The appearance of the 21083 engine is due to the need to increase the power of the serial 2108 internal combustion engine of the AvtoVAZ manufacturer. To achieve this, the designers increased the size of the cylinder, but “forgot” to design the intake manifold for the changed conditions.
ICE 21083 with blue block
As a result, cracks open in the exhaust manifold, the bosses become jammed, and the plane of the head is pressed through. Acceleration to 100 km/h occurs in 14 seconds, but the revs are too high for the resulting torque.
Performance characteristics of motor 21083
In theory, the technical characteristics of the ICE 2108 should have satisfied the travel modes of the three-door hatchback VAZ 2108. In practice, tuning was required to increase power, and a little later, a reduction in volume to 1.1 liters for supplies of the Eight for export to countries with special performance requirements ICE.
Motor 21081
Moreover, the model 2108 was designed by the Germans from the Porsche concern for a 5-speed manual transmission; the budget of the manufacturer AvtoVAZ was not enough for a larger budget, so the engine was boosted by domestic designers, the result was the 21083 engine with a volume of 1.5 liters, and then the 21081 with a volume of 1.1 liters.
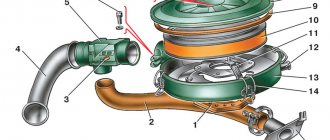
Intake manifold 2108
For the latter option, a special input manifold was created, just like for an export-spec engine. The intake manifold from 2108 was mounted on modification 21083, which was initially incorrect, since the needs for the quality of the fuel mixture for the formed engine were not met. The manual included the same requirements regarding what kind of oil to pour, and the regulations for replacing coolants remained the same.
At the output, the engine characteristics were as follows:
| Manufacturer | AvtoVAZ |
| Engine brand | 21083 |
| Years of production | 1992 – 2003 |
| Volume | 1499.8 cm3 (1.5 l) |
| Power | 50.3 kW (72 hp) |
| Torque | 106 Nm (3400 rpm) |
| Weight | 127 kg |
| Compression ratio | 9,9 |
| Nutrition | carburetor |
| Motor type | in-line |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Location of the first cylinder | TVE |
| Number of valves on each cylinder | 2 |
| Cylinder head material | aluminum alloy |
| Intake manifold | from 2108 or 21081 |
| An exhaust manifold | scheme 4/2/1 (spider) |
| Camshaft | upper |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Cylinder diameter | class A – 82 – 82.01 mm class B – 82.01 – 82.02 mm class C – 82.02 – 82.03 mm class D – 82.03 – 82.04 mm class E – 82.04 – 82.05 mm |
| Pistons | 82 mm |
| Rings | two symmetrical lugs, chrome plated, compression 1.5 mm and 2 mm thick, oil scraper 3.95 mm |
| Piston diameter | class A –81.94 – 81.95 mm class B – 81.95 – 81.96 mm class C – 85.96 – 81.97 mm class D – 81.97 – 81.98 mm class E – 81.98 – 81.99 mm |
| Crankshaft | high-strength cast iron, high-frequency hardening of bearing journals and connecting rods, long crank radius |
| Number of main bearings | 5 |
| Piston stroke | 71 mm |
| Fuel | AI-91 |
| Motor weight | 127, kg |
| Environmental standards | Euro 2 |
| Fuel consumption | highway – 7 l/100 km combined cycle 8.6 l/100 km city – 10 l/100 km |
| Oil consumption | 0.7 l/1000 km |
| Engine oil for 21083 | 5W-30 and 10W-30 |
| Engine oil volume | 3.5 l |
| Operating temperature | 80° |
| Motor life | declared 125,000 km, real 200,000 km |
| Adjustment of valves | washers |
| Cooling system | forced, antifreeze/antifreeze |
| Coolant quantity | 7.3 l |
| water pump | plastic impeller |
| Candles for 21083 | A17DVRM or FE65CPR |
| Gap between spark plug electrodes | 0.5 – 0.6 mm |
| Timing belt | 111 teeth, belt width 19 mm |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Air filter | Nitto, Knecht, Fram, WIX, Hengst |
| Oil filter | catalog number 90915-10001 replacement 90915-10003, with check valve |
| Flywheel | ring width 20.9 mm, surface for clutch disc 196 mm in diameter |
| Flywheel mounting bolts | M10x1.25 mm, length 26 mm |
| Valve stem seals | Corteco, Reserve, Elring, SM |
| Compression | cylinder pressure from 11 bar, pressure difference in individual cylinders within 1 bar |
| Oil temperature | 80°С |
| Tightening force of threaded connections | spark plug – 31 – 39 Nm flywheel – 62 – 87 Nm clutch bolt – 55 Nm bearing cap – 70 – 84 Nm (main) and 44 – 54 Nm (connecting rod) cylinder head – 4 stages 20 Nm, 71 Nm + 90° + 90° |
From the given characteristics it is clear which engine oil is recommended by the manufacturer. Despite the design flaws, the 21083 engine has low consumption of gasoline and other operating fluids.
Description
The first-born of the eighth family of internal combustion engines, the VAZ-2108, was not a bad engine, but it lacked power. The designers were given the task of creating a new power unit, but with one condition - it was necessary to maintain the overall dimensions of the base VAZ-2108. And it turned out to be doable.
