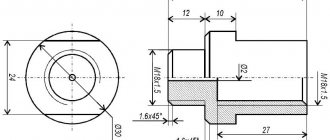
clutch bolt – 19 Nm
bearing cap – 68 Nm (main) and 53 (rod)
cylinder head – three stages 29 Nm, 49 Nm and 90°
The operating manual from the manufacturer includes information on lubricants and coolants. In particular, for these engines it is recommended:
Installation 11183 under the hood
By default, the engine circuit contains a potential of 120 - 160 hp, so upgrading it yourself is possible. The 11183 is unpretentious in operation, the power was added initially by the manufacturer, the compression ratio and compression are standard.
Design Features
After modernizing the 21114 engine taken as a standard, the 11183 engine has the following design nuances:
Cylinder head 11183
To reduce manufacturing costs, a connecting rod-piston group, a pulley and a crankshaft flywheel from the 2110 engine are installed in the engine. The volumes of the combustion chambers are increased for the engine with the sole purpose of ensuring a compression ratio of 9.6 - 10.0.
The manufacturer does not provide hydraulic compensators in this internal combustion engine, therefore, on the one hand, the use of lower quality oil is allowed. On the other hand, the savings in the operating budget when using cheap lubricants are “eaten up” by the costs of periodically adjusting the valves in a service station, since the manufacturer recommends doing it more often.
The main attachments are driven by their own belts. The design of tensioners (for example, a generator) leaves much to be desired. But the internal combustion engine allows you to increase power in the following ways. Moreover, a reasonable boost does not require major repairs to be carried out more often than the established deadline.
Belt drive of the generator
Even without improving the characteristics, the motor is high-torque and torquey, and produces 200% of the resource declared by the manufacturer. The available repair dimensions of the piston group make it possible to increase the service life, taking into account several overhauls, up to a million kilometers.
Overall figures between 21116 and 11186
Both the engine with the index 21116 and the engine 11186 have the same performance in relation to:
Both engines have the same problems:
Both Lada Granta with engine 11186 and Priora with engine 21116 consume fuel:
The engines do not have hydraulic compensators, so the valves need to be adjusted after 15,000 km. mileage _ And for ShPG it is necessary to exclude shock loads. Engines love only high-quality fuel, the reason is a high compression ratio and a tendency to detonation.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantage of the 11183 engine is the cylinder head of the original design. However, it was subsequently further modified into the ICE 11186, adding volume to the combustion chambers. The downside is the generator belt tensioner - the drive is constantly over-tightened, a deflection of 10 mm is not ensured without slipping, so the belt life is reduced and it has to be changed more often. This defect was corrected only in the next version of the motor 11186.
The integrated catalytic collector assembly in the engine was initially unfinished:
Catcollector 11183
When installing the engine on the Lada Granta, the cabin heat exchanger was connected to the thermostat in series. All the coolant passed through it along a small circuit, the response temperature error was 5 degrees instead of the required 2 degrees.
Engine characteristics VAZ 21116 1.6 8V Granta, Kalina 2
| Configuration | L |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Volume, l | 1,597 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 82 |
| Piston stroke, mm | 75,6 |
| Compression ratio | 10,5 |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 (1-inlet; 1-outlet) |
| Gas distribution mechanism | SOHC |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Rated engine power / at engine speed | 66 kW-(90.0 hp) / 5600 rpm |
| Maximum torque/at engine speed | 143 Nm / 3500 rpm |
| Supply system | distributed injection with electronic control |
| Recommended minimum octane number of gasoline | 95 |
| Environmental standards | Euro 4 |
| Weight, kg | 112 |
Engine design
Four-stroke engine with distributed fuel injection; with an in-line arrangement of cylinders and pistons rotating one common crankshaft; with overhead camshaft. The engine has a closed-type liquid cooling system with forced circulation. Combined lubrication system: under pressure and splashing.
Cylinder block
The block is cast from high-strength cast iron. Cylinder numbering is carried out on the installation side of the crankshaft pulley. Each cylinder, based on the results of measuring its diameter, is assigned a size class.
