Recently, an increasing number of car enthusiasts are interested in such a subject as upgrading their car - and this is not surprising, because everyone wants to customize the car “for themselves”, to make it unique. One of the options for such changes is chip tuning for the VAZ 2114. It allows you not only to give individual features to the car, but also to make its driving characteristics much better than the factory ones. We’ll talk about what it is in today’s article.
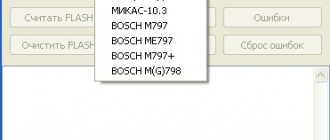
Firmware for VAZ 2114
What does chip tuning give?
Chip tuning is a change in the basic settings of the electronic control unit to more modern (and therefore more advanced) ones. A similar firmware of a VAZ 2114 is performed without any physical intervention in the ECU, only by programming methods.
Thanks to its implementation, you can get:
- increase in engine power up to 25%;
- increase in torque up to 15%;
- reduction in fuel consumption up to 12%;
- reduction of exhaust toxicity;
- facilitating cold engine starting.
Chip tuning VAZ 2114
As you can see from this, flashing the brains of a VAZ 2114 is an extremely desirable and even economically beneficial procedure for the car owner.
Features of engine diagnostics
If you cannot perform a complete engine diagnostic at a service center, do it yourself. To work, you will need certain tools that can be purchased at any store. The main one among them is a special measuring device with which you will perform testing, and a needle from a medical syringe.
Before starting work, you need to determine which electronic control unit controller is installed on your car’s engine. To do this, pay attention to its markings and, using the Internet, determine the type and find the operating instructions. Remember that each controller has individual operating parameters. If there is an on-board computer in the VAZ 2114, they can be easily tracked and the problem can be immediately identified.
To diagnose how the fuel injection system functions, you will need to carefully study the principle of its operation. If the throttle valve is in the closed position, air will bypass, through the regulator responsible for idling the car. He, in turn, receives data from a sensor that monitors the mass air flow in the system and regulates its supply when the car is idling.
Next, the fuel is mixed with air and passes into the combustion chamber. Fuel injection is carried out through the operation of electric injectors, and the direct activation time is monitored by the vehicle control unit, which also operates using electricity.
The CO level is regulated by a sensor responsible for the functioning of oxygen in the system. It is located directly at the place where exhaust gases, leaving the VAZ 2114, enter the air. The pressure must be monitored in order to increase the fuel pressure under the applied load, reducing the vacuum created for this.
Return to contents
Preparing for chip tuning
Before you start an “electronic upgrade” of your car, you should perform several important operations, which are the key to ensuring that the tuning will only be beneficial and will not cause any harm to the car, namely:
- check the condition of all, and especially heavily loaded components and assemblies. After all, the main goal of reconfiguring the ECU is to increase power and torque, as a result of which heavily worn parts can become damaged and even fail;
- clarify whether reprogramming is possible in your case. The fact is that not all programs allow you to establish such “feedback” and make changes, which means that trying to change them is useless;
- find out the value of the inherent potential. Thus, when programming the ECU at the factory, manufacturers in the vast majority of cases leave a “reserve” of power, as a result of which the engine does not operate at full strength and has hidden capabilities, which reprogramming is intended to extract. In the same case, if the engine is already working at its maximum from the factory, no amount of chip tuning will help.
ECU VAZ 2114
In addition to the points listed above, you should also take into account the fact that before starting the upgrade, it is highly advisable to replace all filters in the car (and especially the air filter). After all, only performing programming on a completely “updated” machine will give the maximum result.
It is also worth remembering that after chip tuning the car will need higher octane fuel. So, if before the upgrade the engine was running on 92, then after it is completed you will need 95.
Serial firmware for VAZ cars (January-5.1 / 5.1.1 / 5.1.2 / 5.1.3 / 7.2)
Serial version for Niva 8V 1.7L
1 Serial version for new hardware implementation. 8V 1.5L
1 Serial version for new hardware implementation. 8V 1.6L
1 Serial version for new hardware implementation. 8V 1.6L ECU "Avtel".
1 Serial version for new hardware implementation. 16V
1 Serial version for new hardware implementation. Car "Kalina"
1 Serial version for new hardware implementation
Firmware from a block with the identifier I203EL36 January-7.2 of an old hardware implementation purchased on the market. In fact, this ECU is January-7.2+
1 Serial version
Attention! The firmware has a factory defect, which manifests itself in a noticeable “failure” when shifting gears.
