It is unlikely that any motorist will be happy with the fact that the Check Engine light comes on on the dashboard. Often this does not bode well.
Yes, sometimes false alarms occur, and in reality there is no malfunction. But in most cases there are problems. They can be determined by the characteristic behavior of the car, as well as by reading error codes recorded and stored in the memory of the control unit.
It is enough to connect to the ECU with a diagnostic scanner or use a smartphone to connect to the unit. A universal error coding scheme allows you to understand what kind of malfunction we are talking about or at least in which of the many systems to look for it.
One of the unpleasant errors is considered to be code P0300. The motorist should know what it means, what caused it and how to fix it.
What does the P0300 code mean?
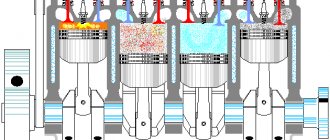
Trouble code P0300 indicates that one or more cylinders are misfiring. If the last digit of the code is not zero, such as P0302, then the number 2 means that cylinder No. 2 is misfiring.
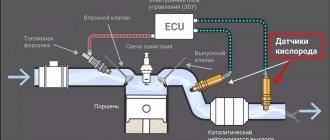
A cylinder misfire causes engine speed instability. If the frequency change increases, the crankshaft position sensor senses this and the engine control module (ECU/ECM) may detect that one of the cylinders has just misfired.
Crankshaft sensor
Misfire means incomplete combustion of the fuel-air mixture inside the cylinder. When the situation worsens, the machine begins to jerk and performance drops significantly. These misfires are what cause the P0300 code.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of a P0300 is the MIL (malfunction indicator light) illumination. It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in the ECM memory as a malfunction).
- The engine stalls or has trouble starting.
- Floating speed, as well as attempts to stall at idle.
- Jerking/misfire at idle or under load.
- Poor speed gain.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Reduced engine power.
- Smell of fuel from the exhaust.
This malfunction is considered serious and must be corrected as soon as possible. Because prolonged driving with a misfire can cause costly damage to the engine and catalytic converters.
Causes of P0300
Trouble code P0300 is caused by many things. Here are some of them.
- Worn spark plugs.
- Faulty wires.
- Ignition coil malfunction.
- Oxygen sensor malfunction.
- Malfunction of fuel injectors
- Burnt out exhaust valve.
- Faulty catalytic converter.
- The throttle position sensor is faulty.
- Faulty engine control module (PCM/ECM).
- Leak in the cylinder head gasket.
- Intake leakage.
On which cars is this problem most common?
The problem with the P0300 code can occur on different machines, but there are always statistics on which brands this error occurs more often. Here is a list of some of them:
- Alfa Romeo
- Audi (Audi a4, Audi a6, Audi q7)
- BMW (BMW X5, E39, E46)
- Cadillac (Cadillac SRX, Escalade)
- Chery (Chery Tiggo, QQ6)
- Chevrolet (Chevrolet Aveo, Captiva, Cobalt, Cruz, Lanos, Lacetti, Rezzo, Silverado, Spark, Tahoe, Trailblazer)
- Chrysler (Chrysler Voyager, Intrepid, Pacifica, Town Country, 300c)
- Citroen (Citroen C5)
- Daewoo (Daewoo Matiz, Nexia)
- Dodge (Dodge Intrepid, Caliber, Caravan, Neon)
- Fiat (Fiat Albea, Doblo, Punto)
- Ford (Ford Mondeo, Ranger, Focus, Fusion, Explorer, C-Max, F-150)
- Geely (Geely MK, MK Cross)
- GMC Safari
- Great Wall Hover
- Honda (Honda Accord, Civic)
