Replacing the Lada Kalina catalyst: reasons for replacement
The most common reason that entails the installation of a spider instead of a catalyst is clogging of the honeycomb of the base of the catalytic element, both by fuel combustion products and by exfoliating particles of the base itself.
Natural degradation is normal. The catalyst, under favorable operating conditions, is designed for a service life of about 100 thousand kilometers.
Let's take a closer look at the moments when replacing the catalyst on a Lada Kalina car becomes necessary.
There are a number of factors that can significantly accelerate the destruction of the device:
- Problems with the formation of the correct fuel-air mixture. Both rich and lean mixtures have a negative effect here. A rich mixture leads to incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons and their deposition on the walls of the base cells. A lean mixture causes an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gases, which has an oxidizing effect on the body at high temperatures. Also, due to an insufficient amount of fuel in the cylinder, misfires occur and unburned fuel is released into the catalyst. It can ignite while already in the manifold with the next portion of hot exhaust gases.
- Incorrect ignition timing. The fuel-air mixture is ignited at the wrong time. This leads to improper combustion and the formation of additional thermal loads on the catalyst.
- Gasoline is of poor quality. Gasoline saturated with impurities, after combustion, leaves soot deposits on the walls of the cells. In this case, rapid clogging of the catalytic element occurs.
- Coolant or oil getting into the cylinders. A leak in the lubrication and cooling systems leads to unauthorized penetration of working fluids into the combustion chamber. When they are burned, compounds are formed that lead to clogging or destruction of the catalyst.
In addition to the breakdown of the catalytic element itself, the housing itself often fails due to design flaws. The weld at the junction of the pipes of the first and fourth cylinders with the catalyst body is often destroyed. The escaping exhaust gases create increased noise. Exhaust also penetrates the interior, causing discomfort.
A failed catalyst increases the load on the engine, as it creates resistance to the passage of exhaust gases. This may manifest itself in the following symptoms:
- increased fuel consumption;
- reduction in engine power;
- failures when trying to accelerate sharply;
- reduction in maximum speed;
- problems with starting.
How does a catalytic converter work?
Exhaust gases passing through the holes of the catalyst honeycomb heat it. When the temperature reaches several hundred degrees, a thin coating of platinum and other metals begins to have a catalytic effect, forcing molecules of carbon monoxide and other unburnt fuel residues to react with oxygen. This reaction leads to the release of even more heat, causing the converter to heat up to a temperature of 500–700 degrees.
Even an absolutely clean converter exhibits significant resistance to the movement of the exhaust gas flow, which is why the engine spends part of the generated energy on forcing smoke through the catalyst.
Any malfunction of the fuel system, engine or ignition, as well as frequent sudden starts, lead to an increase in fuel injection into the cylinders, which means that there are also more unburnt residues. Because of this, not all molecules bind to oxygen molecules; some of them settle on the walls of the holes of the catalytic converter, and this process is especially strong during warm-up of the engine.
To some extent, it helps to clean the channels by driving at high engine speeds with the gas pedal pressed minimally, when the number of unburned particles is minimal, and the amount of oxygen and exhaust temperature are maximum. Under such conditions, even the residues deposited on the walls react with oxygen, turning into carbon dioxide, but some of the slag still remains in place.
Signs and symptoms of a clogged element
If the catalytic converter is clogged, the symptoms will help determine this. Naturally, such symptoms can also indicate other malfunctions. But with more detailed diagnostics, everything speaks specifically about the catalyst. If the element is completely clogged, the engine will start, but stall immediately after that. The car accelerates worse. When the driver presses the accelerator pedal, the car may feel as if something is holding the rear bumper. This indicates that there is a blockage inside the neutralizer. How else can you find out that the catalyst is clogged? Symptoms include increased fuel consumption. But this can only be taken into account when the car has lost power and responsiveness to the accelerator pedal. That is, the car stopped driving, and consumption increased significantly. Also, when starting a cold engine, a pungent and unpleasant odor may appear.
Malfunctions and their symptoms
Catalyst problems usually appear with age: by 150–200 thousand kilometers, the honeycombs that make up its filling are almost completely destroyed and prevent the exhaust gases from escaping. As a result, the pressure in the exhaust system increases, the exhaust gases are squeezed back into the engine, which literally “chokes” it. Signs of a clogged catalyst may include:
- severe deterioration in vehicle dynamics;
- uneven engine operation at idle speed;
- starting deterioration;
- smell of sulfur in the cabin.
If the car “does not drive”, before changing the sensors, it is worth checking the condition of the cata at a service station. in a garage environment : not everyone in the household has the necessary devices. There are two main methods of checking: manometric and pyrometric.
features and types of design
The flame arrester can be classified:
1. According to the noise suppression method, there are two types:
- active. The effect is based on sound absorption. The main element of the active flame arrester is a special filler. For these
purposes, a fiber element of synthetic or basalt type is used.
The disadvantage of the design is the inability to withstand high temperature emissions from the front of the muffler. Along with this,
burnout occurs within 2-3 months (if a stainless steel mesh is installed) and within 10-15 days if there is no protection at all. - passive. With this design, the product reflects sound waves. Passive flame arresters are more reliable. They have two layers, which allows the inner “casing” to dampen external vibrations. Without this, the casing of the device will ring loudly at the first impact.
The outer layer must be made of a material that can withstand the action of liquids and is resistant to rust. If the quality of the material is poor, the action of liquids, acidic solutions from the road and changes in temperature conditions destroy the equipment. Based on this, the ideal option for a flame arrester is not aluminized, but heat-resistant stainless steel.
