10.03.2020
| (Votes: 1, Rating: 5) |
Issues discussed in the material:
- Meaning and design of the clutch
- What is a clutch pedal sensor used for?
- Clutch pedal sensor malfunctions
- How to repair and replace the clutch pedal sensor
The clutch pedal sensor is responsible for the smoothness of speed at idle and during shifts, and also affects the operation of cruise control. Malfunctions of this element will be noticeable immediately, and the driver’s task is to fix the problem in a short time.
There is nothing difficult in troubleshooting and replacing the pedal position sensor - even a novice motorist can remove and replace it by following the instructions given in the article. In addition, the number of necessary tools is small, and there is nothing specific among them. Also in the material we will tell you in more detail about the device and function of this sensor.
Meaning and design of the clutch
Without a clutch, the transmission will not work properly. It is located between the engine and the gearbox and provides stepwise gear shifting, controls torque, and also temporarily interrupts the connection between the flywheel and the transmission.
The clutch operates thanks to the force of friction (sliding) and includes the mechanism itself and the drive. When the driver needs to brake sharply, it allows the transmission to be preserved, eliminating overload.
If the car has a manual transmission, then the driver controls the clutch using the pedal. It allows you to connect and disconnect the motor and gearbox. The person behind the wheel releases the pedal, and it returns to its original position due to the spring.
If you drive a car with a manual transmission, keeping the pedal constantly depressed, the transmission will overheat and fail. Driving with slipping is only possible in exceptional situations in order to increase the speed.
There is no clutch in hydromechanical gearboxes, as well as in variators. However, hydromechanical type gearboxes have friction clutches that allow you to change gears smoothly. The classic assembly is found only in a robotic gearbox; in this case, gears are switched thanks to servos, which can be hydraulic or electronic.
Often, 2 clutches are used in a robotic gearbox to make shifting without delays and also to increase the efficiency of the transmission. How such a box functions: the first clutch works, while the second one is in a waiting state to change gear.
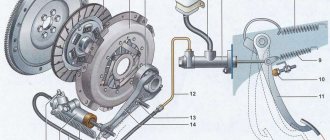
As mentioned earlier, this unit consists directly of the mechanism itself and the drive. The design includes:
- Pressure disk (or basket) . All other elements of the mechanism depend on this part. Contacts the release springs directed towards the center. The dimensions of the site are directly proportional to the two radii of the flywheel of the internal combustion engine. The main difference between the clamping section is that grinding is done only on one side. The disk is tightly connected to the flywheel of the internal combustion engine.
- The driven disk is located between the clamping section and the flywheel . It is in direct contact with the gearbox thanks to a splined coupling and friction linings. The coupling is framed by damper springs, which absorb all the vibration.
- Friction linings are located at the base ; they are usually made from various composite materials.
- Release bearing . Divided into two halves, the first has a round base to allow action on the basket springs. The bearing can be a pull-out or a pressure bearing and is located on the shaft casing. Pulling bearings are used in Peugeot cars. In some cases, a bearing may have multiple retaining springs.
- Drive and also pedal . If your car has an automatic transmission, then there is only a mechanism.
The principle of operation of the clutch is based on friction between the discs. The drive disk is an integral part of the motor, while the driven disk belongs to the gearbox. The person behind the wheel releases the pedal, at which point the springs compress the discs together. Thanks to the friction surfaces, the discs grind in and continue to rotate at the same angular speed. The force of the spring petals determines the abrasive value of the disc.
We recommend
“Partial oil change in an automatic transmission: advantages and features of this method” More details
When you press the pedal, the fork moves due to the drive base. The fork then acts on the bearing, moving it all the way. At the same time, the springs are ready to press the discs. This indicates that the connection between the gearbox and the engine flywheel has been broken by the fork. To absorb transmission shocks (when the pedal is suddenly released when the car starts moving), special springs are used.
Operating principle
The release bearing's job is to connect and disengage the clutch when you press the pedal inside the car. The operating principle of the part is quite simple:
- the driven disk is pressed against the flywheel by a pressure disk, due to which clutch is ensured;
- the pressure on the pressure plate is provided by a diaphragm spring, the inner petals of which are acted upon by the clutch release bearing;
- the movement of the bearing, which initiates the separation of the discs, is ensured by the clutch fork.