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Material | ductile iron |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 82 |
| Intercylinder distance (distance between the axes of adjacent cylinders of the block), mm | 89 |
| Block height (distance between the upper plane of the block and the axis of the crankshaft), mm | 197,10 |
| Diameter of boring of crankshaft supports (for main bearings), mm | 54,52 |
| Weight, kg | 31,000 |
The cylinder block, although with its own index, is exactly like that of the VAZ-21126 engine: with additional nozzles for cooling the pistons with oil and plate-honing of the cylinder walls, which reduces the break-in time. Wall processing is carried out in accordance with the requirements of Federal Mogul. Block 21116 has three classes every 0.01 mm (A, B, C). The cylinder class mark is located on the bottom plane of the block.
connecting rod
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Length, mm | 133,32 |
| Upper head hole diameter, mm | 18 |
| Weight, g | 410 |
The connecting rod is not divided into classes based on the diameter of the upper head hole; there is no such marking on it. Connecting rods are divided into classes based on weight. The marking is stamped on the upper head of the connecting rod (F, L, B, X, M, V, C, N, G). The difference in weight between classes is ±7 grams. For engine 21116, it is possible to install connecting rods with two or three marks.
Piston
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Diameter, mm | 82 |
| Compression height, mm | 25,4 |
| Weight, g | 243 |
Base engine
Throughout the entire production period, engines are improved, adding more power. The introduction of a 39% lighter piston group on the 11186 engine made it possible not only to achieve an increase in power of 7 hp. s., but also reduce fuel consumption, improve elasticity and torque by 20 Nm throughout the entire speed range. Higher traction allows you to change gears less frequently and accelerate faster at crankshaft speeds above 1500.
A modification of the VAZ 11183 engine is currently installed under the hood of the Lada Granta car in the basic configuration and on the Lada Kalina. Engine Specifications:
Both Lada Granta engines - 11186 and 21116 - have good efficiency: 7-7.5 liters per 100 km. The fuel used is AI95, although many owners successfully operate the car on 92-octane gasoline. The valve mechanism of both models has 2 valves per cylinder, and in the 21st century this design has long been considered obsolete. Therefore, the manufacturer relies on high structural reliability and long service life of the motors. The mileage officially declared by the manufacturer before the first major overhaul is 150 thousand km, although in practice the engines run 250 - 300 thousand.
As a rule, Lada Granta power units are not subject to extreme overloads and are considered relatively trouble-free engines. The engine has good tuning potential: up to 120 hp. With. without loss of resource and up to 180 hp. With. with some reduction in durability. Among the disadvantages of the engine, the increased demands on valve adjustment and noise reminiscent of diesel stand out. Also, the engine may stall, knock, overheat, etc.
If the timing belt breaks, the valves are rarely damaged unless the engine has been fitted with a sports camshaft.
Tuning
Initially, the manufacturer builds additional potential into its engines in order to make any changes in future versions. However, the 11186 engine can be upgraded on its own. The following type of tuning is considered standard:
- camshaft - replacement of a standard part with a Nuzhdin 10.93 or Dynamics 108 camshaft;
- cylinder block - boring to 86 - 88 mm (pistons and connecting rods of appropriate sizes will be required);
- intake manifold - zero resistance filter, damper with a diameter of 54 mm, grinding of the internal surfaces of the channels;
- catcollector - replacement with a spider having a 4:2:1 scheme;
- Timing - installation of T-shaped lightweight valves;
- Cylinder head – head milling.
Tuning that adds 30% of power is considered safe (“resource-producing”) for the engine. That is, for 87 hp. With. it will be 29 liters. s., which results in about 115 hp. With. Further tuning becomes dangerous, since the service life will decrease in arithmetic progression. This method is used by athletes, but not by ordinary car enthusiasts.
Thus, the 11186 motor has one significant drawback - it bends the valves. The manufacturer partially corrects the situation through high-life timing belts from Gates. In other respects, the internal combustion engine was superior to its existing counterparts at that time, with the exception of the 21114 engine, which was taken as the basis.
Tools:
- 5 mm hex key
- Ratchet wrench
- Extension
- 8 mm head
- 10 mm head
- 13 mm head
- Torx head E14
- 15 mm straight box spanner
- 17 mm straight box spanner
- Curved box spanner 8 mm
- Torque wrench
- Driver for socket attachment
- 17mm wrench attachment
- Medium flat screwdriver
- Medium Phillips screwdriver
- Screw jack
- Wheel key
- Special wrench for turning the tension roller (or circlip remover)
- A key for fixing the camshaft pulley (or an extension for the end attachment on the wrench)
- Knife (or scraper)
- Funnel
- Universal puller (if necessary)
- Calipers
- Valve adjustment tool
- Tweezers
- Micrometer
Parts and consumables:
- Shoe - 2 pcs.
