December 23, 2015 Lada.Online 1 244 930 115
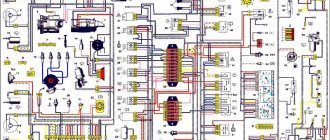
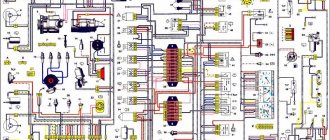
Modern AVTOVAZ SUVs use injection power units. If a malfunction is detected in the electrical equipment of the car, you should first check the serviceability of the fuses and relays. Next, we will show where the mounting block is located (fuse box or black box), as well as the location of the elements inside it.
Protection of the engine compartment from dirt and rust on Niva (VAZ 2121, 2131)
Have you noticed where rust appears in the Niva’s engine compartment? The spare tire disc, side members, the area under the brake fluid reservoir, the battery area, etc. become rusty. This happens due to water and dirt getting under the hood of an SUV. Let's consider an integrated approach to protecting the Niva's engine compartment from moisture.
Installing an additional hood seal
When it rains, water enters the engine compartment through the gaps between the hood and body near the edges of the windshield. This can be prevented by an additional seal, which should be installed as a continuation of the standard one.
- Clean and degrease the surface where the seal will be installed;
- Apply sealant to the seat;
- Install an additional seal (a piece from the Niva rear door seal will do, catalog number: 21213-6307024-30).
Apply the sealant with your finger and remove the excess.
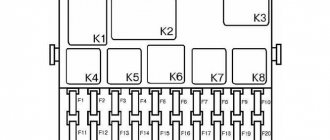
Main and additional fuse blocks
These two blocks are connected to each other. There are 10 fuses in the upper block, and 6 in the lower one. Markings from left to right:
| F1 (16A) | Heater fan, rear window defroster, rear wiper and washer system, windshield washer pump |
| F2 (8A) | Steering column switch, windshield wipers, hazard warning lights, breaker relay (in turn signal mode), reverse light, instrument cluster (coolant temperature gauge, fuel level gauge, tachometer, warning lights: turn indicators, differential lock, parking brake, emergency condition of the working brake system, insufficient oil pressure, fuel reserve, battery charge) |
| F3 (8A) | Left headlight (high beam), high beam indicator lamp |
| F4 (8A) | Right headlight (high beam) |
| F5 (8A) | Left headlight (low beam) |
| F6 (8A) | Right headlight (low beam) |
| F7 (8A) | Side light lamps in the left front and left rear lights, license plate lights, side light indicator lamp |
| F8 (8A) | Side light lamps in the right front and right rear lamps, backlight lamps for the instrument cluster, cigarette lighter, switches, heating and ventilation control unit |
| F9 (8A) | Hazard switch, breaker relay (in hazard mode), heated tailgate glass relay contacts |
| F10 (8A) | Sound signal, interior lamps, brake lamps in the rear lights |
| F11, F12 (8A) | Reserve |
| F13 (8A) | Fog light relay contacts in rear lights |
| F14 (16A) | Cigarette lighter |
| F15 (16A), F16 (8A) | Reserve |
Additional block:
| F11 (8A) | Turn signal lamps and relay-breaker for turn signals and hazard warning lights (in hazard warning mode) |
| F12 (8A) | Daytime running light relay, daytime running light bulbs |
| F13 (8A) | Rear Fog Lamps and Relays |
| F14 (16A) | Cigarette lighter |
| F15 (16A) | Spare |
| F16 (8A) | Spare |
Additional fuse circuits in the Urban package:
| Fuse number and rating | Protected circuit |
| Main unit | |
| 1 (16A)* | Electric windows for front doors Electric side mirrors |
| 2 (16A)** | Air conditioning fan, air conditioning compressor |
| 9 (16A)* | Side mirror heaters |
| 10 (16A)* | Central interior lamp |
| Additional block | |
| 15 (16A)* | Air conditioning fan, air conditioning compressor |
Modification of the drainage tube (extend)
The standard tube drains water in such a way that it gets onto the metal of the body, where rust appears over time. Our task is to lengthen the drainage tube using a dropper so that the water leaves bypassing the spar.
