All engines with an electronic fuel injection system are equipped with devices that maintain the required fuel pressure in the fuel line. In the VAZ-2114 power unit, this function is performed by a special regulator. It is thanks to this that gasoline is supplied under pressure to the injectors in the required quantity, depending on the operating mode of the engine.
In this article we will talk about what the VAZ-2114 fuel pressure regulator is, how it works and where it is located. In addition, we will consider its possible malfunctions and methods for eliminating them.
Design features and principle of operation
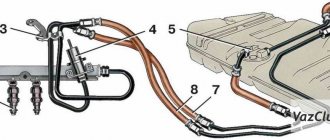
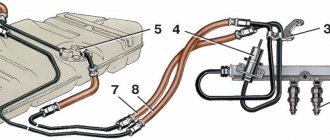
Structurally, the VAZ-2114 fuel pressure regulator is a membrane bypass valve enclosed in a metal casing. It is mounted on the ramp and inserted into it with one of the pipes through a rubber seal. The other output of the RTD is connected to the fuel line. To determine the load on the engine, the regulator is connected to the intake manifold with a vacuum hose. Thus, on the one hand, the membrane is acted upon by fuel supplied under pressure from the fuel pump, and on the other, by air pressure and the force of the valve spring.
The VAZ-2114 fuel pressure regulator has a fairly simple operating principle. When you press the accelerator pedal, excess pressure is created in the intake manifold, which opens the valve slightly, allowing more fuel into the ramp. When the throttle valve is closed, the air pressure in the intake pipe weakens. The valve opens in the other direction, releasing gasoline back into the fuel line.
Symptoms of RTD malfunction
A faulty VAZ-2114 fuel pressure regulator does not pose a critical threat, but its failure disrupts the stable operation of the engine. Symptoms of RTD failure may include:
- difficult starting of the power unit;
- unstable crankshaft speed at idle;
- reduction in engine power characteristics;
- loss of dynamics;
- the occurrence of “dips” when pressing the accelerator pedal;
- increase in fuel consumption.
Having discovered the listed signs of an RTD malfunction, you should diagnose the device and determine the cause of the failure.
Where is the fuel check valve located?
Let's find out where the fuel system valve of various cars is located.
- In power plants with an injector, it can be installed in the gasoline pump housing.
- Mounted on the fuel frame or installed directly in the fuel line. This is the space between the gas tank and the fuel injectors.
On diesel power plants, the mechanical structure is hidden between the fuel injection pump and the low-pressure pump. This arrangement of the product allows you to create a stable pressure at the outlet of the high-pressure pump.
The system has proven itself well:
- on a domestic truck: KAMAZ 740;
- Czech clubfoot Tatra;
- on Mana;
- and Renault Magnum.
In diesel installations where a pre-start heating system is provided, the fuel check valve is located in front of the heating system. A typical example is the same KamAZ or Magirus trucks operating in the Far North.
On domestic passenger cars, such as the VAZ 2110 and 2114 with sixteen valves, the mechanical structure is located in the gasoline pump and on the fuel frame. This is analogous to installing a diesel engine.
Today, old carburetor cars with rear-wheel drive still run on our roads: eights and nines (VAZ 2108 and VAZ 2109). On them, the role of the return device is assigned directly to the gasoline pump.
It stands on the cylinder block and prevents the passage of fuel in the opposite direction: into the fuel tank.
The fuel supply system of automobile gasoline and diesel power units is a technically complex device that should not be approached without knowledge. And even more so, try to carry out technical treatment on your own.
The check valve plays an important role in the regular supply of fuel. Let's focus our attention on its design and installation in the car. Let's look at the problems and characteristic signs of a malfunction. We will also decide on ways to check it.
Possible malfunctions of the RTD
Considering that the design of the pressure regulator is mechanical, malfunctions in its operation can occur quite often. The most common device malfunctions include:
- weakening of the membrane spring;
- valve jamming;
- regulator clogging;
- violation of the tightness of the junction of the regulator and the ramp body.
When the diaphragm spring weakens, the valve cannot cope with the air pressure coming from the intake manifold. As a result, the pressure and amount of incoming fuel are reduced.
Valve jamming leads to an uncontrolled supply of fuel to the manifold and its “waste” into the fuel line. In this case, gasoline consumption increases, and the engine stops starting normally due to interruptions in the fuel supply.