- Technical capacity
- Coolant
- Head gasket
- Head bolts (if necessary)
- Engine oil
- Shims (if necessary)
- Rags
Notes:
If a leak of engine oil or coolant is detected at the junction of the cylinder head with the cylinder block, remove the head and replace its gasket. A leak can also occur due to warping of the block head due to overheating. The cylinder head gasket of the VAZ 11183 engine is made of metal asbestos sheet, and on the VAZ 21116 and VAZ 11186 engines it is metal. The procedure for replacing the cylinder head gasket on a Lada Granta car on all three engines is the same and is shown using the example of a VAZ 11183 engine. Replacing the cylinder head gasket of a VAZ 21126 engine is described separately.
The cylinder head gasket is a one-time use product, so the gasket must be replaced each time the cylinder head is removed.
1. Set the piston of the 1st cylinder to the TDC position of the compression stroke, then leave the front timing cover removed.
Maintenance
According to AvtoVAZ recommendations, the 11183 engine must be serviced according to the regulations:
| Maintenance object | Time (month) or mileage (10,000 km), whichever comes first |
| Timing drive | 36/ 1 |
| Battery | 12/2 |
| Valve clearance | 24/2 |
| Crankcase ventilation | 24/2 |
| Belts that drive attachments | 24/2 |
| Fuel line and tank cap | 24/2 |
| Engine oil | 12/1 |
| Oil filter | 12/1 |
| Air filter | 12 – 24/4 |
| Fuel filter | 48/4 |
| Heating/cooling circuits | 24/4 |
| coolant | 24/4 |
| Oxygen sensor | 10 |
| Spark plug | 12 – 24/2 |
| Exhaust manifold | 12/1 |
By default, the cooling system has a volume of 7.8 liters. Red Felix Carbox 40 antifreeze is usually poured on the conveyor. Replacement is made with any coolant, taking into account the temperature range of 85 degrees. Since the internal combustion engine device is quite simple, the maintenance operation can be performed on your own.
Possibilities for engine modification and tuning
As an option to increase engine power, it is possible to carry out chip tuning in order to remove restrictions on the environmental class. The overall percentage of power increase will not exceed 2-5%.
Replacing the camshaft. It is not economically feasible, just like installing a turbocharger. Replacing the camshaft and receiver will remove 100 hp from the engine. If you additionally modify the cylinder head channels, you can gain an additional 20 hp.
To carry out such modifications, it is first necessary to change the engine design from SOHC to DOHC. That is, it is necessary to replace the cylinder head with a 16 valve with two camshafts. Such a replacement will increase the possible power of the 8-valve engine to 120 hp. without significant impact on the overall engine life.
In fact, modification of the engine comes down to converting it into a 16-valve version with the possibility of further refinement and increased power.
New Lada: Adjusting headlights on a Lada Granta with your own hands - video and photos
Frequency and signs of replacement
There is no specific time frame for replacing the cylinder head gasket on the Lada Kalina. Over time, it can become unusable under the influence of various factors. The gasket can break through in different places and, depending on the location of the crack, the signs of damage will be different. The symptoms will be the same for both 8-valve and 16-valve engines.
Symptoms of gasket damage:
- When the gasket breaks along the side of the cylinder circumference, gases begin to escape outward. At the same time, the noise level of the VAZ Kalina engine increases sharply, which will be immediately noticeable to the driver.
- A hole between the cylinders disrupts the operating mode and the engine begins to operate unevenly and triple.
- Destruction of the gasket with a rupture entering the coolant supply channels. At the same time, gases begin to enter the cooling system. One of the external signs of such a problem will be a decrease in the fluid level and the appearance of white steam in the exhaust gases. Gas bubbles may appear in the expansion tank. Another sign is the appearance of an emulsion in the oil, accompanied by an increase in the level of lubricant in the crankcase. Oil can also go into the cooling system, which is easy to detect by its presence on the surface of the liquid in the expansion tank.
- Another indirect symptom of a gasket burnout is the appearance of stains or leaks of oil or coolant on the parting line of parts and on the side surface of the engine crankcase.
Malfunctions: causes, elimination
If the timing belt of the drive breaks, the 11183 motor does not bend the valve, but it has the following typical breakdowns:
| Floating speed | 1) malfunction of the ignition module 2) breakdown of the gasket 4) failure of the TPS sensor | 1) replacing the module 2) installing a new gasket 4) repairing or replacing the throttle position sensor |
| Extraneous noise | 1) misadjustment of valve clearances 2) wear of pistons | 1) adjustment with valve gaskets 2) replacement of pistons, rings 4) use of new liners |
| Alternator belt break | excessive tension, manufacturing defect | Regular check, replacement as necessary |
Since a feature of the ICE 11183 is a well-thought-out design of valves and pistons, overhauls in most cases are carried out on time without additional user investment.
