The Niva family of cars differs from VAZ passenger cars in permanent all-wheel drive - they have two drive axles. In total, the VAZ SUV has three differentials in its transmission - one for each axle and another center differential.
The Niva transfer case is designed to distribute traction forces between axles, and operates on the principle of a 2-speed gearbox.
The device of the VAZ Niva transfer case
The transfer case is not present in all VAZ passenger cars, but only on cars with two drive axles. In the transmission, the transfer case (TC) is installed at the rear of the gearbox; a rear driveshaft is attached to its shank, which connects the transfer case to the rear axle. The front axle is also driven by the steering wheel; it is connected to the transfer case by a front driveshaft.
The reduction gear in the Republic of Kazakhstan is designed to obtain high torque, it is used to overcome difficult sections of the road, and helps to cope with off-road conditions. The VAZ Niva transfer case contains the following main parts:
- the body itself;
- front axle drive shaft;
- intermediate shaft;
- drive shaft;
- gears;
- bearings;
- differential housing;
- satellites;
- differential lock clutch;
- gear shift clutch;
- flanges (for connection to cardan shafts);
- oil seals;
- control levers.
Assembly options
The first step is to measure the distance for the parts.
Using the subframe drawings, we assemble the structural parts according to the measurements obtained. Here are three build options:
- A simple version of the Niva-Comfort type frame, where you only need 5 main parts and a couple of fasteners for them. It is assembled from five square-shaped channel pieces with an additional reinforcement strip. The ends of the four parts are bent into the frame and holes are drilled into them for bolted connections. The frame parts can be welded or bolted together. A more complex design consists of almost a dozen parts and is assembled according to three drawings.
- In this homemade version, one wide channel is used as a basis, in which there will be a hole exactly for the transfer case. On the sides of the channel there are large corners, and at the ends there are shelves made from smaller corners. All parts are connected exclusively by bolted connections. This design protects the bottom of the machine well, but is more labor-intensive for manual production. The great advantage of this particular option is the installation of engine crankcase protection, which can be connected to the subframe; in addition, the protection of all parts around is improved.
Transfer case Niva 21213
Model VAZ-21213 is an all-terrain passenger car with permanent all-wheel drive and differential lock. Brand 21213 is a restyled version of the first VAZ SUV, VAZ-2121. RK Niva 21213 has three gears:
- the first - with a gear ratio of 1.2;
- the second, lowered – with the number 2.135;
- neutral
21213 is equipped with 4-speed and 5-speed gearboxes, and when the first speed of the transfer case is turned on, the car operates in standard mode, the gear ratios in the transmission are from 5-speed. The checkpoints are as follows:
When you turn on the second position of the transfer case lever (reverse position), the gear ratios change (lower):
On ordinary roads, the transfer case is always in first gear, the transfer case control lever (reduction gear) is pushed forward. The neutral gear of the RK disconnects the transmission, and in this position the car does not drive; there is also a neutral in the gearbox.
Motorists often ask the question: why is neutral gear needed in a transfer case? The neutral is used when connecting additional units to the transmission, for example, a mechanical winch; in this case, a power take-off must also be installed.
Useful tips
To use the lock installed on the Niva effectively, use the following recommendations from experts:
- When driving on good quality road surfaces, install the front transfer handle at the front and the rear at the rear.
- The front handle is moved back if the road becomes slippery. Once the slippery area has been passed, switch the levers to normal mode.
- If the Niva is stopped, the lock may not engage when the clutch is depressed. This occurs due to the alignment of the teeth with the gear teeth. What should you do in this case? Moving as if on a turn, engage the lock. The differential will turn and the gear teeth will come closer to the teeth. If turning off is difficult, do it while the vehicle is moving, maintaining a minimum speed and squeezing the clutch.
Malfunctions of VAZ transfer cases
The transfer case on the Niva is a fairly reliable unit; problems with repairs in the mechanism itself arise mainly due to insufficient oil level in the valve - if for some reason the oil leaks out, intensive wear of all parts occurs. Among the frequently occurring malfunctions are:
- vibration in the body at various speeds when the car is moving;
- vibration when the vehicle starts moving;
- noise in the transfer case when the car is slipping or turning;
- difficult upshift or downshift, difficult engagement of the lock.