The requirements for flame arrester elements installed on the inside are not so stringent. The circumstance is the absence of negative condensation and moisture effects.
2. By design highlights:
- straight-through;
- with diffuser. Products with a diffuser are seen less often. The main difference is the presence of a special pipe welded to the middle part of the product. Its purpose is to move it and create a flow into the flame arrester casing.
Another parameter that matters is the quantity of the product. If the quantity is small, then pressing the accelerator leads to the appearance of strong rattling in the muffler area. If the muffler itself and the resonator have a direct-flow principle of operation, then there will be fewer problems with rattling (excessive noise).
Video: Replacing the catalyst with a flame arrester. cons and pros. Just something complicated
Budget replacement options
In addition to installing a new standard unit on a 1.6 engine, replacing the catalyst on a VAZ 2114 is possible in the “budget option”. To do this, use a zero-resistance catalyst (“spider”). There are two types of spiders - 4-2-1 or 4-1. Option 4-2-1 is the transition of four pipes into two, which are connected into one pipe. Option 4-1 differs from the first in that four pipes coming from the engine are immediately connected into one pipe.
If the spider is designed for one probe, the ECU is flashed from Euro-3 to Euro-2. On such spiders, only the installation of a flange probe is provided. To simulate an injection probe, you need to install an extension cord (wire and female-male connectors).
If there are two sockets on the spider, the injection probe is mounted in its original place. Instead of the second probe, they install a decoy for the ECU. In this case, there is no need to reflash the ECU.
Instead of a catalyst, some owners of cars with 8-valve engines install a flame arrester. The unit can be purchased at a car store or made yourself. The oxygen sensor is installed before the neutralizer, so the flame arrester will not affect its readings.
Catalyst with EURO 3
But in systems with EURO 3 standards, everything is somewhat more difficult. It is necessary to “agree” with the lambda probe, which is located after the catalytic converter, otherwise there will be a check engine “reduced efficiency of the catalytic converter”.
- There are two ways here - mechanical snag or flashing the brain of your car. And finally, where is the notorious catalyst located in our VAZs?
- On VAZ 2104-2107 the Catalyst is like a separate can, on the bottom of the car (often almost touching the ground J). Remove or replace with an insert. Since 2008 We change the controller.
- VAZ 2121 Catalyst as a separate can, underneath the car. Remove or replace with an insert. E3 variants are found regardless of the year of manufacture, since 2008 it is inevitable E3.VAZ 2110, 2111, 2112 1.5L engines Catalyst as a separate can, underneath the car. Remove or replace with an insert. 1.6 l – catalytic collector. Remove the cat or install a spider.
- VAZ 2113, 2114, 2115 1.5L engines Catalyst as a separate can, underneath the car. Remove or replace with an insert. 1.6 l – catalytic collector.
- VAZ 1118 Kalina - catalytic collector installed.
- A cat collector is installed on the VAZ 2170 Priora. Regarding Priora, I would like to add that since 2009, some cars from the factory have been equipped with M73 brains with additional protection against flashing.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Articles and prices
On VAZ 2108–2115, 3 types of catalytic converters are installed: under
- Euro-2 8 valves;
- for Euro-3 and Euro-4 8 valves;
- for Euro-3 and Euro-4 16 valves.
Part number for Euro-2 is 21100120601011, average cost is 4 thousand rubles. The main difference is one hole for the oxygen sensor. This part cannot be installed on cars with Euro-3 and Euro-4 engines, because there is nowhere to install the second lambda probe. Neutralizers for Euro-3 and Euro-4 for eight-valve engines are similar in design to the previous ones, but are equipped with two holes for oxygen sensors, their article number is 11183-1203008, the average cost is 6 thousand rubles.
Neutralizers for 16V engines (this is how the number of valves is designated) are the same not only for all VAZ 2108-2115 models, but also for their modern descendants. Part number 11186-1203008, average cost 10 thousand rubles. Remember, converters for 8V and 16V motors are not interchangeable because they are installed in different places.
Diagnostic methods
Let's move on to specific methods that will help determine the malfunction. The easiest ways to find out about clogged cells:
- it is necessary to start and spin the engine to maximum speed; In the low, medium and high speed modes, sharply press the accelerator pedal to the floor. The engine should not “fail”, but rather respond sharply to the driver’s commands. If there is a weak, delayed response, or the engine does not spin up at all (at 4-5 thousand rpm), then we can safely talk about the need for repairs;
- place your hand on the exhaust pipe. The movement of exhaust gases is of a pulsed nature. You can feel each cylinder pushing out exhaust gases in turn. If you feel a constant smooth flow of exhaust at idle, this is a direct sign of a clogged catalytic converter. You can also ask an assistant to press on the gas, spinning up the internal combustion engine, and then immediately turn off the engine (you need to do everything quickly). After stopping the engine, there may be a slow release of gases that have accumulated due to deposits in the honeycombs. You can bring a fire source (match, lighter) to the exhaust pipe;
- visual inspection method. To do this, it is necessary to remove part of the exhaust with the catalytic element. Shine a flashlight through it to identify clogged honeycombs. Please note that if it was not fuel consumption or a drop in power that forced you to check the catalyst, but Check Engine, then this testing method is not very good. The element may visually look clean, but the special layer will no longer perform its functions. Therefore, the corresponding indicator lights up on the panel.
Counterpressure
You can check the system using a pressure gauge. The essence of the method is to screw in a regular air pressure gauge instead of a lambda probe (before the catalyst). This must be done using a special adapter. You will also need a hose connecting the pressure gauge and the adapter.