TPS sensor for 11183
A little about the design of the Lada 11186 8 valve engine
This power unit traces its history back to the VAZ 21083 engine developed in the late 80s, or rather its injection version. It is based on the same cast-iron block with an in-line arrangement of four cylinders, an eight-valve head and a single camshaft. The timing belt drive, and since there are no hydraulic compensators, periodically adjust the valve clearances.
There are also significant differences. Thanks to the taller block, the working volume has slightly increased, and a new lightweight connecting rod and piston group, cooling nozzles, anti-friction inserts on the pistons, a modern E-gas electronic throttle valve, as well as completely different intake and exhaust manifolds have been used. All this made it possible to significantly increase the power characteristics of the unit and even fit into the Euro 4 environmental class.
However, as a result of all the modernizations, a rather big minus for our realities appeared. The lightweight connecting rod-piston group found itself without the usual holes in the piston heads and now bends in almost 100% of cases when the valve belt breaks. Therefore, an expensive Gates belt with an automatic tensioner and an impressive service life of 200 thousand km is installed here. Only in mid-2022 did the manufacturer finally return non-plug-in pistons to this engine.
Max Akimov conducts an endoscopy of just such a power plant from the Lada Grant.
The most common problems of internal combustion engines 11186
VAZ 11186 borrowed the design from its predecessor. The engine is a cast iron block with 4 cylinders in line and a head with 8 valves. One camshaft. There are no hydraulic compensators, so the valve clearances have to be set manually. The timing belt is driven by a belt.
Similar article Where is the engine number on the Lada Granta
The modernization has made improvements to the characteristics of the engine: it has become less capricious, more reliable and economical. However, the engine is not without its drawbacks:
- While the engine is running, knocking noises are heard. Often the problem is solved by adjusting the valve clearances. If this does not help, install new pistons or crankshaft bearings;
- RPM fluctuates at idle. The cause of the malfunction is glitches in the automatic throttle and sensors;
- increased oil consumption. Observed when the main liners or piston rings are worn;
- misfire. The problem is in the ignition module. It is beyond repair and must be replaced.
Granta owners also complain about the unreliability of the Itelm ECU. The electronic unit fails when exposed to moisture. To prevent damage, the ECU can be moved into the interior to avoid getting wet during rains. It is not recommended to cover the module with film, as condensation will occur.
The most critical problem with the 8-valve Lada Granta is that the engine bends the valves. The damage can only be corrected by replacing it with new parts. It remains to find out why the valves bend and how to avoid trouble.
Repair of power unit components
As practice shows, nothing lasts forever, and neither do the components of VAZ power units. In this part of the article, we will consider the main malfunctions, as well as methods of elimination and repair.
Timing belt or how not to bend valves
Probably the most interesting question for most motorists is whether the valves on VAZ engines bend? As for the VAZ 11189 engine, we can say with confidence that the valves bend when the timing belt breaks. Of course, valves can bend for other reasons, but the most common is considered to be a broken timing belt.
Another question that car enthusiasts ask in car repair shops and on forums regarding the timing belt is how to prevent valve bending? Everything is very simple - change the timing belt and rollers according to the technical recommendations of the manufacturer. Thus, in the maintenance manuals for engine 11189, the recommended belt replacement period is 45-50 thousand kilometers.
What happens if the valve bends? Everything is very simple - after the valve mechanism is bent, such important elements as the valve guide, valve seat, and oil seals fail. Subsequently, it may happen that this problem affects the piston mechanism. In a word, if the valve bends, then you should hope for the best and expect the worst - that is, a major repair.
How to replace the timing belt and rollers:
The procedure for changing the timing belt, at first glance, seems to be quite simple, but not everything is so simple, and not every car enthusiast will be able to carry it out. Therefore, in order not to subsequently bend the valves, it is recommended to contact specialists at a car service center to carry out the procedure.
Water pump malfunction
The water pump circulates coolant through the engine system. This is done for cooling and to prevent the motor from burning out. The failure of such a unit means that further operation of the power unit is impossible, since overheating will occur and the first thing that will be affected is the cylinder head. To avoid this, you should regularly diagnose the part and replace it on time.
There is nothing difficult about replacing the pump. The procedure is similar to changing the timing belt. After removing the belt, unscrew the bolts securing the water pump and replace it. It should be noted that the coolant must be drained from the system and, after replacement, topped up to the required level.