Similar signs of malfunction can be observed when the regulator is clogged. Dirt and deposits reduce the throughput of the system, as a result of which the fuel pressure decreases significantly, the engine “chokes”, and normal idle speed disappears.
If the seal between the regulator and the ramp is broken, the air pressure may drop, which again will lead to a decrease in fuel pressure.
Why does the device fail?
Fuel pipe
The regulator stops working normally mainly for two reasons.
- Low-grade fuel is used, which contains a large amount of water.
- The car sits idle for a long time, is not used and does not start even for the purpose of prevention.
What you need to check the pressure in the system
In order to verify the serviceability (malfunction) of the RTD, as well as the entire fuel system, it is necessary to determine the value of the fuel pressure. Naturally, you will need a special tool for this.
It's called a fuel pressure gauge. It is better if it has a mechanical design and a scale of up to 10 kg/cm2. In addition to the fuel pressure gauge, you will need:
- a piece of high pressure hose (internal diameter 8-10 mm);
- several clamps corresponding to the diameter of the hose;
- pliers;
- screwdriver;
- nipple cap;
- fuel collection container;
- dry clean rag.
Pressure measurement modes
Before checking the pressure in the fuel rail, it is a good idea to find out how this process is carried out. To be able to more accurately determine a possible malfunction, pressure measurements must be carried out in several modes:
- with the ignition on (without starting the power unit);
- with the engine running at idle speed;
- with the vacuum hose disconnected from the regulator (to check the operation of the RTD);
- with a blocked fuel return hose;
- in overdrive mode.
DIY diagnostics
Without testing, an accurate diagnosis cannot be made. So let's look at how to do it correctly. In the case of VAZ 2114 cars and similar models, it is wiser to use the simplest diagnostics - using a mechanical pressure gauge. The order is as follows:
- Unscrew the plug located on the fitting. Pay attention to the elasticity of the O-ring.
- Unscrew the spool in the same way as from the wheel chambers.
- Attach the pressure gauge using a suitable clamp to the fuel rail fitting and take measurements in various engine operating modes.
Immediately before checking the pressure control mechanism, inspect it carefully. There are marks on it showing normal pressure values for several operating modes of the VAZ 2114 internal combustion engine. If the measured values differ greatly from the reference values, the pressure regulator must be replaced with a new one.
How to check fuel rail pressure
The procedure for taking pressure measurements is as follows. First, connect a fuel pressure gauge to one end of the hose and secure the connection with a clamp. We unscrew the cap on the fuel rail (on the side opposite to the one where the RTD is installed). We place a container under the fitting to collect fuel. Using the nipple cap, press the central protrusion, thus releasing the fuel pressure in the system. This process is required! Next, without removing the container, unscrew the locking nipple completely.
When the remaining fuel has drained into the container, put the other end of the hose on the fitting and secure it with a clamp. Turn on the ignition and wait until the gas pump pumps fuel into the system. We check the pressure and compare it with the recommended one.
After this, we start the engine and take measurements at idle. Checking the functionality of the fuel pressure regulator is carried out with the vacuum hose disconnected from it and with the power unit running. If the pressure has increased to 3.3 kg/cm2, the regulator can be considered operational. If it has not changed, the RTD has most likely become unusable.
Similarly, we measure pressure when the return hose is closed, as well as in the gas overflow mode.
When is it necessary to change the regulator?
The main signs of malfunction of this part are described in the preface to the article, but I would like to add a little. The regulator is similar to a valve and has two positions: open (bleeds off excess pressure) and closed (pressure does not leave the system, remaining in it - typical when the engine is turned off, when the pressure should not leave the system so that after some time you can get into the car and start it without any problems). Over time, the regulator wears out and ceases to perform its functions.
Usually, it gets stuck in one position - it either becomes completely open or completely closed. Then the pressure in the system becomes constantly low (the freeze occurred in the “open” position), or it increases significantly (the regulator remains in the “closed” position). In both cases, the malfunction affects the ride quality and wear of parts, therefore, if a problem is detected, we recommend that you replace the failed part and continue to enjoy full driving of the car.
Important! If you are not sure that the problem lies in the regulator, then before replacing, we recommend checking the spare part for functionality. You will need a pressure gauge. The cost of this device in car dealerships ranges from 1000 rubles and more. We strongly do not recommend purchasing a device that is too expensive, since you probably do not intend to use it constantly for professional purposes. You can use a life hack: try driving to a service center and renting a pressure gauge, it will be much cheaper. We filmed the procedure for checking the regulator.
