Detailed diagnostics of hydraulic compensators on Lada Priora
Sometimes, to determine the causes of knocking hydraulic compensators on a 16-valve Lada Priora engine, the thermal state of the engine alone is not enough. A set of tests makes it possible to more accurately determine the factor that causes extraneous noise.
Diagnosing the condition
One of the common complaints is knocking noise both cold and hot. However, as the speed increases, the symptom disappears. One of the following options is relevant:
- Worn or damaged ball valve. You can't do without replacing the hydraulic compensator.
- Contamination of the internals of the hydraulic fluid with wear products due to the choice of incorrect lubricant or untimely replacement. Washing the internals and changing the oil composition to a standard one eliminates the problem.
If the clatter appears only on a hot power unit and disappears at high speeds, and on a cooled unit no extraneous sounds are observed in any mode, the plunger pair has worn out. The hydraulic compensator must be replaced as an assembly.
AVTOVAZ diagnostic technique
Methodology for diagnosing and eliminating the defect “Knocking of hydraulic pushers”
Causes of knocking of hydraulic pushers
The main reason for timing knock is the valve seating at an unacceptably high speed, which occurs as a result of a violation of the kinematic connection between the valve and the camshaft cam. The main reasons for the disruption of the kinematic connection in the 16-valve engines of JSC AVTOVAZ are disturbances in the operation of the hydraulic pusher (hereinafter referred to as GT). Possible causes of such violations are given in order of likelihood of occurrence:
1. Gas content in oil is more than the maximum permissible 7%
a) Emptying of the lubrication system channels during long-term parking of the car due to oil leakage through the gaps in the plain bearings, leakage of the anti-drain valve in the cylinder head, leakage of the oil filter anti-drain valve. Before deciding to search for the causes, it is advisable to try to eliminate the knocking according to the “Recommendations for removing air from hydraulic pushers” given below.
b) Air leakage into the suction line of a leaking lubrication system through:
- oil receiver sealing ring;
- leaky welding seam of the oil receiver;
- leaking oil pump cover casting,
- leaky coupling of the oil pump housing with the cylinder block (for example, discrepancy between the design specification and the non-flatness of the oil pump housing).
c) Oil level does not meet the requirements of the engine design documentation:
- if the level is excessive due to mechanical foaming of the oil by the crankshaft counterweights,
- if the level is insufficient due to an unsettled top layer of oil entering the oil receiver.
d) The presence of water in the oil is above the maximum permissible norm (water turns into a gaseous state when heated).
e) Oil does not meet foaming requirements.
2. Failure of the high pressure cavity valve in the GT
For example, the ingress of chips, dirt particles, sealant, fabric lint, etc.
3. Difficulty moving the GT piston
For example, the ingress of chips, dirt particles, sealant, fabric lint, etc.
4. Unsatisfactory oil supply to the GT
a) Unacceptably low oil pressure in the lubrication system (for various reasons).
b) Mismatch in the coordinates of the outlet hole of the oil supply channel to the GT in the cylinder head.
5. Non-compliance of the GT with the requirements of the design documentation
Production and technological failures due to manufacturing defects (for example, breakage or absence of a GT valve spring, incorrect manufacturing of a valve chamfer, etc.).
It is recommended to search for the cause of the GT knock as a step-by-step analysis of the above factors (adjusted for labor intensity). When diagnosing, you should pay attention to the following factors and take them into account when choosing a plan to search for the causes of knocking:
- What preceded the occurrence of knocking (repair, replacement, oil, etc.).
- One, several or all GTs knock.
As a result of the research, it was revealed that the largest number of cases of the defect “knock of hydraulic tappets” is associated with a contaminated engine lubrication system.
When replacing clogged GTs, you must understand that installing new GTs on an engine with a contaminated lubrication system will again lead to dirt getting into the GTs and causing them to knock.
Recommendations for removing air from hydraulic pushers
A knock from one or more GTs may appear:
- when starting a new engine for the first time;
- when starting the engine after parking the car for a long time;
- when starting a “cold” engine;
- when starting the engine after repair work.
The reason for the knocking is the presence of air in the GT. Air is removed from the GT through a narrow gap (from 5 to 8 microns) in the plunger pair of the GT, so the time for removing air from the GT ranges from a few seconds to a maximum of 30 minutes.
How to identify a faulty hydraulic compensator
Before work, analyze the wear of all pushers, otherwise the case where someone changed the working compensators will repeat. The search for knocking hydraulic compensators of Priora 16 valves involves conducting several experiments or tests. It is basically calculated that Priora hydraulic pushers operate for 100 thousand kilometers.
