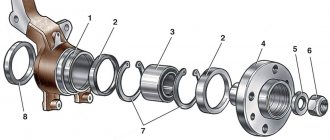
Signs of a bad input shaft bearing
You can determine the need to replace the bearing yourself based on special signs that appear during vehicle operation. A modern car has many bearings that periodically fail. Considering the fact that car mechanisms operate at high temperatures, high rotation speeds, under the influence of aggressive substances and large mechanical loads, bearings often fail. Timely, independent diagnostics of the operation of the input shaft bearings and, if necessary, their replacement can save car enthusiasts, prevent major repairs and ensure safe driving.
When diagnosing the performance of a bearing on the input shaft, its location should be taken into account. You can detect obvious symptoms of problems in its functioning even without dismantling and disassembling the gearbox. Considering the position of the bearing, which is located on the input shaft directly behind the oil seal, it becomes clear that this support unit bears one of the heaviest loads. Currently, roller bearings are most often used, the size of which depends on the make of the car.
The main sign of bearing failure may not be seen, but heard. When a bearing malfunctions, it makes a characteristic howling sound that can be heard at idle. When a knocking sound is heard while driving, this may indicate a bearing failure. In some cases, such a breakdown may make it impossible to engage the clutch. One of the reasons for this may be bearing jamming, which in the worst case scenario can lead to the need to repair the shaft.
Replacement of the input shaft bearing.
We dismantle the gearbox, having previously de-energized it and removed all attachments and disconnected the speedometer drive. We thoroughly clean the gearbox from accumulated dirt and oil stains. Using a screwdriver, we extract the retaining rings, which are the main fastening part of the bearings in most boxes. The next step is to press out the bearing, which is done either using special pullers or using a pry bar and a hammer (experience and an assistant are required). Then, after first checking the seat for defects or contamination, we press in a new bearing. Before installation, lubricate the shaft and bearing seat with a special lubricant.
Disassembling the gearbox
In the situations described above, a simple gearbox adjustment will be sufficient. This is much better than repairing the VAZ 2110 gearbox, disassembling and assembling the gearbox.
Procedure for disassembling the gearbox:
- Remove the oil indicator from the gearbox. Unscrew the bolts that hold the clutch cable.
- Unscrew the bolts that hold the back cover. The lid is hermetically sealed, so when removing it, you can use a hammer.
- To prevent the shafts from turning while disassembling the gearbox, turn on the third or fourth speed. Then unscrew the bolt that secures the fifth gear.
- Remove the fifth gear and fork together.
- Afterwards, remove the gear from the secondary shaft and the fork. Then remove the plate that protects the bearings.
Below you can see a DIY video repairing a VAZ 2110 gearbox.
Signs of a faulty input shaft bearing. learn this list
Car Citroen ZX 1.9i. If you press the clutch pedal in neutral, there is silence. I let go of the pedal and it starts to grunt and grunt. When driving you can't hear it over the noise of the engine. Is it the throwout bearing or the input shaft that's dying? How to determine. If, as they say, an autopsy will show, then what to look for during the autopsy.
esli vizatoe sceplenie i neslisno xrumkanie - slisno pri otpuscenoi pedalji - - eto u Vas pogib podsipnik pervicnogo vala. Pri vskritie smotretj podsipnik ilji vtulku ( nepomnju cto tam ) v maxovike i ljuft pervicnogo vala - xotja ego mozet i nebitj - potomu kak rassipalsja podsipnik i bivaet cto grimit i bez ljufta vala ( ilji ljuft nastoljko neznaciteljen cto rukoij nepocus tvovotj)
More like a throwout bearing. If you press the clutch pedal lightly, does the sound increase or decrease?
Looks like a main shaft bearing. The release bearing usually makes noise when you press the clutch pedal.
Of course, the most correct thing to do was to listen to these sounds (grunts and crunches) and then judge the reason. My statement is based on experience - in 9 out of 10 cases it is a squeeze.
Thank you all very much! I'll try to check when releasing the pedal. Let's say I remove the box (a LOT of work.), change the release lever ($14 - SKF). I'll put the box back in place. And it turns out to be the input shaft bearing!
