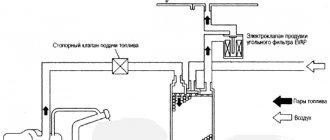
The gas tank of any car always contains vapors formed due to a decrease in atmospheric pressure or heating of the fuel. In order to prevent the leakage of fuel vapors into the vehicle, a special gasoline vapor recovery system (VPSU) is installed. Thanks to it, the vapors retained by the adsorber (essentially activated carbon) enter the intake manifold and burn in the engine cylinders. To regulate the amount of gasoline vapor coming from the adsorber to the manifold, a special solenoid valve is used.
Principle of operation
The adsorber itself allows fuel vapors to accumulate in a special place - the separator. As a result, gasoline turns into condensate and goes back to the tank. Vapors that have not undergone treatment go through double valves of the system, one of which prevents fuel from spilling out during an emergency (for example, a coup), and the second “is engaged” in regulating the pressure in the tank. The adsorber purge valve is located under the hood, and the adsorber itself is located on the tank. The control unit ensures the normal operation of the entire system: it ventilates and removes condensation.
Removal Features
The VAZ absorber is sometimes removed completely. To do this, you need:
- replace the gas tank cap with a leaky one;
- plug the supply and discharge pipes;
- often change the ECU firmware.
As mentioned above, you should not approach the adsorber as an unnecessary thing, and if you decide to remove it, remove it correctly so that the gas tank remains ventilated and not tightly sealed, as if there is an adsorber. Those who convert a carburetor engine to an injection engine have an advantage. If they do not touch the tank pipes, they do not disturb the carburetor ventilation system of the tank, so they do not need an adsorber.
Causes of adsorber malfunctions on a VAZ
But in the case of the VAZ 2114, which has an injection engine, everything is more complicated. However, there is no point in removing the absorber. The advantages that the VAZ absorber has are in reducing harmful emissions into the atmosphere, but that’s where they end. And the high cost and the fact that it can interfere with more important parts in the engine compartment become the main reason for removing the device. Why do some drivers make this difficult decision?
Basically, they just don’t like the device, but that’s not an argument. Experienced car enthusiasts remove it when malfunctions occur, so as not to spend money on a new one. It cleans up easily. A fine filter (usually from a VAZ 2108 carburetor) is put on the hose from the separator; in this case, gasoline vapors escape into the atmosphere. The hose from the valve is closed. The engine control program is adjusted so that the ECU does not turn on the Check Engine.
It is better to drill a 2 mm hole in the tank lid to make ventilation, like on a carburetor engine. Otherwise, the tank may not withstand either external or internal pressure. Most often, a vacuum develops in the tank and it crushes like an empty tin can. Many car enthusiasts talk about this for the edification of beginners. What is needed to remove the adsorbent device for replacement?
First you need to free it from its fastenings. We disconnect the block along with the wires, as well as the hose for supplying gasoline to the throttle assembly. We remove the purge valve and remove the fuel vapor outlet hose from the separator. The adsorber bracket is installed on 3 bolts, which must be unscrewed and the bracket carefully removed. The new device is installed on the same special mount, and the fuel vapor supply hose is connected to the purge valve. Remember: when changing the adsorber, you need to change all the pipes from it.
Take care of nature and do not throw away the adsorber. As a last resort, it is better to install a new one, since this is an ordinary filter that works for a very long time and does not require constant monitoring. Environmental standards were not invented to harm, but so that our children and grandchildren could live after us.
Don’t forget that the traffic police inspector and the inspection station personnel may catch you interfering with the design of the car, then you will not be able to pass the technical control. Listen to the advice of experienced car enthusiasts, take care of your car, be polite on the road, then any trip will only bring you a good mood.
