What does P0422 mean?
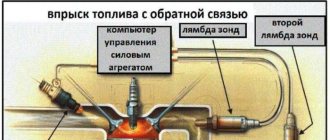
Trouble P0422 is a general trouble code that indicates that the primary catalytic converter (bank 1) efficiency is below acceptable levels. Catalyst efficiency is determined by the transmission control module (PCM), which uses exhaust gas and temperature data from oxygen sensors located upstream and downstream of the catalytic converter to determine efficiency. If the readings from both sensors match or are almost identical, this indicates that the catalyst efficiency is most likely below acceptable levels. In this case, error P0422 .
How to Troubleshoot or Reset Trouble Code P0504
Error p0420
Some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P0504:
- With the help of an assistant, check the brake lights. Make sure they work, turning on and off, and that the bulbs are in order.
- If the brake lights stay on continuously, the brake light switch is either not adjusting properly or is faulty. The same applies to faulty lamps. Move the driver's seat back and look under the dashboard. Squeeze the tabs on the electrical connector located on the brake light switch and remove the connector.
- Using a voltmeter, check the voltage on the red wire in the connector. Place the black wire on the ground and the red wire on the red wire terminal. The voltmeter should show a voltage of 12 volts, if not, you should check the wiring to the fuse box.
- Connect the connector to the switch and measure the white wire with the pedal pressed. You should have 12 volts with the pedal pressed and no voltage with the pedal released. If there is no voltage, replace the switch. If there is voltage on the white wire with the pedal released, also replace the switch.
- If the switch has an adjustment, check it. The switch must be in good contact with the brake pedal lever and fully depressed.
- If the brake lights are working fine but you still have a code, check the other wires at the brake light switch. Remove the connector and check the remaining wires for power. Make a note of the location of the power wires and replace the connector. Secure the rear wire next to the power wire with the pedal pressed. If there is no power, replace the switch.
- If the power was turned on when the pedal was pressed in the last test, the switch is OK. There is a problem when connecting to the control unit or with the vehicle control unit itself.
- Connect the control unit and the brake pedal sensor via ground. If the voltmeter shows 12 volts, then the control unit is faulty. If there was little or no voltage, replace or repair the harness from the control unit to the sensor.
Diagnosis and problem solving
The main problem is considered to be a discrepancy between the data in the PCM and the brake pedal sensor. Therefore, let's take a closer look and describe some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P0504.
The brake light switch is located under the instrument panel at the top of the brake pedal lever. The brake booster raises the pedal to the fully extended position. The brake light switch is mounted on a crossbar support bracket directly behind the brake pedal mounting bracket.
The only way to access the switch is to move the front seat back, lie on the backrest and look up under the dash. You will see a bracket with a switch near the top of the brake pedal lever. The switch will have four or six wires.
The switch rests on the bracket so that its drive rod is in contact with the brake pedal lever when the pedal is fully extended. At this moment, the switch is pressed on the brake pedal lever, cutting off the voltage supply.
When you press the brake pedal, the lever extends to engage the switch and turn on the brake lights. After releasing the pedal, the lever presses the bar again, turning off the brake lights.
Therefore, with a high degree of probability, we can say that replacing this sensor will eliminate problems with error P0504.
Causes of error P0422
The most common cause of P0422 is a faulty catalytic converter. Other reasons are:
- Oxygen sensor malfunction
- Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunction
- Fuel pressure regulator malfunction
- Manifold air pressure sensor malfunction
- Air flow sensor malfunction
- Engine oil contamination
- Engine leak before catalytic converter
- Misfires in engine cylinders
- Damage to wires and connectors
Vehicle diagnostics and troubleshooting
If you nevertheless decide to buy a used car, then you should definitely make a diagnosis, paying attention to any Lada error codes that appear on the device display. Information about existing errors will be very useful, be sure to pay special attention to this
To diagnose and find out information, you should contact a car service center if there is no special insert on the used car you are buying.
In fact, such a procedure is a huge list of information that can tell about any possible danger. Usually this is not given importance, but in vain. For example, if a car’s BC states that the airbags are faulty, you definitely need to check this. Correction: what needs to be done? Immediately press the left button and the right one, from this press the on-board computer adjusts the selected parameter.
Then pressing the keys left or right changes the parameters. After pressing simultaneously, you exit from the adjustment. Reset. By pressing the left and right keys simultaneously, the options displayed on the screen will be reset. If everything is done in the “System error” mode, after that the error disappears. If faults actually exist, the error will remain in memory until reset occurs.
If the BC does not turn on, the causes of the problem are:
- there is no electric current in the BC connectors;
- there is no contact in the terminals.
BC cannot diagnose the reasons for this:
- the wire came loose;
- no contact.
BC cannot calculate the speed of the car, the reasons for this problem are:
there is no contact in the connectors.
BC cannot calculate the remainder in the fuel tank, reasons:
devices do not have software compliance.
The BC incorrectly shows how much fuel is left in the tank, the reasons for this are:
- there is no wire in the wiring at the 8th contact and the 9th terminal in the on-board computer;
- The car panel is showing incorrectly.
There is no BC screen backlight, reasons:
I need to make the screen brighter.
The thermometer shows incorrectly, reasons:
- the wire has broken in the temperature detection sensor;
- incorrect contact with the on-board computer.