The whole process is also shown in the video:
Protection of side members from water and dirt
Water can also get onto the side members from the wheels of the Niva. Standard fender liners (lockers) are not able to protect them fully. We finalize the design by installing plugs made of pieces of plastic or rubber into the opening:
Comprehensive modifications will help protect the Niva’s engine compartment from moisture and dirt, which will significantly extend the service life of parts. Have you modernized the engine compartment this way? Let us remind you that the website provides other instructions for improving the domestic SUV, for example, installing a gas stop on the hood, or how to protect the Niva’s gas tank from thieves.
VAZ-2121 Niva: from sadness to joy
I sold my last Niva ten years ago, after an asphalt road to my summer cottage appeared. But in the year of the fortieth anniversary of the car, with which, it turned out, so much was connected in life, I decided to share my memories.
LADA > 4×4
The reason was a call from Kostya, a young architect, the son of my friends, in love with Niva, asking for help finding tires for his car. It turned out that all this time in the summer he was driving on my tires, which I gave to them after selling my Niva.
I'll start with Nivov tires. Everyone knows that the standard VLI-5, which was equipped with the Niva, was poorly suited for driving on asphalt due to the terrible noise and insufficient traction properties on dry asphalt, and it wore out quickly. To make the ride comfortable, it was necessary to immediately change the tires. Have you tried to find them in the standard 16-inch size for the Niva?
This is still a problem, except for the Kama tires, which are difficult to balance. So I installed Bridgestone tires designed for delivery vans. Having traveled 30 thousand kilometers on my Niva, these tires drove about fifty more on two Nivas in Kostya’s family. Many tire drivers switch to 15-diameter tires to solve the tire problem, but this requires replacing the standard rims. However, such a transition, in turn, gives rise to the problem of placing a spare wheel under the hood. That is why there are options for mounting the spare tire on the rear door.
The unsuitability of VLI-5 tires for normal driving on the Niva was pointed out to me by Jean-Jacques Pocq, the French importer of Lada, when in 1989 he helped us equip three Nivas before the forced march across the Sahara. There was such an episode in the life of the magazine “Behind the Wheel” (the report was published in the last three issues of the same year). But this is a completely different story. I will only note that the tires of all Nivas sold in France were immediately changed to Michelin ones even before meeting the buyer.
Fuse diagram for carburetor VAZ Niva
The only difference between Niva mounting blocks with injection and carburetor systems is related to the block. It is located under the hood of the car in a compartment specially designated for this purpose. His diagram looks like this:
Location of fuses Niva 21213
This scheme is relevant for all models of the family produced from 1997 to 1999.
| Number | Purpose |
| 1 | Ignition switch |
| 2 | Main relay |
| 3 | Used coil |
| 4 | Valve |
| 5 | Carburetor switch |
| 6 | Reserve |
Fuse diagram for VAZ 2121 Niva
In the model with injection supply, the fuels are located in the same way as in other models of the family of this type.
Giz69 › Blog › Getting to know the Lada 4*4 URBAN (Part 3. under the hood)
I will continue the epic journey of getting to know this wonderful car. This time we'll see what's under the hood =)
We open the hood, and there...
And there is a good old jumper with a volume (according to the manufacturer 1.7 liters 8 valves) and a power of as much as 83 horsepower. Of course this is not a super car! This is not even the Chinese parquet of Cherry Tigo with its, if memory serves, 126 fillies. But again, according to reviews from the owners, this engine is quite enough in the city and countryside. But given the fact that now there’s also an air conditioner under the hood, I can vaguely imagine how this little guy will handle everything =)) The actual air conditioner compressor was placed right above the steering wheel, thereby stealing another piece of living space under the hood.
Also, among the latest achievements of the automotive industry, I would like to note the installed electronic gas pedal unit. Still, a tribute to environmental standards...
Otherwise, under the hood, it’s a good old clunker who screams with all his existence: “I’m old! I’m very old!”=)) You can even feel this in the example of attaching hoses to the body =) To prevent anything from dangling, ordinary technical adhesive tape was used, glued somehow crookedly.
Then what catches your eye are the hoses running right on top of the valve cover. God bless him with the hoses, which were not hidden anywhere, but it was possible to make normal fastenings for all this goodness? :) Although this also does not affect the functionality.