Design and operation of the adsorber purge valve
The KPA is an electromagnetic locking device that operates from the vehicle’s on-board network. The valve consists of:
- plastic case;
- valve with spring;
- windings;
- metal core;
- connector
When the vehicle's engine is turned off, no voltage is supplied to the valve and it remains in the closed position. That is, on the motor side, the system that captures vapors is blocked. At the same time, the adsorber begins to “collect” vapors. When the power unit starts, voltage is applied to the valve, causing it to open and fuel vapors to enter the intake manifold. As soon as the ignition is turned off, the control unit is de-energized and the pipeline is closed: no vapors enter the receiver.
Cars of a high price category have a more complex evaporation system. Such machines have special sensors that can “calculate” the amount of air and vapor as a percentage. This allows you to more accurately control the supply of gasoline to the injector.
Installation
If the new valve does not have an o-ring, remove it from the old valve.
Note: A damaged O-ring should be replaced.
Install the valve in the reverse order of removal.
The gas tank of any car always contains vapors formed due to a decrease in atmospheric pressure or heating of the fuel. In order to prevent the leakage of fuel vapors into the vehicle, a special gasoline vapor recovery system (VPSU) is installed. Thanks to it, the vapors retained by the adsorber (essentially activated carbon) enter the intake manifold and burn in the engine cylinders. To regulate the amount of gasoline vapor coming from the adsorber to the manifold, a special solenoid valve is used.
Signs of a malfunction of the control unit
First, start the engine: at idle or in cold weather, you will hear a characteristic, barely audible chirping sound. It indicates that the valve is working properly. In order not to confuse this sound with the noise from a working timing belt, sharply press the gas. The character of the chatter should not change. The following signs indicate a malfunction of the control unit:
- lighting of the CHECK signal on the instrument panel;
- determination of error PO441 during testing;
- increased gasoline consumption;
- unstable operation of the power unit when driving;
- unstable idle;
- increase in CO2 content;
- a hissing sound when unscrewing the tank lid (a vacuum has appeared);
- the appearance of a fuel smell in the cabin.
How to diagnose an adsorber malfunction yourself
As a rule, no serious malfunctions occur with the automobile adsorber, which is due to its simple design and the absence of serious loads. However, over time, the filter layer becomes clogged, which can be judged by a number of indirect signs. The first and fairly obvious signal indicating a malfunction of the adsorber is increased pressure in the gas tank. When it is opened, a strong hiss will be heard, and in some cases the tank cap may simply be knocked off, which can result in injury to the car owner.
Many drivers who do not know why an adsorber is needed in a car and what it is, in the situation described above, do simply - open the tank several times a day, releasing air from it. More “knowledgeable” people can completely exclude the adsorber from the fuel system, not considering it an important element. Both of these actions are fundamentally incorrect, since the absence of an adsorber, as well as its malfunction, significantly reduces engine power, “floating” idle speed appears, and fuel consumption increases noticeably.
It is worth understanding that the presence of an adsorber in a car not only increases its environmental friendliness, but also leads to fuel savings, which without this element would simply evaporate while the car is not in use. This is due to the fact that when the fuel is heated, its vapors “leave” the fuel tank and initially enter the separator, which retains the bulk of them. Condensation occurs in it, and the fuel in liquid form is returned to the tank. The same part of the evaporation that did not have time to condense ends up in the coal filler, where it safely remains, subsequently participating in the process of enriching the mixture.
Valve check on site
You will need a tester (voltmeter, multimeter) and a screwdriver. The KPA itself is installed on the radiator frame. The device can be recognized by seeing two tubes approaching it, through which the evaporation moves. Further:
- disconnect the electrical connector from the control unit by releasing the block lock;
- using a multimeter, check for the presence of voltage by touching the negative (black) probe of the device to ground, and the red probe to “A” (the letter on the block connector);
- turn on the ignition: the multimeter should show the vehicle's on-board voltage. If not, check the wiring.
Checking spark plugs and ignition system
If you have not found which sensor is responsible for the floating engine speed, you should pay attention to the condition of the spark plugs and high-voltage spark plug wires. The cause of the malfunction may be:
- carbon deposits and contamination of spark plugs. Cleaning can only provide short-term improvement. It is better to replace spark plugs with new ones;
- damage to wires. High-voltage spark plug wires are checked visually for damage (at night, if the insulation is damaged, a spark is noticeable when the engine is running).
