Recently, SUVs and crossovers with all-wheel drive have become very popular.
If previously preference was given only to cars with high ground clearance, now the presence of a 4x4 transmission is a priority. But such technology can be implemented in completely different ways; let’s look at the structural features of the center lock and clutch on a Chevrolet Niva car.
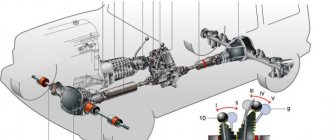
Niva drive device
The chassis of the car is made on the principle of permanent all-wheel drive - torque from the power unit is transmitted to all 4 wheels. This scheme improves the performance of the car when driving in off-road conditions, while simultaneously reducing the load on transmission parts.
The Chevrolet Niva drive consists of the following components:
- Gearbox.
- Transfer case.
- A pair of drive and cardan shafts.
- Front and rear axle gearboxes.
The transfer case is designed to distribute torque between the drive axles of the vehicle. The car is equipped with a two-speed transfer case, which provides:
- stable running of the machine when driving at low speed and at high engine speeds;
- power distribution between drive axles, depending on road grip.
The differential is one of the most important elements of the transmission. Its main purpose is to distribute traction force, and, if necessary, ensure rotation of two consumers at different angular speeds. The Chevrolet Niva drive transmission has three differentials:
- One for each axle (inter-wheel) - they allow the wheels of the same axle to rotate at different speeds.
- The third (interaxle action) - transmits power from the power unit to both axles of the vehicle. It also allows the shafts to operate at different angular speeds, depending on operating conditions, which significantly improves controllability.
A pair of cardan shafts (CV joint or cross design) provide connection between the transfer case and the drive axle gearboxes. Both car shafts have the same design - they are interchangeable.
The front and rear axles transmit force from the transfer case to the drive wheels through external and internal angular velocity joints.
Advantages of Lada 4×4 and Chevrolet Niva cars
Why have these inconspicuously designed cars remained so popular over the years? The secret is the relatively low cost, which is combined with good maneuverability, reliability and simplicity of design. Many people appreciated this vehicle during trips to hunting, fishing, and off-road travel.
Of course, Lada4×4 and Chevrolet Niva have many disadvantages. They are inferior in many respects to modern SUVs, which are distinguished by increased comfort and the presence of many additional options, but for those who are looking for an inexpensive, easy-to-repair car with high cross-country capability, the Niva is a pretty good option.
Lada 4×4
Chevrolet Niva
Location of levers on Lada 4×4
Transmission units
Differential locations
edit this post
The principle of operation of all-wheel drive on a Chevrolet Niva
In normal mode, the Chevrolet Niva operates in high gear with the differential unlocked. Torque is transmitted from the power unit, through the gearbox and intermediate shaft, to a two-stage transfer case gearbox. A center differential is installed in the transfer case housing. It links the front and rear axles, allowing them to rotate at different speeds, depending on road conditions and direction of travel.
How does all-wheel drive work on a Niva with a locked differential?
When all-wheel drive is engaged, both cardan shafts are secured with a locking clutch. This promotes uniform transmission of traction force to both axles of the vehicle. Due to this, the vehicle's cross-country ability increases, but controllability deteriorates.
Advice: It is not recommended to use the lock mode on roads with good grip, as this will lead to accelerated tire wear, increased load on transmission parts and components, and will also increase fuel consumption.
How does the Niva distribution box work?
There are three such differentials in the Niva transmission: each axle has its own (interaxle) so that the wheels of the axle can rotate at different speeds, and the third (interaxle) - in the transfer case - distributes the traction force between the axles. ... And this knob controls the operation of the transfer case differential.
Interesting materials:
How to smooth out rough edges in Photoshop? How to hit your top serve hard in volleyball? How to sync Chrome and Firefox? How do weather forecasters determine air temperature? How do family scandals affect a child? How to scan with a Brother printer? How to scan iPhone WhatsApp QR code? How do you say fool in another way? How to tell a guy that he is good in bed? How to upload a large video to Facebook?
Transmission of Chevrolet Niva and Lada 4x4: what is the difference
The first thing that catches the eye of the average user is that the Lada’s transmission is controlled by two levers, while the Chevrolet Niva has only one, not counting the gearbox control lever. This is due to the fact that Chevrolet’s upshift and downshift ranges, as well as the center differential lock, are implemented using a single-lever design. In addition, the Niva's front axle gearbox is not attached directly to the engine cylinder block, and the transfer case has three mounting points, unlike the Lada, which has two.