These parts may rattle when starting a cold engine, and then continue to make noise even when the engine warms up. Knowing about this malfunction, follow these steps to identify faulty Priora hydraulic pushers:
The main causes of vibration in the steering wheel
Among the popular reasons that cause a slight knock in the front suspension on small bumps is a large gap between the steering rack and gear. This is the result of wear and tear. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is recommended to pull the steering rods up and down. At the same time, carefully observe the movement of the rod. If she doesn't move, then she's fine. If the rod dangles, then most likely the bushings are worn out.
If the rack turns, then the accurate diagnosis is a large gap in the engagement. But this problem can be easily eliminated by tightening this very rail. Also, when pulling the steering rod, you may notice broken or overly worn bushings securing the steering rods to the steering rack.
What to look for when choosing
When choosing a new consumable, you should pay attention to key characteristics. Knowing the basic parameters will allow you to find the optimal part that suits your specific needs.
Length
The ride height depends on the length. Typically, the manufacturer mentions the recommended clearance value in the technical documentation of the model. In rare cases, the spring lengths of the rear and front axles may differ. But it is advisable not to deviate from the technical parameters from the manufacturer. These parameters are determined by precise technical calculations.
You can deviate from the recommendations in two cases:
- “pumping” the car for the sake of visual customization
- modernization of the chassis for transporting heavy loads
Rigidity
The degree of rigidity determines the behavior of the car on the road and distributes the load across the remaining suspension elements. Soft springs are suitable for comfortable, smooth rides, while hard springs cope well with high loads. Therefore, the choice of rigidity largely depends on the purpose of using the machine.
Among owners of VAZ cars (including the Seven), there is a common problem with purchasing new consumables for their “swallow”. In a single set from one manufacturer, sometimes there are elements with different degrees of rigidity. Unfortunately, it is impossible to know about this in advance, and the body defect appears during use.
To resolve the issue, car owners resort to one of two methods. The first option involves purchasing another pair, usually foreign-made. The second method involves installing spacers.
A spacer is a rubber lining that is placed under the seating area of the “glass”. This method will significantly save the budget of the owner of the Lada.
The degree of spring stiffness depends on several indicators:
- The thickness of the rod section. A simple law applies here: the thicker the rod, the higher the level of rigidity. However, there are models with different ring diameters, and therefore the rule applies only to classic straight models.
- Total diameter of turns. Increasing the width of the rings leads to increased softness.
- Number of turns. The higher the number of revolutions of the rod, the lower the rigidity of the part.
Turning parameters
The main characteristics include two indicators: the number of turns and the thickness of the section. They determine the final degree of rigidity of the part.
It is not uncommon to find original springs with different ring diameters. Externally, they have an oval shape: wide in the middle with a gradual decrease towards the edges. The different diameters of the rings are also made of metal of different thicknesses. For massive turns, a thick rod is used, and the small rings on the sides are made of thin material. This design feature gives it versatility: it dampens small vibrations and large shocks equally well.
But the main “disease” of these models is hidden in the extreme turns. Due to the small thickness of the metal, the side parts of the part are very fragile, and therefore often break on uneven roads. This is the price of comfort: for a soft ride you have to pay for frequent repairs.
An alternative to factory springs is products from third-party manufacturers. A non-original product is made from a rod with a constant cross-section. This negatively affects ride comfort due to high rigidity. But non-original consumables are distinguished by their reliability and durability.
The springs of the shock-absorbing system are conventionally divided into 5 categories, which can be presented in table form:
The steering rack is a quiet separate element with sophisticated diagnostics
It often happens that after reassembling the entire chassis, it is time to check the steering rack. By moving the steering wheel left and right, you will hear small knocks if the rack has already begun to wear out. But this does not mean at all that it knocks during operation. It is difficult to give general recommendations here; there are different recommendations for owners of different cars:
- It’s worth visiting specialized forums and reading information about how and when the steering rack fails, how you can check and fix it;
- tightening the steering rack is a solution for a few days; soon it will start knocking again if a problem is identified with this particular element of the car;
- the knock of the rack is often a distinct feedback on the steering wheel, as well as on the body in the area where the control pedals are attached, so diagnosis will not be difficult;
- Sometimes steering tips or rods knock, which is more difficult to check, but you can perform a full diagnosis in a pit without any problems or inaccuracies.
The steering system likes to knock in domestic cars, as well as in cars older than 10 years. Changing the steering rack is very difficult due to the high cost of spare parts and the rather inconvenient location in many cars. Therefore, they prefer to perform this process on a service. Professionals will complete all tasks quite simply and quickly.