In 1987, a new engine was released - VAZ-21083. In fact, it was a modernized VAZ-2108.
The main difference from the base model was the increase in the diameter of the cylinders to 82 mm (versus 76 mm). This made it possible to increase power to 73 hp. With.
Under the hood – VAZ-21083
Installed on VAZ cars:
- 2108 (1987-2003);
- 2109 (1987-2004);
- 21099 (1990-2004).
Engine modifications can be found on other VAZ models (21083, 21093, 2113, 2114, 2115) produced before 2013.
The cylinder block is cast iron, not lined. The internal surfaces of the cylinders are honed. The peculiarity is the absence of coolant flow between the cylinders. In addition, the manufacturer decided to paint the block blue.
The crankshaft is made of high-strength cast iron. The main and connecting rod journals undergo special high-frequency heat treatment. Mounted on five supports.
The pistons are aluminum, with three rings, two of which are compression, one is oil scraper. The upper rings are chrome plated. A steel plate is cast into the piston bottom to reduce thermal deformation.
Special recesses in the upper part prevent contact with the valves in the event of a broken timing belt.
Pistons VAZ-21083
The cylinder head is cast from aluminum alloy. A camshaft with a valve mechanism is fixed in the upper part. The head differs from the base one in having enlarged channels for supplying the working mixture to the cylinders. In addition, the intake valves have a larger diameter.
The fuel supply system is a carburetor; later versions were equipped with an injector.
The intake manifold was taken from the base model, which was a miscalculation of the designers. Because of this oversight, the quality of the fuel mixture for the souped-up VAZ-21083 was not satisfactory.
The ignition system is contactless.
Otherwise, the engine was identical to the base model.
VAZ specialists note the sensitivity of the engine to the slightest deviations from the requirements for the quality of materials and processing of parts. This note is important to consider when repairing the unit.
To put it simply, using analogues of components and parts will lead to a negative result.
Design Features
The main feature of the internal combustion engine, by analogy with sample 2108, was the use of a belt drive on the timing pulley. In addition, the engine diagram has nuances:
- the camshaft remained inside the cylinder head, that is, on top of the block;
- non-contact ignition from a distributor, switch and coil was used;
- to reduce costs, parts from 2108 are used: crankshaft, flywheel and connecting rods, intake manifold and block;
- the pistons were created in collaboration with Kolbenschmitd and Porsche; instead of tin, a microprofile coating was used to retain lubricant on the surface;
- rings are chrome plated to increase service life;
- cylinder head with increased valve size of 37 mm.
ICE design
The modernization also affected the cooling system pump, but the service life of this unit increased slightly. As a result, the increased volumes of the combustion chambers added only 6 liters. With. power, but the gearbox ratios were not selected and the design of the intake manifold was improved. To make the internal combustion engine recognizable, AvtoVAZ management decided to paint blocks 21083 blue.
Tuning
There are several common options for increasing the power of the VAZ 21083 engine:
- For example, it is possible to replace the camshaft with a sports modification. At the same time, lightweight gears are installed, which allows the engine power to be increased to 80 horsepower. Similar tuning of the VAZ engine when modifying the intake manifold, cylinder head and valves allows you to get an additional 10 horsepower.
- An alternative option for tuning a VAZ engine is to install a compressor. In this case, it is recommended to replace the carburetor power system with an injector and use a small-capacity compressor. The power of such a power unit can be 100-120 horsepower. Just remember that such tuning and engine assembly should be performed exclusively by an experienced specialist, which guarantees the performance of the car’s engine.
Disadvantages and advantages
The main advantage is that the 21083 engine does not bend the valve when the timing belt breaks. In addition, the engine incorporates design solutions that provide a number of advantages:
- no oil starvation at startup - a special coating is used to preserve oil on the surface of the pistons;
- free rotation of the pin in the connecting rod bosses - overhauls are performed less frequently;
- massive upper connecting rod head – the life of the crankshaft increases, major repairs are cheaper;
- modification of the pump - the cooling system lasts longer.
Piston group kit
Despite the fact that the cylinders have a maximum diameter, it is possible to tune the internal combustion engine with your own hands in other ways. The disadvantages are:
- it is impossible to install pulleys of additional attachments on the internal combustion engine shaft;
- torque at high speeds is low;
- high thermal loads are dangerous due to the pressing of the head plane, crushing of the bosses and cracks in the exhaust manifold.
The second modification of the 21081 engine was more fortunate, since its volume, on the contrary, was reduced, and the development was carried out more carefully for export abroad.
Reliability, weaknesses, maintainability
Reliability
The VAZ-21083 can be called a reliable engine for several reasons. Firstly, by exceeding the mileage resource. Car enthusiasts write about this in their reviews of the engine.
For example, Maxim from Moscow: “... the mileage is 150 thousand, the engine is in good condition and the car is generally reliable...”. Slava from Ulan-Ude echoes his tone: “... the mileage is 170 thousand km, the engine does not cause problems...”.