Vibration
Vibration in the body is the main “disease” of the Niva; it often occurs due to improper alignment of the transfer case. Most often, vibration occurs on VAZ 21213/21214 cars, since the transfer case is mounted only on two supports on the sides of the body; on the Chevrolet Niva, the transfer case is already installed on three supports. But before you start adjusting the position of the transfer case, you should check the condition of other parts of the chassis - vibration can occur for other reasons:
- driveshafts are poorly secured;
- wheels are not balanced;
- there is play in the cardan crosspieces (vibration is especially affected by play in the rear driveshaft crosspieces);
- The vibration comes from the engine itself.
Transfer case alignment
Correct installation of the transfer case can be done in several ways. Most often in auto repair shops, repairmen use the following method:
- hang the car on a lift;
- loosen the transfer case;
- start the engine;
- engage the gear and accelerate the car according to the speedometer to the speed at which vibration occurs (often it occurs at speeds from 40 to 80 km/h);
- without using the brakes, reduce the engine speed, then turn off the ignition.
The transfer case itself is centered in place, all that remains is to tighten the fastenings of the supports.
You can also adjust the position of the RC using a wire; we do it as follows:
- loosen all four fastenings of the transfer case supports;
- fasten one end of the wire to the rubber coupling of the propeller shaft;
- we attach another piece of wire to the CV joint, bring the other ends of the wire to each other;
- rotate the shaft; if the transfer case is not centered, the ends of the wire will diverge during rotation;
- the task comes down to installing the transfer case using the selection method so that the ends of the wire practically do not diverge from each other in any position when turning the shaft.
Eliminate vibration with additional fasteners
Installing the third support of the transfer case on VAZ 21213/21214 vehicles allows you to reduce the level of vibration of the transfer case; with this support it is easier to center the transfer case. The part can be purchased at auto stores or made yourself. The finished product comes with three long studs (for model 2121); to install the third support on this machine, you will need to unscrew the short studs from the transfer case housing and install new studs from the kit. We carry out repairs as follows:
- dismantle the front passenger seat in the cabin;
- remove the floor tunnel lining;
- in the cabin we move aside the carpet covering the body amplifier (in front of the handbrake lever);
- remove the transfer case (alternatively, you can simply hang it up, but removing the third support makes it easier to install);
- We attach the bracket of the new support to the body of the RC;
- we install the transfer case in place, center it in the optimal position, and fasten the side supports;
- we combine the third support with the body, drill two holes in the bottom;
- Using washers, bolts and nuts (from the kit) we attach the support to the bottom of the body.
Vibration is eliminated more effectively by installing a subframe under the transfer case. You can also make such a device yourself or buy a finished product at a car store.
In order to install the subframe, the transfer case must be removed. It is more convenient to carry out such work in a pit; we carry out repairs as follows:
- leave the car in neutral gear;
- disconnect the propeller shaft from the transfer case, it is advisable to mark the driveshaft flange and the drive shaft so that during installation, align the driveshaft according to the marks - this way, the occurrence of unnecessary vibrations is eliminated;
- dismantle the muffler mounting bracket;
- remove the gearbox traverse;
- jack up the transfer case, remove the side fastenings of the transfer case;
- We treat the places where the subframe fits to the body with Movil;
- place the subframe on the gearbox studs;
- we mark the attachment points of the subframe on the side members, drill holes, attach bolts to the body;
- we tighten all fastenings, except for the transfer case supports themselves;
- we perform alignment of the steering wheel;
- Finally tighten the transfer case supports.
It should be noted that installing an additional support or subframe on the steering wheel does not always lead to the desired effect; in some cases, vibration only increases.
Removing the Niva transfer case
To repair the transfer case on a VAZ 21213 (21214), the unit must first be removed. We carry out removal in the following order:
- in the cabin we dismantle the plastic lining of the gearbox and gearbox levers;
- unscrew the knobs of the transfer case shift levers, remove the casing under them;
- disconnect the speedometer cable, for RK 21214 you will need to additionally disconnect the speed sensor;
- we unscrew the bolts with nuts securing the elastic coupling of the front and rear propeller shafts; in order to remove the bolts, the cardan shafts must be turned - they are removed one at a time in one specific position of the shaft;
- We install a jack (or other support) under the transfer case and mark the places where the side supports of the RC were attached. This is done in order to minimize the alignment of the transfer case during installation;
- unscrew the 4 nuts securing the gearbox to the gearbox;
- unscrew the 4 fastenings of the RC supports to the car body;
- Now all that remains is to dismantle the transfer case.
