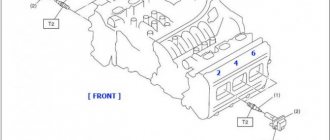
How does a mechanic diagnose trouble code P0304?
When diagnosing the P0304 trouble code, a mechanic will do the following:
- Connects the OBD-II scanner to the vehicle's diagnostic connector and reads all stored error codes.
- Reviews all data stored in the ECM memory.
- Clear error codes from the ECM and test drive the vehicle to see if P0304 appears again.
- Inspects major ignition system components and associated wires for wear and damage, and performs a thorough check for leaks.
- Check the misfire counter in cylinder 4.
- Will check if there is an intake air leak or any problems with fuel injection.
Common errors when diagnosing code P0304
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0304 is failure to follow the diagnostic protocol. It is also a mistake to replace spark plugs, ignition coils, and related wires when the problem is an intake air leak or a malfunction of the fuel injection system. Before replacing any components, you must perform a thorough diagnosis and consider all possible causes of the error.
RIDE IN TEST MODE
- Connect the handheld diagnostic tool to the DLC3.
- Turn the ignition switch to ON (IG) and turn on the handheld scan tool.
- Record the DTC and freeze data.
- Switch the ECM from normal diagnostic mode to active diagnostic mode using a handheld scan tool.
- Count the number of misfires for each cylinder (CYL ##1-4) while the engine is idling. If the number of misfires is displayed for at least one cylinder, skip the next test drive.
- Drive the vehicle several times at engine speed and engine load equal to the values for MISFIRE RPM and MISFIRE LOAD in DATA LIST mode. HINT: To store misfire related DTCs, the vehicle must be driven for the amount of time specified in the table below and the MISFIRE RPM and MISFIRE LOAD values are maintained in DATA LIST mode.
Engine speed Duration Idling 3 minutes 30 seconds or more 1000 3 minutes or more 2000 1 minute 30 seconds or more 3000 1 minute or more - Check for misfire by reading DTCs and freeze data. HINT: Do not turn the ignition switch off without recording the stored DTCs and freeze data. When the ECM switches to normal diagnostic mode (default), all stored DTCs and freeze data are cleared.
- Record the DTC, freeze data, and number of misfires.
- Turn off the ignition and wait at least 5 seconds.
Technical description and interpretation of error P0304
The OBD II error code P0304 is a generic one that reads “Cylinder #4 misfire detected.” Set when the PCM (powertrain control module) detects a misfire in the fourth cylinder.
The misfire detection system uses input data that is sent to the PCM through dedicated feedback circuits. If the PCM does not receive feedback, it interprets this as a misfire.
Trouble code P0304 indicates that the fourth cylinder is misfiring. They occur when insufficient fuel is burned in the cylinder. Efficient combustion of fuel is important. Because fuel combustion is the source of energy for engine operation.
Misfires can be caused by many reasons. Due to a faulty ignition system, fuel system or internal engine failure. Often the fault occurs due to worn spark plugs, spark plug wires or a faulty coil.
Diagnostics
To accurately determine the misfire of cylinders 1 and 4 of the VAZ 2114, you need to run computer diagnostics. This is done using a special electronic module inserted into the diagnostic connector. After running the scan, your computer will automatically display the results in the form of special codes corresponding to specific errors.
Therefore, the following codes are provided for misfires:
- P0303;
- P0301;
- P0302;
- P0304.
In this case, the last digit of the code corresponds to the number of the faulty cylinder. For example, a misfire in the 1st cylinder of a VAZ 2114 will be designated as P0301 and so on...
Misfires. Error codes P0300 P0301 P0302 P0303 P0304 P0305 P0306 on Mitsubishi
Type P error code stands for misfire of the fuel mixture of the cylinder from the first to the sixth, etc.
The classification of misfire errors is as follows:
P0301 – misfire in cylinder 1; P0302 – misfire in cylinder 2; P0303 – misfire in cylinder 3; P0304 – misfire in cylinder 4, etc.
The P0300 code indicates general misfires without indicating exactly where they occur.
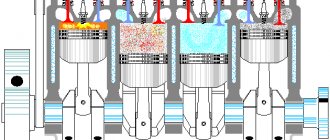
What is a misfire?
An internal combustion engine (ICE) has four power strokes: intake, compression, ignition (power stroke), exhaust. If ignition does not occur in any cylinder (that is, the air-fuel mixture does not ignite), in this case the engine stalls, the engine control unit “sees” the misfires and “throws” a “check” warning light (engine error) onto the dashboard. A misfire in one of the cylinders is equivalent to walking on one leg, so it is urgent to find out the cause and eliminate it.
What should you do if an error occurs?