Errors and possible consequences
When trying to eliminate knocking noises at low costs, the wrong steps are often taken, leading to aggravation of the problem and waste of time and money:
- pistons or rings are replaced without boring the block;
- numerous advertised additives are tried;
- the gas distribution mechanism and other erroneously identified sources of knocking are moved;
- the engine continues to operate until it completely fails.
The consequence is always the same - an increase in the cost of subsequent repairs, up to complete disposal and replacement of the engine. Although in the early stages you can significantly reduce the cost of overhauls, if you do not start the problem and do not clog the engine with foreign substances of unknown origin, as well as wear and oil waste products.
Upper rack support
This can also cause knocking in the front suspension over small bumps. On car forums, the topic dedicated to this knock is very popular. The reasons are different for everyone. In attempts to combat this annoying sound, car owners go through the entire suspension, but often the knock remains.
One possible cause is the upper strut support. It consists of a rubber part as a damper and a bearing. If this rubber element has lost its elasticity, then this is the cause of this extraneous knock that all drivers struggle with. In order to find out for sure whether this is so, measure the gap between the limiter and the support. In most cars this is easy to do, but in some models this unit may be closed. If measurements show that the gap is more than 10 mm, then the support must be urgently replaced. However, this gap is not always uniform. When measuring, it is recommended to focus on the average figure. It is worth checking this support carefully: on many cars this sound appears only on one side.
Constant knocking
Diagnostics and repair
Why do hydraulic lifters knock on the Lada Priora and what to do in this case
First of all, it is worth determining which specific hydraulic pusher is not working correctly, and whether they are the cause of the unpleasant sound. This can be done using acoustic diagnostics or by turning off the engine cylinders alternately. For this, it is advisable to contact a car service or do it yourself. However, trying out repair methods yourself can be more expensive than calling an experienced engine specialist.
Then you need to check the oil pressure in the engine system for compliance with the standards. If it is lower than necessary, then the oil pump or filter may need to be replaced.
Often the cause of incorrect operation of the mechanism is engine oil, which was chosen incorrectly or is present in insufficient quantities. It is necessary to change it to another brand, change its viscosity or add special additives to it that eliminate the knocking of hydraulic pushers.
Sometimes you may notice that oil appears in one of the spark plug wells when the engine is running under heavy load. You need to pull it out with a syringe and clean the spark plugs. Then, to create the required pressure in the system, under the cover of the hydraulic compensators and heads, you need to apply sealant, which was “greedy” when assembling the car at the manufacturer.
Hydraulic pushers do not need any adjustment, since they themselves are able to adapt to the operating mode of the mechanisms.
Everything should be nearby, don’t start without preparation
Lada Priora can serve as an example to consider the replacement process. To avoid unpleasant surprises, any work must be planned and everything necessary must be prepared. In our case we will need:
- Gasket Maker - sealant (anaerobic);
- camshaft plugs and seals;
- 16 INA compensators.
Let's start by disconnecting the battery minus. Then we dismantle the air filter, throttle cables, wires that will interfere with manipulation, injector ignition coils and intake manifold.
Replacing hydraulic compensators on a Priora is complicated by the fact that the manifold mounting bolt is located under the generator.
To get to the hydraulic compensators:
- The generator belt is removed, the generator itself is freed from the mounting bolts and carefully moved to the radiator. Using a wrench with a rotary head, the manifold mounting bolt is unscrewed.
- The ramp with nozzles is dismantled and the air conditioning pipes are disconnected (if equipped).
- The collector is dismantled. First, we lift its left edge and then the entire part, and then we move it to the left.
- The valve cover is removed using a screwdriver inserted into the technological grooves.
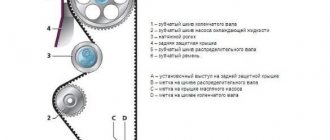
- Next, the timing belt is removed, the pulleys, camshaft bed and the shafts themselves are dismantled.
All compensators are open to view, among them it is necessary to identify the faulty ones. This is done by pushing. Defective ones will sag without much effort.
The hydraulic compensators are removed using a magnet. The entire set must be replaced, since they are used in similar conditions and wear should be approximately the same.
The above modifications have engines with a camshaft located on top. But there are also those in which it is located below. In this case, the rocker (rocker arm) acts on the heel of the automobile valve. Replacing hydraulic compensators on a Chevrolet Niva (where the timing belt is designed exactly like this) will be technologically different from what is described, and the “hydraulics” there are of a different type.