- bad contact. You need to check the condition of the contact of the wires and spark plugs (disconnect and reconnect the spark plugs);
Subscribe to our feeds on social networks such as Facebook, Vkontakte, Instagram, Twitter and Telegram: all the most interesting automotive events collected in one place.
How to check the adsorber valve removed from the car
You need to take a medical syringe of suitable volume, simply pull out the piston 2-3 cm and connect it to the outlet fitting. If you press on the piston, it will move with difficulty, which indicates that there is pressure in the valve. Now connect the battery to the electrical part of the control unit and press the piston again: the resistance should disappear. If this does not happen, you will have to buy a new valve.
Instructions for checking and independently replacing the canister purge valve on LADA Samara 2114, 2113, 2115 cars.
To perform work on replacing and checking the adsorber purge valve you will need:
Disconnect the wiring block from the canister purge valve.- We connect the negative probe of the multimeter to the “ground” of the car
- Turn on the ignition and check the supply voltage at terminal A of the wire block. The voltage should be 12V. If the voltage is less or absent, you need to check the battery charge, the health of the power circuit and the serviceability of the computer.
- Loosen the clamp securing the hose to the valve and remove the hose. In this case, you need to make sure that the hose does not break off.
- Using a screwdriver, remove the valve from the adsorber.
- To check the functionality of the valve, you need to apply 12V voltage to the valve terminals. The plus goes to pin A, and the minus goes to pin B. After power is applied, the valve should open with a characteristic click. If this does not happen, the valve must be replaced.
- Before installing a new valve, check the O-ring. A damaged ring must be replaced.
- We install the new valve in place in the reverse order.
Replacing the adsorber
You can replace the adsorber on a VAZ 2110 without any difficulties.
It is enough to study its fastening and connecting the hoses to it. Buying a new adsorber is a minimal investment. We disconnect the hoses and tubes one by one (to begin with, you can mark them with a felt-tip pen or colored tape), remove the old adsorber, install a new one, then connect the hoses and tubes in the same order. Attention to your car is always justified: timely replacement of the adsorber will help you reduce fuel consumption, will reduce the risk of breakdowns in the fuel system, ensuring the safety of you and your passengers
Few car enthusiasts know what signs of an adsorber malfunction exist. And some have no idea what kind of spare part it is and what it is used for in a modern car. After all, in more “older” domestic models there was no trace of these outlandish things.
Yes, with the advent of Euro 3, an environmental standard, auto designers began to use this device without fail in order to trap fuel vapors and prevent them from entering the atmosphere. This is the order, according to this very standard, and it must be followed. And in the systems of most cars, foreign and domestic, an adsorber (absorber) appeared.
The part looks like a small opaque jar. Inside it, the process of adsorption of gases occurs with the help of coal or other substances with which the adsorbent device is filled. It also has a special electric valve, which during operation makes characteristic sounds - a clattering sound when the engine warms up.
Symptoms of adsorber malfunction vary
. A part, like any other, can become unusable and become clogged. And flaws can occur due to mechanical damage, natural wear and tear during operation, and also due to contamination of the element that absorbs gases.
So, one of the signs that the adsorber has failed may be excessive pressure in the gas tank. Vapors accumulate and simply have nowhere to escape from the system (they do not escape through the adsorber when the engine is not running). The check is simple: open the gas tank cap and if you hear a characteristic hissing sound, then enough vapor has accumulated there that can harm the atmosphere.
fuel systems
If your engine warms up to 60°C
at idle the speed actually drops (so that), then most likely it is necessary to carefully check the adsorber. Perhaps he is the cause of all these troubles. We disconnect the hose leading from the manifold to the valve, plug it by any means (plug, bend, constriction). And if the problem does not disappear, and the engine again plays tricks with unstable speed, then your adsorber is clogged.
A sign that the adsorber or its valve has failed can be that. This happens because the performance of the fuel pump is not enough due to the constant vacuum in the fuel tank.