- Hover (Hover H3, Hover H5)
- Hummer H3
- Hyundai (Hyundai Accent, Getz, Matrix, H1, Santa Fe, Solaris, Sonata, Tucson, Elantra, i30)
- Infiniti (Infiniti fx35, g35, qx56)
- Isuzu
- Jaguar (Jaguar S-Type)
- Jeep (Jeep Grand Cherokee, Commander, Liberty)
- Kia (Kia Picanto, Rio, Sid, Sorento, Spectra, Sportage, Cerato)
- Lexus (Lexus gs300, gx470, lx470, is250, rx300, rx350)
- Lifan (Lifan Solano)
- Mazda (Mazda 3, Mazda 5, Mazda 6, Mazda cx7, Millenia, Protege, MPV)
- Mercedes (Mercedes s500, w166, w220)
- Mitsubishi (Mitsubishi Outlander, Galant, Karizma, Lancer, Montero, Pajero, Space Star)
- Nissan (Nissan Almera, Qashqai, Maxima, Murano, Note, Patrol, Primera, Teana, Tiida, X-Trail)
- Opel (Opel Agila, Antara, Astra, Vectra, Zafira, Insignia, Corsa, Meriva, Mocha)
- Peugeot (Peugeot 206, 307, 308, 406, 407, 607)
- Pontiac (Pontiac Montana)
- Porsche (Porsche Cayenne)
- Renault (Renault Duster, Kangu, Clio, Logan, Megan, Sandero, Simbol)
- Saab 9-3
- Skoda (Skoda Yeti, Octavia, Superb)
- Ssangyong (Sangyong Kyron)
- Subaru
- Suzuki (Suzuki Vitara, Grand Vitara)
- Toyota (Toyota Camry, Corolla, Matrix, Prius, Rav4, Celica, Highlander)
- Volkswagen (Volkswagen Amarok, Golf, Jetta, Passat, Polo Sedan, Touareg, Touran, Tiguan)
- Volvo (Volvo s40, s60, s80, xc90)
- Vortex
- VAZ 2105, 2107, 2110, 2111, 2112, 2113, 2114, 2115
- Volga Cyber
- Gazelle Business, Chrysler
- Lada Vesta, Granta, Kalina, Largus, Niva, Priora
- TagAZ Tager
- UAZ Bukhanka, Patriot, Hunter, 409
You can sometimes encounter other errors with the P0300 fault code. The most common are: P0021, P0100, P0101, P0102, P0131, P0133, P0135, P0151, P0170, P0171, P0172, P0174, P0201, P0202, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P030 6, P0308, P0340, P0341 , P0363, P0404, P0420, P0422, P1297, P1303, P1336, P1396, P1682.
Troubleshooting P0300
- Replace faulty spark plugs.
- Check and repair broken wires.
- Replace the faulty ignition coil.
- Replace or repair the oxygen sensor.
- Inspect the fuel injectors.
- Replace the catalytic converter.
- Replace the faulty head gasket.
- Eliminate air leaks.
- Diagnostics and repair of a faulty engine control unit.
Error p0300, p0301, p0302, p0303 and p0304 causes
Unfortunately, the diagnostic tool has not learned to determine the specific cause of the failure and, in this case, misfire in the engine cylinder, but, fortunately, the most likely malfunctions can develop in two directions - either there is nothing to burn , or it is impossible to ignite . Although it is still too early to rejoice at the possible quick search for the cause of error p0300, since it could be:
Cylinder misfires. How to diagnose the cause.
- In the ignition system
- spark plug failure;
- breakdown of a high-voltage wire;
- faulty ignition coil (or module);
- other reasons related to wiring and connectors in the ignition system.
- In the power system
- poor quality fuel;
- heavily contaminated fuel filter;
- low fuel pressure.
clogged injectors;
The main reasons why error P0300 occurs
If it is not a general problem of multiple misfires , but for a specific cylinder: p0301, p0302, p0303, p0304 or others, the situation is simplified and most likely lies in the ignition system . In such cases, error P0363 may also be displayed, but it also indicates that the fuel supply to the cylinder is blocked.
How to Diagnose DTC P0300?
Once a P0300 code is detected, a professional auto mechanic will perform the following steps. You can do the same thing yourself.
