily do without it. You will understand why this happens as you read this material, but for beginners it will be useful to familiarize yourself with the old proven technique.
To correctly set the ignition of the “seven”, you need to ensure that the following conditions are met simultaneously:
- the notch on the crankshaft pulley is opposite the long mark on the timing cover;
- in this case, the round mark marked on the camshaft chain drive gear coincides with the boss on its body;
- the piston of the 4th cylinder has completed the compression stroke and is at top dead center;
- the contacts inside the distributor are open;
- The movable contact of the slider faces the fixed contact on the distributor cover, where the wire from the spark plug of the 4th cylinder is connected.
Note. On non-contact systems, at this moment the Hall sensor sends a signal to the switch to break the low voltage electrical circuit, which leads to the appearance of a high voltage pulse on the wire leading to the spark plug of the 4th cylinder.
The light bulb is used to control the ignition timing, for which it must be connected with one wire to the “K” contact of the high-voltage coil, and with the second to the vehicle ground. You should know that at the same moment the piston of the first cylinder is also in the TDC position, only there the air-fuel mixture is not compressed, but exhaust gases are released after its combustion. This is why ignorant car enthusiasts often confuse the first cylinder with the fourth when installing the ignition.
When the above actions occur simultaneously, a spark discharge occurs on the electrodes of the spark plug of the 4th cylinder, as evidenced by the flash of the connected light bulb. To achieve these conditions and set the ignition correctly, follow the instructions:
- Turn the crankshaft with a 36 mm wrench, aligning the notch on the pulley with the long notch on the timing cover.
- If at this moment the engine valve cover is removed, then it is better to navigate by the mark on the camshaft gear, placing it opposite the housing boss.
- Take the ignition distributor, remove the cover and turn its shaft to place the slider opposite the wire leading to cylinder No. 4 (there are cylinder number markings on the cover). Insert the distributor into the engine hole, holding the slider and housing in this position, and then secure it with a 13 mm wrench nut.
- Connect the light bulb wires and turn on the ignition by turning the key. Loosen the nut securing the distributor and slowly turn it by the housing until the lamp flashes, indicating the moment of sparking. Reattach the distributor.
- Turn off the ignition and make sure that the contacts inside the distributor are currently open. Take a 0.35 mm feeler gauge and check the gap between them, if necessary, adjust it by loosening the fastening screws with a screwdriver.
Signs of Camshaft Wear
The operation of the camshaft is associated with constant exposure to high loads, as a result of which the part gradually wears out and requires replacement. The need for repair arises when characteristic symptoms appear:
- knocking when the engine is running under load;
- reduction in power indicators.
There are a number of reasons why the RV fails:
- natural wear and tear;
- low-quality motor oil;
- low oil pressure in the lubrication system;
- insufficient oil level or so-called oil starvation;
- engine operation at high temperatures, which leads to deterioration of the lubricant properties;
- mechanical damage (wear or broken chain).
The main malfunctions that impair the performance of the camshaft are scuffing on the working surfaces (journals and cams) and deterioration of the limiter.
It is quite problematic to determine from the sounds coming from the engine compartment that the problem is related specifically to the camshaft, but it is still possible. The knocking sound of the engine resembles the dull blows of a hammer, which become more frequent as the engine speed increases. However, the best way to diagnose a shaft is to dismantle, disassemble and troubleshoot it. During inspection, the shaft should not move in the housing relative to the axis, otherwise a dull sound will be produced when hitting the limiter.
Video: reasons for the longitudinal play of the VAZ camshaft
Power reduction
The drop in power on classic Zhiguli cars is a phenomenon caused by wear of the camshaft and rockers. With proper engine operation (timely oil changes, monitoring its level and pressure), the problem only appears over long vehicle runs. When the cams wear out, the required phase width and valve lift at the intake are no longer ensured.
The RV can become deformed under extreme heat, which is caused by problems in the cooling and lubrication systems. At first, the problem may manifest itself as a knocking sound. Therefore, if there is a suspicion of this breakdown, for example, the motor has overheated, then it is recommended to diagnose the shaft in order to avoid more serious troubles with the engine timing belt.
Timing marks on the injection VAZ 2107
The gas distribution mechanism and its drive of the seven engine produced by the Volzhsky Automobile Plant remained the same - chain. Extraction and excessive wear of the timing chain on the VAZ 2107 power unit by the injector-type power supply system leads to:
- difficulty starting the engine;
- unstable operation in all modes, especially at idle;
- a sharp increase in fuel consumption;
- formation of carbon deposits on valve seats;
- Damage to the injection control system sensors and catalytic converter may occur.