They continue to cover the wiper motor with some piece of rubber obscenity. Maybe this is a tribute to fashion? How do they say “Old School” now? :)
Further more. The jack remained the same and in the same place.
Fuck him with the jack and his work, but I don’t understand why it rests so directly on the wiring of the dimensions.
Although maybe it can be moved or thrown into the trunk and then the wiring won’t be in any danger =) I’ll definitely warn the owner about this jamb!
I also managed to discover and still don’t really understand WHAT IS THIS? some tubes “from a dropper” sticking out in the engine compartment.
What else is left under the hood? One of the niceties on the hood itself is a well-glued heat reflector.
Maybe they now glue it on regular Lada 4*4s, but on an old car this element is definitely not there!
FAREWELL TO NIVA
All-wheel drive jeep VAZ-2121 "Niva".
This car became a real sensation in the domestic automobile industry. Her appearance was preceded by numerous rumors, conjectures and gossip. The Soviet car enthusiast, not spoiled by the quality of roads, has long needed a comfortable passenger all-wheel drive SUV, which could be used with equal success both on asphalt and off-road. And in 1977, it rolled off the assembly line of the Volzhsky Automobile Plant - the first mass-produced all-wheel drive Niva. It cannot be said that before the release of the Niva there were no off-road vehicles in the country. Were. True, mostly not civilian jeeps, but military cargo-passenger all-terrain vehicles, intended primarily for use in the armed forces. Of course, a certain number of these vehicles ended up in the national economy, but there were practically no all-terrain vehicles in personal ownership.
Nevertheless, the Soviet automobile industry has repeatedly made attempts to create comfortable passenger SUVs. Thus, back in pre-war 1938, a prototype of the first Soviet passenger all-terrain vehicle, intended for the senior command staff of the Red Army, was created at the Gorky Automobile Plant.
The car, named GAZ-61, was created on the basis of the GAZ-11-73 emka with a six-cylinder engine producing 85 hp. The car turned out to be extremely successful - on the highway with a full load, the all-wheel drive Emka reached speeds of up to 107.5 km/h, and its cross-country ability was such that even today it could easily compete off-road with the coolest modern jeeps. SUVs. Serial production of the GAZ-61 began at the beginning of 1941; it continued until August of the same year. Many of these vehicles survived the entire war; Such prominent Soviet commanders as G. Zhukov, I. Konev and K. Rokossovsky drove the GAZ-61.
In the post-war years, with the launch of the GAZ-M20 Pobeda car into production, the question of creating a domestic comfortable all-terrain vehicle was again raised - mainly for the party and economic leadership of rural areas. This SUV, called the GAZ-M72, was created on the basis of the Pobeda body and units of the GAZ-69 army all-terrain vehicle. This car became the embodiment of the concept of comfortable jeeps - foreign automobile companies did not even think about such cars at that time.
The first domestic passenger SUV GAZ-61 (1941)
All-wheel drive GAZ-M72 is a hybrid of the GAZ-69 army jeep and the Pobeda M-20 passenger car (1955)
Comfortable subcompact jeep "Moskvich-410" produced by MZMA (1957)
Rural SUV LyA3-969M based on the units of the Zaporozhets car (1979)
Experimental "Moskvich-416" based on the all-wheel drive vehicle "Moskvich-410N" (youth of the 1950s)
The domestic comfortable jeep VAZ-2121 is the first original development of the Volga Automobile Plant (1977)
The car was equipped with a transfer case with a range and a switchable drive front axle. With 16-inch wheels with increased lugs (such as the all-wheel drive Niva is now equipped with), the car had significant ground clearance, which provided it with good cross-country ability in mud, sand, snow, arable land and broken roads. The car was produced in a small series from 1955 to 1958. It’s a pity that the production of this kind of car was not properly continued - for our country, with its off-road conditions, such a car would be priceless. With the completion of the Pobeda production, the production of the GAZ-M72 also ceased.
The need for a similar all-terrain vehicle, however, not only remained, but even increased. In the 1950s, ordinary passenger cars “Muscovites” and “Pobeda”, which did not have all-terrain qualities, increasingly began to become the personal property of citizens. During these same years, the mass allocation of gardening and dacha plots to city residents began, which, as a rule, were cut off by off-road conditions from the few paved roads.