No voice accompaniment, reasons:
- speaker is faulty;
- the software has crashed;
- The voice accompaniment is not reproduced (you must press the “up” key and hold it for more than three seconds).
BC writes incorrectly, the program has gone wrong, etc., reasons:
- The on-board computer is not connected or there is no contact with it;
- there is no contact in the connected battery terminal (the contact should be securely fixed).
Initialize the BC:
- previous settings will be reset;
- reset all parameters for the previous ride;
- set the clock to 8 hours 00 minutes;
- The alarm clock should be at zero, its notification is disabled.
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0422 code?
Error P0422 can be diagnosed using a standard OBD-II scanner. The mechanic uses a scanner to view data and gather information about the code, as well as check for other error codes that may be present. The mechanic will then clear the error codes from the PCM memory and retest the system to see if P0422 again. If the code disappears, it may indicate an intermittent error or that the code appeared in error.
If the P0422 appears again, have a mechanic inspect the wires and connectors near the catalytic converter. He will repair or replace any damaged items. The mechanic will then inspect the catalytic converter and also perform a thorough check of the exhaust system for leaks.
If the catalytic converter is the problem, the mechanic will examine other vehicle components to determine the cause of the catalytic converter damage.
How is self-diagnosis performed?
We have sorted out the main errors on the Priora, now it’s worth finding out how self-diagnosis is performed. The VAZ 2170 with 16 valves has a special controller with which diagnostics are performed. If you have an on-board computer installed, then diagnostics are performed on it. There is also special equipment that allows for a more in-depth check of Priora 16 class systems.
Since most Priora 16 cars already have an on-board computer, we will consider the option without the use of special devices. Diagnostics begins with activation of the test mode. The work proceeds according to the following scheme:
Common errors when diagnosing code P0422
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0422 is failure to follow the diagnostic protocol, which leads to hasty replacement of the catalytic converter. Before replacing the catalyst, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of its damage, and also consider other error codes present.
It is also a mistake to hastily replace oxygen sensors. Before replacing them, it is necessary to perform a thorough diagnosis, since usually sensor failure is not the only cause of error P0422 .
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0422 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi
- Chevrolet
- Chrysler
- Dodge (Dodge Caravan)
- Ford
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Elantra)
- Kia (Kia Spectra, Sportage)
- Mercedes
- Mitsubishi
- Peugeot (Peugeot 206)
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Beatle, Jetta)
- Volvo
- VAZ 2104, 2105, 2107, 2110, 2111, 2112, 2113, 2114, 2115
- Volga Chrysler, 31105
- Gazelle Business, Next
- Lada Vesta, Granta, Kalina, Niva, Priora
- UAZ
With fault code P0422, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common are the following: P0304, P0326, P0420, P0441, P0455.
How serious is the P0422 code?
The severity of the P0422 depends on the cause of its occurrence. If the problem is a bad catalytic converter, the engine may stall frequently or be difficult to start. In this case, problems with the vehicle's handling may occur. However, if everything is in order with the catalyst, there should not be any serious problems. In any case, if this code is detected, it is recommended that you contact a qualified technician as soon as possible to diagnose and repair the error to avoid serious damage to the catalytic converter.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0422 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light) illumination. It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in the ECM memory as a malfunction).
- The engine stalls or has trouble starting.
- Decrease in engine power.
- Increased emissions of harmful substances from the exhaust pipe.
Replacing the adsorber purge valve on Kalina
If the check shows that the Evap-Solenoid is faulty, the part must be replaced (catalog number - 11181164200). There is no point in repairing the device:
- the price of the valve is in the range of 400-800 rubles;
- You can buy the device in almost any store that sells VAZ spare parts;
- changing the KPA is very easy and simple.
But before making a replacement, it would be a good idea to check the control circuit; quite often the valve does not work due to a break in the wires going to it. To complete the work, you will not need a pit or a lift, and the procedure itself will take no more than one to two hours, even if the operation is performed by an inexperienced worker without metalworking skills.
We change the valve as follows:
- turn off the ignition, raise the hood;
- find Evap-Soleno >
Replacing the purge valve could be considered a very simple task, if not for one “but” - it is very difficult to remove the plastic tube from the CPA without damaging it, and it does not come with the new valve. There are two options here:
try to carefully heat the connection with a hairdryer and pull off the pipe; cut the tube at the connections, and instead buy an ordinary fuel hose with a diameter of 8 mm and two clamps.
Having measured the required length of the hose, cut it, connect it to the valve and connector, we get approximately the same design as in the figure below.
We install everything in place, start the engine, and test the car on the move.
Conditions for generating DTC P0420
The ECM, in the process of monitoring, compares the signals of the 1st and 2nd sensors during a given time interval, calculating the duration of the voltage signal, and if it goes beyond a given threshold, the “brain” of the car interprets this as a malfunction of the neutralizer. The threshold value of the difference between the amplitudes of the front S1 (taken as the standard) and rear S2 oxygen sensors is more than 0.7 times per minute. But the check light, indicating that an error has been recorded in the memory of the ECM unit, does not light up instantly, but only when a decrease in the performance characteristics of the catalytic converter occurs for 100 seconds, and the engine load should be from 21 to 63% when the crankshaft rotates 1,720 - 2,800 rpm, and the catalyst temperature exceeds 500 degrees.
Signal from oxygen sensor
As the catalyst wears out (its throughput), the rear sensor readings approach the readings of the front oxygen sensor.