3 Serial version for engine 21114 (1.6)
The firmware has fixed a bug that led to over-enrichment when releasing gas. Recorder functions are supported.
3 Serial version for engine 21124 (1.6)
The firmware has fixed a bug that led to over-enrichment when releasing gas. Recorder functions are supported.
3 Serial version for Kalina 1.6 l. The difference from I201CO57 is separate on/off thresholds. fans
1 Serial version
Attention! The firmware has a factory defect, which manifests itself in a noticeable “failure” when shifting gears.
3 Serial version for engine 21114 (1.6)
Firmware for engine 21128 (1.8L)
Firmware based on I204DO57 software for the “long” Niva. Without DF.
Note: Firmwares starting with “I” are completely similar and compatible with firmware starting with the letter “A”. This letter code means “Itelma”, “A” - “Avtel”. OPP - Pilot industrial production.
Attention! Some firmware for January-7.2 are presented in two forms, in the compressed “Combiloader” format and regular bin files (with the prefix “c”). Some archives contain firmware merged from factory cars, but, nevertheless, with different CS, different from the official information.
Current production version, phased injection, wideband knock sensor.
Attention! The firmware has a serious manufacturing defect, which manifests itself in an excessively late shutdown when opening the throttle.
| Software ID | ECU | VAZ number | Engine | Toxicity standards | Note |
| January-7.2+ new hardware implementation | |||||
| I122KG02 | January-7.2+ | 21230-1411020-92 | 21230 | Euro 2 | |
| I203EM36 | January-7.2+ | 2111-1411020-82 | 2111 | Euro 2 | |
| I204DP57 | January-7.2+ | 21114-1411020-32 | 21124 | Euro 2 | |
| A204DP57 | January-7.2+ | 21114-1411020-31 | 21124 | Euro 2 | |
| I205DP57 | January-7.2+ | 21124-1411020-32 | 21114 | Euro 2 | |
| I201CP57 | January-7.2+ | 11183-1411020-22 | 11183 | Euro 2 | |
| I226FN11 | January-7.2+ | 21067-1411020-12 | 21067 | Euro 2 | |
| I214MF36 | January-7.2+ | 2111-1411020-82 | 2111 | Euro 2 | |
| January-7.2 produced by Itelma | |||||
| I203EK33 | January-7.2 | 2111-1411020-82 | 2111 | Euro 2 | Pre-production commercial version, read from the vehicle. 48 pieces were produced. |
| I203EK34 | January-7.2 | 2111-1411020-82 | 2111 | Euro 2 | |
| I203EL35 | January-7.2 | 2111-1411020-82 | 2111 | Euro 2 | 2 Serial version |
| I203EL36 | January-7.2 | 2111-1411020-82 | 2111 | Euro 2 | 3 Serial version |
| I204DM52 | January-7.2 | 21114-1411020-32 | 21114 | Euro 2 | 1 Serial version for engine 21114 (1.6). Absent from official VAZ information |
| I204DM53 | January-7.2 | 21114-1411020-32 | 21114 | Euro 2 | 2 Serial version for engine 21114 (1.6) |
| I204DO57 | January-7.2 | 21114-1411020-32 | 21124 | Euro 2 | |
| I205DM52 | January-7.2 | 21124-1411020-32 | 21124 | Euro 2 | 1 Production version for engine 21124 (1.6) |
| I205DM53 | January-7.2 | 21124-1411020-32 | 21124 | Euro 2 | 2 Serial version for engine 21124 (1.6) |
| I205DO54 | January-7.2 | 21124-1411020-32 | 21124 | Euro 2 | |
| I226FM10 | January-7.2 | 21067-1411020-10 | 21067 | Euro 2 | 1 Serial version for the classic 1.6 l. |
| I201CO56 | January-7.2 | 11183-1411020-22 | 11183 | Euro 2 | 1 Serial version for Kalina 1.6 l. |
| I201CO57 | January-7.2 | 11183-1411020-22 | 11183 | Euro 2 | 2 Serial version for Kalina 1.6 l. |
| I201CO58 | January-7.2 | 11183-1411020-22 | 11183 | Euro 2 | |
| January-7.2 produced by Avtel | |||||
| A203EK34 | January-7.2 | 2111-1411020-81 | 2111 | Euro 2 | |
| A203EL35 | January-7.2 | 2111-1411020-81 | 2111 | Euro 2 | 2 Serial version |
| A203EL36 | January-7.2 | 2111-1411020-81 | 2111 | Euro 2 | 3 Serial version |
| A204DM53 | January-7.2 | 21114-1411020-31 | 21114 | Euro 2 | 1 Production version for engine 21114 (1.6) |
| A204DO57 | January-7.2 | 21114-1411020-31 | 21114 | Euro 2 | |
| A205DM53 | January-7.2 | 21124-1411020-31 | 21124 | Euro 2 | 1 Production version for engine 21124 (1.6) |
| A226FM10 | January-7.2 | 21067-1411020-11 | 21067 | Euro 2 | 1 Serial version for the classic 1.6 l. |