How to eliminate the knocking of hydraulic pushers on Lada Priora
Timely and high-quality maintenance of the engine oil system is the key to flawless operation of the hydraulic compensator mechanism. After all, the unit is designed for use throughout the entire resource of the power plant.
Use of recommended lubricant
When the hydraulic pushers just start knocking, the manufacturer recommends changing the lubricant to a proven option. Therefore, when the question arises of what kind of oil to pour in principle, it is worth analyzing reviews to determine the acceptability of a certain model of oil product for hydraulic compensators.
Of course, the best choice for Lada Priora will be the composition recommended by the manufacturer, specified in the instruction manual. However, not all current popular products are included in the list.
An analysis of opinions shows that, indeed, with the universal viscosity of 10W-40 or 5W-40 specified by the factory, not every oil is suitable. For example, Shell Helix Ultra 5W-40 causes knocking already at 15,000 km, while on Liqui Moly Optimal Synth 5W-40 the hydraulics are silent even at 80,000 km.
Reviews show that it is optimal to choose the following lubricants:
- Total Quartz 9000 Energy 5W-40.
- Mobil Ultra 10W-40.
- Wagner Windigo 10W-40.
Flushing
Many owners, in advanced cases, resort to general engine flushing. However, the effectiveness of such an event in the fight against knocking GCs is low. This is explained by poor oil pumpability in the area of the hydraulic pusher chambers.
Effective removal of carbon deposits inside the cylinders is their local washing. Worn assembly modules cannot be repaired.
Additives
Additive compounds help delay identifying the causes and cleaning the timing belt. There are several products available in the market. The most popular products are from Liqui Moly and XADO. The effectiveness of substances depends on the specific case. Fans of motor additives often equate this class of chemistry with a waste of money.
Sometimes the Priora electrician fails
Electrical equipment often suffers from breakdowns:
At the first stages of Lada Priora sales, problems arose with a new function - electric power steering. This was a trial step for AvtoVAZ, and it is logical that there were some disruptions. Jerks were observed when the steering wheel rotated, as well as jamming and stiff movement. The electrical diagram provided in the owner's manual helps to trace the steering drive circuit and identify faults. Sometimes the problem was solved by simply cleaning the contacts and strengthening the wiring. But often the breakdowns were much more serious, and only the service station workers could solve them.
Over time, the plant developed optimal assembly technology. Therefore, problems with the amplifier occur much less frequently. If the drive performance deteriorates, open the “Electrical equipment” section of the VAZ operating manual. We check the entire drive circuit for continuity and short circuit, and also clean the contacts.
On already “middle-aged” Priors, problems with the ignition coil can be traced. Also, over time, malfunctions in the operation of the windshield wiper drive occur, and headlight bulbs burn out. You can repair these parts yourself, following the instructions in the manual.
The standard battery on the Priora is not entirely successful. There are often complaints that the battery lasts for a year or a year and a half. Normal service life is up to three years. The battery on the Lada is a non-separable type, so you only have to replace it.
Basics of the design and operation of a hydraulic compensator
Configuration
The idea of automatic regulation of thermal clearances can be implemented in two versions: a conventional hydraulic pusher and a hydraulic support. The latter is used in gas distribution modules with rocker arms. On the Lada Priora in the sixteen-valve version, the intake and exhaust are equipped with individual camshafts. The optimal solution for this arrangement is the use of a hydraulic pusher.
The Priorov hydraulic compensator on the 126 engine consists of the following parts:
- A plunger pair, including a cylindrical cage and a piston with a ball valve.
- The outer housing is a pusher.
- System of grooves and holes for oil supply.
Principle of operation
The oil composition enters the internal cavity of the piston and, overcoming the resistance of the spring, pushes the ball away to fill the closed cylinder. When filling the liner, oil pushes the piston out and the hydraulic tappet rests against the cam. Next, the ball valve is locked and the assembly unit works like a regular pusher on motors with an adjustable valve mechanism.
Replacing hydraulic compensators on VAZ-2110, 2111, 2112
Hydraulic compensators (hydraulic pushers) of valves are used to automatically adjust thermal valve clearances. In essence, they are a kind of gaskets between the camshaft cams and valves, capable of changing their thickness.
Their use in the engine makes it possible not to systematically adjust thermal clearances.
The design of the hydraulic compensator consists of a cylinder-shaped body and a plunger, including a bushing, a ball valve and a spring.
The principle of its operation is as follows. When the cam turns its blunt side towards the pusher, a gap appears between them. At this time, the spring-loaded plunger rises up, closing it, and the oil enters the plunger cavity through a channel with a ball valve.