An interesting attempt to create a small passenger SUV was made during this period by the Moscow Small Car Plant - MZMA. In 1957, on the basis of the Moskvich-402 model produced at that time, he developed the Moskvich-410 all-terrain vehicle, which had two drive axles and a dependent wheel suspension on longitudinal springs. The transmission included a two-stage transfer case and constant velocity joints. The car's ground clearance was 220 mm - like a modern Niva. A year later, the car was equipped with a more powerful 45-horsepower engine and a four-speed gearbox.
The car had enviable cross-country ability, but, according to those who happened to own this “jeep,” it had an insufficiently rigid and durable body. The total production of “Muscovites” all-terrain vehicles of several modifications amounted to about 12 thousand vehicles; These comfortable SUVs were discontinued in 1960.
At the end of the 1950s, MZMA designers made an attempt to use the units of the Moskvich-410N off-road vehicle, the production of which was already ending, to create a comfortable rural jeep, Moskvich-416. The car had a frame structure, an all-metal three-door body with an efficient heater and reliable door seals; The ground clearance of the all-terrain vehicle was 220 mm. Unfortunately, the production of the car, which could have become the first “civilian” Soviet jeep, was limited to only two dozen prototypes.
Well, the lucky few who became the owners of all-wheel drive “Pobeda” and “Muscovites” were able to replace their off-road-torn cars with a serial domestic jeep only in 1967 - with the launch of the LuAZ compact subcompact car into production at the Lutsk Automobile Plant. The car was developed by designers of the Zaporozhye Automobile Plant based on the experimental all-wheel drive vehicle NAMI-049A; At first it was produced only with front-wheel drive, but later, with the development of production of units for driving rear wheels, it was also produced in an all-wheel drive version. The plant's capacity was designed to produce 16 thousand cars per year - this was already noticeable even for our country with its vast expanses and impassable primers. The jeep, which had good cross-country ability, did not have very high reliability - the “Zaporozhye” units that were part of its design were let down.
A full-fledged, reliable, mass-produced all-wheel drive jeep appeared in our country only after the giant Volzhsky Automobile Plant was built. The enterprise, designed to produce 660 thousand passenger cars, quite modern cars for that time, was built in technical cooperation with the Italian company FIAT - the Italians supplied us with equipment, documentation for production technology and a license to produce the FIAT-124 car.
The first “kopecks,” as the VAZ-2101 passenger cars were later called, rolled off the VAZ assembly line in September 1970. In the very first year of VAZ's operation, the plant's design bureau began experiments with front-wheel drive cars. As a result, this allowed the team of designers, headed by V. Solovyov, to design, build, comprehensively test and offer for production the all-wheel drive VAZ-2121 Niva. The first production Nivas rolled off the assembly line in April 1977.
Some automotive historians claim that the civilian Niva ended up on the VAZ assembly line completely by accident. Initially, the jeep was developed for army needs - as in the distant thirties, “for the command staff of the Soviet Army.” However, for some reason, already at the stage of launching the series, the VAZ jeep was rejected by army specialists. And, since the curtailment of almost established production threatened considerable losses, the release of Niva was given the go-ahead. True, a reservation was made that the new machine “is intended mainly to meet the demand of rural workers.”
It is interesting that the VAZ-2121 Niva was the first in-house development of the plant, ahead of many Western companies - in 1977 there were practically no mass-produced comfortable passenger jeeps with permanent all-wheel drive. “Niva” became the first mass-produced comfortable SUV with a load-bearing closed all-metal body.