The all-terrain vehicle VAZ 2121 is a reliable universal SUV. Unlike vehicles with one drive axle, it is equipped with all-wheel drive and has high maneuverability. The Niva 2121 transfer case provides conditions for operating the vehicle both on difficult roads and on city streets with heavy traffic. Thanks to the all-wheel drive wheel arrangement, a series of cars produced by AvtoVAZ became known as “Niva 4x4”.
Full technical specifications of the Chevrolet Niva - summary table
| Parameter | Chevrolet Niva 1.7 80 hp |
| Engine | |
| Engine code | 2123 |
| engine's type | petrol |
| Injection type | distributed |
| Supercharging | No |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Cylinder arrangement | in-line |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 |
| Volume, cubic cm. | 1690 |
| Power, hp (at rpm) | 80 (5000) |
| Torque, N*m (at rpm) | 127.5 (4000) |
| Transmission | |
| Drive unit | full |
| Transmission | 5 manual transmission |
| Suspension | |
| Front suspension type | independent multi-link |
| Rear suspension type | dependent |
| Brake system | |
| Front brakes | disk |
| Rear brakes | drums |
| Steering | |
| Amplifier type | hydraulic |
| Tires | |
| Tire size | 205/75 R15 / 205/70 R15 / 215/65 R16 |
| Disk size | 6.0Jx15 / 6.0Jx15 / 6.5Jx16 |
| Fuel | |
| Fuel type | AI-95 |
| Environmental class | Euro-5 (Euro-4*) |
| Tank volume, l | 58 |
| Fuel consumption | |
| Urban cycle, l/100 km | 13.2 (14.1) |
| Extra-urban cycle, l/100 km | 8.4 (8.8) |
| Combined cycle, l/100 km | 10.2 (10.8) |
| dimensions | |
| Number of seats | 5 |
| Number of doors | 4 |
| Length, mm | 4048 |
| Width, mm | 1770 |
| Height, mm | 1652 |
| Wheelbase, mm | 2450 |
| Front wheel track, mm | 1466 |
| Rear wheel track, mm | 1456 |
| Front overhang, mm | 721 |
| Rear overhang, mm | 748 |
| Trunk volume (min/max), l | 320/650 |
| Ground clearance (clearance), mm | 200 |
| Geometric parameters | |
| Entry angle, degrees | 37 |
| Departure angle, degrees | 35 |
| Weight | |
| Curb (min/max), kg | 1410 |
| Full, kg | 1860 |
| Maximum trailer weight (equipped with brakes), kg | 1200 |
| Maximum trailer weight (not equipped with brakes), kg | 600 |
| Dynamic characteristics | |
| Maximum speed, km/h | 140 |
| Acceleration time to 100 km/h, s | 19.0 |
Also interesting: Niva Chevrolet transfer case: device, connection diagram and how to use?
* – engine data before modernization in 2020 is indicated in brackets.
| Parameter | Chevrolet Niva 1.7 80 hp | Chevrolet Niva 1.8 122 hp |
| Engine | ||
| Engine code | 2123 | Z18XE |
| engine's type | petrol | |
| Injection type | distributed | |
| Supercharging | No | |
| Number of cylinders | 4 | |
| Cylinder arrangement | in-line | |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 | 4 |
| Volume, cubic cm. | 1690 | 1797 |
| Power, hp (at rpm) | 80 (5000) | 122 (5600) |
| Torque, N*m (at rpm) | 128 (4000) | 167 (3800) |
| Transmission | ||
| Drive unit | full | |
| Transmission | 5 manual transmission | |
| Suspension | ||
| Front suspension type | independent multi-link | |
| Rear suspension type | dependent | |
| Brake system | ||
| Front brakes | disk | |
| Rear brakes | drums | |
| Steering | ||
| Amplifier type | hydraulic | |
| Tires | ||
| Tire size | 205/70 R15 | |
| Disk size | 6.0Jx15 | |
| Fuel | ||
| Fuel type | AI-92 | |
| Environmental class | n/a | |
| Tank volume, l | 58 | |
| Fuel consumption | ||
| Urban cycle, l/100 km | 14.2 | 12.8 |
| Extra-urban cycle, l/100 km | 8.9 | 8.5 |
| Combined cycle, l/100 km | 10.9 | 10.1 |
| dimensions | ||
| Number of seats | 5 | |
| Number of doors | 4 | |
| Length, mm | 4048 | |
| Width, mm | 1770 | |
| Height, mm | 1652 | |
| Wheelbase, mm | 2450 | |
| Front wheel track, mm | 1450 | |
| Rear wheel track, mm | 1440 | |
| Trunk volume (min/max), l | 320/650 | |
| Ground clearance (clearance), mm | 200 | |
| Weight | ||
| Curb (min/max), kg | 1400 | 1520 |
| Full, kg | 1850 | 1870 |
| Maximum trailer weight (equipped with brakes), kg | n/a | n/a |
| Maximum trailer weight (not equipped with brakes), kg | n/a | n/a |
| Dynamic characteristics | ||
| Maximum speed, km/h | 140 | 165 |
| Acceleration time to 100 km/h, s | 19.0 | 12.0 |
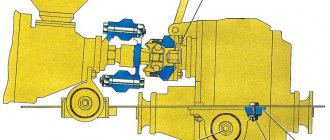
The main purpose of the Niva 2121 transfer case
The transfer case (another name is the range multiplier) is connected directly to the gearbox, participates in the distribution of rotation on the axis of the all-terrain vehicle and helps to increase the torque when transmitted to the wheels of the vehicle.