Turning the other side, the cam presses on the pusher, directing it down. The valve is closed by a ball. In this way, the plunger transmits the force of the cam directly to the valve.
Malfunctions of hydraulic compensators
The main indicator of failure of hydraulic compensators is their characteristic knocking sound. It is he who signals that it is time for a replacement. There may be several reasons for this:
- spent resource;
- premature wear of the plunger pair due to wear products entering the device;
- clogged oil supply channels.
If the hydraulic pushers have become unusable after working for the required period, it means that the car owner paid maximum attention to the engine.But the other two cases are a consequence of the use of low-quality, inappropriate oil, its untimely replacement, malfunctions of the oil pump or other elements of the lubrication system.
The hydraulic compensator will work ideally only when its internal space is completely filled with oil. Otherwise, dynamic loads will gradually destroy it and they begin to knock.
Cost of a set of hydraulic compensators and labor to replace them
It is advisable to buy and replace hydraulic compensators not one at a time, but as a set. The price of the kit for sixteen-valve VAZ 2112 engines is approximately 2,200 rubles; in order not to run into defects, check each hydraulic compensator.
The occurrence of knocking in the Lada Priora engine
If it seems to you that there are sounds when the engine is running that were not there before, immediately check whether everything is in order with the engine.
Most often, knocking in the engine is associated with serious malfunctions, to diagnose and eliminate which you will have to disassemble the engine in a service center or garage.
You can try to independently determine the cause of the knocking noises in order to decide whether to go to a car service center under your own power or in tow.
If you have the slightest doubt about the results of your self-diagnosis, remove the tow rope.
Major repairs to a damaged engine will cost more than a towing service.
Knocking noise from main bearings
- very dangerous; Stop the engine immediately; you will have to be towed to a car service center or garage.
Low pitch knocking.
It can be heard in the lower part of the crankcase, noticeably intensifies under load and with increasing rotation speed.
Often its appearance is accompanied by a drop in oil pressure (the emergency oil pressure drop lamp is on almost constantly).
Oil consumption after replacing valves
Increased oil consumption in Lada Priora, which appears after replacing valves, is associated with the reasons described above. Considering that the piston is misaligned, excess gaps appear, the oil scraper rings on one side experience excessive load and wear out, and on the other side they do not perform their function. Oil consumption is also affected by carbon deposits that form in the piston grooves and rings, depriving the latter of mobility. The consequences of incomplete combustion of gasoline are fully discussed and described here.
Do you have doubts about the choice of additive?
We know EVERYTHING about additives.
We will help you choose. We'll consult. Call us or request a call back. +7(499) 504-34-05- or - Call back
Engine knocking appears and disappears: reasons
It is well known that a car engine consists of a large number of moving elements that are under mechanical and thermal load. Also, each type of internal combustion engine has a limited resource, that is, parts gradually wear out. As a result of such wear, a knock appears in the engine over time, the engine begins to smoke, draft is affected, oil and fuel consumption increases, etc.
Also, various problems can occur in the engine, which lead to noise and knocking even on “fresh” units. In this case, we are not talking about wear, but about breakdown, which becomes the main cause of extraneous sounds. It also happens that the engine knocks only “cold” or “hot”.
Also, a knocking sound in the engine may appear and disappear in different modes, or the engine knocks regardless of the degree of warming up and the load on the internal combustion engine. Next, we will talk about what can lead to knocking, as well as how to determine what is knocking in the engine.
What type of repair will be required
If a knock on the beam is clearly detected, and mechanics can easily determine this, then a major overhaul is inevitable. The block will need to be bored to repair size and larger pistons installed. Where this is not provided, the motor is lined by pressing thin-walled liners under standard pistons and rings. Overhaul technologies that eliminate piston knock are clearly regulated and unambiguous.
Many people rely on the use of advertised restorative additives. Allegedly, a special material is deposited into the increasing gap and the surfaces are restored. In fact, it is possible to remove piston knock using an additive only in rare cases and for a short time. Most often this is due to a change in the viscosity of the oil after adding the substance from the “magic” jar. What can be done without additives, just fill in another oil.
Detailed diagnostics of hydraulic compensators on Lada Priora
Sometimes, to determine the causes of knocking hydraulic compensators on a 16-valve Lada Priora engine, the thermal state of the engine alone is not enough. A set of tests makes it possible to more accurately determine the factor that causes extraneous noise.
Diagnosing the condition
One of the common complaints is knocking noise both cold and hot. However, as the speed increases, the symptom disappears. One of the following options is relevant:
- Worn or damaged ball valve. You can't do without replacing the hydraulic compensator.