During normal operation of the catalytic converter, the downstream heated oxygen sensor signal switches slowly between rich and lean conditions. Frequent switching of the lambda probe between these states indicates a decrease in the efficiency of the converter. As a result, its ability to accumulate oxygen is reduced.
The task of the catalyst is to oxidize carbon monoxide and neutralize CO2 hydrocarbon emissions in order to reduce the concentration of harmful substances. This process, starting with the Euro 3 standard, is monitored by two oxygen sensors. There is a constant comparison of the signals of the first and second lambda in order to register the convergence of their readings. Therefore, error code P0420, in due time, will bother all owners of cars, including VAZ, Nissan, Toyota, Chevrolet, Ford, Honda or others produced after 1996 and having 2 lambda probes in the exhaust system.
Trouble code P0420 appears when oxygen and unburnt fuel residues are detected in the exhaust gases.
What does it indicate?
The occurrence of error P0420 makes it clear to the car owner that not everything is in order with the operation of the catalyst and it is not able to cope with the entire volume of incoming exhaust gases. However, this does not always mean that the catalyst has failed. It is likely that it became clogged and this, in turn, negatively affected the throughput.
It is important to note that if there are two neutralizers on one car, this error code is P0430. This is typical for vehicles of Euro 3 standard from above.
Eliminating error P0422
This problem can be resolved in the following ways:
- To begin with, the VAZ-2114 ignition is turned on, after which the diagnostics are connected. Then you need to turn off the ignition and familiarize yourself with other existing errors. This must be done without fail, since they are the ones that are eliminated first.
- Next, you will need to diagnose the catalyst for various damages. If malfunctions occur, it must be replaced with a new one. Otherwise, let's move on.
- The next step is to inspect the exhaust system, which is located between the converter and the muffler. It must be sealed and without any damage. If there are any, they need to be eliminated. If, on the contrary, no dents or scratches are found, then most likely the problem lies directly in the neutralizer. In this case, it must be replaced.
- The final step after eliminating defects or replacing the device is to warm up the engine to +70 °C and set the speed to 2000-3000. Then you should wait at least four to five minutes and see if the error appears again. Ideally it shouldn't exist.
It is also worth noting that to fix this problem, it may be necessary to replace one of the following elements:
- neutralizer;
- oxygen or air flow sensors;
- coolant temperature sensor;
- fuel pressure control.
Note: measurement of the effectiveness of the neutralizer must be carried out using a specially designed device - a gas analyzer.
If the above actions do not have an effect, it is recommended to take the car to a car dealership for a more thorough check.
Reviews. Auto News. Test drives
Main Menu
- Home
- Adviсe
- Error P0422 - Main catalyst performance too low (bank 1)
Error P0420 - what does it mean, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, solutionAre you trying to get rid of the P0420 error code? Then this article is for you. The P0420 fault can be difficult to diagnose. You think you have fixed the error, but after 100 km the Check Engine light comes on again. This code is triggered when the engine control module detects a faulty catalytic converter. It uses one oxygen sensor at the front of the exhaust manifold - before the catalyst, and another oxygen sensor - after the catalytic converter to measure the efficiency of the catalyst. In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about the P0420 code to fix it once and for all. Contents What does code P0420 mean? P0420 is triggered in the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) when there is a problem with the performance of the catalytic converter. The controller uses two oxygen sensors - one before and one after the catalyst to measure its efficiency. The error occurs if the converter or oxygen sensor malfunctions, which begins to transmit incorrect data. We receive many messages asking about the P0420 code. It keeps coming back after several repairs and you just end up spending more and more money on auto repair work. This trouble code may confuse you because there is a lot of misinformation about it. Catalytic Converter The front O2 sensor measures the air/fuel mixture. It tells the control unit if the engine is running rich or lean. The rear O2 sensor is the diagnostic oxygen sensor for this error code. If the rear oxygen sensor receives incorrect values, a P0420 fault will be stored in the ECU. This could be due to a faulty catalytic converter or one of the O2 sensors failing. There may also be many other problems with the engine that are destroying the catalytic converter, and if you install a new one, it may be damaged again. The oxygen sensor is also called a lambda probe. Many people think that a lean or rich mixture can cause this error code. Yes, it is possible, but not in the way you think. A rich or lean mixture can damage the catalytic converter and when it is damaged/full of fuel it will be low in efficiency and the rear oxygen sensor will see this and trigger a P0420 code. Symptoms of the Error You probably won't have any symptoms other than an illuminated Check Engine Light with code P0420. You may experience other engine problems that damage your catalytic converter. This could include a rough (“rough”) idle, acceleration problems, misfires, or harsh gear changes. Always fix these problems first. The Check Engine light is on. Misfires. Rich mixture. Poor mixture. Engine oil is burning/gray-blue smoke coming from the exhaust pipe. Slow acceleration. Causes The most common cause is the catalytic converter. It may simply be old and worn out. But there are many cases where the neutralizer is new, but at the same time it is a non-original part. Some cheaper catalytic converters may not be efficient enough, and then you will have to buy an original catalytic converter. Sometimes converters are installed too far back on the exhaust pipe. This will cause it to not get hot enough and cause a P0420 code. Damaged catalytic converter (most common cause). Non-original catalyst. Incorrect installation (placement) of the catalytic converter. Front oxygen sensor damaged / wiring fault. Rear oxygen sensor damaged / wiring fault. Exhaust gas leak. Leak on the intake manifold. Oil burns (damage to catalyst). Rich/lean mixture (damage to catalyst). Misfires (damage to catalyst). Faulty engine control unit (rare). Troubleshooting These are just possible solutions and you should never replace parts without proper diagnostics as you could be throwing money away if you are unlucky. Read the entire article if you want to learn how to properly diagnose this trouble code just like an experienced auto mechanic would. It will take time and may require some skill, but you won't spend $1000 to replace a good catalytic converter. Replace the catalytic converter. Replace with original catalyst. Replace the front oxygen sensor. Replace the rear oxygen sensor. Repair of faulty electrical wiring. Correct oil burning. Correct misfire. Correct lean/rich mixture. Check the data using an OBD2 scanner. Replace the engine control unit (rarely). Troubleshooting Chart Code Symptoms Causes Causes of Catalyst Damage Error P0420 Check Engine Misfire Rich Lean Burning Oil/Blue Smoke from Exhaust Pipe Slow Acceleration Faulty Catalyst Front O2 Sensor Rear O2 Sensor Exhaust Leak Oil Consumption Misfires/Lean Mixture Damaging Catalyst Misfires Ignition Oil Consumption Exhaust Leaks Intake Leaks Rich Composition Lean Composition ECU Malfunction Causes of Catalytic Converter Damage There are several causes of catalytic converter damage that can trigger the P0420 code. Here are the most common ones. Misfire. Oil consumption. Leaks at the outlet. Inlet leaks. Rich mixture. Poor mixture. Malfunction of the ECM/PCM control unit. There are many reasons that lead to malfunctioning oxygen sensors or catalytic converters. You should make sure to correct these problems before you replace any part. Otherwise, they may be damaged again. Check the controller DTC memory for any other trouble codes. Fix them first. Make sure your car is not burning oil by checking the exhaust smoke, blue smoke = oil, white = water, gray/black = rich mixture. How to Diagnose a P0420 Code Here is a guide on how a professional auto mechanic will diagnose the trouble code. This guide may require knowledge of vehicle electrical systems, and you may need some tools to complete the task. But even if you have no idea about car electronics, you can still gain useful information. You should always connect your car charger when troubleshooting your car. Low battery voltage can cause other unrelated error codes that will confuse you. Low voltage may damage the control unit or other electronics. 1. Connect the charger Connect the charger to the battery and make sure it charges the battery correctly. You should use a charger that provides at least 4 Amps while troubleshooting. A lower charging current may result in the battery being discharged when the ignition is turned on. 2. Connecting an OBD2 scanner Connect an OBD2 scanner to read the P0420 code. You can use a diagnostic scanner or an ELM327 adapter with the Torque program. 3. Check for other fault codes Check for other faults that could damage the converter or any oxygen sensor faults. If there is an error in the lambda probe, then replace or check it first, this may also fix the P0420 code. Correct all other trouble codes before correcting the P0420 code. Always write down any error code numbers, do not simply erase them. 4. Check for gray-blue smoke while the engine is running. Increase engine speed and check for gray-blue smoke from the exhaust pipe. Blue smoke = burning oil. Replacing the catalyst will not help. It will most likely fail again very quickly. Burning oil can also damage the oxygen sensors and cause them to read the mixture incorrectly. You should always check for white, gray and black smoke. White smoke comes from water in the exhaust pipe, gray/black smoke comes from a rich mixture. 5. Check for exhaust leaks Raise the vehicle while it is running. Listen and look for any exhaust leaks in front of the rear lambda probe. An exhaust leak can cause the O2 sensors to receive incorrect data and may trigger a fault. If you have an exhaust leak behind the rear oxygen sensor, this should not cause an error. Tips on how to find exhaust leaks: 6. Test Drive Take the car for a test drive and make sure there are no leaks or other symptoms. Drive fairly vigorously for some time so that the catalytic converter warms up. If skipping or other strange behavior appears, start diagnosing it first. 7. Drive to the garage and jack up the car. Raise the car and keep it idling. Make sure you have proper ventilation. Connect an OBD2 scanner and check the current data from both O2 sensors. Open the signal graph from oxygen sensors. Start the car engine and make sure that the temperature of the catalytic converter is at least 400 °C. You can use a digital laser thermometer to check the temperature. Both charts should be open so you can see them. The front sensor should constantly jump between 0 - 1 Volt, and the rear sensor should show a stable 0.7 - 0.9 Volt. This means everything is working properly. If the catalytic converter is damaged or not hot enough, the rear lambda probe signal will fluctuate in the same way as the front one. You can also use a digital multimeter. To do this, you need to check the voltage from the rear O2 sensor. But the signals are high speed and it can be difficult to read such voltages with a multimeter. 8. Check the temperature of the catalyst You can also check the temperature on the converter. Make sure it is still hot before checking. Use a digital laser thermometer to measure. Check the temperature just before, in the middle and after the catalyst. If you get the same temperature at all points when the neutralizer is hot (over 400 C°), then it is most likely empty or damaged. If the catalytic converter is working correctly, the temperature should be 100-150 C° higher directly behind it than in front of it. If the temperature in front of the catalyst is much higher, the car may be running rich and the converter is working too hard. This may also be due to the catalytic converter being blocked or having poor exhaust flow. Video on how to test your catalytic converter using the Torque Pro app: 9. Summarize your results Summarize your diagnostic results. If you have no other error codes, the front oxygen sensor signal changes, the catalytic converter temperature is uniform, and you do not see blue smoke, replace the catalytic converter. Code P0420 can be a problem to diagnose correctly. If you have read this repair guide and received incorrect results, you can replace your catalytic converter with reasonable confidence. If your diagnostic results look good but you still get a P0420 code, there is a small chance that the catalytic converter is still causing the fault. In rare cases, you may have a faulty ECM. If you find any gaps, gray-blue