Replacing the RTD
The RTD can be replaced either with the fuel rail removed or without dismantling it. The latter option is more preferable as it requires less time. But before removing the fuel rail or the regulator itself, do not forget to reduce the pressure in the system as described above! Otherwise, the entire engine compartment will be splashed with gasoline.
So, let's look at how to replace the VAZ-2114 fuel pressure regulator without dismantling the ramp. For this you will need:
- key to “10”;
- key to "17";
- key to “24”;
- hexagon to “5”;
- screwdriver with Phillips bit;
- clean dry cloth.
Which way to go
There are two options for eliminating the problem. Take the car to a service station and wait for the repairs to be completed. In this case, you need to shell out a certain amount of money, it’s a pity.
Having knowledge and understanding of the car’s structure, you can carry out repairs yourself. Saving money in person. However, there is a possibility of stepping on a pitfall. Can't deal with the problem.
Then you will have to shell out additional money for repairs in a specialized center, how do you like this prospect? In any case, the decision is yours to make.
Experts recommend not to reinvent the wheel, but to give the car to professionals who will replace it quickly, with a guarantee of quality.
Decide what is more important to you: savings or stable operation of the power unit, good luck to everyone!
Return problem. Where is the check valve, 8 valve, 1.5 engine injector located? Is it in the gasoline pump itself or not??
1.6 8kl. Where is the check valve located? Is it the RTD or on the fuel pump motor itself?
Now 2nd gear won't hold
by Adminrive · Published 03/26/2015
New at a very good price
by Adminrive · Published 04/11/2017
Work order
- First, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery (key to “10”).
- Disconnect the regulator vacuum hose from the intake manifold fitting.
- Using a “17” wrench, unscrew the nut securing the drain hose. Disconnect the hose.
- Using a Phillips screwdriver, unscrew the bolt of the return pipeline clamping plate.
- Using a hex wrench set to “5”, unscrew the screws securing the RTD to the fuel rail.
- Using a “24” wrench, unscrew the nut connecting the drain hose fitting and the RTD.
- Remove the fuel pressure regulator.
That's basically the whole process. Installation of the RTD is carried out in the reverse order. Important: do not lose the rubber seal that comes with the regulator. Without it, the connection between the RTD and the fuel rail will be leaky, which will lead to a change in the operating pressure in the system.
Installing a new sensor
Before removing, be sure to relieve the fuel pressure in the rail. To do this, turn off the power to the fuel pump and start the engine. Or carefully unscrew the spool valve from the fitting in the ramp (this option will be more suitable if the internal combustion engine does not start at all). Then you work according to this scheme:
- Disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Disconnect the hose from the VAZ 2114 vacuum pump.
- Unscrew the nuts and drain the gasoline. Please note that there may still be pressurized gasoline in the fuel system. Therefore, take precautions.
- Fix the tube and washer.
- Unscrew the bolt screwed into the clamping element.
- Remove the clamping element.
- Unscrew the nut that holds the drain hose and pressure sensor.
- Remove the bolts connecting the fuel rail to the pressure sensor.
- Dismantle the pressure regulator in the system.
Install the new device in the reverse order. As you can see, there is nothing complicated. The main thing in repair is to imagine what this or that element of the system is responsible for. And then you can quickly give an accurate diagnosis based on the signs.
Source
Some useful tips
To ensure that the fuel pressure regulator does not cause you trouble and works as long as possible, use these tips.
- When planning to replace an RTD, buy only a branded device recommended by the manufacturer.
- Fill your car tank with only high-quality fuel. Do not use fuel additives of unknown origin.
- Do not forget to promptly replace the fuel filter.
- At each maintenance check the fuel pressure in the system. If problems are identified, correct them promptly.
- If you find problems with the regulator, do not delay replacing it.
Troubleshooting
To find problems, we suggest you use the appropriate methods.
- Pump fuel into the system, turn off the ignition and monitor the behavior of the pressure gauge. In a normal situation, the pressure drops to 0.7 Bar and stops at this level. If the regulator fails, the pressure gauge will tend to zero. The problem may lie in the device itself, or in the fuel pump motor valve.
- Increase the engine speed to 3 thousand and again look at the pressure gauge readings. If the arrow points down, the fuel pump is broken. It needs to be replaced.
- If the pump takes a long time to build up pressure, the problem lies in the filter or mesh of the tank, which is clogged with debris.