As soon as you start it, you can’t hear it right away - you need to warm it up a little.
In any case, the box will have to be removed. Immediately check the release lever for rolling (it should turn easily, without any extraneous noise). Check the release bearing guide sleeve (the part along which it moves), sometimes the sound is caused by it. Rotate the input shaft and check its play (axial and radial). If possible, remove the input shaft and rotate the bearing.
Good luck.
The input shaft bearing makes more noise when the car is not warmed up. As it warms up the sound should become quieter. Just in case, check the oil level in the box.
Ops. It may not be a bearing. Try this, try to engage the gear (just try, without effort, just move the gearshift lever and press down a little) without squeezing the clutch. The sound is gone or not. Try reverse in all gears. And another question, when you turn off the engine, is there a knocking noise? Is it very audible, stronger than when it is set to XX?
The release lever will only make noise when the clutch is depressed. In general, it looks like your primary one is not in order.
Perhaps the Citroen ZX 1.9i is a unique car (I don’t know, I haven’t done it - XM doesn’t count), so I want to find out two questions for myself - 1. Colleague Frieman - tell me on which front-wheel drive car with a transverse engine a bearing (bushing) is installed in the flywheel primary shaft? 2.To Kluff - If we assume that on the specified car the release bearing is always in engagement with the basket, how will the sound change when the load on it increases (when you press the clutch pedal)? Best regards, Kenkel.
The release bearing is double-row, and when engaged it operates without load (rolling only) and is subject to minimal wear, but when pressed, the direction of forces changes and it is loaded in three directions, subject to maximum load and wear. That is. it has two states - idle and working. That's it, I'm done loading.
Perhaps double-row release bearings are installed on Citroens (it is not clear why) - the question is different. If we assume that this bearing did not jam and still retained its mobility, then the main reason for its failure should be fatigue spalling (pitting) of the treadmills. I would like to clarify - in this case, when will it make more noise under load or without it?
Replacement
Many people turn to a service station to replace this bearing. It is noteworthy that car services often refuse to perform such work. It’s understandable, because the procedure is painstaking, and you can’t get a lot of money for it.
To do the job yourself, follow the instructions.
- You can often find advice about the need to completely disassemble the gearbox to replace the bearing. But this is optional. You can do without such complex manipulations.
- In any case, you will have to remove the box, so familiarize yourself with this procedure.
- Before removing the gearbox, remove the negative terminal from the car battery.
- All the chips are removed from the box, the wire from the speedometer is unscrewed.
- Next, the trousers of the vehicle exhaust system are dismantled.
- After this, you can completely remove the gearbox.
- At the next stage, the bell is dismantled. You can try to do without it, but then it will definitely constantly interfere with your work.
- Thoroughly clean the box from accumulated dirt.
- The bearing is secured using retaining rings. To remove them you will need a flathead screwdriver.
- The rings are pryed off and loosened a little, after which there will be no more problems with removal.
- To make it more convenient, arm yourself with tweezers that can be used to remove the ring.
- Using a flat-head screwdriver, pry the bearing by the ring groove, and at the same time move the input shaft slightly forward.
- Insert a pry bar between the gearbox and the bearing. It is unlikely that you will be able to do this without an assistant.
- You will operate the tools, while your friend will hold the pry bar.
- Your main task is to press out the bearing. To do this, precise, strong, but most accurate blows are applied to the input shaft.
- In the process of striking, the shaft must rotate.
- This work will take you about 20 minutes. But if you have a special puller at your disposal, you can speed up the work. Although it is really convenient to work with a puller only if you decide to disassemble the gearbox.
- Before installing a new input shaft bearing, be sure to lubricate the element with regular engine oil.
- Carefully press the component into place using gentle, light blows with a hammer. It is better to use a pipe of diameter or a stand.
- When pressing, apply blows to the inner race, in a circle, as evenly as possible.
- Once the bearing is pressed in, make sure it is seated properly. Scrolling should be calm, without obstacles.
- Reassemble the box in reverse order and install it on the car.
Main manual transmission malfunctions and their causes
The transmission is designed to change and transmit torque from the engine to the wheels, that is, it is one of the main systems of the car, determining its dynamic and speed characteristics. The key role in the transmission is played by the gearbox (gearbox, or simply gearbox, gearbox), when it fails the car loses its driving characteristics or cannot move at all.