- Contamination of the internals of the hydraulic fluid with wear products due to the choice of incorrect lubricant or untimely replacement. Washing the internals and changing the oil composition to a standard one eliminates the problem.
If the clatter appears only on a hot power unit and disappears at high speeds, and on a cooled unit no extraneous sounds are observed in any mode, the plunger pair has worn out. The hydraulic compensator must be replaced as an assembly.
The knocking is observed only at high speeds in any thermal state, and at idle there is silence, a problem with the oil level or in the low emulsion suction system. It is not recommended to go beyond the extreme marks on the dipstick; driving with a damaged oil receiver is also not recommended. Restoring the acceptable level resolves the problem.
Causes of problems
The knocking noises are clearly distinguishable when the unit is cold and when the engine is already warm. The reasons for cold knocking are:
- It can be caused by too thick oil, which is not heated, and therefore is poorly pumped into the compensator cavity. It happens too slowly when cold and a knocking noise occurs.
- If the compensator valve or line is clogged with dirt. Such contamination usually occurs when the oil is of poor quality, or when a timely oil change is missed. Clogging may occur due to the appearance of chips and other wear products of motor elements.
- Jammed compensator plunger. This happens due to abrasive debris getting into the oil, or natural wear of the part.
- There is a lack of oil in the engine; there is simply not enough of it for normal operation.
Now let's look at the reasons for knocking on a hot Priora:
- A jammed hydraulic compensator pair due to contamination or wear. The resulting scuffs block the movement of the plunger. The gap is not compensated for and knocking noises appear. Such a knock will be heard both with a cold and hot engine.
- Low viscosity of heated oil. When the lubricant is too liquid, it manages to flow out faster than the pump pumps it into the compensator. The leaking oil does not allow the cylinder to expand and the gaps are not compensated. The reason is poor-quality oil, or a mistake by the owner himself with the viscosity of the lubricant.
- The oil foamed due to too much oil, water getting into it, or poor quality.
- Camshaft problems.
If you hear such sounds, immediately check the oil level and color. Adjust the high or low level to normal, this may solve the problem. By the color of the oil, you can understand the degree of contamination and remember that you missed changing it. Oil mixed with water becomes gray or rusty, this will be noticeable on the dipstick.
Features of replacing silent blocks on different models
VAZs 2108-21099 and 2113-2115 use strut mounting brackets. Therefore, it is easier to replace silent blocks. Unscrew the nuts securing the brackets and remove them.
Next, pressing and pressing is carried out using a vice using a piece of pipe and an extension.
In models 2110-2112, the spacer is attached to the cross beam. Therefore, replacing silent blocks is usually carried out without removing the beam from the car. And a puller is used to carry out all work.
READ ON THE TOPIC: Typical malfunctions of the VAZ 2110 and other cars in the series.
Definitely, when replacing silent blocks on any VAZ model, you will have to suffer a little. Here, in addition to dexterity and flexibility of thinking (in the technical aspect), you also need strong nerves.
Therefore, it is no wonder that many car owners entrust such work to car services. And not everyone has a garage with the necessary tools and equipment.
One of the important elements of car suspension is silent blocks. These hinges, consisting of two metal bushings and a polyurethane or rubber gasket between them, are installed on both the front and rear axles and serve to connect other elements. In addition to this, the elastic gasket of the silent block allows you to absorb all kinds of vibrations and shocks that occur while the car is moving.
Since quite a significant load is constantly placed on these hinges, the closest attention must be paid to the quality of these hinges and their technical condition
Life hack: hydraulic compensators for a Priora car with 16 valves, device, price
Compensators are needed for automatic valve adjustment; if they were not there, it would be necessary to adjust the valves every 10 thousand, as on 2109. On the Prior, hydraulic compensators knock under different circumstances - and this is not always a malfunction.
They have a special knock, so experienced car enthusiasts will recognize it almost immediately. A knock that comes from the engine of a Priora car is not a very good sign that should alert you. Each car needs to be approached differently. Therefore, when hydraulic compensators on a Priora knock, make proper preparations for repairs - you need to find out what is the reason for what is happening and how you can eliminate it by correcting the situation. In this article, we have collected for you the main signs: why these parts make noise, whether the car is cold or hot.
These parts have 16 valves on the Priora. (if taken as a complete set) they are not so little. The price starts from 4000 rubles and above. Replacing hydraulic compensators is labor-intensive and I don’t recommend getting into the engine yourself without experience. At a service station, such work for a Priora car will cost from 5,000 rubles and more.