In order to avoid the negative consequences of weakening or stretching the chain drive of the VAZ 2107 car engine, it is necessary to carry out routine maintenance in a timely manner. The list of maintenance operations for the power unit with the injector power system is determined by the service book. The condition of the timing chain and the gaps between the camshaft cams and valve levers is monitored every 30 thousand km.
On warranty VAZ 2107 with an injector-type power system, such work is best carried out at an authorized auto repair center. If malfunctions occur due to the fault of the car plant, they will be eliminated at the expense of the manufacturer. At the end of this period, maintenance of the timing belt and other vehicle systems can be performed independently.
Where can this work be done and with whom?
The work can be done either in a workshop or with the help of a private trader. The most basic things can be adjusted at a car service center. At the moment they are present in all cities. Usually they advertise on the Internet and an order can be made either via telephone, online messages or by coming in person to the specified address. But at the same time, ordinary adjustment does not require any very specialized tools. All you need are keys, dipstick, gasket. Therefore, this work can also be done by private owners, in garage cooperatives.
Preparation for service operations
Control of the tension of the chain drive of the gas distribution mechanism begins on an engine with a power system such as an injector or carburetor, similar to each other. The operation is performed in the sequence established by the manufacturer:
- We place the car on a flat area with a hard surface and fix its spontaneous movement by installing chocks under the wheels and applying the parking brake. Set the gear shift lever to the neutral position.
- Remove the cover from the cylinder head by unscrewing all the nuts along its contour using a tubular wrench. It is recommended to replace the old gasket; the use of sealants is not allowed.
- Using a key set to “38”, we turn the crankshaft of the VAZ 2107 engine in order to align the marks on the moving parts and the stationary ones. Care must be taken when performing this action, and the locations of the control points should be illuminated with a flashlight or carrying device.
- We combine two marks: the first is on the generator drive belt pulley with a special protrusion on the cover body, the second is on the upper sprocket of the gas distribution mechanism of the VAZ 2107 power unit with an injector power system.
With this relative arrangement of parts, the piston of the fourth cylinder is at the dead center at the top. Now you can begin performing service work on engine systems, in particular, timing belt and some others.
Installing a new shaft
The new camshaft must be lubricated with engine oil before installation.
- Check the lever springs. If they are broken or bent, replace them.
- Screw the adjustment bolts into place.
- Install the springs, then attach the rocker to them.
- Now you can insert the camshaft with housing. Lubricate the levers, cams and journals of the camshaft with oil. Fit them on and tighten them with a torque wrench. The procedure is performed from the center to the edge. Tightening torque – 2 kgf*m.
The diagram for tightening the camshaft nuts of the VAZ 7 model is in the photo
Diagram of the camshaft nut tightening order
Performing powertrain maintenance
[ads1] A number of operations and repairs are carried out on a vehicle prepared in this way, including the following:
- Tensioning the timing chain, as well as replacing its components and parts, both on power units with a carburetor-type and injector-type power supply system.
- Adjustment of the valve, or rather, the thermal gap between the camshaft cams and the rocker arm. In this case, marks on the timing parts are placed at the beginning of the procedure and at the end of it.
- When setting up the ignition system of the power unit, in this case, to achieve the best result, it is recommended to use a special device - a tester.
VAZ 2107 cars with injection engines are still produced at enterprises in our country. They are highly reliable and economical at an affordable price, which is what determines their high popularity among consumers.
Replacing the front oil seal
It is recommended to replace the front oil seal yourself in the following sequence:
- use a screwdriver to remove the oil pump;
- remove the worn oil seal from the cover of the removed pump using a screwdriver;
- By resorting to the frame, a new part is installed in place of the worn one. The outer size of the new element should not exceed 41 mm; during installation, the working edge should be directed inside the pump;
- After making sure that the oil seal is well pressed, the oil pump is installed in its original place.
At this stage, the process of replacing the front valve that has become unusable is completed.
How to set the timing belt on a VAZ 2107 by marks
To perform some repair and adjustment work on the VAZ 2107 engine, the gas distribution mechanism must be set to the marks. They are applied to both the camshaft gear and the crankshaft pulley. To perform this work, we will need to perform some preliminary actions, namely, removing the valve cover from the engine.
To do this, use a head with a knob to unscrew all the fastening nuts that are located along the entire perimeter of the cover and remove it, after which you should pay attention to the camshaft gear. It is necessary that the protrusion on the cover exactly coincides with the mark on the star, which is clearly shown in the photo below:
To turn the camshaft, you can use either a large wrench and turn the ratchet, or you can use your hands to grasp the crankshaft pulley.