First of all, you need to read the error code. If the code indicates one of the errors from the list: P0300 P0301 P0302 P0303 P0304 P0305 P0306, additional diagnostics will be required to find out why there is no ignition.
What are the causes of misfires and how to look for them?
In fact, there can be many reasons, but we will indicate the most common ones on Mitsubishi cars.
1. First of all, you need to check the spark plugs, ignition coil tips or high-voltage wires for breakdown. A spark plug, like a high-voltage wire, looks for a place where it is easier (at the place of least resistance) to conduct a spark, and if the insulation of the spark plug core, or the tip of the wire, as well as if the coil itself is already damaged (caused by time/aging, oil ingress, etc.), then the spark will go “outside”, accordingly, each time not reaching its intended place, that is, to the end of the spark plug electrode.
2. Next you need to do a compression measurement in the cylinder. The lack of compression for any reason leads to a lack of pressure, hence the compression and creates problems with ignition of the mixture.
3. Another reason for misfires is faulty injectors. Problems with improper fuel-air mixture supply also lead to ignition problems in the cylinder (for example, excess or lack of fuel supply)
4. And finally, it is necessary to diagnose and possibly repair the engine control unit. Although, this (failure) is the most unlikely problem on a Mitsubishi.
We wish you good luck in independently searching for the causes of engine misfires. But as we always do, we recommend entrusting this process to professionals. Contact our technical center and we will do all the work quickly and efficiently. And don't delay. Misfires can be caused by:
- deterioration of exhaust gas toxicity
- increased fuel consumption
- power loss
- bad engine start
The video clearly shows misfires in cylinder 2 of the car engine.
Recommendations for checking and troubleshooting
You should not delay engine repairs if error p0300 appears. Almost any inaccuracy in the operation of the motor during long-term operation of the power unit can cause the need for complex repairs. Most of the causes of misfire can be determined independently by using a minimum number of tools and devices to restore the performance of the power unit.
How to Diagnose Error Code P0300
Error p0300 can be diagnosed using special scanners, as well as visual and instrumental studies. Purchasing a diagnostic device will allow you to check the ignition system at any time without visiting specialized car services. Despite the expense, having your own scanner will save time and money in the future. Other ways to determine the causes of error p0300 are practically free or require minimal financial investment.
Connect your car charger
The process of finding the causes of errors can take considerable time. Most of the research is carried out with the ignition on, so it is important to maintain the battery charge at the proper level. To prevent new errors from appearing during the inspection due to a dead battery, it is recommended to connect a charger to it for the entire repair period.
Connect OBD2 scanner
An OBD2 scanner makes it easy to scan and resolve the P0300 error code. This device model is used only for diagnosing cars that were produced after 1996. If the car is older, then you should use an OBD 1 scanner.
Check wiring
If the wiring is damaged, errors may also appear indicating misfires. You should look not only for breaks or loose contacts, but also for places where the insulation has melted or abraded. In such places, current leakage to ground may occur, which can cause unstable operation of the ignition system.
Check the spark plugs
If there are signs that the ignition of the fuel mixture in one of the cylinders is impaired, then finding a faulty spark plug will not be difficult. It is much more difficult to identify an unstable part in which only minor deviations in operation are observed. Replacing all engine spark plugs will completely eliminate the cause of the p0300 error.
Inspect the distributor distributor cap
If, after replacing the spark plugs, problems with engine operation remain, you should carefully inspect the high-voltage wires and the distributor cover. If damage is found on the parts, they should also be replaced.
Check other error codes
If, as a result of using the OBD2 scanner, other errors were discovered in the operation of various engine systems, it is recommended to eliminate them first. After completing the setup and repair work, error p0300 may no longer appear.
Replace engine control unit
If all possible measures have been applied to eliminate the p0300 error, but the problem has not been resolved, then the engine control unit may need to be replaced. You can also try to reflash the unit using a special program by contacting a specialized car service center.
Errors in the operation of the ignition system are quite common. Almost all problems of this type can be resolved independently. It is recommended to start work by checking the ignition system components, the diagnosis of which will take the least time, gradually moving on to more complex studies.
What repairs can fix the P0300 code?
- Replacing faulty spark plugs
- Replacing worn or damaged spark plug wires and/or ignition coils
- Repair or replace clogged EGR pipes and/or valve
- Repairing Vacuum Leaks
- Repairing or replacing a damaged cylinder head gasket
- Replacing a faulty camshaft position sensor
- Replacing a faulty crankshaft position sensor
- Replacing a faulty air flow sensor
- Replacing a faulty oxygen sensor
- Replacing a faulty throttle position sensor
- Replacing a faulty fuel injector
- Replacing a faulty catalytic converter
- Elimination of all present errors
- Replacing the ignition distributor cap and slider (if equipped), as well as wires, spark plugs and ignition coils
- If necessary, repair faulty internal engine components
- Engine replacement (if cylinder is damaged)
- Replacing a faulty PCM
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0300
It should be noted that the cause of the P0300 code is not always worn or damaged spark plugs and wires. Sometimes the problem may lie in other components of the system. Before starting repairs, it is necessary to perform a thorough diagnosis and consider all possible causes of the error.