To check the catalyst, start the engine. In any of the operating modes, pressure readings should not significantly exceed the range of 2-3 kPa (0.2-0.3 Atm.). If you do not want to do the diagnostics yourself, contact a diagnostic center. Instead of a spark plug, specialists screw in a special sensor that measures the counter pressure. Reliable information is obtained by analyzing oscillograms of engine operation. Testing the efficiency of the exhaust system in this way at home is an impossible task. The device itself and diagnostic software cost a lot of money.
Now you know how to check the catalyst or particulate filter yourself, if we mean a diesel car.
First signs of trouble
- The dynamics of the car have deteriorated significantly.
- The engine is difficult to start.
- There is a sulfur smell inside the car.
- At idle, the engine is unstable.
If you feel that the car has become worse, you should first check the catalyst. But, unfortunately, this is not easy to do at home, since you will need special equipment for diagnostics. Still, there are a couple of ways to check.
Checking with a pressure gauge
Method one. A pressure gauge should be screwed into the place where the lambda probe is installed. Then start the engine and see what pressure is in the exhaust system. If it exceeds 0.5 atmospheres, this is the first sign that the catalyst is faulty.
Pyrometer
Method two. In this case, you need to use a remote pyrometer and check the temperature before and after the catalyst. If the device is faulty, the temperature before and after the catalyst will be the same. This means that the internal honeycombs are destroyed and the flame suppression function is impaired. In this case, the catalyst must be replaced with a VAZ 2114. If the device is working properly, then the temperature before it will be an order of magnitude higher than after it. Depending on what power unit is installed on the car, eight or sixteen valves, replacing the catalyst has its own nuances.
Learn more about verification methods in this video:
How to make a replacement
The entire replacement of the VAZ 2114 spider takes place in several stages:
- Place the car on an overpass or pit, put the handbrake on and secure the wheels with stops (shoes).
- If the car has been running recently, let it cool down.
- Remove the crankcase protection.
- Unscrew the bolts securing the exhaust manifold pants to the catalyst inlet (to make unscrewing easier, they should be treated with WD-40 lubricant before starting work).
- If the replacement is partial, then leave the catalyst and muffler in place; if it is complete, then remove it.
- Unscrew the nuts securing the manifold to the cylinder head.
- Dismantle the “original” manifold and the gasket located under it.
- Install the spider instead of the standard manifold (if the spider matches the model, then it will definitely fit into its place). Before installation, you should place a new gasket under it.
- If the old fasteners are severely corroded, then new ones should be installed instead, preferably coated with copper or brass.
- If a partial replacement is performed, then you need to check the alignment of the spider pipe with the catalyst inlet. As a rule, the exhaust pipe of the spider is longer, so you will have to cut off and dismantle not only the catalyst, but also part of the exhaust pipe, instead of which a resonator should be welded.
- Connect the spider's output pipe to the resonator.
- If a complete replacement occurs, then the same operations are performed as in the previous paragraphs, but instead of the entire “original” exhaust system, a direct-flow exhaust system is installed.
After installing the spider, you will also have to replace the lambda probe (with a new one, with an extended wire). The completion of the entire modernization process will be the flashing of the ECU, which should be performed at a car service center. It will help register the new system in the computer as “standard”, and will also show the increase in power obtained as a result of the upgrade.
REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT
Replacing a catalyst on a VAZ 2114 costs the same as repairs. Therefore, it is quite difficult to decide whether to change or repair this device. The most common solution is replacement, since repairs take much longer. Replacement can be done both at a car service center and at home. The problem with replacement is that simply cutting out the catalyst and welding a piece of pipe will not work, because, in addition to cleaning the exhaust gases, this mechanism also muffles the exhaust sound. And without it, the sound will be simply catastrophic.
This problem can be solved by installing a flame arrester. This device is sold in almost every car store. It costs much less than a new catalyst. You just need to buy it, and you can install this device at a service station, and it won’t cost much, and the result will be obvious.
Why do you need a catalyst?
I already have an article - what is it, I won’t repeat it. You need to understand that a catalyst (and scientifically, a catalytic converter) is needed only to clean the car's exhaust from harmful emissions and make them less harmful.
In simple words, it purifies harmful gases (while glowing almost “red hot”) and “almost” harmless CO2 and N2, O2 emerge from harmful CO, CH and other compounds. This way we save the environment at least a little.
Its structure is quite simple - it is a thickened pipe, which inside has something like a honeycomb, only long and hollow. They are usually made of ceramic elements coated with noble metals (usually platinum group metals are used - iridium, rhodium, palladium).
In order for gases to transform from toxic to less harmful, the temperature of the catalyst must be about 750 degrees Celsius, otherwise the chemical reaction will not occur. The gases that come out of a car engine have a temperature of approximately 500 - 550 degrees Celsius (which is not enough), when they pass through the catalyst, a chemical reaction occurs with the release of heat, thus heating just the right amount (750 - 900 degrees).
Model 2114: removal of the catalyst as a result of breakdowns
The consequences of operating a car with a problematic catalyst affect not only the environment and driving comfort, but also the durability of the engine.
In case of malfunctions associated with a decrease in permeability, the temperature load on the parts of the piston group and valve increases. If the temperature threshold for destruction is not reached, then the high temperature leads to accelerated wear. If the thermal strength of the metal is reached, burnout of the piston or destruction of the valve is possible.