smoke or other problems, correct them and remove the error. With luck, the P0420 code may not return. What are the causes of oil leakage? If you see blue smoke coming from the muffler and you have a P0420 code, you need to fix the oil leak first. But how to do this, you ask? Internal oil leaks can often be costly. Sometimes complete disassembly of the engine is required, but in some cases this may be the cause of the error. We will describe the most common causes of internal oil leakage. The best way to find the problem is to check the compression to see if there is any pressure loss in the cylinders due to the piston rings. Clogged PCV System (Most Common) A clogged PCV system is the most obvious cause of blue smoke. You can start by unscrewing the oil cap while the engine is running. The cap should be sucked back in because most engines have a vacuum if everything is working properly. If you feel excess pressure in the crankcase, the first thing you should check is the crankcase ventilation. There are often 1-3 hoses running from the crankcase to the air filter housing. Check them and make sure the tubes are not clogged. A clogged crankcase vent can cause oil to be forced past the piston rings and valve guides. Turbine Wear Another common problem if your car is turbocharged is oil leaking, which is sucked into the engine and burned there. How to find out? You need to check the presence of oil in the intercooler (intermediate air cooling radiator). In this case, your turbocharger may be worn out. You can also remove the charge tubes and check the turbocharger impeller to make sure it feels good and isn't loose. The clearance should be ~1mm on the sides, depending on whether the turbine is ball bearing or not. Worn valve guides Worn valve guides and seats can cause oil to burn. However, this is not an easy fault to diagnose or repair. Always check the piston rings for leaks before replacing them. The easiest way to replace the valve guides is to lift the cylinder head and remove the valve springs. There are tools that can be used to increase the pressure inside the cylinder and replace the liners without removing the head, but the procedure is not simple, we recommend having a qualified mechanic do this for you. Worn/Damaged Piston Rings Worn or damaged piston rings are a fairly common problem when it comes to internal oil leaks. Most often this can be checked by measuring the compression. You can inspect the pistons with an endoscope in the form of a small camera through the spark plug holes. If you find that the piston rings are damaged, the only way to fix this is to disassemble the entire engine and remove the pistons from the block. If you are installing new piston rings, be sure to check the pistons and piston ring clearance. Cracks in the cylinder head Cracks in the cylinder head or engine block are also a possible cause of oil combustion. However, this problem is not very common, but it is possible. If you find cracks, you will have to contact a specialist who will weld them, if possible. In many cases, the entire cylinder head or cylinder block will have to be replaced. It is not always possible to weld cracks. How does a catalytic converter work? Here is a video of how a catalytic converter works: The picture shows the parts of a catalytic converter. The catalyst is used to purify exhaust gases. If you look at it, you will see that it looks like a honeycomb in a beehive. Engine exhaust produces hydrocarbons (unburnt fuel), carbon monoxide (from combustion in the engine), and nitrogen oxides (formed when heat in the engine causes nitrogen in the air to combine with oxygen). The catalytic converter contains platinum and palladium (which is why you get paid for the used catalyst). The ceramic structure converts carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide CO) into carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide CO2). It also converts hydrocarbons into water and carbon dioxide. Nitric oxide is converted back to oxygen and nitrogen. If the conversion fails, the rear oxygen sensor will sense this and send a signal to the control unit, which will activate the P0420 code. How does an oxygen sensor work? Video of how the lambda probe works: What is the function of the front oxygen sensor? Oxygen Sensor The front O2 sensor is adjustable. It will measure the mixture of exhaust gases that pass through it. Using this data, the ECU determines whether the mixture is rich or lean. The front oxygen sensor can be installed either directly in front of the catalytic converter or on the exhaust manifold. Some vehicles use multiple front O2 sensors for different cylinders. There are two types of oxygen sensors: narrowband sensor (most common) wideband sensor (newer vehicles). A wideband sensor reads the signal much faster. Narrowband usually uses four wires. One is the power supply, one is the signal and two wires are for heating. You can simply determine whether you have a narrowband or wideband sensor. Look at the number of wires. A broadband sensor will have 5 or more wires, and a narrow-band-2-4 wires. If the front sensor O2 is faulty, then the ECU thinks that the engine works on a rich mixture, while it works on the poor in fact. This can cause an error P0420. What is the function of the rear oxygen sensor? The rear lambda-zond does not differ in the structure from the front. The difference is that the rear sensor does not provide any information for adjusting the mixture to the engine control unit. The purpose of the rear sensor O2 is only to check whether the catalytic neutralizer works correctly. If the rear sensor feels that the catalyst is working incorrectly, it will send this information to the control unit, which will launch and save the P0420 malfunction code. What does Bank 1, Bank 2 mean? The designation Bank 1 and Bank 2 is usually used if the car has more than four cylinders. But it is also used on four -cylinder engines. This means that you probably have two exhaust pipes or that the engine cylinders are divided into several O2 sensors. "Bank" means which side or on which exhaust pipe the sensor is located. Bank 1 is always installed on cylinders 1-3-5-7-9, etc. The Bank 2 sensor controls the cylinders 2-4-6-8-10. You can turn off one oxygen sensor and consider errors by the OBD2 scanner. This will find out where the sensor is installed-in Bank 1 or Bank 2. Is it possible to remove any detail to get rid of the P0420 code? You cannot just remove any details to fix the P0420. This will most likely provoke another error or other malfunctions. You can reprogram the control unit to remove the control of the catalytic neutralizer. But this is not recommended, because in most countries