Niva 2121 transfer case cross-sectional diagram
Transfer case functions:
- Blocking of the interaxle differential mechanism.
- Disabling one bridge.
- Increased torque transmitted to the drive wheels when turned on
- downshift.
- Distribution of torsional moment on the vehicle axle.
- Ensuring the operation of the power take-off shaft when installing additional units.
Varieties
There are several types of these elements:
Read also: Dress with a pleated skirt (104 photos)
- Equipped with coaxial drive shafts. This type is used on many SUVs. It gained such popularity due to the use of a single main gear for both axles.
- With a misaligned driven shaft. There is no intermediate shaft here. The advantages of this system are high efficiency and noiselessness. Also, this box has a low curb weight.
- With drive axle drive blocking. It is also installed on the Chevrolet Niva. Here it is possible to use all the torque without slipping the wheels, which is very important when driving off-road. The front axle engages only on difficult sections of the road. On asphalt surfaces, the SUV has a single-wheel drive (only the rear axle works). This allows you to reduce fuel consumption and, if necessary, increase cross-country ability (when the drive “closes”). There is also an interaxle forced locking.
Niva 2121 transfer device
The Niva SUV transfer case includes:
- shafts – drive, intermediate, rear and front axle drives;
- differential mechanism;
- gear shift clutch.
Two gear wheels, rigidly located on the drive axle of the transfer case, are designed to engage high or low gears. When manufacturing the drive shaft, special heat treatment is carried out in places where the greatest load from operating gears is expected. This is necessary to ensure sufficient shaft strength in order to eliminate possible defects when operating the vehicle in extreme conditions.
The transfer case gears are designed with straight and oblique teeth arranged in two rows. The helical teeth of the wheels are in constant mesh with the corresponding gears, tightly seated on the intermediate shaft. Direct - connected to the mode switching clutch. The clutch has three working positions: middle - neutral and connection with one of the two gears on the drive axle.
Idle move
The Chevrolet Niva idle speed sensor ensures the supply of air to the engine during idling. When a signal is received by the ECU, the sensor moves the valve, changing the flow hole in the air valve. If it fails, it will not be possible to repair it, since it has a non-demountable design.
To replace it, you need to prepare a thirteen socket wrench, pliers and a Phillips screwdriver and do the following:
- Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove the housing from the throttle valve
- Disconnect the wiring connector of the engine regulator
- Unscrew a couple of screws on the throttle body
- Removing the regulator
- Remove the O-ring from the existing hole.
To summarize, we can conclude that the failure of any of the above elements can seriously affect the operation of the car, therefore, in the event of a malfunction, you need to replace a new part as soon as possible. All replacement work can be carried out independently.
The transfer case is used to change the amount of torque and distribute it between the front and rear axles. The box has two gears with ratios of 1.20 and 2.135. The front and rear axles are constantly driven and connected by a center differential, dividing the torque equally. To increase the vehicle's cross-country ability, the differential can be blocked, and the front and rear drive shafts become rigidly connected to each other (their rotation speeds are equal).