As you know, today there are two main types of transmissions in the world - manual (mechanical) and automatic. These transmissions have different designs and operating principles, so they are characterized by different malfunctions. Here we will only talk about malfunctions of a manual transmission; read about problems with an automatic transmission in a separate article.
The following malfunctions are typical for a manual gearbox:
• Noise during operation and when changing gears; • Inability to engage any gear or all gears; • Difficulty shifting gears; • Spontaneous gear disengagement; • Oil leakage from the gearbox.
Location
Since we are talking about the VAZ 2114, the first thing we will do is determine the location of the element.
On the fourteenth, the primary bearing is located on the shaft behind the oil seal.
It is noteworthy that on some gearboxes this bearing additionally plays the role of an oil seal, taking on the load together with the release bearing.
To get to the damaged transmission component, you will have to remove the transmission. When choosing a new element, be sure to check the recommendations from the instruction manual for your VAZ 2114 regarding the overall dimensions of the component.
Self-diagnosis of a manual transmission
The problem with self-diagnosis of a manual transmission is that it is impossible to do without removing and disassembling it. The fact is that most mechanical malfunctions in one way or another occur due to wear of parts, and a worn gear or other part can be identified and replaced only after disassembling the entire box. And only problems with the gear shift drive can be solved without removing the gearbox - to do this, it is enough to conduct a visual inspection of the drive parts (levers, rods, cables, hinges, etc.), try their operation and, if necessary, replace them.
The procedure for removing a manual transmission is approximately the same for all cars:
• Jack up or suspend the car (its front part) and the gearbox - this will insure against falling and damage to the gearbox after it is disconnected from the engine; • Disconnect from the box all controls, wires and everything that interferes with its dismantling; • Drain the oil from the box; • On a rear-wheel drive car, disconnect the driveshaft; • On a front-wheel drive car - remove the wheels, disconnect the CV joints and some suspension parts; • Unscrew the bolts holding the gearbox to the engine; • Remove the fastenings of the hanging support pads; • Remove the gearbox; • Disassemble the gearbox and carry out diagnostics.
When disassembling the gearbox, the condition of gears, synchronizer couplings, splined shaft joints, bearings and other parts, the integrity of all seals, etc. are checked. If a faulty part is identified, it is replaced, after which the box is installed on the engine and filled with transmission oil.
Not every one of us can or has the desire to independently remove, disassemble and check the gearbox, so if you are unsure of your abilities, it is better to contact a service center. And, of course, owners of new cars whose warranty has not yet expired should definitely contact the service.
Device
Needle bearings are mainly used to support the shaft. The use of thin and long rollers allows the thickness of the ring to be minimized while maintaining high load resistance.
Fastening the part has its own characteristics. During operation, the element wears out its installation location. Due to increasing play and vibrations, the part is gradually destroyed, and then it is necessary to replace it.
Manual transmission malfunctions and their elimination
All gearbox malfunctions are characterized by certain external signs - it is from these manifestations that one can judge the nature of the breakdown. However, many malfunctions manifest themselves in the same way, so in the table presented here all manual transmission breakdowns are grouped according to their external signs.
This table does not indicate troubleshooting methods, since they, for the most part, require high qualifications and car repair skills. Only some operations can be carried out even by an unprepared car owner - this is replacing and filling oil, as well as replacing gear drive parts. If other manual transmission malfunctions are detected, it makes sense to contact a car service center.
Conclusion
The gearbox bearing is one of the components of the gearbox, without which the entire unit will not be able to function normally. Unfortunately, a car enthusiast may encounter the need to replace this bearing up to two or three times during the entire life cycle of the car. If inexpensive analogues were previously installed, then there is a high probability that there will be many more replacements. We recommend purchasing only bearings from well-known manufacturers or automaker originals, and delegating the installation work itself to a trusted specialist. If problems arise with the gearbox, diagnosis and repair should not be shelved.
Recommendations for manual transmission operation and maintenance
The durability and quality of the transmission largely depends on how the gearbox and clutch are operated. Extending the service life of the gearbox, and therefore increasing the comfort, controllability and safety of the car, is not difficult; all you need to do is follow a few simple recommendations.