there is a law according to which the catalyst should work. If you reprogram the controller, you can also remove the catalytic neutralizer. Remember that if you remove the catalyst, then most likely you will not pass the inspection for the number of emissions into the atmosphere. There is another way to deceive the ECU-to replace the rear lambda zond. This method is for those who want to get rid of the P0420 error by any methods. We don't recommend doing this. Here you can see the prices and types of deceit of the oxygen sensor. How can the burned oil damage the catalyst? If there is an internal leak of oil in the engine that burns in the cylinders, it will go through the exhaust pipe. This creates blue smoke that we mentioned earlier. The oil stuck and burns in the neutralizer, damaging it. The catalyst temperature can reach more than 600 C °. And if it overheats, it is damaged. Then, if you replace the catalytic neutralizer without eliminating oil leakage, the oil will continue to get stuck and burn in it. Thus, you will also damage your new catalyst. How can a rich or poor mixture cause an error P0420? A rich or poor fuel mixture can damage your neutralizer in several ways. Due to the rich mixture, too much fuel will fall into the catalyst. It will ignite and destroy it. The poor mixture can cause a high temperature of exhaust gases. It can also damage the catalytic neutralizer. However, the catalyst is not damaged quickly due to this kind of problem. But in the long run, it wears out much faster than if the fuel mixture was correct. How can the passes cause an error P0420? Ignition misses are a common cause of damage to catalytic neutralizers. This is because during ignition passes, unbroken fuel appears, which enters the neutralizer through the exhaust manifold. Since it is hot, fuel is ignited and causes a reverse reaction. These ignitions are fatal for any catalytic neutralizer and can quickly damage it. Another option lies in the fact that unsecured fuel comes out, and immediately after that there is fire from another cylinder, which ignites the mixture, and it explodes inside the exhaust pipe. These explosions can quickly damage the catalyst. Tools for eliminating the P0420 error to correct this malfunction code, you may need several tools to make diagnostics much easier and better. OBD2 scanner is necessary to diagnose an error code for viewing data in real time, etc. We recommend lending or buying a diagnostic scanner that can show signals in the graphs to facilitate the diagnosis. You should always have a car charger when you diagnose a car. The low voltage of the battery can cause other errors that will lead to incorrect conclusions. Low voltage can also damage control units or other electronics, if you are not very lucky. The digital laser thermometer is necessary to check the temperature of the catalytic neutralizer. The temperature issued by the OBD2 scanner is calculated, not real. The thermometer is also useful for many other tasks when you repair the car. Ideal for eliminating the malfunctions of the cooling system. A digital multimeter is required for any electrical measurements and is absolutely necessary. You will need a multimeter to search for almost all electronics malfunctions. He is not so dear. Buy a multimeter depending on your needs - there are both very cheap and expensive. The deceit of the oxygen sensor can be used in order to deceive the control unit, and this can correct the error P0420. This is a non -recommended method. If you think that your catalytic neutralizer is contaminated or there is oil from earlier internal oil leaks, you can try to use the catalyst cleaner. It is also used for other tasks when cleaning the exhaust system. The known reasons for the error P0420 by car models in some cars P0420 error are better known than in others. Here is a list of the most common reasons for each brand. These cars, as you know, have problems with the P0420 error. Remember that these are only general recommendations, and you must make the correct diagnosis before changing any details. Toyota Corolla The most common cause of the P0420 error on Toyota Corolla is a catalyst malfunction. But, this can often be caused by oil passing through the piston rings, which stuck in a catalytic neutralizer. First, check the presence of leaks on the inlet and release. Then check if there is a gray -haired smoke from the exhaust pipe. If you see him, then this is an occasion to contact a car service to find the oil comes from. The standard reason may be the crankcase ventilation. If you do not see blue smoke at any engine speed, most likely your catalytic neutralizer is worn out. Ford Focus Ford focus usually has an air leak. It can also be any broken solenoid that causes an incorrect fuel-air mixture, activating the error. Check the controller’s memory using a diagnostic scanner to count errors associated with the air-fuel mixture. If everything looks normal, check the presence of exhaust gas leaks. Replace the catalytic neutralizer if you cannot find any malfunctions or other mixture problems. Subaru / Subaru Forester Subaru usually has the same problem as Toyota Corolla. Check the presence of air leaks or other malfunctions associated with the fuel mixture. Check the presence of exhaust gas leaks in front of a catalytic neutralizer. The most common problem on Subaru engines is the catalyst itself. Volkswagen (VW) / Skoda / Seat / Audi A4 1.8 T / V6 2.4 These VAG cars have some well -known malfunctions that cause the P0420 code. Check the work valves at the inlet. Make sure that the crankcase ventilation is not contaminated, as a result of which the engine burns the oil that clogs the catalytic neutralizer. Check the presence of exhaust gas leaks around any folds on the exhaust pipe (general reason). Check the presence of any codes of malfunctions O2. If no problems are found, replace the neutralizer. This is a very common problem both at 1.8 T and on V6 gasoline engines. The 1.8 T catalyst can be quite difficult to replace if you have no experience in this. V6 has two catalytic neutralizers, so make sure that you eliminate problems and replace the catalyst on the right side. The conclusion in most cases the catalytic neutralizer is faulty and this is evidenced by the error code P0420. But there may be other reasons why the catalyst was damaged. Always correct all other fault codes before eliminating P0420. You can use special tools or reprogram control unit to deceive it. This will help get rid of the P0420 error. Bank 1, Bank 2 (Bank 1, Bank 2) indicate which of the O2 sensors or which catalytic neutralizer is faulty. The catalytic neutralizer cleans the exhaust gases and its removal is illegal.