Layout of the VAZ-2121 Niva car:
1 - headlight; 2 — sidelight with turn indicator; 3 - jack; 4 - radiator; 5 - engine; 6 — expansion tank; 7 — air filter; 8 - battery; 9 — differential lock lever; 10 — gearshift lever; 11 — range lever; 12 — steering wheel; 13 — front seat; 14 — rear seat; 15 — license plate light; 16—rear light; 17 — muffler; 18— rear brake; 19 — rear suspension spring; 20 — rear shock absorber; 21 — rear suspension transverse rod; 22 — lower longitudinal rod of the rear suspension; 23 — rear drive axle; 24 — fuel tank; 25 - resonator; 26 — rear axle drive drive shaft; 27 — reservoir for hydraulic brake fluid; 28 — reservoir for hydraulic clutch fluid; 29—transfer case; 30 — clutch pedal; 31 — brake pedal; 32 — drive shaft of the front axle drive; 33 — steering mechanism; 34— front brake; 35 — front suspension spring; 36 — front axle; 37 — side direction indicator; 38— windshield washer fluid reservoir
Geometric diagram of the VAZ-2121 Niva SUV
Geometric diagram of the elongated Niva VAZ-2131
Transmission diagram of the VAZ-2121 Niva car:
1 — external hinge of the front wheel drive; 2— front wheel drive shaft; 3 — internal hinge of the front wheel drive; 4 — clutch housing; 5 — gearbox; 6 — intermediate cardan shaft; 7— rear axle; 8 — rear propeller shaft; 9 — transfer case; 10 — front driveshaft; 11 — front axle
Jeep controls and monitoring devices:
1 — instrument lighting switch; 2—lever for switching headlights; 3 — direction indicator switch lever; 4— steering wheel; 5 — instrument panel; 6 — windshield wiper switch; 7 — sound signal switch; 8 — headlight wiper switch; 9,11,19 — plugs; 10 — cigarette lighter; 12 — alarm switch; 13 — decorative cover; 14 — gearshift lever; 15—handbrake lever; 16 — range lever; 17 — differential lock lever: 18 — heater fan switch; 20 — gas pedal; 21 —external lighting switch; 22—brake pedal; 23 — throttle control handle; 24—clutch pedal; 25 — ignition switch; 26 — fuse block; 27 — hood lock lever
Front suspension
Rear suspension
Before the release of the Niva, all domestic all-wheel drive vehicles were equipped with either Bendix-Weiss-type constant-velocity ball joints or Tracta-type constant-velocity ball joints. On the Niva, for the first time in our country, more compact and durable Bierfield-type ball joints were used, designed for light vehicles.
The car quickly gained popularity, not only in our country, but also abroad. Experts say that it was the Niva that became the prototype of the all-wheel drive passenger cars SUZUKI VITARA and DAIHATSU ROCKY.
In the mid-1990s, the plant produced modernized versions of the Niva - BA3-21213 with a carburetor engine of increased power (78.9 hp) with a displacement of 1690 cm3 and VAZ-21214 with an engine of the same volume, equipped with a fuel injection system; both modifications of the Niva had an enlarged rear door, the threshold of which was located at the level of the bumper, which made loading and unloading the car easier.
On the basis of the updated Niva, small-scale production of long-wheelbase versions of the jeep was mastered - for such vehicles the distance between the axles was increased by 500 mm. A number of extended cars were produced in a three-door version, but the main part had five doors. Some of these machines were produced with an engine with a displacement of 1774 cm3 and a power of 82.3 hp.
The plant also produces a number of compact pickup trucks with a carrying capacity of 0.3 tons - with double (BA3-2328) and four-seater (BA3-2329) cabs.
Design of the VAZ-2121 Niva car
The VAZ-2121 is an all-wheel drive passenger car with a 4×4 wheel arrangement, with a closed three-door monocoque body and a front engine.
Engine with a displacement of 1570 cm3 and a power of 73 hp. together with the clutch housing and gearbox housing, it forms a compact power unit, mounted on the car on rubber cushions at three points.
Engine cooling is liquid. The water pump is driven by the engine using a V-belt drive; A six-blade fan is also attached to the pump shaft. The radiator is tubular-plate; the cooling system also includes a body heater.
The exhaust system has two mufflers located in series - a resonator and a main muffler.
The power system includes a fuel tank, fuel pump, carburetor and air filter. Carburetor - with falling flow; it has two sequentially activated chambers, a heated idle system, a crankcase gas suction system behind the throttle valve, a diaphragm accelerator pump, a strainer at the fuel inlet to the carburetor and an idle jet solenoid valve in the primary chamber. The fuel tank with a capacity of 42 liters is located under the rear seat.
The vehicle's transmission consists of a clutch, gearbox, transfer case, cardan gears, front and rear axle gearboxes with cross-axle differentials, axle shafts with constant velocity joints on the front axle shafts.
The clutch is dry, single-plate, with a diaphragm pressure spring and a torsional vibration damper on the driven disc. The clutch drive is hydraulic, with master and slave cylinders and an expansion tank.