One of the first signs that the adsorber valve has “closed” is its constant silence. After all, when the engine warms up, it makes a characteristic clattering or tapping noise. If there is no hearing, then a malfunction is coming soon.
What is the threat?
In addition, if the gas tank is poorly ventilated, this can lead to a vacuum
And as a result - deformation and damage to such an important spare part as the fuel pump. And an unventilated adsorber can also cause fuel accumulation in the intake manifold. And this can already affect the stability of the entire engine.
And this can already affect the stability of the entire engine.
How to replace?
It seemed like such an inconspicuous element, which at first glance is not important for the car, but without which it cannot work properly. Dips appear, the engine “troubles” and the gas tank may even collapse! And all this is due to a faulty adsorber valve
Many people don’t know what it is, how it works and MOST IMPORTANTLY what it affects. Today I will try to put everything into simple terms and describe the main symptoms of a malfunction. It will definitely be useful, so read and watch...
It will definitely be useful, so read and watch...
First, let's start with a definition.
Adsorber (from Latin sorbeo - absorb)
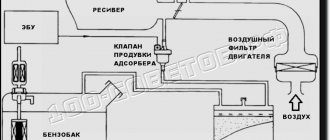
- This is a car system that serves to capture gasoline vapors that come out of the tank. When the engine is running, they are sent to the fuel injection system, namely to. When the engine is turned off, some of the vapors are captured by the separator (it directs them back to the tank), and the remaining vapors enter the adsorber, where they are neutralized.
Device
Engines with distributed fuel injection first appeared on front-wheel drive Ladas, starting with the 2111 model. They differ greatly from their carburetor predecessors in a more complex power system design. It consists of 2 subsystems: fuel supply to the fuel rail and gasoline vapor recovery. One of the components of the latter is the adsorber in the VAZ-2114.
A solenoid valve is placed on top of the plastic cylinder and is controlled by the engine control unit. This part is removable and secured with plastic latches. The valve body is rectangular, and there are 2 fittings (inlet and outlet) and a connector for connecting the ECU.
The hoses are secured to the fittings using clamps. The incoming one is connected to the gravity valve and then to the separator and the gasoline tank. The outlet is connected to the throttle valve assembly.
From which Euro standards is it installed?
According to international requirements, the installation of an adsorber is mandatory on cars with Euro-2 standards and higher. As for the standard known in Russia (Russia-83), there is no installation of an adsorber here.
So, in VAZ-2108 cars there is no adsorber. Here the separator and the fuel tank are connected to each other using a drain tube.
During operation, condensation occurs and returns to the fuel tank.
In addition, the separator interacts with the atmosphere using a 2-way valve, which does not allow the pressure in the tank to increase or decrease.
The connection between the tank and the neck occurs using a gasoline-resistant tube, fixed with clamps. It turns out that when the pressure in the tank decreases (increases), fuel vapors escape into the atmosphere.
The system is organized differently in VAZ Priora cars. Here, the fuel vapors that entered the separator from the fuel container condense. The condensate then accumulates and returns to the tank.
A gravity valve is mounted in the upper part of the separator, which prevents the fuel mixture from leaking out of the tank if the machine overturns.
If the engine is started, the vapors of the fuel mixture are mixed with air masses and discharged through the throttle assembly into the intake pipe - to the cylinders of the power unit.
It turns out that fuel vapors in a stationary position of the car accumulate in the adsorber, and if the car is moving, they are purged by the valve and sent to the receiver and to the engine for afterburning.
According to Euro-2 requirements, the fuel tank ventilation must not come into contact with ambient air, and vapors must be collected and directed to the engine (or adsorbed by the device in question).
As for the Russia-83 standards, contact between the atmosphere and ventilation of the fuel bank is not prohibited.
Operating principle
So, what does the process of purging the adsorber in a VAZ 2114 look like? When the car is parked, gasoline from the tank evaporates and first enters the separator. There, some of the vapor turns into liquid and flows back. The remaining gaseous fuel, moving along the line, enters a sealed adsorber. Activated carbon absorbs vapors and holds them until the engine starts.