The main thing in operating a manual transmission is smooth gear shifting with the clutch pedal fully depressed. Under no circumstances should gear shifting be allowed with the clutch not fully disengaged, as this leads to accelerated wear of the gears and increases the likelihood of their failure. It is also very important to move in the gear that best matches the current speed, and, if possible, switch to direct (usually fourth) gear - in this case, the torque transmission uses a minimum number of gears and two shafts (bypassing the intermediate one), therefore, wear of parts is reduced Checkpoint.
When switching to a lower gear, you should reduce the speed of the car, which is also necessary to reduce the load on the parts of the gearbox and the engine itself. Under no circumstances should you engage reverse gear even when the car is moving forward at a low speed - this will certainly lead to damage to the gearbox. And finally, if the first gear does not engage immediately, then you need to first depress the clutch (you can do it twice), and only then engage first gear again. Next, gear shifting must be done smoothly and with a mandatory pause between shifts.
A manual transmission also has operating features that many people are not even aware of. For example, in the winter season, especially at significant subzero temperatures, it is not recommended to park the car with the gear engaged - in this case, there is a high risk of the synchronizer ring freezing, and the next time you start the engine, even after the gear is turned off, the car may start moving. This is also fraught with some malfunctions.
Maintenance is also of great importance for the reliable operation of the gearbox. Firstly, periodically after long and active trips you need to inspect the gearbox for oil leaks. Typically, drips can appear in the area of the filler and drain plugs, along the perimeter of the junction of the box to the engine, between the crankcase and the gearbox cover, and also (in the case of a two-wheel drive vehicle) on the flange of the driveshaft coming out of the box.
How to remove the transmission?
To remove the box you need an inspection hole or a lift. Also, for work you need a standard set of tools - a wrench, sockets, wrenches and a pry bar. The dismantling process is carried out in several stages:
- First of all, disconnect the terminal on the battery. Then the neutral gear is engaged and the parking brake is released. Raise and remove the rear axle. Next, unscrew the bolts holding the cardan and the gearbox flange. After this, you can disconnect the driveshaft.
- Then unscrew the bolts and dismantle the exhaust pipe of the exhaust manifold, disconnect the oxygen sensor, and remove the starter. Next, inside the car you need to dismantle the console and
- After this, remove the box protection and unscrew the clamps that connect the exhaust pipe to the catalyst. After this, you can dismantle the slave cylinder of the clutch system. Next, unscrew and remove the boot and reverse gear cable. Now you can remove the driveshaft. Then the traverses are unscrewed (you must hold the box so that it does not fall). Finally, you can unscrew and remove the gearbox assembly.
Input Shaft Bearing: Troubleshooting
The input shaft bearing is a part that is part of the vehicle’s gearbox (gearbox). The following symptoms will tell the motorist about its malfunction:
- while driving when the clutch is released, a foreign noise occurs;
- when the vehicle moves through the gearbox, knocking noises unusual for normal operation occur;
- spontaneous shutdown of gears is observed;
- Difficulty disengaging the clutch.
If such malfunctions are detected, you should begin repairing this unit as soon as possible. By postponing restoration work until later, the driver risks seriously damaging the gearbox, since a worn, skewed input shaft bearing destroys the clutch disc while driving. This leads to the car losing control and resulting in accidents. Replacing a unit when the first signs of a malfunction appear does not require significant costs, while eliminating the consequences of a breakdown is much more expensive.
The nature of the interaction of contacting surfaces
In a bearing assembly, moving and stationary surfaces of contacting parts are distinguished. Inspection should begin sequentially - from the bearing seating surface to the seating surface of the inner ring on the shaft.
If the landing was carried out incorrectly or weakened, then the static position will be violated, which leads to rotation, unplanned movement. This may cause noise and knocking, and the metal will begin to heat up more due to the increased load.
If the surfaces come into contact under the influence of regular vibrations, a layer of corrosion (fretting corrosion) appears. Dark spots and signs of oxidation appear on the rings. In the future, as the process progresses, cracks will begin to diverge. Manifestation: knocking at speed.