Noises when hot
Hot tapping is more systematic. It is observed even when the engine is already warmed up. The reason for the occurrence of such periodic sounds is the increased gap between the hydraulic compensator sleeve and the plunger. It occurs for the following reasons:
- wear of the hydraulic pusher parts or “sticking” of the valve through which the lubricating fluid passes;
- the use of low-quality motor oil or the wrong choice of its viscosity;
- blockage of oil channels;
- oil filter contamination;
- high air content in the engine oil and, as a result, in the hydraulic pushers themselves;
- flaring of the hydraulic pusher seating area, which expands even more when heated.
In these cases, it may be necessary to replace the hydraulic compensator itself, the oil filter, the oil, or clean the oil channels.
Unlike tapping when cold, in this situation it is not recommended to ignore this malfunction.
Detailed diagnostics of hydraulic compensators on Lada Priora
Sometimes, to determine the causes of knocking hydraulic compensators on a 16-valve Lada Priora engine, the thermal state of the engine alone is not enough. A set of tests makes it possible to more accurately determine the factor that causes extraneous noise.
Diagnosing the condition
One of the common complaints is knocking noise both cold and hot. However, as the speed increases, the symptom disappears. One of the following options is relevant:
- Worn or damaged ball valve. You can't do without replacing the hydraulic compensator.
- Contamination of the internals of the hydraulic fluid with wear products due to the choice of incorrect lubricant or untimely replacement. Washing the internals and changing the oil composition to a standard one eliminates the problem.
If the clatter appears only on a hot power unit and disappears at high speeds, and on a cooled unit no extraneous sounds are observed in any mode, the plunger pair has worn out. The hydraulic compensator must be replaced as an assembly.
The knocking is observed only at high speeds in any thermal state, and at idle there is silence, a problem with the oil level or in the low emulsion suction system. It is not recommended to go beyond the extreme marks on the dipstick; driving with a damaged oil receiver is also not recommended. Restoring the acceptable level resolves the problem.
For your information
- New hydraulic compensators can also tap. This usually happens after capitalization and is observed within a short period of time after the first start-up. It is not a malfunction if it does not recur during subsequent starts.
- If the hydraulic modules knock after changing the oil, the reason is the quality of the lubricant or the filter.
- The knocking of hydraulic pushers during startup should not be considered a malfunction. Over a long period of parking, the oil is drained from the working chambers and at the beginning of work the containers are filled.
What are the consequences of ignoring the fact that the hydraulic compensators on the Lada Priora 16-valve engine are knocking or neglecting to investigate the causes of the noise? At a minimum, acoustic discomfort. At the most, the camshaft cams will wear out and will have to be replaced.
Assembly nuances
After replacing 16 hydraulic compensators, everything must be restored to its original form. The most important operations in order:
- We clean and degrease the camshafts and seats of the bed and valve cover, both on the parts and on the engine.
- We change the seals, plugs and put both shafts in place. The inlet has a special belt, which is not present on the outlet. This is its distinctive feature.
- Apply Gasket sealant to the mounting location of the camshaft bed and mount it (no gasket required).
- We treat the fit for the valve cover with sealant and mount it (no gasket required).
- We install injectors, condenser tubes, mount the manifold, generator, its belt, pulleys and timing belt.
- We restore the operation of the throttle valve, filter and connect all the wires.
Replacing hydraulic lifters sometimes results in the engine not starting due to lack of compression. As a rule, hydraulic valves are installed oil-filled and it may happen that due to the incompressibility of compensators, some valves will be open. To avoid this, it is necessary to tighten them with a clamp before installation.
Why are hydraulic compensators knocking?
The 21126 engine is a reliable design with a long service life, but even with such characteristics, difficulties may arise in the operation of the gas distribution mechanism. Over time, when driving a Priora, a characteristic knocking sound of the hydraulic compensators occurs when cold or hot. In this case, there is a drop in the power of the power unit and an increase in the noise level of the latter.
The main reason why knocking occurs is the characteristics and quality of the engine oil. The design of hydraulic compensators implies increased sensitivity to the characteristics of the lubricant and, accordingly, deviations from the manufacturer’s recommendations directly affect the service life of the hydraulic fluid.
Video on the topic:
Quite often the knocking problem is solved by changing the engine oil. In this case, it is necessary to flush the engine with a special liquid.
Almost always, after an oil change, a characteristic noise from the compensators follows, because the new oil has not had time to rise to the plunger pair of the hydraulic valve. This is observed for about the first five minutes of engine operation, after which the knocking stops.