Release bearing in a car clutch system
What is a clutch pedal sensor used for?
In order for the engine to function normally, you need to know what mode the clutch is in. For example, when it is open, fuel will be supplied in a smaller volume, and the engine speed will also decrease. Moreover, the changes made must correspond to the current speed of the machine; switching should not occur at idle.
When a motorist does not have enough driving experience, he makes mistakes, as a result the clutch and motor wear out. The on-board computer reads the readings from the clutch pedal sensor to control the engine operating mode, selecting the desired speed. In addition, it, together with the speed sensor, transmits information to the computer about the state of the internal combustion engine, and also warns of breakdowns.
A clutch pedal position sensor is installed in the car to:
- reduce fuel consumption;
- make driving comfortable;
- monitor the condition of the coupling;
- increase the service life of the mechanism.
How long the entire mechanism will last and how much fuel the machine will consume depends on its proper operation. It also affects the functioning of the electronic control unit. It operates exactly the same as a standard limit switch. If the pedal is released and the mechanism is turned on, the sensor contacts will be open. As soon as the driver presses the clutch drive, the limit switch closes. The electronic control unit will receive a signal that the disk and basket have become disconnected.
The device is located in the place where the pedal is attached so that the end of the pedal comes into contact with the limit switch.
Replacing the clutch pedal sensor is rarely required, because its design is simple and it rarely fails. However, it still has to be replaced if it malfunctions or is damaged.
Instructions for replacing the brake controller
- Pump out the liquid.
- Place the vehicle on a support stand and remove the wheel.
- Use a wrench to unscrew the two wheel pins.
- Remove the brake drum.
- Then, using a screwdriver, pull out the hook of the upper tension spring and remove the part. Perform the same manipulation with the lower tension spring.
- Then remove the front pad and spacer bar, while disconnecting the pressure spring and lower the pad.
- Remove the shoe lever from the parking brake hole, straighten the cotter pin and remove it from the parking brake drive.
- Remove the washer and lever.
- Install a new block and assemble the part in the reverse order.
Re: Clutch sensor
Posted by bugens » Oct 18, 2012 12:16 pm
Re: Clutch sensor
Post by Sunny » Oct 18, 2012 12:37 pm
Re: Clutch sensor
Post by LM_74 » Oct 19, 2012, 00:21
Hello, dear Forum members!
Let me introduce myself. I, Mikhail Ledyaev, am the leading tester on topic 21214M. Having looked through your section, I realized that the worst evil is information hunger, a car with E-gas has been produced for more than 1.5 years, and there is not enough information “for the masses.” I will try to answer your questions in parts. First, some general information about what E-gas is. It is necessary to understand that E-gas is not just a replacement of a mechanical throttle valve drive with an electric analogue, but a completely different logic for controlling the engine’s operating process. Here on the Forum there was already a link to a TV VAZ video about E-gas, where the deputy head of the Engine Design Department mentioned it. I’ll try to “popularize” this idea a little. In the initial versions of electronic injection, engine control systems actually “copied” the operation of a conventional carburetor, i.e. mixture formation was organized based on the required amount of air and fuel consumed, depending on the angle of opening of the throttle valve, adjusted according to the amount of oxygen remaining after combustion. In a “rough” approximation, this is how the controllers of the BOSCH MP 7.0 family worked. Starting with M7.9 controllers. the control logic changed and the concept of “torque structure” appeared, i.e., in addition to the throttle opening angle, another control parameter appeared, which “told” the engine what maximum possible torque it could develop if it had an “ideal” mixture. But it is not possible to fully implement such an idea on a mechanical drive, because the controller cannot control the amount of incoming air, but only controls the fuel supply. E-gas solves this problem, i.e. The driver, by pressing the gas pedal, DOES NOT CONTROL the air supply, but SHOWS HIS DESIRE to accelerate or slow down or move at a constant speed, and the controller itself determines the amount of air required for this (the angle of opening of the damper) and the amount of fuel. With such engine control logic, in order for the car to be adequate to the driver’s desires, it is necessary to provide the controller with sufficient information about the adjacent systems of the car - primarily the brakes and the state of the transmission (closed or open). May our “engine experts” forgive me for such a free retelling.