The gearbox is four-speed, with synchronizers for all forward gears. The optimal selection of transmission gear ratios provides the Niva with confident starting, dynamic acceleration and good efficiency.
The transfer case is two-stage, three-shaft, with a center differential with forced locking. It provides an increase in torque by 1.2 or 2.135 times, as well as differential locking, for which there are two transfer case control levers on the body floor tunnel.
The Niva has three cardan shafts: an intermediate one, which connects the gearbox to the transfer case; front axle driveshaft.
Long wheelbase "Niva" BA3-2131
The classic Niva is being replaced by a new model - CHEVROLET NIVA (2003)
The main gears, consisting of a pair of bevel gears with hypoid spiral teeth, increase the supplied torque and transmit it at right angles to the axle shaft. Torque is transmitted from the driven gear to the axle shaft through a bevel differential with two satellites.
The Niva's chassis consists of suspension units for the front and rear wheels with shock absorbers and an anti-roll bar in the front suspension, as well as hubs and wheels with tires.
The front wheel suspension is independent, lever-spring, with coil springs, with double-acting telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers. The suspension is equipped with an anti-roll bar and compression buffers that limit suspension travel.
The rear wheel suspension consists of a pair of coil springs with double-acting telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers, four longitudinal and one transverse rods, two compression buffers at the ends of the rear axle beam and one central one.
The steering system of a jeep consists of a steering gear and a steering gear. The steering gear worm gear housing is mounted on the left side member of the body on the inside of the engine compartment. On the opposite side, on the right side member, there is a bracket for the pendulum arm.
The Niva brake system has two independently operating drives. The front brakes are disc brakes, consisting of a disc and a movable caliper with three-cylinder blocks. The rear ones are drum-type, with self-aligning shoes, driven by one cylinder with two pistons. The hydraulic brake drive consists of two independent braking circuits for the front and rear wheels and is driven by a pedal with a vacuum booster and a brake master cylinder with two coaxial pistons.
The ignition system is classic, consisting of a coil, an ignition distributor with a breaker, high and low voltage wires, a spark plug and an ignition switch. In the low voltage circuit, powered by a battery or generator, there is an ignition switch, a capacitor, the primary winding of the ignition coil and a breaker. The high voltage circuit contains the secondary winding of the ignition coil, distributor, high voltage wires and spark plugs.
The car body is monocoque, three-door, all-metal. Side doors - with front hinge, rear, lifting, hinged on two hinges. In the open position, the rear door is held in place by gas-filled stops.
The hood opens in the direction of travel and is locked with a lock. The cable drive of the lock ends with a handle on the left side, under the instrument panel.
The front seats are separate, reclining, with adjustment in the longitudinal direction. The rear sofa forms a cargo area when folded.
The car is equipped with a body ventilation and heating system, consisting of a heater with a two-speed fan and air duct casings.
Technical characteristics of Niva cars
Today we say goodbye to it - to that same classic Niva - heavy, angular, far from modern automotive style, but at the same time truly all-terrain, capable of coping with almost any off-road conditions, and, importantly, quite affordable by price. Over more than a quarter of a century, more than one and a half million jeeps were produced, with the export share of SUVs accounting for about a third of production.
A holy place is never empty - today the new CHEVROLET-NIVA is rolling off the VAZ assembly line - a car of a completely modern design, comfortable, comparable in its all-terrain qualities to the old Niva, but alas! possessing all the same design flaws, assembly defects and low-quality components. And, of course, the price! For the American accent in the car name and its Latin style, the consumer will have to pay twice as much as for a classic domestic jeep - from $8,000 to $9,500, depending on the configuration.
Today we say goodbye to the Niva - the decision to discontinue its production at the Volzhsky Automobile Plant has already been made.
I. EVSTRATOV
We recommend reading
- “SANDWICH” TO REPLACE BALZE Over the past ten years, aircraft modelers from the SUT Votka Iska club have been performing with constant success at all-Russian competitions held by the Ministry of Public Education,…
- THE LATEST ZAPOROZHETS (Soviet compact car, ZAZ-968M) In the post-war years, our state was, perhaps, the only one where second-hand cars were significantly more expensive than new ones. The reason for this was, as we know, the distribution system...