ECU diagnostics
One of the most common procedures that motorists carry out is diagnosing faults in the electronic engine control unit. This procedure is often performed in a car service center, since not every driver has a special portable diagnostic PC.
Source
Replacement process
The replacement process itself on the Kalina 8 cl unit is simple and can be carried out under normal conditions, in the most ordinary garage with good lighting. When dismantling, place all removed parts in some previously prepared container so as not to lose anything. If the car has high mileage, you may need to purchase new bolts for tightening. But it will be possible to say more definitely after dismantling the head.
Required Tools
One type of torque wrench
- a set of keys;
- set of heads;
- hexagon;
- durable screwdriver.
- The first step is to remove the casing of the 8 cl power unit.
- The number one cylinder piston should be set to the top dead center position.
- De-energize the system by disconnecting the negative battery cable.
- Drain the coolant.
- Disconnect and set aside the air filter element.
- Disconnect the heating hoses, other pipes and connectors.
- Don't forget to disconnect all the wires from the spark plugs.
- Next, remove the cylinder head cover.
- Remove the camshaft drive cover located in front.
- Insert a screwdriver into the hole in the pulley hub to prevent the camshaft from turning, and loosen the bolt securing the timing pulley.
- Next you need to remove the timing belt.
- Completely unscrew the bolt that secures the camshaft pulley.
- Remove the pulley.
- Next, you need to remove the camshaft drive cover, which is located at the rear.
- Remove the remaining pipes and wires.
- After disconnecting all the wires and pipes, you need to loosen the bolts that secure the cylinder head of the viburnum 8 class. This is done strictly according to the scheme. Be sure to strictly adhere to this diagram when loosening the bolts
- Next, you need to completely unscrew the cylinder head mounting bolts.
- They are removed along with the washers.
- We remove the cylinder head.
- It is worth knowing that during long-term operation, the bolts with which the cylinder head is secured increase in length. Therefore, it is better not to save money, but to install new ones.
- Before installing new bolts, they must be lubricated with oil.
- We remove the Kalina cylinder head gasket.
- The place where it was installed must be cleaned. This is done not mechanically, but using a special liquid. If you use a file or a wire brush, there is a high risk of scratching the surfaces. As a consequence, loss of tightness with all the ensuing consequences. The surface was polished with an abrasive tool. Scratches are noticeable.
Install a new gasket.New part installed
- We install the cylinder head. Make sure the crankshaft and camshaft are at top dead center. This is a very important condition.
- We insert bolts into all holes and tighten them in a certain sequence: Diagram for tightening the bolts.
- First, we walk around the first circle and pull, applying a force of 20 N•m (2 kgf•m);
- Then we go around the second circle and pull, applying a force of 69.4-85.7 N•m (7.1-8.7 kgf•m);
- Next, use a wrench to turn the bolts 90 degrees;
- We go through it again and turn it 90 degrees again.
- Next, you need to connect all the removed wires and pipes. Many car enthusiasts, performing this work for the first time, mark the parts or take photos.
Stages
Power point
How to change the cylinder head gasket of LADA Kalina: do-it-yourself replacement
Domestic cars have a fairly simple design, which allows them to be repaired on their own. Replacing the K Alina cylinder head gasket can be done independently, but only if you have a garage, a good set of tools and the owner has experience.
Frequency and signs of replacement
How to replace it yourself?
Tools and materials
Step by step instructions (8 valves)
Step by step instructions (16 valves)
Comments and Reviews
Tightening torque for Lada Granta 8 valve cylinder head
Domestic cars cannot boast of such reliability as foreign cars and therefore, in order to save on their maintenance, the car owner has to do many of the works himself. Replacing the Kalina 8 valve cylinder head gasket can be done with your own hands and you do not need to be a high-class auto mechanic.
The cylinder head gasket on an 8-cl engine cannot be called a weak point in the car’s design. But still, even with careful operation of the vehicle, there may be a need for replacement. You can do it yourself, but if you are hesitant and want to take on this work for the first time, then invite a friend who has experience in similar work (replacing the cylinder head gasket). Be sure to carefully read the material we offer and you will definitely succeed. Let’s say right away that replacing the cylinder head gasket on Kalina units with 8 cl and 16 cl is very similar, but there are some nuances regarding the tightening of the cylinder head bolts. Therefore, be careful.