And the last contact is undesirable. This is unplanned contact with foreign elements, which only loosen the unit and cause it to swing incorrectly.
Simple repair of the input shaft support
You can purchase the parts required for this repair at the representative office. Here you will find bearings for all brands of cars. The products presented are original products produced by domestic and foreign manufacturers.
If this unit fails on your car, consider purchasing the materials that will be needed for this type of restoration work, namely:
Even though new bearings are supplied with factory grease, they must be further treated. This needs to be done for several reasons:
1. Over time, any lubricant loses some of its performance qualities;
2. The latest generation of sealants can significantly improve the performance of the unit, increase its working life, and protect the part from the influence of aggressive factors.
This type of bearing is not insulated with an oil seal. But, to remove it, the technician needs to partially dismantle the parts that make up the gearbox. The optimal solution would be to replace all rubber elements removed during repairs. This will allow you to postpone the period of preventive maintenance to prevent oil leaks from the gearbox.
Where is the bearing located, how to dismantle it?
On domestically produced cars, the input shaft bearing is located on the secondary shaft, directly behind the oil seal. When the gearbox is completely removed from the car, take out the bell, as well as the retaining rings. There is no need to disassemble the assembly further.
In order to replace the part, you need to use a screwdriver to hook the bearing into its annular groove. Next, the input shaft is pushed forward using the bearing as a support. Then slowly pull the bearing off the shaft by tapping it with a hammer. There's no need to rush. Replacing the VAZ input shaft bearing can take from several minutes to one hour.
Shaft bearing: features of part selection
The type and brand of bearing you will need for repairs can be found by consulting your vehicle manufacturer's information. In the future, you should inform the seller of its catalog number. The consultant will select the required part for you. When reinstalling, it is not necessary to use the brand recommended by the factory.
A wide range of products allows you to choose an analogue that is not inferior or superior in its performance qualities
. If you do not know the information about the catalog number of the unit installed on your car, you can search by make and year of manufacture of the car.
When purchasing, pay special attention to the date of manufacture of the sample. The shelf life of products should not exceed three years. In this case, the lubricant located inside the product retains its performance qualities. If this time is exceeded, the sealant thickens and does not work as effectively. It is permissible to use parts in a car after re-preservation - the date of the operation should be marked accordingly on the box. But at the same time, the product should not have signs of warping and rusting on its metal surfaces. It is undesirable to buy goods whose packaging has lost its integrity.
Signs of a faulty gearbox - manual transmission failure
Basic malfunctions of manual transmissions. Frequent manual transmission breakdowns. How to promptly identify a fault in the gearbox and prevent complete breakdown of the manual transmission. Regular transmission oil changes and manual transmission diagnostics will extend the life of your gearbox.
Possible reason: wear of the support bearings of the secondary shaft of the manual transmission.
Worn support bearings of the gearbox input shaft.
Wear of the lead-in splines of the gear and fifth synchronizer clutch or shift fork.
A possible cause of a manual transmission breakdown is a faulty differential or breakdown of the satellites.
Possible cause: the drive seal is damaged or the differential housing of the drive inlets is worn.
Possible cause: breakdown of the manual transmission gear or gear fork.
Possible reason: the manual transmission synchronization unit is faulty, the synchronizer blocking rings are worn out.
Possible cause: the oil seal is damaged or the gearbox input shaft bearing is worn.
Possible cause: clutch wear.
Possible cause: malfunction of the speed selection mechanism or the rocker.
Possible cause: worn differential bearings or differential housing.
Possible reason: breakdown of the reverse gear of the manual transmission.
Possible cause: wear of the synchronizer clutch.
Possible cause: clutch disc wear.
Possible cause: wear - broken gear fork
Forces acting on the system
This refers to all impacts exerted on the mechanism - both translational or rotational movements, and unintentional actions that cause point deformation. If forces were applied at one point, then the bend will result in the form of a continuous trace. Outside or inside - depends on which ring is movable and which is deformed. How to determine whether a clutch release bearing is faulty and what are the signs of breakdown and wear in the faulty part:
- light spots will appear on the end of the rollers;
- the inside can be painted - a dark spot will appear;
- A clear line will appear on the outside of the treadmill.