How to solve the problem of low catalyst efficiency
Since most often the P0420 error appears when the catalyst has expired, most likely the problem of low efficiency of the catalytic converter system below the threshold level will have to be solved by replacing it with a working one or flashing the ECM to a different toxicity standard (under EURO2).
The most expensive (about 40,000 rubles) repair method will be replacing the catalyst with a new original one.
Much cheaper (5-6 thousand rubles) - replace it with a universal catalyst. Its operating efficiency is somewhat worse (the original is ceramic, while this one is often made of iron), the service life is only about 30-50 thousand km, and not all cars will react positively to such a change. But you won't have to make any software changes. It will cost about the same to buy a used original from disassembly.
When toxicity standards are not important to you, installing a flame arrester is a relatively inexpensive option. This solution involves cutting out the catalyst can and installing a second lambda blende.
A budget option, including re-flashing and installation of a blende (mechanical or electronic), is a transfer of the car to a lower toxicity standard. Such a solution to the problems that appeared with code p0420 will not only eliminate the malfunction, but also allow the engine to “breathe deeply,” because all these standards greatly reduce power capabilities in order to comply with environmental standards. This method involves removing the catalyst from the exhaust system, and installing a two-channel emulator will make it possible to fine-tune the response time parameters, signal speed and its offset.
And if the throughput of the catalytic converter is still within the normal range (0.21 kg/cm² at 2000 rpm), since a signal about the need to replace the catalyst can appear even at 70% efficiency, then you can temporarily install a spacer under the lambda probe. This solution is the cheapest, but not a panacea and is not suitable for everyone.
I hope that all the above methods for solving the problem associated with code P0420 will help you, and you will no longer have questions like: “why did error P0420 appear and how to fix it,” and you will share the knowledge gained on social networks with your friends. Write us a review, whether you managed to fix the problem, how much it cost, and which method helped to figure out the reason for the poor efficiency of the catalyst.
Catalyst performance too low
Decoding OBD-2 error p0422
Error p0422 appears in the controller logs when it detects low catalyst efficiency. The catalyst is installed in the exhaust system and acts as a filter, purifying exhaust gases from harmful substances. But they all accumulate in it and over time the neutralizer becomes clogged, and the second oxygen sensor monitors its condition.
A neutralizer is needed solely to improve the environmental class of cars, many people get rid of it, after this procedure they need to install a lambda probe blende or flash the ECU. Car enthusiasts who have carried out this procedure notice an increase in power and the engine begins to breathe easier.
Sometimes it is very difficult to remove the catalyst and replacing it is a much cheaper and faster option.
Error p0422 indicates that the difference between the readings of the first and second oxygen sensors differs by a value less than the threshold, that is, the catalyst does not perform its functions, retaining soot and other fuel combustion products.
A car with error code p0422 can be used normally, but its presence cannot be tolerated.
Possible symptoms due to error p0422
For the engine, such an error cannot make big changes, but the controller is working with an error and the following changes may appear:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Exhaust toxicity;
- Power reduction;
- Possible increase in engine volume.
Reasons for registering error code p0422
Some errors may appear as a result of erroneous operation of the brain ECU, and if after removing error p0422, it appears again, you need to pay attention to the following reasons:
- Serviceability of oxygen sensors;
- Catalyst condition;
- Safety of lambda probe wiring;
- Exhaust system integrity.
Error “P0422 Main Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)” or “P0422 Main Catalyst Efficiency, Below Threshold)” means “The efficiency of the main catalyst B1 (neutralizer) is below the permissible threshold.” Most likely this is already replacing the catalyst or, as an option, removing it, but the reason may be less significant... oxygen sensor, wiring.
Repair prices vary greatly, because... depend on the reason for the appearance of P0422 in Lada (2104,2105,2107)
Trouble P0421 - Catalytic converter heating efficiency below threshold (Bank 1).
11 months ago AutoTime 0
Error DTC P0421 - catalyst performance too low during warm-up (bank 1).
What does the P code mean?0421?
Trouble P0421 means that the engine control module has determined that the catalyst is not working effectively when warmed up to operating condition. Warming up of the catalyst begins from the moment the engine is first started and ends after about five to ten minutes.