When the ignition is turned on, voltage is applied to the valve from the controller that controls the engine and it opens. While the engine is running, the filler heats up and dries, releasing gasoline vapor back. Under the influence of vacuum in the intake receiver, they are sucked into the engine along with the main portion of fuel.
How to check the serviceability of a car adsorber - a step-by-step guide
The absorber is designed to absorb fuel vapors from the tank. This part plays an important role in the normal operation of the fuel pump and engine. A malfunction of the device causes a cascade of problems associated with the stability of the power unit. How does the failure of the auto adsorber manifest itself and how to check its serviceability?
What is it needed for
The main role of the adsorber is to capture fuel vapors. The collected vapors are condensed and sent to the intake manifold.
This solves several issues:
- firstly, the level of hydrocarbon emissions into the atmosphere is reduced;
- secondly, the fuel tank is ventilated and the state of rarefaction in it is eliminated;
- thirdly, engine operation is stabilized and gasoline consumption is reduced.
The 5 most unsuccessful modern engines - the cars in which they are installed. Unsuccessful engines create many maintenance problems for the car owner. In the ranking of the most unsuccessful...
There are several signs by which you can identify the problem:
- floating engine speed;
- the engine stalls at idle;
- fuel consumption increases;
- gasoline vapor accumulates in the tank;
- when the power unit is heated, starting it is difficult;
- loss of engine power at low speeds.
A car with a faulty adsorber will continue to drive, but the power unit will no longer operate stable. Operating the machine without cleaning the fuel system from gasoline vapors can lead to damage to the fuel pump.
A button that can check the entire dashboard Today, all modern cars have an instrument panel that informs the driver about the status and stages of...
To identify problems in operation, it is necessary to carry out a step-by-step check:
- Disconnect the car's electrical network from the battery.
- Disconnect all tubes and wires from the device.
- Disconnect the purge valve.
- Using a vacuum tube, attach a syringe to the valve nozzle. When pressure is applied to the syringe piston, resistance should be observed, as a result of which the piston returns to its original position.
- Perform the same manipulation, but with the valve connected to the network. Press the plunger of the syringe and turn on the power to the valve. A “poof” should be heard as a result of the valve opening to relieve pressure.
If the valve does not open, it is beyond repair and must be replaced.
If you hear a hissing sound from the gas tank when you open the cap, what should you do? When unscrewing the gas tank cap of their own car, many car enthusiasts often hear a short hissing...
Checking the performance of a car adsorber becomes necessary as the mileage increases. If poor engine performance or a malfunction of the purge device is detected, the device must be replaced.
Loading... Stay up to date with AUTO news - subscribe to the channel in Yandex.Zen
Why is an adsorber needed on a VAZ-2114?
The main purpose of the fuel vapor recovery subsystem and adsorber as a component of this system is to make the car less harmful to the environment and to comply with international environmental standards Euro-2 and Euro-3.
The adsorber does not affect the technical characteristics of the VAZ-2114 in any way. It is designed to prevent gasoline vapors from leaving the power system circuits. This measure allows you to use the fuel supply a little more efficiently. There will be no savings like when using forced idle, but you can drive 1-2 kilometers during long-term operation.
Bottom line
An adsorber is one of those devices that does not in any way affect the dynamics of the car and is intended primarily to reduce the level of harm to the atmosphere.
As for , it is too insignificant to concentrate attention on it. At the same time, you shouldn’t throw the product out of the system either - just monitor its serviceability and change it on time
At the same time, you shouldn’t throw the product out of the system either - just monitor its serviceability and change it on time.
If there is a video in the article and it does not play, select any word with the mouse, press Ctrl+Enter, enter any word in the window that appears and click “SEND”. Thank you.
Do you need an adsorber? This question worries many Togliatti car owners. The VAZ 2114 adsorber appeared after the introduction of Euro-3 environmental standards, which required the installation of devices on cars that allow them to retain evaporating fuel so that it does not enter the atmosphere. The black cylinder installed on the VAZ on the right in the corner of the engine compartment near the radiator is the VAZ 2114 absorber, the design of which we will consider.