Mechanical failure is just as dangerous. Especially for a ceramic type of base laid in a collector. When the engine stops, small ceramic particles can penetrate into the cylinders under the influence of resonance and anti-pressure. Ceramic particles have high hardness and, when mixed with oil, form an abrasive paste that eats up the piston.
Replacing the catalyst on a 16-valve VAZ 2114
On a VAZ 2114 with a 16-valve engine, the catalyst is structurally combined with the output manifold and is located in the engine compartment immediately behind the cylinder block. To replace it, a special insert is used, a zero-resistance catalyst, better known as a “spider”. Removing the catalyst and installing a spacer can also be done in a garage. To gain access, you will need to remove the fuel rail.
The peculiarity of removing the catalyst on 16-valve VAZ 2114 cars is that there are two lambdas. The first is installed on the catalyst itself and is responsible for setting the fuel mixture, and the second, “ecological”, is located on the flange after the catalyst. Its absence will inevitably cause a sensor error, a check engine indication, incorrect injection operation, increased fuel consumption and poor traction. There are two ways out of this situation.
- If you purchased a spider for one sensor, the ECU needs to be flashed from Euro-3 to Euro-2. In addition, the spider for one sensor has a drawback: the only thread for the lambda probe is located on the flange. To screw in the “injection” lambda, you need to assemble an extension cord from two male-female connectors and a wire.
- If there is a spider for two sensors, the “injection” lambda can be installed in its original place. The thread for the second sensor can be plugged or a “dummy” for the computer can be installed there. In the second case, flashing the ECU to Euro 2 will not be required.
Before removing the catalyst, you need to understand why it is needed. The power gain from this procedure is a myth. As well as the belief that an engine with a catalyst “does not breathe.” Removing a working cat (and if the odometer shows less than 100 thousand kilometers and diagnostics show the system is working, it works) will not add additional horses. However, the belief that driving with a clogged catalyst is more environmentally friendly than driving without it is also a fallacy.
Depending on the year of production of the VAZ 2114, they are equipped with catalysts that meet the requirements of Euro 2 or Euro 3 (2003-2008 and 2008-2013 model years, respectively).
Breakdowns and their signs
Typically, this element begins to “strange” when it travels about 150 thousand kilometers. That is, this is more likely an age-related problem with the car.
Standard and Modified
Typical signs that the catalyst is clogged are:
- The car's dynamics deteriorate significantly and noticeably;
- The engine starts with problems;
- There is a characteristic smell of sulfur in the cabin;
- The engine is unstable at idle.
If the car stops driving normally, it is advisable to immediately check the condition of this device. Alas, this cannot always be done in a garage environment, since special equipment and devices are required. But there are still two ways.
- Replace the lambda probe with a pressure gauge. Start the engine and check the pressure. If it is more than 0.5 atmospheres, things are bad.
- In the second case, you will need a remote pyrometer. If the catalyst is working normally, the temperature of the pipe before it will be higher than after it. But at the same temperature, this indicates the destruction of the honeycomb and a violation of the flame extinguishing function.
The second method allows you to obtain indirect data, so the pressure must be checked in any case. If a breakdown is detected, the catalyst must be replaced.
Removing the catalyst
To properly remove the catalyst from the car, you need to jack it up or put the car on a viewing hole. The process of removing the catalytic converter will not take more than thirty minutes and no special tools are needed for the work. The catalyst housing is located on the Samara behind the engine exhaust manifold. So:
- we find the mounts for the resonator, which is located behind the exhaust manifold or pants, as experts call it;
- unscrew the fastenings;
- remove the spring type washers;
- unscrew the fastenings of the exhaust pipe (in this case, you need to remove the bolts along with the springs, holding the catalyst with the other hand from below):
- remove the catalyst.
Now the owner himself decides what to do. He can put a new catalyst on the car, or he can make a homemade flame arrester and install it.
Making a flame arrester
A flame arrester and a catalyst have a lot in common. But the flame arrester, compared to the catalyst, does not delay the flow of hot exhaust, thereby increasing the jerk and power of the engine. In addition, it has a direct-flow design, and it will cost less to install than a new catalytic converter. It is not possible to buy a ready-made flame arrester. Therefore, you will have to do it yourself. On a VAZ 2114, replacing the catalyst with a flame arrester will require a little skill and knowledge of certain secrets. Let's start with the pipes. We take two metal tubes of different sizes. The diameter of the first pipe should be the same as that of the exhaust system. The second one has much more. Replacing the VAZ 2114 catalyst begins with the following:
- drill 3-6 mm holes in the first pipe around the circumference and the entire length;
- we insert the pipe in the center into the second one, which has a much larger diameter;
- connect the welding machine;
- We weld one edge of the pipe connection;
- leave the other edge and cut it lightly with a grinder (this is done to leave room for bending);
- take metal sponges and stretch them;
- they should be inserted alternately onto the edge of the pipe;
- taking a metal rod, push the washcloths as deep as possible (basically, it takes about 30 washcloths used by housewives in the kitchen);
- we bend the cut edge of the large pipe (this must be done so as not to remove the metal wool from the pipe);
- bends should be welded (scouring pads and tight welding will help to avoid the noise that the flame arrester will make while the car is operating);
- take good anti-corrosion paint (high-quality paint is sold in cans);
- we treat the flame arrester with it;
- cut out the old catalyst;
- insert the flame arrester there.
It is worth noting that even a homemade flame arrester meets all Euro 2 standards. In this article you can see how to replace the VAZ 2114 video catalyst and understand the main nuances of the work.