The engine control module (ECM) compares the readings from the primary and secondary oxygen sensors mounted on the catalyst. If the sensor readings are identical or their values are very close to each other, the “CHECK ENGINE” warning indicator will light up and error code P0421 will be stored in the unit’s memory. If this problem occurs only while the vehicle is warming up, then the P0421 error will be recorded in the memory.
Causes of error P0421
Causes of DTC P0421 may include:
- Faulty catalyst (most likely the cause if there are no other errors)
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Damage to the oxygen sensor wiring
- Faulty Engine Control Module (ECM)
Symptoms of DTC P Error0421
Symptoms of the error that a driver may encounter:
- The “CHECK ENGIN” indicator lights up on the dashboard
- The engine will not start.
- The engine stalls and there is no full power. Power loss during acceleration.
- Strange sounds appear while driving.
Diagnosis of the error
If error P0421 is the only code stored in the system, then it is best to start diagnostics with a visual inspection of the exhaust system. It is best to start any diagnosis with a visual examination.
To check the condition of the catalyst, you can check the smell of exhaust gases for the presence of excess fuel, check the heating of the catalysts while the engine is running, whether it is red-hot. And also conduct a test drive to confirm the symptoms of the malfunction.
What does Bank 1, Bank 2 mean?
The designation Bank 1 and Bank 2 is usually used if the vehicle has more than four cylinders. But it is also used on four-cylinder engines.
This means that you probably have two exhaust pipes or that the engine cylinders are split into multiple O2 sensors. “Bank” indicates which side or exhaust pipe the sensor is located on.
Bank 1 is always installed on cylinders 1-3-5-7-9, etc. Bank 2 sensor monitors cylinders 2-4-6-8-10.
You can disable one oxygen sensor and read errors with the OBD2 scanner. This will allow you to find out where the sensor is installed - in Bank 1 or Bank 2.
Error 0422. Kalina 1.6 16cl. 2010
CO check at the service station first, if the exhaust really sucks, then you can stupidly change the cat.
If the CO is ok, check to see if the muffler is cutting somewhere between the catalytic converter and the exhaust manifold.
And then think about candles and so on.
Take your time > “Low catalyst efficiency.” > Before changing the catalyst, I would like to check the oxygen sensors. How to do it? ===Using the on-board computer. For example, State-DST, and many others that provide instant readings on DK1 and DK2. For example, on warm DCs, jump within 0.1-0.9V. On DK1 the upper readings should be higher than on DK2. The greater this difference, the better, i.e. the better the catalyst works, burning oxygen in the exhaust. The less, the corresponding. worse, and the controller, under certain conditions, considers that the catalyst is in trouble and lights up the CE due to error 422. But. Let's think about the reasons why the controller might interpret the data as an error. 1. Exactly what d.b. according to the authors' intentions. The catalyst is depleted, DC1 and 2 are working correctly, the system understood everything correctly. And then it begins: what if DK1 fails and produces an insufficient upper threshold? And if also according to DK2 with the issuance of an increased threshold? What if the controller firmware is not working correctly? What if the ADC at the controller inputs does not work correctly? Etc. etc. As a result, so many sensors and catalysts that were in good working order were replaced and thrown away. (Despite the fact that the tales about gasoline killing the catalyst and oxygen sensors are very exaggerated by service technicians, because it’s a waste to understand. There are either no diagnostic tools, or too lazy to use them. > Or maybe just change them (sensors) because according to the regulations this had to be done for a long time. Not harmful, but the price of each is 1200-1500 rubles plus work.
What to do? 1. What is the mileage? 2. By and large, you need the following set of equipment - a motor tester (not to be confused with a fart, which is used to reset errors at services), a gas analyzer and a backpressure meter in the DK1 zone. The motor tester will measure the true values at the output of the sensors, and not those that the controller outputs to the on-board computer or to the service technicians. The gas analyzer will show whether the catalyst is really depleted and there is excess CO. Measuring the back pressure will show the degree of clogging of the catalyst honeycomb if the permeability is impaired.
And one last thing. Have the spark plugs been changed recently? There is a phenomenon that with new spark plugs the engine heats up a little more, respectively. the catcollector heats up a little more and it works better, burning oxygen as it should, and the 422 error lags behind.
From my experience I get 422 error almost at first. 2011 The measurements showed the perfect DC of both, excellent CO, no blockage in the catalytic collector, but there was an error. Controller Itelma, burn with blue flames in hell. Everything agrees that the problem is there, but it cannot be proven under warranty.
On the lkforum I read a terrible story about THIS. Usually this glitch appears after a year of operation, and the exhaust warranty is for a year or 30 tkm. Therefore, most of the flames are carried out by users who are not under warranty or who have neglected the warranty altogether. But there was one case when this happened before a year.
The funny thing is that after the warranty replacement of the catalytic collector complete with sensors, the jamb came out again a month later.
AvtoVAZ even updated the firmware for this reason. Those who are serviced by the officials have had their service altered. But the victory over the school was not clear.
Mostly the first 8-cl cars with E-gas suffered. Those who are in their 11th year, almost all of them collided. It also happened at 16, but less often.
Most have given up on this. Someone made a trick, someone changed the firmware, someone just ignored Dzhekichan and threw out an error.
You need to look at the BC, what data from sensors and graphics would be good to look at, incl. and in dynamics. If everything is OK according to the indications, then think about what to do. But there is no point in changing the cat and sensors.