Removal and installation
Dismantling of the part is carried out according to the following algorithm:
Step 1. Disconnect the clamp from the negative terminal of the battery and block the wheels using the parking brake (“put the handbrake on”).
Step 2. Remove the wire from the adsorber valve (VAZ-2114).
Step 3. Using a Phillips screwdriver, loosen the clamps and remove the hoses from the fittings. The latter are made of plastic and break easily.
Step 4. Use a flathead screwdriver to pry the latch on the valve body and remove it.
Step 5. Loosen the clamp securing the adsorber body and pull out the latter.
Is it possible to remove
Some motorists neglect environmental standards and remove the adsorber valve. The words are basically like this: “why do I need it, the car has become slower, the consumption has become higher, I’ll throw it away altogether.” But realistically, is it possible to do this? Will this make the car worse?
It is worth understanding that a working system does not affect the operation of the engine at all, and even saves a little fuel, because the vapors that remain in the main body are then burned out in the engine. Of course, you should not expect that the savings will be huge, but you get a few kilometers of mileage.
Of course, you can clean it, the car is simply OK with it! It will even be better, because the evaporation from the tank will not condense (purify), but will go directly into the atmosphere. That is, you kind of remove all the cans - valves and give an open air flow to the tank.
Physically, they do it this way: they hang a fine filter from a carburetor VAZ on the hose from the separator, and gasoline vapors escape into the atmosphere. The hose from the adsorber valve is blocked, the engine is flashed ( chip tuning ), otherwise an error will appear, that’s all!
However, there are also disadvantages to this:
Pros of unplugging:
I think the system is quite useful; personally, I was often annoyed when a carburetor car smelled of gasoline, wherever possible. If you inhale and then get a headache, this system allows you to avoid this, saves fuel a little and does not pollute the atmosphere.
This is where I end, I think my article was useful to you, read our AUTOBLOG, subscribe to the channel.
(
32 votes, average: 4.47 out of 5)
What is an adsorber, what task does it perform, what problems can there be, we’ll talk about this and much more in today’s article.
Many car owners have no idea, let alone the structure of the system, and sometimes even its existence. Therefore, the goal of this article is to “put everything into perspective,” including finding out how the device works, as well as where it is located.
Why do you need an adsorber?
It was originally created as a tribute to environmental standards, more precisely under EURO2. By and large, the motor can be configured so that it can do without it. But, taking into account modern standards, vapor leaks are unacceptable. Plus, the adsorber does not allow fuel vapors to enter the cabin, which, as you understand, is also unpleasant. If on old cars, still of the carburetor type, such a system did not exist, in principle, on all modern injectors, it is mandatory.
What is the adsorber and where is it located?
The adsorber is structurally a cylinder, a hollow one, inside of which there is a so-called filter component. The adsorber also consists of a number of additional modules, for example:
• The first is the container in which the filter is placed.
• The filter element is often simple granular activated carbon.
• Separator, a device that receives and sends retained fuel vapors back to the tank.
• Magnetic valve responsible for changing operating modes.
• The gravity valve prevents fuel overflow if the vehicle rolls over.
• Various connecting hoses and tubes.
Perhaps one of the main elements of the entire adsorbing system is the magnetic valve. The mode of operation and the change of modes depend on it. That is, it is responsible for the timely switching of the accumulation mode, when vapors accumulate in the tank, to the mode of transferring vapors back to the tank.
Depending on the car and even models from the same manufacturer, the location may vary. Here you need to find out specifically by model and even year of manufacture. An excellent example is the Audi A4 B5, where in different years the systems were located under the front and rear fender liner, under the spare wheel, directly on the tank. Therefore, study the operating instructions; it usually indicates where the adsorber may be located. On domestic Ladas, on almost all models, the adsorber is located in the right corner, when viewed in the direction of travel of the car, next to the headlight.
How does the adsorber work?