What is a lambda probe
The replacement of the VAZ 2114 catalyst, as mentioned above, meets all the parameters. But if, nevertheless, the standard should be higher than Euro 2, you can use a lambda probe. This is a special sensor that, after removal, transmits an error to the control unit. But this is not a solution either, since this installation will affect engine performance or fuel consumption.
- A sensor is a special device that measures the oxygen content in exhaust gases.
- It then transmits this information to the electronic power system.
- The power system, in turn, begins to control the composition of the combustible mixture, that is, fuel, and maintains the optimal ratio of air and gasoline.
- If the sensor is faulty, it gives a signal to the control to maximize the enrichment of the working mixture.
The same thing happens not only when the sensor is faulty, but also when it is turned off. Measuring CO at the moment, the device shows up to 9%. Well, the deterioration in engine performance and an increase in fuel consumption by as much as 50% is unlikely to go unnoticed by the driver. It turns out that on cars such as the VAZ 2114, where a catalyst is installed or to replace the catalyst with a VAZ 2114, a special device operates in the exhaust system , which measures CO.
Attention: you can also check the operation of the catalyst using the sensor. First of all, you need to find it
It is located in the exhaust pipe, where the manufacturers successfully screwed it in.
Removing the VAZ-2115 catalyst: when is it necessary?
When your catalytic converter is failing, there are certain signs that indicate it is happening. The appearance of an ECU error in most cases accurately indicates the failure of the catalyst. There are several indirect signs that can only imply the presence of a problem:
- increase in gasoline consumption without changing operating conditions;
- reduction in engine power qualities;
- extraneous noise from the catalyst body;
- strong smell of gasoline from the exhaust pipe.
What is needed for replacement
In order to install the spider on a VAZ 2114, you will need a minimum set of tools and accessories, namely:
- set of keys;
- angle grinder (grinder) - in some cases;
- cutting discs for angle grinders;
- welding machine - in some cases;
- WD-40 composition;
- new fasteners for the exhaust system;
- new lambda probe (equipped with an extended wire).
In addition, when installing the spider, you should also replace the exhaust manifold gasket.
As for choosing a spider manufacturer, you should give preference to the Stinger company, since its products are of high quality and have long been popular among motorists. In addition, you can purchase parts from other companies, but preference should be given to the middle or high price range. You should not purchase cheap spiders, as low-quality products can quickly fail.
Why is there not a catalytic converter on all VAZ 2108-2115 models?
Early models of these cars were produced with carburetor engines, for which this part is not required. Then the first injection models appeared, on which a catalyst with one oxygen sensor was installed. As the technology of injection power units was mastered, catalysts with two lambda probes began to be installed.
How to find out if a catalytic converter is worth it
Therefore, a catalyst in a VAZ 2114 car is needed if the vehicle is equipped with an injector; carburetor cars are not subject to European environmental requirements, which means there is no point in installing an expensive part.
Popular myths
Varieties
Some people deliberately get rid of the catalyst, others deliberately ignore the clogged unit. All this caused the spread of myths.
- By removing it, the engine gains power. A misconception that arose for unknown reasons.
- The engine cannot “breathe” normally due to the catalyst. Absurd. It functions quite well if the cat itself is in working order.
- A clogged element ensures a more environmentally friendly ride. Another myth, the origin of which can only be guessed at. Rather, on the contrary, a clogged device harms nature and your car even more.
Therefore, monitor the condition of the catalyst on the VAZ 2114, check its functional condition, and if necessary, replace it with a new one or replace it with a flame arrester. Both options have shown their effectiveness.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=j8h-zE9LUR4
Planned replacement
The catalyst resource ranges from 60 to 100 thousand kilometers. During operation, the ceramic honeycombs become clogged with waste and the VAZ 2114 neutralizer must be replaced.
If you refuel with low-quality gasoline, the catalyst will fail much earlier. All fuel filters will also deteriorate.
Types of catalysts
Over time, the carrier breaks down and the internal pressure of the exhaust system increases. Most of the exhaust gases return to the engine. In addition, there are factors other than the age of the node that affect its condition.
Video on replacing the catalyst on a VAZ 2114 spider:
In the context of the fight for the environment, car manufacturers are coming up with more and more sophisticated ways to reduce harmful emissions into the atmosphere, thereby preventing the engine from developing its full power.
The catalyst plays an important role in trapping harmful substances.
Installed in the exhaust system, it captures harmful substances from the exhaust, turning them into less harmful ones, acting as a kind of filter.
However, it is known that over time, every filter becomes clogged. With high mileage, the catalyst can cause deterioration in the vehicle's driving characteristics and increased fuel consumption. In addition, over time, the filter element, honeycomb, begins to crumble due to low-quality gasoline, thereby preventing the car from driving normally.
Since a new catalyst is expensive, many car enthusiasts resort to such a thing as removing the catalyst. Usually it is simply cut out or a so-called insert is installed instead.
Catalyst action
Platinum, palladium, and rhodium are applied to the surface of ceramic honeycombs. They speed up the neutralization process. Platinum and palladium oxidize harmful carbon monoxide (CO). This produces harmless carbon dioxide and water vapor. Rhodium, a reducing catalyst, breaks down nitrogen oxide into harmless gases. At a temperature of 300 °C, the catalyst neutralizes up to 90% of harmful substances.