It is also necessary to eliminate all present errors. Every time after repair work is performed, you should clear the error code from the PCM memory and test drive the vehicle to find out if the P0300 error code appears again. This will help determine if the problem is resolved.
It is important to make sure that the spark plug has the correct gap. To do this, you need to use a gap gauge.
If the spark plug is not properly gapped, it can cause the cylinders to misfire. Typically, car manufacturers provide spark plug specifications. These characteristics can be found on a label under the hood of the car or obtained from any auto parts store for your car.
Reasons for the error
A P0304 code may mean that one or more of the following problems have occurred:
- Faulty or worn spark plugs.
- Worn or damaged ignition wires.
- Coil failure.
- The oxygen sensor is faulty.
- Damage to fuel injectors.
- Vacuum leak.
- Low fuel pressure.
- The camshaft position sensor is faulty.
- Malfunction of the crankshaft position sensor.
- Clogged pipes or valve of the exhaust gas recirculation system.
- Catalytic converters are clogged.
- The air flow sensor is faulty.
- Throttle position sensor malfunction.
- Leaking cylinder head gasket.
- Low engine compression.
- Poor quality fuel.
- Sometimes the cause is a faulty PCM.
P0300 - misfire error. Causes, consequences, elimination
Almost every car owner who has some problems during the operation of his car, throughout the entire time, independently eliminates minor breakdowns, or makes the necessary replacements of any parts. But, unfortunately, sometimes the help of a specialist from a car service is necessary, since car enthusiasts do not have enough skills, experience or knowledge in any of the areas regarding the repair of their vehicle. But don’t worry, because our instructions will help you figure it out and do everything yourself.
The error code P0300 indicates an incorrect ignition order, which means random multiple misfires in the cylinders; in English, the diagnostic device will display: “Random cylinder misfire detection system.” If gaps are found in a certain cylinder, then the outermost number P030x will change from 1 to 4 and so on up to 6, or maybe up to 12, it all depends on which specific “pot” the transmission is in. Therefore, error p0300 is the original one from such errors as P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304. They often happen due to the fact that there is no spark, the supply of the fuel mixture is disrupted, or there are problems with the release of exhaust gases.
Error P0300
We will talk in more detail about all the probable causes of misfire and errors p0301, p0302, p0303, p0304, what the consequences are and how to eliminate them.
What causes the P0300 code to appear?
If a misfire occurs in the engine, the level of intoxication of exhaust gases in the exhaust pipe increases, which also leads to an increase in degrees in the catalyst device, because of this it is damaged (the cells will melt, since the degrees are more than 800). On a few cars, to reduce the burnout of the fuel mixture in the catalyst and, of course, the level of toxicity, the ECM detects the frequency of misfires using a crankshaft sensor, a camshaft sensor and, in addition, registers error p0300, indicating this with a check-in lamp. In addition, the unit is able to turn off the injectors of a specific cylinder where leakage was found. It should be noted that drivers of cars such as Lacheti, Matiz, Priora and other VAZs with an injector, as well as Opel, Nissan, and Kia models, are often interested in the appearance of this error.
When does error code P0300 appear?
It is worth noting that the P0300 error code is recorded by the controlled unit only when some cylinders have misfires at the same time, since a misfire in one of them can only be recorded after 2 repetitions at once; the frequency of rotational movements of the CV is important here. At idle, the error will be entered into memory after three and a half minutes of engine activity, and at revs of more than two thousand km - a little more than 1 minute. The extreme rate of DTC registration in the ECM memory is more than 3.25 percent, missed flashes per thousand revolutions. When misfires are found only in a specific cylinder, then it is not error p0300 that is generated, but another one, with the order number of the combustion chamber of the internal combustion engine.
Method for determining cylinder misfires
It will be easy to find out that the yellow check lamp is on due to a disturbed flammability order, since, due to the ignition being started, the engine begins to “sausage” at low speeds, there are jerks and jerks during acceleration, and there is still no traction, and the consumption of the fuel mixture increases.
Error p0300, p0301, p0302, p0303 and p0304 causes of occurrence
Unfortunately, the diagnostic device is not able to find a specific cause of the malfunction and with regard to misfire in the engine cylinder, but more possible breakdowns occur in 2 cases - either there is no fuel, or there is nothing to burn it with. But, do not rush to experience the joy of quickly finding the cause of error p0300, as this may also become:
Cylinder misfires. Method for diagnosing the cause.