Gasket selection
When purchasing a gasket, you need to know the type of engine installed on Kalina. There are two versions of 8-valve engines - VAZ 11183 and VAZ 11186. These engines have different piston groups and differ in many external elements. On the older version 11183, a thickness of 1.2 mm is used (article 21080-1003020-12, manufacturer ZAO Lada-Image), and the new 11186 requires a gasket with a thickness of only 0.43 mm. This nuance must be taken into account when choosing new parts. For a 1.4-liter 16 valve engine, a gasket 11194-1003020-00 manufactured by Federal-Mogul Corporation is required, or you can get a cheaper option from Trialli (GZ1015001).
Photo gallery
The photo below shows some stages of replacing the gasket on an 8-valve VAZ engine.
Engine with valve cover removed
Unscrewing the exhaust pipe from the converter
Interior of engine cylinders with damaged gasket
The gasket itself
Place of gasket punching
Cylinders washed with gasoline
Head removed from engine
Carbon deposits on valves and combustion chambers
The photo below shows some of the stages of disassembling a 1.4 liter engine.
Removing the washer reservoir
Removed ramp with injectors
Probe guide
Timing drive removed
Camshaft gears removed
Removing the camshaft supports
Cylinder interior
16 valve head
How to replace it yourself?
Replacing a burnt gasket requires a large amount of work. Self-repair and replacement of the Kalina cylinder head gasket can only be carried out by an experienced car owner who has the skills to disassemble and reassemble engines. For novice drivers and people who are not confident in their capabilities, contacting a specialized service would be an advisable step.
Tools and materials
Before starting work, you need to find a room for the replacement and check the availability of the necessary tools and equipment.
The minimum set of tools and spare parts is as follows:
It is not recommended to use old cylinder head bolts.
Step by step instructions (8 valves)
After preparing the tools, you can begin replacing. The gasket replacement procedure is quite lengthy and takes about 8-9 hours even for experienced craftsmen.
Below is an approximate sequence of actions when replacing the cylinder head gasket of a Kalina with a 1.6-liter 8-valve engine:
Video from the channel Sdelaj Sam! Pljus interesting! Demonstrates basic methods for identifying faults and replacing worn parts.
Step by step instructions (16 valves)
Removing the head for replacement on such motors has its own characteristics that must be taken into account during disassembly and reassembly. The engine design is much more complex than the 8-valve version and requires careful assembly and subsequent adjustment of the valve timing.
How to remove the head from a 1.4-liter 16-valve engine with an injector, model VAZ 11194:
The procedure for removing the cylinder head on a VAZ 2108-2109
Of course, it will be necessary to first carry out some preparatory procedures, without which it will be impossible to remove the head.
- First, you need to remove the air filter housing
- Then disconnect all fuel hoses and power wires from the carburetor or injector (depending on the type of engine)
- Completely drain the coolant from the system
- Disconnect the pants from the exhaust manifold
- Remove the distributor, although this is not a prerequisite - it will be enough to disconnect the high-voltage wires
- Unscrew and remove the valve cover
In general, it is necessary to free the head from everything unnecessary so that during dismantling there are no unnecessary problems. Of course, if you decide to completely replace it or repair it, then you will have to perform more operations, both the carburetor and the manifolds. Well, if it’s just a matter of gasketing, then you can get by with a minimum of actions.
To unscrew the cylinder head on a VAZ 2109-2108, you need to use a powerful wrench and a hexagon, since the bolts securing it to the cylinder block are tightened with a large torque. In total you will have to unscrew 10 bolts, which are shown in the photo below:
As a lever, you can use a nozzle in the form of a regular metal pipe:
Then you can remove the bolts along with washers, as shown in the picture:
And now you can carefully lift the VAZ 2109-2108 cylinder head up, removing it from the engine block:
After which the following picture opens to us:
Price issue
Changing the head gasket yourself will be quite inexpensive, since its cost ranges from 220 (for 8-valve engines) to 550 rubles (for 16-valve engines). In addition to it, you will need a gasket between the exhaust pipe and the catalyst, which costs no more than 100 rubles, and 10 new head bolts, costing 40–50 rubles each. Often the manifold gasket is damaged, which in this case must be replaced. A new part costs about 750 rubles. The total cost of spare parts will not exceed 1,500 rubles. It must be remembered that when disassembling and troubleshooting the engine, other parts may appear that need to be replaced.
Performing such work at a service station depends on the territorial location and ranges from 4 thousand rubles in small cities (Tula, Bryansk) and up to 10 thousand rubles in large cities (Moscow, St. Petersburg).