The transfer case is attached to the body floor on three brackets - rubber-metal supports. The transfer case housing parts are cast from aluminum alloy and connected to each other with studs and nuts. There is a hatch in the upper part of the crankcase, closed with a stamped steel cover. The front cover is centered on the crankcase using two locating pins.
There are cardboard gaskets between the covers and the crankcase (during repairs, a sealant gasket can be used instead). All shafts are sealed with rubber-metal seals (oil seals). The speed sensor drive shaft, gear shift fork rods and differential locks are sealed with rubber rings. There are two holes in the front cover - a filler hole (also known as a control hole) and a drain hole.
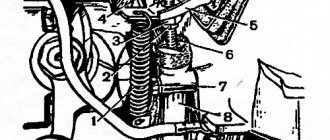
Transfer case with drive: 1 — differential lock clutch fork; 2 — differential lock fork rod; 3 — protective cover of the rod; 4 — lock washer; 5 — bushing of the lever axis; 6 — lever axis; 7 — differential lock lever; 8 — fork locking bolt; 9 — switch for the differential lock warning lamp;
10 — gear shift fork rod; 11 — differential lock lever rod; 12 — control lever bracket fork; 13 — control lever; 14 — gear clutch fork; 15 — spacer sleeve; 16 — spring and locking ball; 17 — clamp spring bushing; 18 — drive shaft flange;
19 — front cover; 20 — drive shaft oil seal; 21 — thrust ring of the bearing; 22 — front bearing of the drive shaft; 23 — high gear; 24 — gear clutch; 25 — transfer case housing; 26 — low gear; 27 — rear bearing of the drive shaft; 28 — adjusting ring of the rear bearing of the drive shaft;
29 — drive shaft; 30 - bushing; 31 — hub; 32 — back cover; 33 — rear bearing of the intermediate shaft; 34 — intermediate shaft; 35 — rear differential bearing; 36 — rear axle drive shaft bearing; 37 - flange; 38 — rear axle drive shaft oil seal; 39 — rear differential housing;
40 — gear support washer; 41 — rear axle drive gear; 42 — satellite axis; 43 — retaining ring; 44 — spring washer; 45 — side suspension bracket; 46 — satellite thrust washer; 47 — front axle drive housing; 48 — satellite; 49 — differential driven gear; 50 — front differential housing;
51 — retaining ring; 52 — spring washer; 53 — front bearing of the differential housing; 54 — differential lock clutch; 55 — installation ring of the front differential bearing; 56 — oil deflector; 57 — front axle drive shaft oil seal; 58 — front axle drive shaft bearing;
The drive shaft is mounted on two ball bearings, the outer rings of which are located in the sockets of the front cover and crankcase. The front bearing inner race is sandwiched between the shaft shoulder and the thrust ring by a self-locking shaft flange nut. The rear bearing inner race is sandwiched between the shaft shoulder and a thrust washer located under the shaft rear end nut.
The nut is locked by pressing its edge into the grooves on the shaft. The drive shaft is secured against axial displacement by an adjusting ring in a groove on the outer ring of the rear bearing, sandwiched between the crankcase and the rear cover. There are two drive gears on the drive shaft. The front (large) is the highest gear; it rotates freely on a heat-treated shaft journal.
Rear (smaller) - lowest gear, rotates freely on a heat-treated bushing mounted on the shaft with tension. The gears have two crowns. The helical (large) rings are in constant mesh with the corresponding gears of the intermediate shaft, and the gear shift clutch is connected to the spur (small) rings when the gear is engaged.
View of the front side of the transfer case: 1 - right suspension bracket; 2 - filler plug; 3 - intermediate shaft; 4 — speed sensor; 5 — speed sensor drive housing; 6 — front driveshaft; 7 — front axle drive housing cover; 8 — left suspension bracket; 9 — rear propeller shaft; 10 — front cover of the transfer case; 11 — transfer case housing; 12 — drain plug.
Handout operation on Niva 2121
By analogy with the gearbox, the transfer case on the Niva Chevrolet jeep also has gears. When the corresponding gearing of the gears on the shafts is engaged, gear ratios equal to 1.2 and 2.135 are provided. Using a differential mechanism, the redistribution of torsional moment between the wheels is ensured, in accordance with their resistance to movement.
The operation of the transfer case, while the VAZ Niva SUV is driving on a dry, flat highway, the wheels of the car rotate at the same speed. In this case, the gears are not engaged, the gears and clutch are in the neutral position. As soon as the vehicle's driving conditions worsen, the transfer case on the Niva turns on. The driver uses a special lever to downshift the transfer case so that the SUV confidently continues moving at a stable speed.