| A201CO56 | January-7.2 | 11183-1411020-22 | 11183 | Euro 2 | 1 Serial version for Kalina 1.6 l. |
| A201CO57 | January-7.2 | 11183-1411020-22 | 11183 | Euro 2 | 2 Serial version for Kalina 1.6 l. |
| A205DO57 | January-7.2 | 21124-1411020-31 | 21124 | Euro 2 | 2 Serial version for engine 21124 (1.6) |
| OPP firmware for January-7.2 | |||||
| ASUPER11 | January-7.2 | — | — | Euro 2 | |
| I233LO10 | January-7.2 | 2130-1411020-13 | 2130 | Euro 2 | |
| January-5.1/5.1.1/5.1.2 | |||||
| J5V13F02 28-10-1999 | January-5.1.1 | 2111-1411020-71 | 2111 | Russia-83 | Old non-serial version, simultaneous injection, wide-band knock sensor. |
| J5V13H02 02/16/2000 | January-5.1.1 | 2111-1411020-71 | 2111 | Russia-83 | First production version, simultaneous injection, wide-band knock sensor. |
| J5V13I02 03/27/2000 KS #B4CE | January-5.1.1 | 2111-1411020-71 | 2111 | Russia-83 | Current production version, simultaneous injection, wideband knock sensor. |
| J5V13L05 06-01-2004 KS# | January-5.1.1 | 2111-1411020-71 | 2111 | Russia-83 | Latest production version, simultaneous injection, wideband knock sensor. |
| J5V03F21 11/27/1999 KS #63D6 | January-5.1 | 2111-1411020-61 | 2111 | Euro 2 | Rare production version. PP injection, broadband DD |
| J5V03G21 11/27/1999 KS #647A | January-5.1 | 2111-1411020-61 | 2111 | Euro 2 | First production version, pair-parallel injection, wide-band knock sensor. |
| J5V03H21 02/16/2000 KS #EF63 | January-5.1 | 2111-1411020-61 | 2111 | Euro 2 | Second production version, pair-parallel injection, wide-band knock sensor. |
| J5V03I21 05/25/2000 | January-5.1 | 2111-1411020-61 | 2111 | Euro 2 | Third production version, pair-parallel injection, wide-band knock sensor. |
| J5V03J21 02-03-2001 KS #552B | January-5.1 | 2111-1411020-61 | 2111 | Euro 2 | Fourth production version, pair-parallel injection, wide-band knock sensor. Driver diagnostics of MI. |
| J5V03K22 08/22/2002 KS #A84C | January-5.1 | 2111-1411020-61 | 2111 | Euro 2 | Current production version, PP injection, wide-band detonation sensor, MI diagnostics (driver-based diagnostic), APS-4 IMM support, immobilization function bypass mode, misfire diagnostics, additional. starter relay. |
| J5V03K22a ROM control disabled | |||||
| J5V03L25 08/25/2003 KS #906B | January-5.1 | 2111-1411020-61 | 2111 | Euro 2 | Latest production version |
| J5V07G26 02/18/2000 KS #5A03 | January-5.1.2 | 2112-1411020-71 | 2112 | Russia-83 | First production version, phased injection, wideband knock sensor. |
| J5V07I27 07/18/2001 KS #15B6 | January-5.1.2 | 2112-1411020-71 | 2112 | Russia-83 | |
| J5V07I27a ROM control disabled | |||||
| J5V07J28 01/11/2002 KS #CA3F | January-5.1.2 | 2112-1411020-71 | 2112 | Russia-83 | Latest production version, phased injection, wideband knock sensor. |
| J5V07J28a 04/28/2002 ROM control disabled | |||||
| J5V05F16 02/18/2000 | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | First production version, phased injection, wideband knock sensor. |
| J5V05F16 02/18/2000 | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | Factory version with air conditioning |
| J5V05H16 02/21/2000 KS #3C40 | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | Second production version, phased injection, wide-band knock sensor. |
| J5V05I16 05/26/2000 | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | Exotic small-scale version, phased injection, wide-band knock sensor. |
| J5V05J16 02-03-2001 KS #8B3C | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | Third production version, phased injection, wideband knock sensor. |
| J5V05K17 07-05-2002 KS #D14D | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | Fourth serial version, MI diagnostics (driver diagnostic), APS-4 IMM support, immobilization function bypass mode, misfire diagnostics, additional. starter relay. |
| J5V05K17a ROM control disabled | |||||
| J5V05L19 KS #7602 | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | Fifth serial version, MI diagnostics (driver diagnostic), APS-4 IMM support, immobilization function bypass mode, misfire diagnostics, additional. starter relay. |