- In the incendiary system:
- spark plugs fail;
- holes in high-voltage wires;
- the ignition coil (or module) is faulty;
- other reasons related to wires and connectors in the ignition system.
- In the power system:
- low quality fuel mixture;
- nozzles are clogged;
- the fuel filter is very dirty;
- low pressure of the fuel mixture.
The main causes of error P0300
3. In the intake and exhaust mechanism:
- valves are clamped or hanging;
- air mass is sucked in;
- compression is rather weak;
- the catalyst device is clogged;
- The operation of the timing belt is disrupted.
4. In the controllability electronics system:
- HF and RF sensors go astray;
- knock sensors go astray;
- sensors for flow rate and degrees of intake air mass go astray;
- The ECU goes astray.
Not a common problem of multiple misfires lies in the ignition system
Tips for checking and troubleshooting
First, let's check the ignition wires and ignition coils (module) if the ignition misfires. Often they come with knocked out insulation, torn or with an oily surface. We measure the wiring using a multimeter (good resistance is about 4-10 kOhm), in resistance mode. To check individual ignition coils, you just need to swap places with the exact working cylinder and clear the error again. If the code designation has changed to the license plate of a different cylinder, the coil turns out to be broken. With the ignition module, everything is not so simple; you need to check it with a tester.
All elements of the ignition mechanism must be checked with great care for signs of wear or damage.
Afterwards, we go to the spark plugs - the electrode is damaged, the gap is incorrect or there is oil deposits, a failure occurs or the spark plugs are unstable.
The spark plug insulation should be white, without any yellow marks from spark holes. Having taken out the spark plug to inspect it, we measure the compression in the cylinder. If it is low or absent, this will lead to incomplete compression and will also create problems with the mixture ignition.
If the fuel injectors are clogged, this leads to interruptions in the supply of the fuel mixture to the combustion chamber, but, unfortunately, without a stand it will not be possible to quickly check. In this case, we can only recommend adding a fuel mixture with a high octane number and driving the car a little at higher rpm (4-5 thousand rpm).
If the fuel filter has not been changed for a long time or bad gasoline has been used, this often leads to improper operation of the injector. Therefore, you need to remember when you changed the filter and where you filled the fuel mixture.
The EGR valve is stuck or there is a leak through the intake manifold gasket - something that also often becomes the reason for detecting random misfires. It is unlikely that you will be able to determine this on your own, so when diagnosing with a computer, you need to pay attention to the indicator of long-term correction of the fuel mixture. It will indicate how much the ECU will compensate for the imbalance in the air/fuel mixture. If this parameter in a certain cylinder differs by ten percent, then this indicates a vacuum leakage and air mass being sucked in.
A good adjustment will not exceed one to three percent or one side. It also happens, but rarely, that the cause of a disrupted ignition order is disrupted gas distribution phases or disrupted exhaust gas outlets; they are controlled by the controlled unit and, in addition to the P030X code designation, there are other errors that relate to the catalyst device, oxygen sensor, camshafts.
Possible causes of the P0300 error code
Let us once again remember the saying about “there is nothing to set on fire and nothing to set on fire with.” This is where the list of possible faults comes from.
- These are old and dirty spark plugs that, due to carbon deposits or destruction of the electrodes, misfire. This is easy to check - by turning out the spark plugs and, to be on the safe side, replacing them with a new and known good set.
- This is a malfunction of the ignition coil itself or the distributor on old engines with central ignition (for example, the Japanese had distributor injection engines that survived almost until the two thousandth century). More modern engines with individual ignition coils or paired coils (separate, as on ZMZ engines, or interlocked, as in VAZ ignition modules) in this case, problems will arise only with a specific cylinder or with a pair of cylinders, that is, error P0300 will not be recorded.
- “Nothing to set on fire” may also be due to insufficient compression in the cylinders or incorrect operation of the gas distribution. The first is checked with a basic compression tester, or in a car service - with a motor tester. Measuring intake vacuum and cylinder pressure directly while the engine is running gives a much more accurate picture of the engine's condition.
- Incorrect operation of the gas distribution mechanism is, first of all, the “loss” of marks due to a stretched timing chain, a skipped belt, or assembly errors of “keyless” engines, where there are no marks at all, and the shafts are set with special devices. A classic example is Ford keyless engines, where a deviation of several degrees can already cause tripping at idle and the recording of numerous misfires.
- The air-fuel mixture may also refuse to ignite normally due to an incorrect composition. A mixture that is too lean is ignited with a candle “every other time,” while a mixture that is too rich will cause the candles to become fouled with soot. A characteristic sign of this is the presence in the controller’s memory of errors in the composition of the mixture (P0172, P0171), or at least a fuel correction noticeably different from zero. We only note that chaotic misfires on engines with plastic intake manifolds are most often caused by warping or cracking of the plastic and the occurrence of an error. Neither “basins” nor foreign cars are immune from this.