There is nothing difficult about the work. The algorithm is as follows: vapors, let's say gasoline, form in the tank, rise and fall into the so-called separator. Here they condense, turning into liquid. The formed liquid goes back into the tank, and the remaining unconverted vapors go directly into the adsorber. In the adsorber, vapors are absorbed by an activated carbon filter; it copes with this task most effectively. Remember that the accumulation of vapors in the adsorber occurs only when the engine is turned off.
After the engine starts, the ECU sends a signal according to the available operating modes and a magnetic valve opens, connecting the adsorber to the throttle or intake manifold. Next, purging occurs when the vapors are driven through the system and connected with air through the throttle. “Passing” is carried out due to the vacuum created in the intake manifold. Then they enter the cylinders, where they ignite along with the main “portion” of fuel.
In principle, it is clear that while the car is not running, the evaporating fuel in the form of vapor settles on the separator, then some in the form of condensate returns to the tank, and the other part in the form of vapor through the adsorber enters the throttle and further through the system. There is nothing complicated, everyone can figure it out.
Malfunctions and symptoms
Remember that the signs listed below may not always indicate problems with the filter system. So:
• The readings from the fuel level sensor constantly vary, sometimes it shows an empty tank, and after a while it shows full.
• Floating speed, but with the caveat that this can only happen on a warm engine, after about 10 minutes of driving.
• At idle, when you put a little pressure on the gas, it feels like the car is about to stall, as if the gas has run out.
• When opening the tank lid, a whistle is heard.
• Magnetic valve knocking, often confused with valve knocking.
As for malfunctions, let's return to the section about the design of the system, what does it consist of and what can fail?
1. Hoses, tubes. It is clear that everything does not last forever, each manufacturer may have its own resource; as a rule, owners begin to experience loss of tightness, cracking of hoses, somewhere after 130,000 km. average.
2. Clogged adsorber channels, hoses. Subsequently, all kinds of debris accumulates, including destroyed container membranes or activated carbon itself.
3. Inoperative valve. Stuck in one position is a fairly common problem, and to be honest, in most cases it is the magnetic valve that is faced with problems. There are two options: replace it with a new one (a very expensive business) or look for craftsmen and repair it, you can, of course, do it yourself, but your hands must be from the right place.
4. The voltage on the magnetic valve has disappeared. Check the wiring, perhaps some relay is “buggy” or even a failure in the ECU (rare, but it happens). After all, opening/closing signals come from the “brains”.
5. Separator, what’s the problem with it? It may crack, because they are often plastic, so there is a loss of tightness, as a result, the vapors are not converted into liquid, etc. Soldering this container is extremely difficult, the plastic has such a property that it is very difficult to melt.
6. Out of coal. The problem is rare, we immediately note, most likely associated with some other malfunction, for example, depressurization of the system, as an option.
Conclusion
What I would like to emphasize in the article is, firstly, that you can do without an adsorber, just turn it off, it’s a matter of minutes (unless, of course, you don’t care about the atmosphere and your own health), secondly, during normal operation of the device, the car feels behaves quite adequately, moreover, it saves fuel.
Therefore, if such a problem occurs, try to identify the true cause, and then decide whether you are ready to spend a tidy sum on new spare parts (as a rule, a new adsorber will cost 5,000 - 6,000 rubles) or not.
Adsorber, a term coined from English, denoting a part of a vehicle responsible for absorbing combustion products by liquid (solid) bodies in a special container. The VAZ 2114 adsorber (some call it an absorber) uses activated carbon as an absorbing element, which is what the domestic model is filled with.
The adsorber is a complex mechanical joint, sold and installed on the car, according to the kit, from the following elements:
Malfunctions, symptoms and solutions
Due to the extreme simplicity of the design, the adsorber in the VAZ-2114 has two malfunctions: it is clogged or the solenoid valve does not work. If this part breaks, the following problems may appear in the operation of the car:
- Unstable engine operation at idle (speeds fluctuate). To check, you need to disconnect the hose between the throttle assembly and the purge valve and plug it. A candle, for example. If the engine speed does not become normal, then the adsorber is clogged.