Connect your car charger
The charger is extremely important when diagnosing the P0300 code. Because troubleshooting requires that the ignition remain on, and this can lead to battery discharge. As a result, additional error codes will appear, which will complicate the search. A car charger will help preserve battery charge.
Connect OBD2 scanner
An OBD2 scanner is required to scan and resolve the P0300 code. With the help of it, you can track the issues related to the error and also troubleshoot them easily.
For cars manufactured before 1996, an OBD1 scanner is used. If the car was manufactured after 1996, use an OBD2 scanner.
Check wiring
Before replacing any part, first make sure all wires and connections are in good condition. Visually inspect the wiring, check for corrosion and correct if necessary.
Check the spark plugs
Spark plugs do not wear out quickly. But if a cylinder is misfiring, it's a good idea to check the spark plugs and notice any signs of trouble.
If the spark plug appears to be faulty, replace it. As part of regular maintenance, you should change the spark plugs every 30,000 km. You should also check the ignition coils!
Inspect the distributor cap
If you replaced the spark plugs, but the problem persists, check the fuel injectors for defects. If you have an old car, check the ignition distributor cap.
Check other error codes
If the OBD2 scanner detects more than one fault code, take the necessary measures to diagnose and resolve them. After doing this, check if the P0300 code returns.
Replace engine control unit
If you have checked everything above, but the error does not go away, there is a possibility that the problem is related to the control unit (PCM). It may need to be re-flashed or replaced.
Diagnosis of misfires
Let us note right away that the correct term is “misfire”, and not “misfire” (in English terminology - misfire). Since the cylinder may not fire for two reasons, according to the saying: “there is nothing to ignite or nothing to ignite with,” then ignition malfunctions are only a special case of the causes of misfires.
While the engine is running, the injection electronic control unit (ECU) constantly receives pulses from the crankshaft position sensor - for the common “60-2” rings, each pulse follows after 6 degrees of rotation, with the exception of the missing reference point. By measuring with high precision the time interval between adjacent pulses, the controller can determine the amount of acceleration of the crankshaft at any moment. Although this is not noticeable at first glance, the speed of rotation of the crankshaft is constantly changing: at the beginning of the power stroke in one of the cylinders, the speed begins to increase, then decreases again. Accordingly, by comparing accelerations in individual sections of the rim, the injection controller can calculate the comparative contribution of each cylinder: the absence of acceleration at the start of the stroke in one of the cylinders means misfire in it.
On engines without a phase sensor, the detection of a dead cylinder is limited to pairs of cylinders where the pistons move simultaneously, since the difference between their working strokes is exactly one revolution. For an inline four, these are the pairs “first-fourth” and “second-third”. Having a phase sensor, the controller already distinguishes which of the two cylinders should have fired. When the misfire counter reaches the value specified in the firmware, the fuel supply to a specific cylinder or pair of cylinders is turned off so as not to drive gasoline into the catalyst. At this moment, motors without phase sensors begin to characteristically abruptly switch from “triple” to “doubling”.
The OBD-II standard provides error codes from P0301 to P0312 (from cylinders 1 to 12) for misfires in a specific cylinder. However, if the fault is not detected in a specific cylinder, the P0300 code is used - multiple random misfires.
Something else useful for you:
How to replace a spark plug?
Replacing the spark plug is a simple task and you can do it at home. Before changing spark plugs, make sure the engine temperature is low.
Step 1: Open the hood and locate the spark plug
Open the hood and you will see several wires running in the engine compartment. The spark plugs are located in the engine at the end of these wires.
Step 2: Pull the wire
Pull the wire and you will see the spark plug installed.
Step 3: Remove the candle
Insert the spark plug wrench and turn to loosen the spark plug. Remove the old spark plug and note its condition.
Step 4. Install a new spark plug
Using the same spark plug wrench, install the new spark plug and tighten it correctly. Then connect the wire as it was before. All is ready.