- There is another way to make the engine stall, and it works best at idle, when engine vibration is more noticeable and crankshaft accelerations are calculated more accurately: a malfunction of the exhaust gas recirculation system. On engines with EGR, the supply of exhaust gases to the intake is controlled by an electric valve, the throughput of which is determined for each specific mode by firmware. An abnormal supply of exhaust gases literally “chokes” the engine, forcing it to work intermittently - hence the recording of error P0300. In this case, there will be associated errors associated with the operation of the EGR, and physical suppression of the exhaust gas supply channel will lead to a noticeable normalization of engine operation.
- And finally, let’s not forget about the “quality” of gasoline itself: we have repeatedly encountered liquid in gas tanks that only vaguely resembles flammable liquid. It doesn’t have to be a “palenka” - often the culprit is the gas station attendants, who regularly manage to pour diesel fuel into the gasoline, and gasoline into the diesel fuel.
Subaru - Misfire Detected
The cars that came to us already )) had new spark plugs, coils and washed injectors. And in theory this is correct, repairs begin with this.
We, in turn, began the repair by checking the power and pulses on the coils and injectors.
And we ended up repairing the engine ECU, in each case, because the wires and connectors were intact.
Apparently a typical, but completely curable malfunction. Moreover, cars with 6-cylinder engines suffer from it:
EZ30D
- 2000–2004 Subaru Outback H6 2000–2002 Subaru Legacy GT30 2000–2002 Subaru Legacy Lancaster 6
EZ30R
- 2003–2009 Subaru Legacy 3.0R 2005–2009 Subaru Outback 3.0R 2006–2007 Tribeca
EZ36D
- 2010-current Subaru Legacy 2010-current Subaru Outback 2008-2014 Subaru Tribeca
What's the result?
Taking into account the above, it becomes clear that in some cases it is not possible to immediately determine the cause of the misfire. It happens that a powerful spark is formed on the spark plugs, the timing is normal, the valves are adjusted, there are no comments on compression. Also, there is normal pressure in the fuel rail, and the fuel pump itself stably provides the specified performance.
As practice shows, in such cases the electrical circuits of the injectors are often to blame. For example, the engine may stall when cold, although after warming up the operation returns to normal. The complete opposite can be considered misfires after the internal combustion engine reaches operating temperature.
The fact is that it is enough that one wire to the injector “shorts”, as a result of which the injector works intermittently, and the problem itself manifests itself to a greater or lesser extent in certain operating conditions of the internal combustion engine (on a cold engine, after heating, under exposure to vibration when driving, etc.).
Finally, we add that this statement is also true in the event of malfunctions of the ECM sensors. As for spark plugs, during normal testing they may produce a good spark in the open air, but while the engine is running, there may no longer be such a spark. The fact is that spark plugs in the combustion chamber operate under high pressure conditions.
This means that the sparking process occurs when the piston compresses the mixture in the cylinder. To diagnose and check functionality, it is recommended to test the elements in a special device that creates conditions similar to the actual operation of spark plugs inside an internal combustion engine.
What causes misfires
The occurrence of misfires on a VAZ 2114 is a real problem that can become a prerequisite for more serious consequences. The car not only jerks, jumps and cannot work at full power. But it also starts with great difficulty; when driving, characteristic popping noises are heard, which occur due to detonation of the combustible mixture in the problem cylinder.
Checking the operation of the cylinders on a VAZ 2114 using computer diagnostics helps to detect many errors. If error P0301 lights up, then this indicates problems in the first one, if P0302 means misfires were detected in the second one.
Code 0302 - errors in the second cylinder
The VAZ 2114 electronic control unit continuously monitors the operation of the power unit through sensors. In this case, the rotation speed of the sensor on the crankshaft and the cylinders involved in a certain period of time is estimated. When a misfire occurs, the crankshaft rotation speed slows down slightly and this is determined by the computer. Modern electronics, if a miss is detected and the specified interval is exceeded, turns off the problematic cylinder. It simply will not receive fuel.
The cylinder can be turned on after a certain time, or after the engine is restarted. No more than 2 cylinders can be turned off at the same time. This is enough to get to the service station and keep the catalyst intact. On early versions of controllers, errors very often occurred when misfires were detected when driving on a bad road. However, now on the VAZ 2114 this problem has been completely solved after installing a road quality sensor.
VAZ 2114 car engine
The difficulty in identifying this malfunction lies in the fact that the misfire is not constant, but appears periodically. It often happens that in cold weather (until the engine is warmed up) it “troubles”, but after warming up, it starts working normally. This occurs due to wear of the cylinders, because after warming up, the metal parts expand and compression is restored.