If after changing the oil the situation has not changed and the knocking continues, then there is the option of flushing the power unit, which is done in two ways:
- Use of special flushing fluid. It is poured into the engine and temporarily used in it. However, its effect is questionable, since there are often fakes on the market, and they do not help.
- Dismantling and manual washing of each hydraulic compensator.
Knock of hydraulic compensators: why it occurs and how to get rid of it
There are a lot of problems that owners of used cars can face. One of the most common is the knocking of hydraulic compensators.
Why do hydraulic compensators knock and how can you understand that they are the ones knocking? Is this malfunction related to the quality of the oil and how can I fix it? Let's figure it out.
What is a hydraulic compensator and how does it work?
As the temperature rises, the metal parts of the engine expand. The designers took this feature into account and created special thermal gaps for the gas distribution mechanism. Engine elements gradually wear out, so it is necessary to regulate the size of these gaps. Older car models (30 years and older) used adjusting bolts or a set of washers. The adjustment mechanism required intervention every 10–15 thousand kilometers; servicing the car was not cheap. This problem was solved by hydraulic compensators.
Hydraulic compensator (hereinafter referred to as HK)
— a device for automatically adjusting the thermal gap in the valve drive. This is a miniature hydraulic cylinder that changes length when engine oil is pumped inside.
The volume of oil compensates for the gap between the valve stem and the camshaft cam. Oil enters the cavity of the hydraulic compensator through a valve with a very small hole, and comes out through the natural clearances of the valve pair. The operation of the hydraulic valve depends on the supply of oil and on the condition of the plunger pair, the absence of wear or jamming.
Types of knocking hydraulic compensators
Hydraulic compensators may knock constantly or periodically. If knocking occurs when the engine is cold and disappears some time after starting, there is no need to worry.
.
If the extraneous sound does not go away as it warms up, this is already a signal for action. A knocking noise is heard when the hood is open, and the sound comes from under the valve cover. The tonality of the sound is specific - it resembles the impact of metal parts against each other. Some compare it to the chirping of a grasshopper.
The knocking frequency of faulty hydraulic compensators is twice the engine speed. As the speed increases or decreases, the sound will become more frequent or less frequent. When the gas is released, sounds are heard like unadjusted valves.
The reasons for the knocking of the main engine “on hot” can be different:
- malfunctions in the lubrication system of the power unit (low oil pressure);
- low-quality motor oil (contamination of the engine oil with wear/carbon deposits);
- mechanical wear of the main valve (wear of main valve parts: plunger, spring, check valve).
If the hydraulic lifters are knocking “on hot”, the engine needs diagnostics.
What to do when hydraulic compensators knock when “cold”
As we have already said, knocking of the engine “when cold”, as a rule, is NOT a sign of a malfunction. With mileage, HAs have a certain depletion and degree of contamination. Unheated engine oil is thick and does not have the required viscosity. After the engine warms up, the clearances return to normal, the viscosity decreases and the knocking disappears.
If there was no knocking of the engine “on cold” before, and the engine oil was changed recently, you should check its level and make sure that the lubricant was selected correctly.
Complete failure or jamming of the main valve when knocking only “on cold” can be excluded.
What to do when hydraulic compensators knock when “hot”
A broken hydraulic compensator knocks constantly. To fix the problem, you first need to check the oil level in the crankcase
. Its circulation through the oil channels depends on this.
Make sure there is sufficient oil pressure - even if the oil light is not on.
Each engine has its own operating oil pressure, it depends on the design (the specific indicator must be clarified in the documentation). It is believed that at idle the pressure should be 1.6-2.0 bar, at high speed - up to 5-7 bar.
If there is no such pressure, check the oil pump
.
Often the problem is caused by oil. Even if you change it according to the regulations, it could become unusable ahead of schedule. This happens under difficult operating conditions of the machine or when the oil is fake.
You can learn how to choose motor oil from our article. And to select a product for a specific make and model of car, use the online selector.
If you find plaque and sludge on the surface of the pump parts, flush the oil system - most likely the oil channels are clogged. LUKOIL flushing oil is useful for the procedure. This is a mineral oil with detergent additives that protect the engine from corrosion and increased wear. It is suitable for flushing all types of engines. If the knocking sound of the hydraulic compensators does not disappear after changing the oil and flushing the engine, the cause of the problem may be worn parts, a malfunction of the pressure reducing valve, or wear on the working surfaces of the parts. If after washing the hydraulic compensators and oil channels the knocking noise remains, diagnostics of the hydraulic valve itself is needed.