Nevertheless, both cars are absolutely identical in transmission design, have one engine for two, but due to the transfer case set back, the Niva’s intermediate shaft is longer than that of the Lada 4x4 by exactly 250 mm. Moreover, both cardan shafts driving the front and rear axles are completely interchangeable.
External CV joint Niva, history
The main difference that the owner of a Niva or Chevrolet Niva should know. CV joints come in 22 or 24 splines, for cars with and without ABS. Grenades with 22 slots were installed mainly on carburetor fields. With the transition to injection and restyling in 2008, they were no longer produced. Then there are only 24 slots. The 22 slot grenades had two serious advantages. They were smaller in diameter and, as a result, there was more “meat” on the hub. Such a breakdown as a hat breaking off on the hub almost never happened. Second point. Old fields were exported to Europe in fairly large quantities, and there they spit on AvtoTAZ and made their own spare parts. I brought grenades from Loebro, SKF, GKN-Spidan, GLO - all of these are high-class manufacturers in the field of drives and CV joints. Unfortunately, none of these companies makes CV joints for 24-spline fields. There are a lot of bright boxes on the market, but most of them are brands made only for Russia. In the future we will only talk about CV joints with 24 splines.
Design and diagram of the Chevrolet Niva transmission
The Chevrolet Niva transmission, in terms of operating principle and architecture, completely replicates the donor car, the VAZ 2121 and its modification, the VAZ 21213. This means that the drive is carried out to all four wheels constantly, without the possibility of disabling the front axle. The design provides a number of reduction gears, as well as a manually lockable center differential.
The main elements of the transmission are as follows:
- dry single-plate clutch;
- five-speed gearbox;
- intermediate shaft;
- transfer case;
- 2 cardan shafts driving the front and rear axles;
- front split axle with a gearbox separately mounted on the load-bearing frame;
- continuous, solid rear axle with integrated gearbox and differential, as in classic Tolyatti models.
The transmission structure is shown in the drawing and it is no different from most SUVs with permanent all-wheel drive, as well as the operating principle.
Torque is transmitted from the engine crankshaft through a dry single-plate clutch to the gearbox input shaft. Next, the torque enters through the reduction gears in the box and is transmitted through the output shaft to the transfer case, where it is evenly distributed between the drive axles. The stock Chevrolet Niva does not have a power take-off shaft, which can be used to transmit rotation to the winch.
Description of possible problems with the transfer case
During the operation of off-road vehicles, parts and components of the transfer case gradually become unusable due to wear. Most often, the following interruptions in the operation of the mechanism occur:
- The front axle does not engage.
- The transfer case is overheating.
- Leaks and increased oil consumption of the transfer case.
- Unauthorized disabling of the front axle.
Changing the oil in the transfer case Niva 2121
To ensure the performance of the vehicle, it is necessary to carry out timely maintenance. Changing the oil is included in the mandatory list of machine maintenance work. To change consumables in the Niva 2121 transfer case, you will need 0.8 - 1.5 liters of gear oil.
The frequency of replacing lubricating fluid is equal to 45,000 km of distance traveled. The first procedure is carried out after 60,000 km, and then in accordance with the established schedule.
The procedure for changing the oil in the transfer case of a Niva SUV:
- warm up car systems and mechanisms, to do this you need to start the engine and drive a short distance;
- install the machine on an overpass or over a special inspection hole;
- clean the filler and drain plugs of the transfer case from dirt and dust;
- place a container under the drain to collect waste material;
- unscrew the plugs and drain the liquid;
- remove metal fragments, shavings, splinters and other wear elements;
- screw in the plug;
- pour into the washing liquid (about one liter);
- start the engine;
- move the lever through the transfer case gears with slight delays;
- turn off the engine;
- drain the flushing composition;
- fill the transfer case with new oil;
- check the oil level;
- if necessary, add the required amount.
For the transfer case of the Niva 2121 SUV, transmission oils of the famous brands Mobil, TNK, Castrol of the GL-4 class are most often used.