Often, at idle speed, the VAZ 2114 power unit functions perfectly, but when the load increases, it throttles and functions with noticeable interruptions.
The problem is a burnt-out gasket, as a result of which, when the pressure in the combustion chamber increases, a leak appears.
The combustion chamber
It happens that the VAZ 2114 engine coughs a little, and then its operation returns to normal. In this case, nothing definite can be recommended, because a complete check of the power unit is required. There may be various reasons.
Description and meaning of error P0300
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic powertrain code. It is considered general because it applies to all makes and models of vehicles (1996-newer), although the specific repair steps may vary slightly depending on the model. So this engine code article applies to Chevrolet, Ford, Nissan, Toyota, Dodge, Honda, GMK, etc. Basically this P0300 code means that the car's computer has detected that all of the engine's cylinders are not firing properly. Diagnostic code p0300 indicates random or multiple misfire. If the last digitis is a non-zero number, it corresponds to the cylinder number that is misfiring. For example, code P0302 will tell you that cylinder number two is faired. Unfortunately, the P0300 doesn't tell you specifically which cylinder(s)/aremis are firing, nor why.
Signs of misfire
There are several different symptoms that you may experience when it comes to engine misfire. Here are some of the most common ones.
Uneven acceleration
When a misfire occurs, you may feel it as a slight or strong jolt coming from the engine. These misfires often occur while the engine is running under load and you are accelerating at high RPMs and high gears. Acceleration problems are a common sign that your engine is misfiring.
Unstable idle
Sometimes there will be passes at idle. The engine sensors receive incorrect readings and the air/fuel mixture becomes incorrect. This can result in a very rough idle. The revolutions can jump up and down, until the engine stops.
What can multiple misfires lead to?
Single misfires are just a signal to the owner of a VAZ 2114 about problems with the engine.
Numerous accidents have the following consequences:
- As a result of misfires, unburnt fuel will enter the catalytic gas reduction system. Because of this, the converter overheats and fails.
- With repeated passes, some of the gasoline will enter the lubrication system through the walls of the idle cylinder. Oil diluted with gasoline will lose its properties and will not be able to provide high-quality lubrication of loaded engine elements.
- All of these factors can lead to engine failure and the need for costly repairs.
How to Troubleshoot or Reset Trouble Code P0304
Some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P0304:
- Use an OBD scanner to make sure there are no other errors. If they are present, it is recommended to eliminate them first.
- Inspect the looseness of the connectors on the ignition coils or any damage to the wiring. Also look for loose engine ground wires. This may cause random misfires. Tighten or correct if necessary.
- Check the condition of the spark plugs and their wires. Worn and old spark plug wires are common causes of random misfires. Replace spark plugs and wires if necessary.
- It is necessary to measure the fuel pressure. Low pressure can cause intermittent misfire in multiple cylinders. When the pressure is below specification, the engine does not receive the proper amount of fuel and begins to lean the mixture. The fuel pump or pressure regulator may be the source of low pressure.
- Make sure the fuel injectors are working properly and activating. Random misfires may be a sign of faulty or clogged fuel injectors that need to be replaced. Also check that the fuel injector wiring is not damaged and is connected correctly.
- If the ignition and fuel system pass inspection, you can perform an engine compression test and a leak test to see if there are any mechanical problems causing the misfire.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Sometimes, when P0304 is detected, no symptoms are observed. The easiest thing to do in this case is just reset the code and see if it comes back.
If the problem manifests itself in the form of uneven idle or engine jerking, check all wiring and connectors leading to the cylinders. Next, it’s worth checking the spark plugs, wires, and coils.
In some cases, the cause is a failed catalytic converter. If you smell a rotten egg smell in your exhaust, the catalytic converter needs to be replaced. Faulty fuel injectors should also not be overlooked.
Random misfires may be due to lean fuel. This may be due to a vacuum leak in the intake manifold or air flowing past the airflow sensor. And also because of the exhaust gas recirculation valve stuck in the open position.
Error codes indicating a car malfunction by computer using the OBDII protocol
When a car breaks down, the on-board computer produces a certain number that needs to be deciphered. Digital codes can be divided into groups in different car systems.