Catalyst device
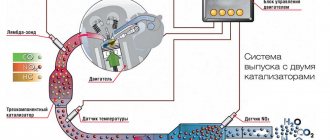
Exhaust system VAZ 2109 (carburetor, injector): diagram, device
VAZ-2109 owners are often interested in how the exhaust system of their car works. Curiosity in this case is far from idle. Some want to do repairs and want to know what and how it works here. Others thought about such an option as tuning, that is, modification, for example, installing a Stinger exhaust system. In any case, if you want to do this work yourself, you first need to familiarize yourself with the design features. Well, don’t forget about the main purpose of this system – to remove exhaust gases to the outside and reduce noise. Accordingly, incorrect intervention can lead to unpleasant consequences.
The design of the exhaust system of a VAZ-2109 car
It’s worth noting right away that there is nothing particularly complicated here. In fact, the exhaust system of the “nine” is very simple, without any electronic gadgets, and it can be called classic. Accordingly, if you decide to do repairs or tuning, then no unexpected problems are expected here. The exhaust system of the “nine” consists of:
- intake pipe;
- catalyst;
- additional and main mufflers;
- exhaust manifold.
Speaking about the components listed above, it is worth explaining their purpose. In particular, a lambda probe is located inside the exhaust pipe of cars with an injection engine. It analyzes the composition of the exhaust gases and at the same time the mixture going into the cylinder block. The pipe itself is connected with four studs to an exhaust manifold made of cast iron.
Thanks to the installed catalyst, the harmfulness of the exhaust emitted into the atmosphere is reduced to a minimum. And finally, mufflers. An additional one (also called a resonator) is attached to the catalyst using a special unit. It should be noted that this scheme is used on cars with injection engines. On carburetor “nines”, an additional muffler is connected to the main pipe. The only exceptions here are models sent for export. A catalyst was also installed on them. The task of the resonator is to take on the main noise. Accordingly, the output sound will no longer be as strong. And finally, the main muffler. This is what you can see by looking under the rear bumper of your car.
The main problems with the exhaust system of the VAZ-2109
Due to the simplicity of the design mentioned above, there is essentially nothing to break here. The main enemies of the VAZ-2109 exhaust system are low-quality fuel and bad roads. In the first case, the insides of the muffler simply burn out, resulting in the sound made by the car more like a roar. The same problem, by the way, can arise with the lambda probe. However, here the sound made by the car will not change. Often, due to a faulty ignition system, the catalyst fails. This is explained simply. Not completely burned gasoline enters the catalyst in sufficiently large quantities. Already there it burns out, sintering the ceramics.
Even if you have to face the need for replacement, there is nothing particularly difficult here. It is best to do this work by driving the car onto a pit or lift. All elements are attached to the body using hangers. They are connected to each other with clamps. Therefore, dismantling the problematic unit and putting a new one in its place will not be difficult. And in this case, a minimal set of tools will be required.
The only thing I would like to warn you about is safety precautions. Before starting work, wait a while for all elements of the system to cool down.
Particular attention should be paid here to the catalyst. The thing is that during operation it heats up to 600 degrees
Accordingly, the catalyst takes much longer to cool down than mufflers or the exhaust pipe.
Device
By design, this part includes the following elements:
- frame;
- thermal insulation;
- block carrier.
Particular attention should be paid to the last point. The carrier block is the basis for a part such as a catalyst. VAZ-2114 and many other domestic cars are equipped with ceramic carriers that are not subject to deformation at high temperatures and vibrations. By its design, this element is a collection of longitudinal honeycombs that increase the area of contact with exhaust gases.
Let's look at the pros and cons of removing the catalyst.
- Pros: fuel consumption decreases, the engine begins to “breathe” easier, it turns easier, the exhaust becomes freer.
- Cons: air pollution, inability to legally pass inspection, the need to change the firmware (if there are two oxygen sensors), the exhaust will become a little louder.
Many people ask the question: is it necessary to flash a car after removing the catalyst?
If your car has two oxygen sensors (Euro-3, Euro-4, etc.), then you will have to flash it; if there is only one (Euro-2), then it is not necessary.
And now a short report on replacing the catalyst with an insert on a Lada Kalina car with a VAZ 21114 1.6 l, 81 hp engine.
In order to get to the exhaust manifold, you must first disassemble the intake, because the intake/exhaust gasket is common on this engine.
To unscrew the hard-to-reach nuts located under the exhaust manifold, I came up with the following: I bought a spark plug type wrench, only 13, inserted a hex of the appropriate size on the back side, in my case it turned out to be a 12 hex.
Try to buy a high-quality tool; the edges of cheap wrenches quickly lick off and you won’t be able to unscrew anything with them.
Before starting work, be sure to lubricate all nuts with WD-40 penetrating lubricant.
After reading the forums of various sites, I still haven’t found a clear opinion on whether it is necessary to drain the antifreeze when removing the exhaust manifold or not. I decided not to risk it and drained the antifreeze from the cylinder block.
As is appropriate for such work, you first need to disconnect the terminals from the battery and remove it from the car, I also removed the air filter housing with the corrugation so that it does not interfere (this may not be necessary). Then I disconnected the injector power plug and disconnected the fuel rail, took it out and put it aside. I removed the throttle cable. In general, I removed everything unnecessary on the way to the catalyst.
Then he unscrewed the nuts securing the receiver to the intake pipe and removed it along with the throttle valve, having previously disconnected the wires from the idle air control (IAC) and the throttle position sensor (TPS). Then I disconnected the inlet pipe.
Once the intake pipe was removed, I removed the nuts that hold the exhaust manifold in place. If you managed to do this without breaking a single pin, then you are lucky. As you know, the nuts securing the exhaust manifold to the engine can become stuck due to exposure to high temperatures and, if they are not treated with a special penetrating lubricant, the stud can break.