VAZ 2121 Niva has established itself as a reliable and versatile Soviet SUV. In 1977, the first domestic all-terrain vehicle rolled off the assembly line, which, unlike ordinary passenger cars, the VAZ 2121, had all-wheel drive and increased cross-country ability. The Niva transfer case design was developed by experienced AvtoVAZ designers in order to increase the functionality and versatility of the vehicle both when driving off-road and in city conditions.
Gearbox and clutch Niva Chevrolet
The Niva has virtually the same VAZ gearbox, but with minor changes designed to increase the durability of the unit. Firstly, this is the replacement of the VAZ rear bearings of the primary shafts and intermediate bearings on the secondary shafts with similar, but sealed types. This eliminates bearing malfunctions associated with contamination and premature wear. Secondly, the gear shift control drive has been changed. It is easy to notice that in a Chevrolet the gearbox control lever is closer to the driver, which makes control more convenient. This was achieved through the use of an extension with a 250 mm horizontal rod. Gear ratios remain the same, as does the gear shift pattern.
The clutch device in the Chevrolet Niva transmission has undergone some changes and received a number of improvements and more progressive parts from front-wheel drive VAZ cars.
Features and malfunctions of the transfer case
The Chevrolet Niva transfer case not only moved back by 250 mm, but also changed the installation angle by 4 degrees. Chevrolet engineers calculated that this angle would be optimal for the operation of driveshaft joints. The design of the transfer case uses small-module, low-noise gears, so the howling of the transfer case, as on the old Niva, is now completely eliminated.
Another common malfunction of the transfer case on old Nivas was vibration. On Chevrolet, this issue has been practically resolved by installing new pillows and the appearance of a third attachment point. This will eliminate not only operational vibrations and noise, but also the likelihood of incorrect installation of the transfer case after repair, prevention or troubleshooting.
There is another malfunction that few people think about, however, this problem is related to the resource and endurance of constant velocity joints. The fact is that a cermet valve is installed directly under the CV joint boot mounting clamp. Its task is to compensate for excess pressure inside the cover, thereby protecting it from rupture, and the CV joint itself from water and dirt. If you monitor the performance of the cermet valve during repairs or replacement of hinges, the boot will last a long time and will reliably protect the CV joint.
Even such a complex system as the Chevrolet Niva transmission can be succinctly described in an accessible way. Each owner is required to know the basic principles of operation of the systems of his car.
Chevrolet Niva transmission device
Transmission is a purely technical concept and does not relate exclusively to a car. Literally, it is a power transmission that ensures the integral functioning of the mechanisms. Applicable to a specific car model, we can conclude that the Chevrolet Niva transmission is represented by mechanisms that implement the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels with the possibility of changing it. We have another video on the topic of Chevrolet Niva transmission.
The VAZ-2123 transmission includes the following units:
- Variable gearbox;
- Transfer case;
- Intermediate shaft;
- Drive and cardan shafts;
- Rear axle;
- Front axle.
The transmission provides permanent drive. This means that it is impossible to disable the front axle of a Chevrolet Niva. This scheme increases fuel consumption and also reduces noise and vibration insulation characteristics, but is considered the most optimal in off-road conditions.
The torque transmission diagram can be represented as follows: engine – clutch – gearbox – intermediate shaft – transfer case. The drive is transmitted to the axles via cardan shafts. The Chevrolet Niva transfer case has a center differential. In operation, it provides different angular displacement of the front and rear wheels. The differential lock allows you to equalize the angular speeds of rotation of both cardans. (you can see it more clearly in the video)
Important. The operation of the transmission with a locked differential is intended only for overcoming obstacles. Driving along a straight section of the road at high speed leads not only to excessive vibration of the car, but also to increased loads on the transfer case, which can cause its early failure.
The transfer case can operate in two modes. When you turn on the reduction mode, the torque increases. The features that the Chevrolet Niva gearbox has in conjunction with the transfer case allow you to control the torque and engage the center differential lock with one lever, and not two, like the predecessor VAZ-2121.
We help with all our wheels
How to enable all-wheel drive on a Chevrolet Niva? You can block the center differential of the Chevy Niva both when the car is stationary and while driving.
This is done with the clutch pedal depressed using the transfer case control lever, which is located behind the large gear selector. When the lever is in the neutral position, you need to pull it towards the driver. If you then press in the opposite direction, a lower gear will be engaged with a center differential lock and a gear ratio of 2.1. If you pull it towards you, a lower gear is activated (gear ratio 1.2).