Air supply system
| Error codes | Description of digital designation |
| 0030 | The electrical circuit of the sensor heater is damaged |
| 0031 | Oxygen sensor heater circuit low voltage |
| 0032 | In the same place, only increased voltage |
| 0100 | Damage in the air flow sensor circuit |
| 0101 | The mass air flow sensor circuit is damaged, the sensor sends an incorrect signal |
| 0102-0103 | The air flow sensor sends a false signal (low or high), possibly an open circuit |
| 0112-0113 | Incorrectly low or high signal level of the ambient air temperature sensor |
| 0115 | Invalid DTOZh signal |
| 0116 | Engine overheating signal, false signal from coolant temperature sensor |
| 0117-0118 | A malfunction has been detected in the coolant temperature sensor circuit (low or high signal) |
| 0122-0123 | Malfunction of the TPS, possible short circuit or damage to the insulation, the sensor sends an unreliable low or high signal |
| 0130 | Failure in the electrical circuit of the oxygen sensor, there is an incorrect signal |
| 0131-0132 | Problems with oxygen sensor 1, low or high voltage |
| 0133 | Slow action of DK1 on commands |
| 0134 | There is no signal from DC1, the power cable may be broken |
| 0135 | DK1 heater failure |
| 0136 | Broken or malfunctioning oxygen sensor 2 |
| 0137-0138 | Incorrect signal from DC2 |
| 0140 | The fuse at the oxygen sensor 2 has blown |
| 0141 | DK2 heater is faulty or broken |
| 0171 | The fuel mixture is too lean (the throttle is sharply opened) |
| 0171 | An excessively enriched fuel mixture, this applies to carburetor engines, when the filter becomes dirty and there is little air flow. There is no such problem with injection engines. |
Fuel supply system
| Error codes | Decoding of the digital designation |
| 0201-0204 | An open circuit was detected in the injector control circuit, respectively, from 1 to 4 |
| 0217 | Engine overheating |
| 0230 | The fuel pump does not work or the relay has failed, replacement is required |
| 0261 | Open circuit or short circuit in injector control 1 |
| 0262/0265/268/271 | Short circuit at +12 V in the injector circuit in series |
| 0263/266/0269/272 | The injector driver refuses to work adequately or there are “glitches” in sequence from 1 to 4 |
| 0264 | Short circuit to ground for injector 2 control circuit |
| 0267 | Short circuit of injector 3 control circuit (wire shorts to housing) |
| 0270 | Short circuit to ground (auto body) injector circuit 4 |
How does error P0300 affect engine performance?
Before diagnosing, the driver can easily determine from the vehicle's behavior that the diagnostic scanner will indicate error P0300, P0301, or another of the series. Symptoms of engine operation with the error in question are characteristic of a misfire problem:
- The engine shakes violently at low speeds and at idle;
- When accelerating, the car “throws and jerks”;
- Fuel consumption increases significantly;
- There may be problems starting the engine;
- Craving decreases.
If these symptoms occur and the Check Engine light is on on the instrument panel, you can rest assured that the diagnostic scanner will show one of the P0300 family of errors.
Engine operation with misfires
Previously and now, most engines (including approximately those for the VAZ-2114) were equipped with four-cylinder engines, and by the time one of them failed, the car began to behave unstably and the power could decrease upward by up to 25%.
This engine trembles when starting
This behavior of the engine was called the "triplet" engine, popular and famous even today.
Nuances in the misfire problem
If there is a problem such as a misfire in your car, you should not delay solving it, as this can lead to much more serious consequences. Initially innocent and difficult engine starts can turn into extreme moments of engine operation associated with constant detonation of the exhaust system from the non-combustible mixture.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0304 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light). It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in the ECM memory as a malfunction).
- The engine stalls or has trouble starting.
- Floating speed, as well as attempts to stall at idle.
- Jerking/misfire at idle or under load.
- Poor speed gain.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Reduced engine power.
- Smell of fuel from the exhaust.
This malfunction is considered serious and must be corrected as soon as possible. Because prolonged driving with a misfire can cause costly damage to the engine and catalytic converters.
Fault diagnosis
The ignition of a VAZ 2114 is diagnosed according to the following scheme: the power plant check light lights up on the panel; during testing, error P0300 may light up. This means:
- problems in the first - P0301;
- problems in the second - P0302;
- problems in the third - P0303;
- problems in the fourth - P0304, etc.
Error code 0304 - error in the fourth
There are many factors that cause the air-fuel mixture to not ignite, and they are different.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0304 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
With fault code P0304, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common ones are: P0171, P0202, P0204, P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0305, P0306, P0308, P0354, P0402, P0420, P130A, P1399, C1201.
No matter what car you have, the reasons may be the same.
The scanner or on-board computer generated the error “multiple misfires” and the “check engine” light is on. At the same time, the motor shakes all over and works unstably and intermittently. Of course, continuing to move (if an error occurs along the way) is highly not recommended.
And even if you reset the error with a scanner or by removing the terminal from the battery, the check lamp will stop lighting for a while, but the instability of operation will remain. There may be several options here, so it’s not at all necessary to immediately get into the ignition system.
So let's take a closer look at what could have happened.
Before we figure out what the problem is, it is advisable for us to know how such an error occurs in the memory of the control unit. It is detected by a knock sensor, which compares the engine knock readings with the readings of the rough road sensor. The control unit “knows” at what moment and in which cylinder the process of ignition of the working mixture occurs.