Electrical wiring of VAZ 21213: differences in the engine compartment and the possibility of self-diagnosis
Did you like the article? Follow our channel for new ideas of useful car tips. Subscribe to us in Yandex.Zen. Subscribe.
Like any other domestic car, the VAZ 21213 is in most cases serviced by the hands of its owner. This is the specificity and even the mentality of our car enthusiasts, who, in addition to tools, also require a technical description of the main components and assemblies.
And the detailed wiring diagram of the Niva VAZ 21213 is just one of them, since in harsh operating conditions it is often necessary to restore the car in field conditions, because:
- VAZ 21213 is an off-road vehicle;
- Used by owners away from service stations and workshops;
- The life and safety of people (the owner and his family members) living far from large cities often depends on its technical condition.
Advice: self-service of a car is a practical and widely used solution, and detailed instructions for care and operation make this possible.
Historical reference
The VAZ 2121 car first appeared in public in 1977.
In its first configuration the car had:
- Power unit from VAZ 2106 with a volume of 1580 cc and a power of 80 hp;
- 4-st. gearbox;
- Permanent all-wheel drive;
- Load-bearing all-metal body;
- Interior of a passenger car (from VAZ 2106).
Later, the car received a modernized engine with an increase to 1690 cc. cm volume, and increased to 82 hp. power.
The new modification received the factory index - VAZ 21213, and had differences in:
- Power system - a Solex carburetor was installed on the model;
- Ignition system - the car was equipped with a contactless ignition system built on a microcontroller;
- Equipped with a silumin oil radiator.
For reference: a new carburetor and contactless ignition reduced fuel consumption, but increased oil consumption. And since in those years the price of oil was insignificant, car owners were not afraid of this feature.
Transmission
The clutch is a single-plate, dry clutch with a diaphragm pressure spring and a hydraulic release drive. Gearbox – mechanical, three-way, five-speed. The transfer case is a two-stage three-shaft with an interaxle lockable bevel two-satellite differential.
The intermediate driveshaft connecting the gearbox to the transfer case has an elastic coupling and a constant-velocity universal joint. The cardan shafts of the rear and front axles at the ends with cardan joints on needle bearings with grease fittings transmit torque from the transfer case to the main gears of the axles.
The main gears of the front and rear axles consist of a pair of bevel gears with spiral teeth of hypoid engagement. Differentials - conical two-satellite.
Features of electrical equipment
The standard wiring on the VAZ 21213 differed from the circuit used on the VAZ 2121. In particular:
- The fuse box on the VAZ 21213 uses more modern “knife” fuses, for which the contact pad is modified;
- The power system uses EPHH - forced idle economizer, for which there is a separate harness with a block in the engine compartment wiring;
- The ignition system uses a non-contact circuit built on a microcontroller.
For reference: the biggest breakdowns in the electrical circuit of the VAZ 21213 occur due to oxidizing contacts. This is a feature of the design and operating conditions - the car often overcomes deep puddles and snow drifts, and due to the poor routing of the wiring along the body, the terminal blocks are subject to excessive load.
Differences in the engine compartment
The EPHH control unit is located in the engine compartment and is a plastic box with a connector for connecting a wiring harness to it. Its purpose is to ensure stable engine operation when coasting, including fuel economy.
Fuse box VAZ Niva old and new model
The main difference between the schemes of old and new Niva lies in the method of connecting the additional mounting block, which is located below. If in older models only two fuses are used for this purpose, then in the updated ones there are already four.
In general terms, the difference between the two blocks looks like this:
| New additional block | Old additional block | ||||
| Fuse no. | Current (amps) | What is he responsible for? | Fuse no. | Current (amps) | What is he responsible for? |
| 11 | 8 | Turn signal lamps, relay-breaker for turn signals and emergency lights | 11 | 8 | Reserve |
| 12 | 8 | Daytime running light relay, Daytime running light bulbs | 12 | 8 | Reserve |
| 13 | 8 | Rear fog lights and their relay | 13 | 8 | Fog lights and their relays |
| 14 | 16 | Cigarette lighter | 14 | 16 | Cigarette lighter |
| 15 | 16 | Reserve | 15 | 16 | Reserve |
| 16 | 8 | Reserve | 16 | 8 | Reserve |