| J5V05L19a ROM control disabled | |||||
| J5V05M30 05-11-2003 KS #A71C | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | Sixth serial version, MI diagnostics (driver diagnostic), APS-4 IMM support, immobilization function bypass mode, misfire diagnostics, additional. starter relay. |
| J5V05N35 02/11/2004 KS #3F4B | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | Latest (seventh) serial version, MI diagnostics (driver diagnostic), APS-4 IMM support, immobilization function bypass mode, misfire diagnostics, additional. starter relay. |
| A5V05N35 02/11/2004 KS #5E9A | January-5.1 | 2112-1411020-41 | 2112 | Euro 2 | Latest (seventh) serial version, MI diagnostics (driver diagnostic), APS-4 IMM support, immobilization function bypass mode, misfire diagnostics, additional. starter relay. Avtel firmware. |
| J5V26K23 KS #968D | January-5.1.3 | 2104-1411020-01 | 2107 | Euro 2 | First production version. DK, adsorber, catalyst. There are no phase or knock sensors. |
| J5V26L52 01-03-2004 CRC #DD82 | January-5.1.3 | 2104-1411020-01 | 2107 | Euro 2 | Second production version. DK, adsorber, catalyst. There are no phase or knock sensors. |
What is needed for electronic tuning
The main “tools and devices” that will be needed when performing firmware for the VAZ 2114 8 valves are:
- Programmer.
- Disk with the required firmware version.
- PC or laptop.
ChipTuningPRO at work
If there are no problems with the last two points, then the programmer will need to be purchased. This can be done either in a car store (if not in stock, then order it) or via the Internet. It is worth considering that this device is far from cheap, and buying it for a single use is not at all profitable.
The best option would be to purchase it together with other car enthusiasts or contact a specialized workshop, where all reprogramming can be performed by professionals.
How to remove the on-board computer on a VAZ 2114
Unfortunately, many drivers are not satisfied with the performance of the electronic system of the car installed during the assembly of the VAZ. You can remove this gadget yourself without any problems.
The first step is to study the machine's instructions; it provides for the process of dismantling the on-board system.
Be sure to check with the car dealership where you purchased the car about the warranty period. Most dealerships can cancel the warranty if you tamper with the car yourself.
Let's start removing the on-board computer:
First you need to take out the radio, but first disconnect the negative terminal from the battery. Remove the outer panel of the radio. Then remove the entire body of the radio, making sure to unfasten the wires connected to it. Place your hand through the opened hole and carefully open the fastenings of the computer unit. Remove the on-board computer, having first unfastened all the wires connected to it. If you do not plan to install a new electronic system, it is necessary to connect the wiring. Also gently remove all devices connected to the computer. Connect the radio tape recorder back and install it in its place.
You can watch the video from YouTube hosting:
You can watch the video from YouTube hosting:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=grVMDc_lXSs
How to do chip tuning yourself
As already mentioned, the best option for tuning is to contact a car service center. There, specialists will be able to accurately change important settings of your ECU without damaging the operation of other vehicle systems.
Flashing the VAZ 2114 ECU
If you really want, you can try to flash the firmware yourself - to do this you will need to connect the PC to the ECU via a programmer and set the required settings in the working window of the screen (on different machines, electronic units can be programmed using different programs, each of which has its own operating features; according to For this reason, it won’t be possible to give any specific advice here on how to flash a VAZ 2114 step by step).