We also immediately pay attention to the marks on the crankshaft and the central mark of the housing of the front engine cover - they must also match.
It is with this position of the pulley and timing star that cylinder 1 or 4 is at TDC - top dead center. Now you can begin to carry out those procedures that are planned next, either setting the ignition, or adjusting valve clearances, etc.
How to understand that the camshaft needs to be changed?
You can determine a camshaft malfunction without opening the hood by two signs:
- knock;
- reduction in engine oil pressure.
The main reason for malfunctions in the camshaft is the appearance of gaps. They appear between the shaft bearing journals and the bed bearings on which the camshaft rests. The cracks are formed due to the fact that parts of the camshaft are worn away. Gaps cause the shaft to move in the vertical or horizontal axis. If the shaft play is 1 mm, then this affects the operation of the engine. Reasons for the appearance of gaps:
- the camshaft was not replaced in a timely manner;
- do not change the oil on time;
- use of low-quality oil;
- the driver drives at low speeds, so little oil enters the timing belt and parts wear out faster.
Wear of the rocker in the form of a scuff Ring scuff on the main journal of the camshaft The valve stem left a ring mark
The camshaft also needs to be changed if the oil channels in it are clogged. Before changing the part, look for any play, fracture, deformation or scuffing of the shaft.
How to tighten a hub nut without a torque wrench
Many car enthusiasts, when repairing their car, consider it not advisable to purchase torque wrenches or other specialized devices (pullers, etc.). There is a good way to tighten the fastener to the required torque without using a torque gauge. The following devices will be required: 1. Ratchet with a head for a lock nut; 2. Pipe for extending the ratchet to create the required “shoulder”; 3. Roulette; 4. Marker; 5. A weight that can be hung on the “shoulder” (for example, a 32 kg weight).
The essence of the method is to calculate the moment using the formula from elementary physics classes:
P is the applied force, N; l is the distance from the hub to the point of application of force - the “shoulder”, m. The ready-made formula for our case will be as follows:
P1 = (M2•100)/(M1•10) ( • 10 (or • 9.8) - translated into Newtons), where
P1 is the distance at which the sinker is attached to the “shoulder” relative to the torsion point, cm; M1—cargo mass, kg; M2—required torque, N•m.
Calculation example for a Ford Focus 2 car
P1 = (M2•100)/(M1•10) (•10 (or •9.8) = (45•100)/(32•10) = 4500/320 = 14 cm. Conclusion: to ensure a tightening torque of 45 N•m will require a sinker weighing 32 kg, located on the pipe at a distance of 14 cm.
- First screw on the locknut and tighten it slightly.
- We mark a distance of 14 cm, where the rod should hang;
- We hold the ratchet with one hand and hang the sinker with the other, thereby tightening the fastening;
- The operation continues until the fasteners stop tightening under weight, which means that we have achieved the required force. Accuracy +/- 5%.
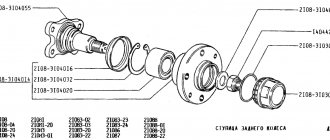
Rear wheel bearing
Structurally, the rear hub of the Lanos uses a pair of roller angular contact bearings. This type of bearing is very torque critical. An undertightened or overtightened bearing does not last long. The service manual indicates the following sequence for tightening the rear wheel bearing:
1) Tighten 20 Nm (2 kgf) 2) Release 180 degrees 3) Tighten 1 Nm (0.1 kgf)
The rear hub is easy to tighten without using a torque wrench - by hand. Tightening MUST be done with the wheel installed!
Mark a distance of 25 cm on the ratchet. At this distance we will apply force when tightening (see footnote). For this, you can use household spring scales, although with some experience you can not use scales. The main thing is not so much the exact tightening torque, but rather the fact that the bearing is tightened in such a way that the thermal gap is maintained
.
— Tighten the bearing by rocking the wheel with an approximate force of 8-10 kg. When turning the wheel, you should feel resistance to rotation. That. We are trying to install bearings. - Release it half a turn. -Tighten to 500 grams or slightly higher. We focus on the fact that the wheel rotates without effort
IMPORTANT!
When rocking the wheel, we should not feel any play. Next, we loosen the nut a little to align the hole for the cotter pin, while rocking the wheel. We must achieve very slight radial play. It should be felt when the wheel rocks, literally on the verge of play appearing. Although this is actually not a backlash, but the same thermal gap.