And this is fraught with serious consequences, because you will have to drill it out, which is not very convenient, I tell you. Usually in such cases the cylinder head is removed, the old stud is drilled out and a thread is cut for a new one.
And so, if all the nuts are unscrewed, then you still have to unscrew three more nuts at the junction of the central muffler (resonator) with the exhaust manifold, located under the car and that’s it.
Assembly must be done in the reverse order, the main thing is to lay the manifold gasket evenly and tighten the nuts from the center to the edge alternately, pull carefully, but until it stops.
The only difference is that on the new manifold there are no studs at the junction with the resonator, so the connection must be made with nuts and bolts.
Finally, a photo of the new catalyst (inserts 4-1) and the old one.
In the photo you can see that there is only one hole for the lambda, so there is no point in flashing the ECU. I only had to extend the wires, since the hole for the sensor on the new manifold is lower than on the factory one.
At the same time, I cleaned the IAC and throttle valve, which had carbon deposits on them.
I removed the catalyst by replacing it with an insert without a hole; I only had to jack up the car in order to disconnect and connect the manifold and resonator.
This article is not a promotion to remove the catalyst. Whether to remove the catalyst or not is up to you. I simply spoke about my experience.
HOW TO DETERMINE THAT THE CATALYST HAS BEEN UNUSED
Bad catalyst
Typically this can be seen, heard or even felt through the sense of smell:
- So, if the ceramics crack, it begins to rattle in the metal case.
- In addition, exhaust gases acquire an unpleasant odor while driving if the catalyst is faulty.
- As for the color of gases, they also change dramatically. Instead of the usual color, gases with a faulty catalyst become like black soot.
- Engine power is also reduced, especially on inclines.
What shortens the life of the catalyst on a VAZ 2114?
In general, the average service life of catalysts is hundreds of thousands of kilometers, and significantly exceeding this period, up to 120 or even 150 thousand, cannot be considered an exception to the rule. However, owners of products from the domestic automotive industry request to replace it with a flame arrester, as a rule, earlier. Why does this happen?
- Mechanical damage. As for the dirt roads of the Russian outback (and sometimes just directions that road services maintain only in the winter), there is no need to explain. Sometimes it is enough to run into a deep hole hidden by a puddle, or a stone thrown from under the wheels gets into the catalyst housing, and replacing this device becomes an inevitable necessity.
- Poor quality fuel. Not only diluted fuel, but also a modified (enriched) fuel mixture can damage honeycombs by burning.
- Bad spark plugs. If, due to them, unburned fuel residues enter the catalyst, it flares up at the temperature of the exhaust gases (600-800 degrees), causing the honeycombs to melt and become clogged.
- Corrosion. Unfortunately, the welded joints on the VAZ 2114 initially have insufficient factory anti-corrosion protection, which is why condensate corrodes the pipes with rust.
Loose fasteners, broken hangers
Here you shouldn’t blame the manufacturer, the VAZ owner just needs to look under the bottom of the car more often and pay attention to signs indicating that it’s time to replace the catalyst with a flame arrester
Replacement for an 8-valve engine
If you have a VAZ 2114 with an 8-valve engine, you need to look for this element in front of the middle resonator and after the exhaust manifold directly under the bottom of the car. Many, alas, ignore the need to replace it, believing that their car will not stop polluting the atmosphere and the engine will be able to continue to operate normally. The opinion is wrong, as you understand.
Device option for eight-valve
Some believe that instead of a failed filter device, you can install a regular corrugated pipe . Also a wrong decision. This will make the noise incredibly loud, and the exhaust gases will very quickly destroy the muffler. You can get by with a budget replacement option - cut out a section of the catalyst, knock out a honeycomb of ceramics from it and perform welding, thereby sealing the body. But be prepared for noise to become your constant companion.
It is best to replace the factory catalyst with an effective flame arrester. They assemble it with their own hands or seek help at a service station, and also purchase ready-made solutions at auto parts stores. Whichever option suits you best, choose that one.
Removing the unit and replacing it with another device is a matter of one hour. At the same time, there is no need to worry about electronics. There is only one oxygen sensor, and it is installed before the catalyst. Therefore, replacing it with a flame arrester will not affect the measurement readings in any way.
Removing the catalyst on Niva 21214: consequences
Once removed, you will notice a significant increase in power. But let us immediately note that it will be within the factory values. After all, before this, the engine simply suffocated on its own gases and the power could drop by almost half. Gases will freely leave the combustion chamber - the risk of valve burnout is minimal.
Fuel consumption after removing the catalyst is within the factory values. But malfunctions will occur very rarely. After all, “when cold” the ECU is guided by average lambda values. And so on until the catalyst warms up. After removing it and flashing it, the unit will think that the neutralizer is already warmed up and will immediately begin to prepare the correct mixture.
The car will become less demanding on the quality of the fuel used. Even if there are deposits, all the dirt will fly straight into the pipe without being trapped in the filter honeycombs.
As for the negative aspects, after such “tuning” your environmental standards will immediately drop to Euro-2. But in Russia there are no penalties for this. It is completely legal to drive a Chevrolet Niva without a catalyst.
Firmware for EURO2 and snag – what does this mean?
As I wrote above, the second oxygen sensor (lower lambda) controls harmful emissions. Their number is now strictly regulated by European standards, which are called “EURO”; I will not talk about EURO “0-1” now; we are interested in the second generation.