Many people note that there are no problems starting the engine. Lesha’s statement about this from Novosibirsk is typical: “... I drove both +40 and -45 every day. I didn’t get into the engine at all, I only changed the oil and consumables...”
Secondly, the reliability of the engine is characterized by the possibility of boosting it, i.e., the safety margin. In the unit under consideration, the power can be increased to 180 hp. With. But in this case, you need to take into account a significant reduction in mileage.
The reliability of some engine components has been increased. For example, the design of the water pump has been improved. Its uptime has increased. Short-term oil starvation when starting the engine has been eliminated. These and other innovative solutions have had a positive impact on the reliability of internal combustion engines.
Weak spots
Despite many advantages, the VAZ-21083 also had weaknesses. Operation of the engine revealed shortcomings of the manufacturer when designing the engine.
Oil filter. Oil leaks constantly occur through its seals. Untimely detection and elimination of a malfunction can cause oil starvation, and, as a result, very serious problems.
The weakest link in the fuel supply system was the capricious Solex carburetor. The reasons for failure to operate are different, but are mainly associated with low-quality gasoline, violation of adjustments and clogged jets. Its malfunctions disabled the entire power system. Later, Solex was replaced by the more reliable Ozone.
Increased demands on fuel quality. The use of low-octane gasoline grades led to unit breakdowns.
Noisy engine operation with misregulated valves. It should be noted that this is a problem for all VAZ internal combustion engines that do not have hydraulic compensators.
Tendency to overheat. Caused by a malfunction in the thermostat or cooling fan. Additionally, the occurrence of this phenomenon is facilitated by the high thermal load of the CPG due to the lack of coolant flow between the cylinders (a design flaw).
Less common, but such malfunctions as tripping, unstable and floating engine speeds occur. The reason must be sought in electrical equipment (faulty spark plugs, high-voltage wires, etc.) and carburetor malfunctions.
The negative impact of weak points can be weakened by timely, and most importantly, high-quality engine maintenance.
Maintainability
The engine is repairable. It must be taken into account that when restoring, only original components and parts should be used. Replacing them with analogues leads to rapid breakdown of the unit.
Finding and purchasing spare parts for repairs does not cause problems. As Evgeniy, a car enthusiast from Novoangarsk, writes: “... but one thing is good that there is a ton of spare parts on the shelves and as my uncle, the owner of a foreign car, says: “Compared to my pieces of hardware, they give everything away almost for nothing” ....” Konstantin from Moscow confirms: “... repairs and restoration after accidents are very cheap, which eliminates headaches...”.
Depending on the complexity of the repair, it is worth considering the option of purchasing a contract engine. You can find such an internal combustion engine on the Internet at prices ranging from 5 to 45 thousand rubles. The cost depends on the year of manufacture and engine configuration.
The VAZ-21083 is reliable, economical and durable, subject to careful operation and timely, high-quality maintenance in full.
Cars of the VAZ line using the 21083 engine
The 21083 engine was used to equip the following models of the VAZ manufacturer:
- 2108 – three-door hatchback;
- 21083 – three-door hatchback;
- 2109 – five-door hatchback;
- 21093 – five-door hatchback;
- 21099 – sedan;
- 2113 – three-door hatchback;
- 2114 – five-door hatchback;
- 2115 – sedan.
VAZ 2115
That is, the entire line of front-wheel drive cars produced before 2013 was equipped with these internal combustion engines.
Maintenance
The classic internal combustion engine design in combination with a transverse engine arrangement under the hood of front-wheel drive cars is subject to the following maintenance regulations:
| Maintenance object | Time or mileage (whichever comes first) |
| Timing belt | replacement after 100 thousand km |
| Battery | 12 months/20 thousand km |
| Valve clearance | 24 months/20 thousand km |
| Crankcase ventilation | 24 months /20 thousand km |
| Belts that drive attachments | 24 months /20 thousand km |
| Fuel line and tank cap | 24 months /40 thousand km |
| Motor oil | 12 months/10 thousand km |
| Oil filter | 12 months/10 thousand km |
| Air filter | 21 – 24 months /40 thousand km |
| Fuel filter | 48 months/40 thousand km |
| Heating/Cooling Fittings and Hoses | 24 months /40 thousand km |
| Coolant | 24 months /40 thousand km |
| Oxygen sensor | 100 thousand km |
| Spark plug | 12 – 24 months /20 thousand km |
| Exhaust manifold | 12 months |
The accompanying instructions contain a description of the parameters; the manufacturer strongly recommends following the maintenance procedure for engines 21083.
Malfunctions: causes, elimination
The main problems of this type of internal combustion engine are:
| Malfunction | What caused | Remedy |
| Gasoline consumption has increased | clogging of the fuel system and attachments | flushing fuel lines, pump, carburetor |
| Engine won't start | ignition system failure, carburetor blockage or misadjustment | diagnostics of electronics, adjustment of quality and quantity screws |
| The motor "troits" | gasket breakdown, compression change | replacing consumables, restoring compression |
Specifically, the modification of the 21083 engine is characterized by burnt-out valves that cannot cope with the temperature conditions of the internal combustion engine. This design flaw is “treated” by tuning existing units.
Adjustment of valves