On Russian cars, since the introduction of Euro-3 environmental standards (and on foreign cars even earlier), self-diagnosis of misfires was introduced into the algorithms of engine control systems. This was caused not only by tightening requirements for hydrocarbon emissions into the atmosphere, but also by a logical desire to preserve the life of the catalyst. Every time the cylinder, having collected a portion of the working mixture during the intake stroke, cannot burn it, all the fuel and free oxygen from the mixture enters the hot catalyst, where they are either further oxidized, increasing the temperature of the catalyst (the risk of “sintering” of the honeycomb), or gasoline accumulates, at one “wonderful” moment, exploding with a characteristic bang, the force of which is enough to destroy the catalyst.
What does P0300 mean?
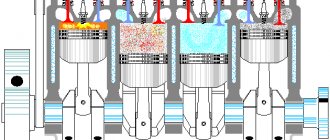
In most cars the engine has 4-6 cylinders. A spark plug fires sequentially in each cylinder, igniting the fuel mixture. Energy is then released from the fuel to drive the crankshaft, which must rotate smoothly as the vehicle moves.
If misfire occurs in more than one cylinder, this will result in an increase or decrease in the number of revolutions (RPM) of the crankshaft. If the crankshaft speed increases or decreases by 2 percent or more, P0300 will remain in the PCM (automatic transmission control module) memory.
If the RPM increases or decreases by 2 to 10 percent, the Check Engine Light will illuminate on your vehicle's dashboard. If the deviation percentage exceeds 10 percent, the Check Engine light will flash, indicating a more serious problem is present. The P0300 code indicates that multiple engine cylinders are misfiring randomly.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with code P0302 can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Audi (Audi a4, Audi A5, Audi q3)
- BMW (BMW X3, BMW X5, E46, F10)
- Chery (Chery Fora)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Cobalt, Cruz, Orlando, Suburban)
- Chrysler (Chrysler 300c)
- Dodge (Dodge Neon, Ram)
- Fiat
- Ford (Ford Kuga, Mondeo, Fiesta, Focus, Fusion, Explorer, F-150)
- Honda (Honda Jazz, SRV, Civic)
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Getz, Santa Fe, Solaris, Sonata, Elantra)
- Infiniti
- Jeep (Jeep Wrangler, Grand Cherokee)
- Kia (Kia Rio, Sid, Sorento, Sportage, Cerato)
- Lexus (Lexus rx300)
- Mazda (Mazda 3, Mazda 6, Mazda BT 50, Mazda cx7, Millenia)
- Mercedes
- Mitsubishi (Mitsubishi ACX, Outlander, Galant, Karizma, Lancer, Pajero, L200)
- Nissan (Nissan Almera, Altima, Qashqai, Tiida)
- Opel (Opel Antara, Astra, Vectra, Zafira, Corsa, Meriva)
- Peugeot
- Pontiac (Pontiac Montana)
- Renault (Renault Duster, Logan, Megan, Sandero, Fluence)
- Skoda (Skoda Octavia, Superb, Fabia)
- Ssangyong (Sangyong Kyron)
- Subaru (Subaru Outback, Impreza, Legacy, Forester)
- Suzuki (Suzuki Liana)
- Toyota (Toyota Venza, Camry, Corolla, Rav4, Highlander)
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Golf, Jetta, Passat, Polo Sedan, Tiguan)
- Volvo (Volvo s40)
- Vortex (Vortex Tingo)
- VAZ 2110, 2112, 2114, 2115
- Volga Cyber
- Gazelle Business, umz 4216
- Zaz Sens, Chance
- Lada Kalina, Largus, Niva, Priora
- UAZ Patriot
With fault code P0302, you can sometimes encounter other errors. The most common ones are: P0016, P0171, P0175, P0201, P0202, P0300, P0301, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0306, P0357.
Causes of error P0300
- Worn or damaged spark plugs
- Worn or damaged spark plug wires and/or ignition coils
- Damage to the distributor cap (if equipped)
- Worn or damaged ignition distributor runner (if equipped)
- Fuel injector damage
- Clogged pipes or valve of the exhaust gas recirculation system
- Incorrect ignition timing setting
- Vacuum leak
- Low fuel pressure
- Damage to the cylinder head gasket
- Distributor cap wear
- Camshaft position sensor malfunction
- Malfunction of the crankshaft position sensor
- Air flow sensor malfunction
- Oxygen sensor malfunction
- Throttle Position Sensor Malfunction
- Malfunction of the catalytic converter
- PCM malfunction
How to replace a spark plug?
Replacing the spark plug is a simple task and you can do it at home. Before changing spark plugs, make sure the engine temperature is low.
Step 1: Open the hood and locate the spark plug
Open the hood and you will see several wires running in the engine compartment. The spark plugs are located in the engine at the end of these wires.
Step 2: Pull the wire
Pull the wire and you will see the spark plug installed.
Step 3: Remove the candle
Insert the spark plug wrench and turn to loosen the spark plug. Remove the old spark plug and note its condition.
Step 4. Install a new spark plug
Using the same spark plug wrench, install the new spark plug and tighten it correctly. Then connect the wire as it was before. All is ready.
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0300 code?