When the lever is in this position, the corresponding yellow pictogram lights up on the dashboard. If you cannot follow these instructions, try repeating the procedure while driving the vehicle.
The correct sequence for engaging the rollover lock is given in the owner's manual for that vehicle.
It states that such blocking must be carried out in advance, while the car is moving along a section of the road with a hard surface. The action must be performed when changing the steering wheel position. To prevent breakdowns and damage to differential parts, locking is prohibited during slipping or when the wheels (wheels) are sliding. The mode is switched using the same lever. If the lock does not engage using this method, do not use excessive force. Just repeat the entire sequence of actions from the beginning.
Switching to a lower gear is also allowed without stopping the Niva completely, but this can only be done by experienced drivers. The fact is that the transfer case, unlike the gearbox, does not have synchronizers installed. Changing from a lower gear to a higher gear while the car is moving is undesirable, although it is allowed in extreme cases.
It is not recommended to keep the center differential of the wheels in locked mode at all times, especially when driving on asphalt roads, as this will not only lead to increased fuel consumption by the vehicle and poor handling, but also to the breakdown of expensive transmission components.
Transmission
The Chevrolet Niva gearbox has no structural differences compared to the Lada 4x4 box, and they are identical in design. The difference can only be noticed in the mounting and length of the gear shift drive. Another important feature is the presence of 5th gear.
The main parameter of the gearbox is the gear ratio. By trivial definition, this is the ratio of the number of teeth of the driven shaft to the number of teeth of the drive shaft. Naturally, we talk about the gear ratio when there is actually a transfer of torque from one shaft to another. If the specified parameter is greater than 1, then such a mechanism works to increase torque. The gear ratio for IV gear is 1, and for V – 0.82. That is, in V gear there will be an increase in the number of revolutions of the secondary shaft with a parallel decrease in torque. It is more convenient to imagine the value of the gear ratio using the sprockets of a high-speed bicycle.
Transfer case
The transfer case and differential control lever (multiplier) allows you to combine one of two modes with turning on or off the center lock. Together with neutral, there are 5 lever positions.
- Neutral position. There is no engagement in the main pair. The car cannot move.
- Differential unlocked, reduction disabled. Essentially, this is normal mode for everyday driving. The distribution of the moment of force occurs in a ratio of 1:2.
- Differential locked, reduction disabled. The distribution of the moment of force between the axles occurs in equal shares, but due to the operation of the cross-axle differential, the force on each wheel depends on the road surface.
- Differential is unlocked and reduction is engaged. The torque has been increased, but its distribution between the axles is 1:2.
- Differential locked, reduction enabled. Bridges work in a rigid connection. The car has the most increased cross-country ability.
How does it work?
In normal mode, the car moves in high gear. In this case, the center differential is unlocked. This reduces fuel consumption and slows down tire wear. If necessary, the cardan shafts are fixed with a locking clutch and equal force is transmitted to the two axles. This improves the vehicle's maneuverability.
Important: differential locking impairs handling and causes skidding when cornering. Also, when the locking clutch is engaged, tire wear accelerates. Therefore, you should not engage the lock when driving on the highway.
To overcome steep climbs or get out of mud, sand or snow, the transfer case is equipped with a low gear. It provides high torque and reduces driving speed.
Resource of transmission elements
With proper maintenance, all transmission elements have service lives that comply with the regulations. The existing stereotype about unreliability is not confirmed either documentary or practically. Until now, the Chevrolet Niva remains one of the most popular cars on the market. The owners claim that the car is taking care of its 200,000 km, which the plant lays down as a resource. This means that the transmission resource is determined by the manufacturer and cannot be less than 200,000 km.
Once again, emphasis should be placed on timely maintenance as a guarantee of flawless operation of the system.
When to use a differential lock
The Chevrolet Niva has high cross-country ability in all types of off-road and mountainous terrain. Many of them can be easily overcome with a locked differential. This driving mode is recommended:
- on roads with reduced cross-country ability;
- on steep ascents and descents;
- when moving on dry (loose) sandy surfaces;
- when driving on ice, deep snow or crust.
As a conclusion, the story “How to turn on all-wheel drive on a Chevrolet Niva: diagram and video instructions” is offered. By the way, it is recommended to lock the car at least once a week, especially in winter.
Source