So, what is EURO2 ? It was introduced a long time ago, namely in 1996. AT that time, the cars received an innovative system, namely a catalyst. As we all know, over time it can become clogged, and the fuel then was not the same as now, it had a lot of sulfur, which contributed to the honeycombs clogging much faster, and as you and I know, the car began to choke itself. Then the engineers installed an oxygen sensor, there was only one, and it was needed to capture CO2 in the chamber in front of the catalytic converter.
If the CO2 level increased, this indirectly indicated that the catalyst was clogged (that is, a backpressure effect was manifested); the sensor sent this information to the ECU and the ignition was adjusted, namely, a decrease in the supply of the fuel mixture. Thus, the power dropped significantly, the car did not drive and the owner “willy-nilly” had to go to a service station and change this spare part.
BUT, as you and I know, the price tag is, to put it mildly, HIGH, so many owners simply removed these honeycombs and the POWER RESTORED!
But how? YES, everything is simple, the CO2 level in the chamber in front of the neutralizer dropped significantly, the oxygen sensor recorded this (that everything is in order) and the car drove cheerfully and without constraint. This suited everyone, BUT NOT ECOLOGISTS! Therefore, they introduced the EURO3 standard (now the EURO5 standard already exists). What has changed is that a second oxygen sensor (lower lambda) just appeared behind the catalyst. The principle of operation here is this : the first lambda (before the filter) records the level of harmful substances, the second (after it) should record a much lower level, because the harmful substances have decomposed.
If you remove the catalyst cells , then both sensors will record the same values (“the second one” supplies information to the ECU), thus, CHECK ENGINE will light up, the power will drop, and the car will not drive. Now this doesn't solve the problem.
What is done with firmware for EURO2? The firmware in the ECU is changed, instead of EURO3.4 standards, EURO2 standards are installed. The essence of all these actions is banal - we simply turn off the second lower lambda (only the upper one remains), the car begins to drive as expected, without underestimating the power.
But such interventions in the firmware are not entirely good. The whole point is that they don’t produce them themselves, okay, the second “lambda” is simply turned off, that is, they simply adjust the readings. Or maybe this programmer will want to put some incomprehensible algorithms into the ECU, the engine will definitely not benefit from this. You need to be very careful here.
Therefore, we found a second solution, and I think it is more correct - installing a blende. What is a snag - essentially it is a “spacer” in front of the second oxygen sensor, it seems to move it a greater distance from the exhaust gases, it detects more oxygen and starts working normally.
Now there are several options for deception:
- Empty . It's just a tube with a very thin hole at the end (the part that screws into the muffler), and an oxygen sensor is screwed into the other side. A limited amount of harmful substances from the exhaust passes through it, there are no excesses and therefore CHECK does not burn.
- With a mini-catalyst inside . That is, right in the “spacer” there are, as it were, mini honeycombs, which also clean the exhaust precisely to record normal values.
- Angular . These are both of the types described above, only they are made at an angle of 90 degrees; they are needed for difficult places.
The advantages of the decoy are that you don’t need to go into the ECU and change the standard firmware, as well as the price (knocked out the cells, screwed on the decoy and that’s it, you can spend 3,000 - 5,000 rubles).
Solution
In fact, the cleaning element itself cannot be repaired. Only replacement is possible. And this is where the fun begins. Many car owners simply refuse to replace a faulty converter with a new one. The main reason for this is the high price. Sometimes it exceeds the residual value of the car. The quality of the fuel also plays an important role.
Most car enthusiasts use a simple and inexpensive replacement method - install a flame arrester instead of a catalyst. This device almost completely replaces the neutralizer. The only drawback is that there will be slightly more harmful impurities in the exhaust. But within the limits of the norms accepted in Russia. Moreover, the installation of a flame arrester is officially permitted by the relevant authorities.
There is another option for replacing the catalyst - installing an insert, or “spider”. This is also an approved replacement device. Like flame arresters, it is produced by industrial factories. It has several varieties for different engines. The main difference is in the product configuration.
The catalytic converter is knocked out, is this bad for the car?
As I wrote above, this is simply an environmental system, and if it is not there, then the car, on the contrary, will improve its characteristics (power, consumption). To put it simply, initially the engine doesn’t care about this converter, but it creates an obstacle in the muffler, overcoming which takes part of the engine’s energy (more on this below).
But why on many cars, if this unit fails (say, melted, clogged or crumbled), the CHECK ENGINE and the car begins to behave abnormally, traction disappears, sometimes it trots a little, and simply may not start at all.
And here, friends, everything is simple. If the catalyst is melted or clogged, then the exhaust gases cannot pass through it normally, which means that some returns back into the combustion chamber and makes the newly introduced combustible mixture less efficient. The motor is choking itself.
If there is no melting, but the “CHECK” light comes on, then perhaps it has simply worn out due to high mileage. In modern cars there are so-called oxygen sensors (lambda umbrellas), one is located in front of the catalyst, the other after and detects the presence of harmful compounds; if their percentage has increased, then the second (or also called the lower “lambda”) gives a signal that the converter is not working ( or it doesn’t do its job as it should) AND IT NEEDS TO BE REPLACED. By the way, some cars may not even start (a tribute to the environment).
Thus, by knocking out or removing it, you simply free the car’s exhaust tract from the obstacle in the form of a filter and lower its environmental standards. BUT AGAIN - THIS DOES NOT AFFECT THE RESOURCE OF THE POWER UNIT !
BUT in order for your car to drive normally, you need to upgrade to a lower environmental class (usually EURO2) or install a fake one. Otherwise, the program in the ECU will not allow you to drive normally.