The only thing you should remember when performing independent chip tuning is the relationship between all operating parameters of the engine. So, by increasing its power to the maximum possible value, we will get a significant increase in fuel consumption, and along with it - increased toxicity.
It should be said once again that if you are completely ignorant of programming and have only basic PC knowledge, then doing chip tuning yourself is absolutely not worth it. After all, the result obtained can be not only zero, but also negative.
You may lose your factory warranty
If you run into an unqualified Lada chip tuning specialist. The program may install with errors. Sometimes programmers change only one characteristic, for example, fuel delivery. A constantly enriched air-fuel mixture breaks down the catalyst. Excessive thrust significantly reduces the resource of the Lada CPG. And so on.
Unqualified specialists write a program without making changes to the operation of the motor; it remains unchanged. It's not nice to pay for zero results.
Do you want to go to the Kulibins' garages? We strongly do not recommend doing this.
Disadvantages of ECU flashing
As mentioned above, an electronic upgrade of the control unit has not only a large number of advantages, but also certain disadvantages that should be kept in mind.
These may include:
- increased load on the engine and adjacent units;
- increased fuel consumption;
- increased toxicity of exhausts;
- rapid wear of parts;
- refueling a car with more expensive fuel.
True, it should immediately be noted that most of these shortcomings (for example, excessive fuel consumption) can only appear as a result of independent and, at the same time, not very successful tuning. When performing flashing at a car service center, technicians will be able to set the operating parameters of the engine to the maximum so that they do not “overlap” each other and do not interfere with themselves.
Achieving similar results at home and in the absence of the necessary skills is extremely difficult. As a result, the by-products will be increased toxicity and waste.
Speaking of the latter, it should still be noted that when the engine power is set to maximum, the consumption will increase in any case. The only thing that can be different is the number by which it changes. If, on the contrary, you want to reduce fuel costs, then when carrying out chip tuning, you should focus on this. True, the power characteristics of the engine, on the contrary, may decrease.
OBD2 pinout - 16 PIN
Brands and years:
Gasoline passenger cars and light commercial vehicles manufactured or imported into the United States since 1996 (US CARB and EPA legislation) and in Europe (EOBD) since 2000-2001 (European Union Directive 98/69EG) and Asia (mainly since 1998). ).
Conclusions and their purpose:
| № | Color | Purpose |
| 2 | J1850 Bus + | |
| 4 | Body grounding | |
| 5 | Signal Ground | |
| 6 | Line CAN-High, J-2284 | |
| 7 | K-line diagnostics (ISO 9141-2 and ISO/DIS 14230-4) | |
| 10 | J1850 Bus- | |
| 14 | Line CAN-Low, J-2284 | |
| 15 | L-line diagnostics (ISO 9141-2 and ISO/DIS 14230-4) | |
| 16 | Power supply +12V from battery |
Diagnostic connector pins for used protocols
Pins 4, 5, 7, 15, 16 - ISO 9141-2.
Pins 2, 4, 5, 10, 16 - J1850 PWM.
Pins 2, 4, 5, 16 (without 10) - J1850 VPW.
The ISO 9141-2 protocol is identified by the presence of pin 7 and the absence of pins 2 and/or 10 on the diagnostic connector.
If pin 7 is missing, the system uses the SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width Modulation) or SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) protocol.
All three data exchange protocols operate via a standard OBD-II J1962 connector cable.
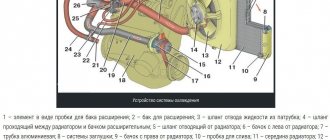
Why do you need an on-board computer?
In previous articles we have already talked about what an on-board computer is. what is it for and what types are they? But let me repeat myself so that you clearly understand all the advantages of having an on-board computer, and there are probably no disadvantages, except perhaps spending money on the purchase and that’s all.
Let's take, for example, the on-board computer STATE 115×24. With this model in your possession, you can:
- set the radiator fan start temperature; this function is very useful, for example, in winter, when you can control the temperature of the coolant, thereby monitoring the temperature of the heater radiator.
- The function of drying and warming up the spark plugs before starting the engine is very useful.
- The function of resetting settings and ECU adjustments is needed to switch to gasoline with a higher or lower octane number (from 92 to 95 and vice versa), and this function is also needed to reset settings after a long trip with increased load on the engine.
- The ability to read errors allows you to monitor the condition of the car and change non-working sensors and elements in a timely manner.