- When you unscrew the gas tank cap, you hear a hissing sound or gasoline vapors squeeze it out of the filler neck.
- Poor acceleration due to decreased pressure in the fuel line. If the purge valve is faulty, atmospheric air does not enter the tank. This leads to the fact that when the engine is running, a vacuum is created in the gas tank, interfering with the operation of the fuel rail. Also, a strong vacuum can lead to the tank being severely deformed by the force of atmospheric pressure.
- No repetitive clicking noises during overclocking.
You can check the functionality of the purge valve in the following way. A voltage of 12 volts must be supplied to the power connector (where the wires from the ECU are connected). For example, using 2 wires connected to the “plus” and “minus” of the battery. If the part is working properly, the mechanism will respond with a click. Otherwise, the element needs to be replaced.
The second way to check the functionality of the adsorber valve on a VAZ-2114 is to blow it out. To do this, you need to blow into the fitting for the supply hose. If air flows freely from the valve outlet, it must be replaced.
Useful video
You can get additional information about the design of the adsorber and options for replacing it from the video below:
According to the requirements of new environmental standards that limit the content of harmful substances in exhaust gases, vehicles must be equipped with an EVAP system. This equipment prevents harmful fuel fumes from entering the atmosphere. The main function in the fuel vapor recovery system is performed by the adsorber. Some people underestimate the importance of this element in the operation of a car. However, a malfunction of this seemingly minor component can lead to damage to the fuel pump and affect the operation of the entire engine. Therefore, experts recommend checking the adsorber valve when signs of engine malfunction appear.
Complete removal of the adsorber from the power system
Some VAZ 2114 owners decide to completely remove this part from their car for reasons of savings and to prevent future malfunctions. There are two ways to do this.
Method 1. After completely removing the adsorber from the VAZ-2114, the hose leading to the throttle valve assembly is closed using a plug. A fuel filter from any VAZ carburetor engine is inserted into the hose running from the gas tank to the adsorber.
Method 2. The adsorber is removed along with the support. The hoses previously connected to it are closed using plugs. A small hole (1-2 mm) is drilled in the standard gas tank plug to connect the cavity to the atmosphere. You can also use the cap from a carburetor “eight” or “nine” to depressurize the fuel tank.
After upgrading the power system, it may be necessary to update the firmware of the engine control unit, since it will perceive the absence of an adsorber as a malfunction in the engine and switch to emergency operation. This threatens to significantly reduce the traction qualities of the car.
The adsorber in the VAZ-2114 is an important element in the engine power system, which allows you to slightly reduce fuel consumption and eliminate the smell of gasoline in the cabin.
Determining possible damage
We have figured out why the adsorber is needed, now let’s determine the signs indicating its failure. Considering the quality of fuel at gas stations in our homeland, this part often becomes dirty and fails.
Any malfunction of this mechanism can be easily determined by obvious signs:
Damage to the absorber - the fact that this mechanism of your car has problems can be determined by hearing a hissing sound when opening the tank, it indicates the accumulation of an excess amount of gasoline vapor.
Excessive pressure appears in the tank when you open the lid, there is a moment when the contact area with the external environment is small, and the pressure is quickly “relieved” through it, and the tank “hisses”, similar to a bottle of soda.
In the event of a breakdown, the adsorber is often removed completely, we will discuss how to do this below, but there are no unnecessary parts in the car, it is worth remembering. If you don’t want to remove and gut the ECU, you can try to fix everything yourself. The weakest point in the absorption kit is the VAZ 2114 valve.
Before repairing, you need to make sure that the problem is here:
- Use a flat-head screwdriver to unscrew the fastener on the motor cover (be careful, the fastener is plastic, you shouldn’t break it), and then very carefully remove the clamps.
- We remove the part and blow out the valve. If air does not pass through, then the valve is operational, and the breakdown is elsewhere; if air passes through the valve, then you have found the problem.
A valve failure, in addition to unstable idle speed, will soon give you CheckEngine and significantly increased consumption.