Therefore, he can determine with 100% probability a misfire in a specific cylinder. If there is no indication of any one cylinder, namely multiple misfires, then it is quite possible that the mechanical part of the engine is to blame.
Yes, yes...mechanics can be the cause of such a fault code. And it would be more correct to say “multiple misfires.” That is, it is not correct to blame the ignition system for everything.
The valves may simply be to blame (burnt out or pinched, incorrectly adjusted). But the simplest reason is, of course, the spark plugs, unscrew the spark plugs and check on the bench. If there is no stand, then at least visually inspect for the presence of a breakdown. It is certainly rare for several candles not to work at once, but not an exception. Moreover, knowing the quality of this product. If the spark plugs are turned out, immediately check the compression in all cylinders. It is advisable that the spread does not exceed +-1bar. If in any cylinder the compression differs by more than 2, then pour 10 grams of engine oil into this cylinder and measure the compression again. If it rises to the level of the other cylinders, the cause is the oil scraper rings. If it has increased slightly, then it is still the valve.
Another “banal” reason for such an error is high-voltage wires. Which is also unlikely for several wires to fail at once. But I met this on a Nexia and an old six, because of the wires it completely stalled while driving. You can check the wires with a simple tester by measuring their resistance. Typically it should be within a few kOhms. It varies on different cars.
On old Nexias, high-voltage wires are located directly above the hot exhaust manifold. Therefore, even despite the metal protection, they constantly dry out.
Let's figure out how to set the ignition on a VAZ 2114 correctly
The first cars in this series were produced with a contactless ignition system, and an electronic one appeared only later. Due to the fact that throughout its history the car has been equipped in different ways, before setting the ignition on the VAZ 2114, you need to find out what it is.
Ignition systems of the 8-valve injection VAZ-2114
You can determine the type of ignition by looking under the hood:
- If you find a switch near the “heart” of your car (analogous to a distributor installed on contact systems), it means that your car belongs to the first series, and the ignition of the VAZ 2114 injector on it is non-contact, based on the switch-distributor block. The ignition in such systems is adjusted by gradually turning the distributor, and the results of the work depend on the experience of the performer and the availability of special equipment. Then, using a strobe light, you can debug the system exactly as the car owner wants.
- If this part is missing, your car belongs to the tenth family and is equipped with an electronic ignition system. It cannot be installed manually and its operation is completely controlled by the ECU. However, it is not completely unregulated, because by connecting to the on-board computer, some of its parameters can be reconfigured to your liking, but only a few specialists know how to do this correctly.
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0304
To properly diagnose a P0304 trouble code, a mechanic will need an advanced scanner that will not only read stored trouble codes, but also view sensor readings in real time. This data can help determine the root cause of the error.
The recommended service interval for replacing spark plugs is usually indicated in the vehicle's service book. Worn or damaged spark plugs are one of the most common causes of cylinder misfire, especially in high-mileage vehicles. If the vehicle is equipped with an ignition distributor with a cap and slider, these must also be replaced according to the vehicle manufacturer's recommendations. These components are mechanical and wear out over time. Spark plug wires are usually replaced when the spark plugs themselves are replaced.
Newer vehicles may be equipped with ignition coils, which typically last longer than the above components. To quickly determine whether the problem is a faulty ignition wire or coil, you must move the wire and/or ignition coil to a different cylinder. If the error code appears again, it is a sign that a worn or damaged ignition wire and/or coil is causing the cylinder to misfire.
What does error P0300 mean?
The code in question is directly related to malfunctions on the part of the ignition system.
Error P0300 indicates the presence of misfires in the ignition system, that is, the ignition order is disrupted.
Also, such a malfunction can be described as random multiple misfires that were detected in the ignition system. This is if we take the translation of the English message as a basis. A literal translation yields a similar explanation. This problem is expressed in the form of code P0300 when scanning the memory of the control unit.
If multiple random leaks are detected in the system, the air-fuel mixture ignition system will not be able to function normally. The P0300 error that appears indicates this, helping the driver roughly understand what to look for and in which area to look for a fault.
Error P0300 on some cars varies from 0300 to 0312.
This is due to the fact that certain electronic control units can independently detect in which specific cylinder misfires are recorded. Depending on the final digit in the error code, the motorist understands which cylinder should be entered.
For example, if the engine has 6 cylinders, then the error will vary from 0300 to 0306. If code 0305 appears, then the problem is, accordingly, in the fifth cylinder.
But keep in mind that not all computers determine the exact location of the malfunction, and therefore the diagnostic scanner screen may simply display code P0300. Then, through additional checks, you will have to determine which of the cylinders has leaks.