How the transfer case works on the Niva 2121 in extreme off-road conditions. Experienced car enthusiasts know how to professionally use a transfer case on a Niva. They know that in such situations they need to use levers to lock the differential gears. This is necessary to ensure uniform rotation of both shafts of the vehicle’s drive axles in order to create increased cross-country ability of the vehicle.
Important: The transfer case is switched to a lower gear only after the Niva 2121 SUV has come to a complete stop (not while driving).
Differential
This mechanism is a kind of distributor of traction forces coming from the motor to the wheels. An important feature is that the latter have the ability to rotate at different speeds. The importance of having a differential mechanism is due to the fact that during turning maneuvers, the wheel located inside makes fewer revolutions when compared with the number of turns of the outer wheel.
In the absence of a differential mechanism, this would cause detrimental consequences, such as wear and damage, because the result would be the following: when turning, one wheel would be in a slip state, and the second would simply rub against the road surface. The design features of the Niva transmission provide for the presence of 3 differentials. They are located in each of the bridges and in the transfer mechanism.
When the car moves on a flat road and in a straight line with differentials, the traction force is divided equally between all 4 wheels. If there is insufficient adhesion of the wheels to the surface or slipping occurs, the differentials will redistribute the load on the slipping and sliding wheel so that the first receives more force, and the second, accordingly, less.
We have already mentioned UAZ. Despite many similarities, it should be understood that the VAZ’s all-wheel drive is made in the “pat-time” style. This means that when connected, the axes are firmly connected to each other, and rotation occurs at the same speeds. This device imposes some restrictions on the use of all-wheel drive - it can only be used in cases where road conditions allow slipping. In cases with hard asphalt roads and highways, it is recommended to switch the car to single-drive mode.
Sometimes you can come across a misconception about why a small handle is needed next to the shift lever on a Niva. Some car owners believe that it is needed to connect front-wheel drive. However, the front-wheel drive of this car is permanently connected. As is the rear one. Cars of the Niva family have permanent all-wheel drive. The handle actually serves to switch the operating modes of the differential of the transfer mechanism.
In the “forward” position, the differential operates as usual, but if you move it back, the differential is locked, and the forces from the motor are applied to the differentials of the axles, which makes the drive more rigid. It is worth noting that there are also special types of locks for front and rear axles.
In theory, when used in conditions where the car is stuck, it will be able to overcome the obstacle if there is sufficient traction on at least one wheel. In this case, it is better to lock the differential before overcoming an obstacle, but never after entering an area that is difficult to overcome. This application of locking will avoid wear and damage to the transmission.
Description of possible problems with the transfer case
During the operation of off-road vehicles, parts and components of the transfer case gradually become unusable due to wear. Most often, the following interruptions in the operation of the mechanism occur:
- The front axle does not engage.
- The transfer case is overheating.
- Leaks and increased oil consumption of the transfer case.
- Unauthorized disabling of the front axle.
Changing the oil in the transfer case Niva 2121
To ensure the performance of the vehicle, it is necessary to carry out timely maintenance. Changing the oil is included in the mandatory list of machine maintenance work. To change consumables in the Niva 2121 transfer case, you will need 0.8 - 1.5 liters of gear oil.
The frequency of replacing lubricating fluid is equal to 45,000 km of distance traveled. The first procedure is carried out after 60,000 km, and then in accordance with the established schedule.
Attention: If problems arise with shifting gears, extraneous sounds, vibrations and vibrations, it is necessary to check the condition and amount of oil in the transfer case and the transmission as a whole.
The procedure for changing the oil in the transfer case of a Niva SUV:
- warm up car systems and mechanisms, to do this you need to start the engine and drive a short distance;
- install the machine on an overpass or over a special inspection hole;
- clean the filler and drain plugs of the transfer case from dirt and dust;
- place a container under the drain to collect waste material;
- unscrew the plugs and drain the liquid;
- remove metal fragments, shavings, splinters and other wear elements;
- screw in the plug;
- pour into the washing liquid (about one liter);
- start the engine;
- move the lever through the transfer case gears with slight delays;
- turn off the engine;
- drain the flushing composition;
- fill the transfer case with new oil;
- check the oil level;
- if necessary, add the required amount.