When diagnosing this error code, a mechanic will do the following:
- Reads all data and error codes stored in the PCM memory using an OBD-II scanner
- Clear error codes from the PCM memory and test drive the vehicle to see if P0300 appears again
- Determines which cylinders are misfiring
- Check the wires connecting the ignition coils to the spark plugs for wear and damage
- Check spark plugs for wear and damage
- Check the ignition coils, as well as wires and connectors for corrosion and damage
- If necessary, replace spark plugs, ignition coils, as well as related wires and connectors
- If the P0300 code appears again after replacing the above components, check the fuel injector and fuel delivery system
- Check the ignition distributor cap and slider for wear and damage
- If there are other error codes stored in the P0300 code, the PCM will clear any existing errors and test drive the vehicle again to determine if the P0300 error code appears again.
- If the P0300 error appears again, check the compression in the cylinders.
- If the P0300 code persists, the problem may be a faulty PCM. In this case, the module may need to be replaced or reprogrammed.
Common errors when diagnosing code P0300
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0300 code is to rule out a failed cylinder, fuel injector, or PCM.
It is also a mistake to not look at other error codes that appear along with the P0300 code. If you do not resolve all present errors, this may cause the P0300 code to appear again.
Recommendations for checking and troubleshooting
The first thing you should check when misfiring is the explosive wires and ignition coils (module), they often turn out to have broken insulation, a break, or an oily surface. We measure the wires with a multimeter (normal resistance is about 4 - 10 kOhm), in resistance mode, but to check individual ignition coils, you just need to swap places with a known working cylinder and clear the errors again. If the code has changed to the number of another cylinder, then the coil is faulty. The ignition module is more complicated; it needs to be checked with a tester.
What repairs can fix the P0300 code?
- Replacing faulty spark plugs
- Replacing worn or damaged spark plug wires and/or ignition coils
- Repair or replace clogged EGR pipes and/or valve
- Repairing Vacuum Leaks
- Repairing or replacing a damaged cylinder head gasket
- Replacing a faulty camshaft position sensor
- Replacing a faulty crankshaft position sensor
- Replacing a faulty air flow sensor
- Replacing a faulty oxygen sensor
- Replacing a faulty throttle position sensor
- Replacing a faulty fuel injector
- Replacing a faulty catalytic converter
- Elimination of all present errors
- Replacing the ignition distributor cap and slider (if equipped), as well as wires, spark plugs and ignition coils
- If necessary, repair faulty internal engine components
- Engine replacement (if cylinder is damaged)
- Replacing a faulty PCM
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0300
It should be noted that the cause of the P0300 code is not always worn or damaged spark plugs and wires. Sometimes the problem may lie in other components of the system. Before starting repairs, it is necessary to perform a thorough diagnosis and consider all possible causes of the error.
It is also necessary to eliminate all present errors. Every time after repair work is performed, you should clear the error code from the PCM memory and test drive the vehicle to find out if the P0300 error code appears again. This will help determine if the problem is resolved.
It is important to make sure that the spark plug has the correct gap. To do this, you need to use a gap gauge.
If the spark plug is not properly gapped, it can cause the cylinders to misfire. Typically, car manufacturers provide spark plug specifications. These characteristics can be found on a label under the hood of the car or obtained from any auto parts store for your car.
Is it possible to drive a car with a permit?
Driving with a misfire can damage the catalytic converter, which is an expensive component of a vehicle's emissions control system.
When one of the engine's cylinders fails, unburned gasoline entering the exhaust can overheat and melt the catalytic converter.
Some manufacturers advise against driving with misfires. Others recommend driving only in a very moderate manner and getting your car checked as soon as possible. See your vehicle's owner's manual.
Technical description and interpretation of error P0302
The OBD II error code P0302 is a generic one that reads “Cylinder #2 misfire detected.” Set when the PCM (powertrain control module) detects a misfire in the second cylinder.
The misfire detection system uses input data that is sent to the PCM through dedicated feedback circuits. If the PCM does not receive feedback, it interprets this as a misfire.
Trouble code P0302 indicates that the second cylinder is misfiring. They occur when insufficient fuel is burned in the cylinder. Efficient combustion of fuel is important. Because fuel combustion is the source of energy for engine operation.
Misfires can be caused by many reasons. Due to a faulty ignition system, fuel system or internal engine failure. Often the fault occurs due to worn spark plugs, spark plug wires or a faulty coil.
Cause of engine errors P0301, P0304, P0302, P03003, P0328, P0343
During the operation of LADA Granta, Kalina and Priora cars (with a 1.6l, 8kL engine), there are cases of malfunctions that are not described in the technological instructions. For example, at first a slight knocking and vibration appears in the engine, then you can observe a frequently flashing Check Engine indicator and the appearance of a number of errors on the on-board computer (misfire in the cylinders, high levels of the phase sensor and knock sensor). Moreover, errors P0328, P0343 can occur in a random sequence and under different conditions. The cause of the malfunction may be on the surface.
Pay attention to the operation of the crankshaft damper pulley:
Possibly the reason is the presence of play:
The cause of the play can be not only a weakened fastening bolt, but also a broken hole in the pulley for the spring key (the place where the bolt presses the pulley to the crankshaft can be flattened and the bolt and washer will not reach the pulley).
Solution
: replacing the crankshaft pulley with a new one (part number 21100-1005058-04).
Have you encountered similar errors in engine operation? How did you solve the problem?
Source