A serviceable and efficient braking system of a car is a guarantee not only of road safety, but also often the safety of the life of the driver, passengers and pedestrians. And one of the signs of serious problems for the car and its owner is a situation when the brake pedal fails. This process can occur either slowly or quickly. It happens that a recessed pedal does not return to its place at all. In any case, all of the above signs are a reason for serious diagnostics of the brake system. However, first you should find out what caused the emergency situation.
Why does the brake pedal fail?
One of the elements of the described hydraulic system is a special composition circulating through tubes and other cavities. The main feature of brake fluid is that it cannot be compressed. As a result, the force from pressing the pedal is transferred “unchanged” to the pads, which stop the rotation of the wheel. “Sinking” indicates that the line has become larger in volume or has depressurized. The main causes of the problem are discussed below.
Low quality brake fluid
The composition circulating in the system is quite aggressive. Gradually, bad brake fluid begins to corrode rubber and even metal parts, hoses, and tubes through which it moves. The walls of the latter become thinner to such an extent that they swell when pressure is created. Because of this:
- an excess volume is created into which the brake fluid goes;
- when you add it, the pressure is restored, but the tubes may not be able to withstand it: microcracks form through which the liquid gradually leaves and air enters instead (when the pedal moves in the opposite direction, it is literally sucked in). In the worst situation, the hoses may burst.
Air in the brake system
Its entry into the line is a consequence of depressurization of components and parts of the brake system. A plug may also form due to the fact that the fluid level in the tank has dropped below the existing MIN mark. Another reason is improper bleeding of the brakes when replacing the circulating compound. The danger with air in the system is that, unlike liquid, it is compressed. As a result, the force applied to the pedal goes to waste - in the literal sense of the word.
Master cylinder malfunction
Its main problem is most often related to depressurization. This occurs due to deformation and rupture of seals - cuffs. Their destruction is caused by poor-quality brake fluid or natural aging of the elements. The main brake cylinder becomes leaky even if scratches or wear appear on its walls.
This occurs due to the appearance of foreign particles in the line. They can get inside if the system is carelessly and inaccurately filled. Sometimes “extra” elements are wear and tear products if the car has been in use for a long time.
Repairing a brake cylinder is a difficult task. If you do not have the relevant experience and do not have special tools or devices, it is better to take the part to a workshop or buy a new one.
Problems with the vacuum booster
If it is faulty, then most often this can be determined by the characteristic hissing sound that occurs when you press the brake pedal. This situation may indicate depressurization of the vacuum pump. The reason may lie in a ruptured diaphragm, seals, or a broken equalizing valve. To solve the problem, purchase a repair kit and replace all rubber parts. Air can also enter the vacuum booster due to cracks in the underwater pipes: tighten the clamps on them or, if damaged, replace them (in a carburetor car, such a hose fits at the bottom of it).
Incorrect clearances
We are talking about the presence of a gap between the main brake cylinder (its rod) and the pedal. The latter in this case fails and remains in this position. If the clearance is correct, the pedal will initially move smoothly, but at a certain period of travel it will become stiff. If the distance to the GTZ rod is large, resistance to pressing will be felt only at the very end of the stroke.
Unprofessional repair
The reason when the brake pedal fails may lie in the caliper, the fastenings of which are not tightened well enough. Then its vertical axis will be shifted in relation to the brake disc and the pads will not be able to get used to function properly. Also, any unprofessional actions (poor tightening, lack of spring washers where needed, etc.) when repairing or bleeding the brake system will lead to its ineffective operation.
Corrosion
The metal that makes up some of the brake system elements can simply rust. In such cases, the pedal goes down and freezes there, from where it has to be “picked out” with a pry bar or other improvised tool. Corrosion usually succumbs to traction, which just needs to be sanded off.
Brake pad wear
In this situation, an increased gap appears between the disc and the pads. As a result, the pressure created in the system is not enough to brake the wheel. The solution is obvious: replacing the pads.
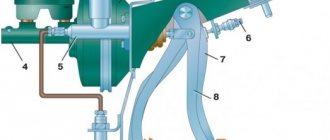
Description of the front suspension design of Lada Kalina 1117 2004 - 2013
Front suspension:
1 — cover; 2 — ball joint; 3 - retaining ring; 4 — hub bearing nut; 5 — protective cap; 6 — hub; 7 — hub bearing; 8 — steering knuckle; 9 — front wheel brake disc; 10 — brake mechanism shield; 11 - nut; 12 — eccentric (adjusting) bolt; 13 — rotary lever; 14 — front suspension spring; 15 — shock absorber rod; 16 — upper spring cup; 17 — upper support of the shock absorber strut; 18 — shock absorber rod nut; 19 — bearing of the upper support of the shock absorber strut; 20 — spring gasket; 21 — front suspension compression buffer; 22 — protective casing; 23 — telescopic stand; 24 — front wheel drive shaft; 25 — bracket for mounting the anti-roll bar cushion; 26 — front suspension stretch; 27 — anti-roll bar; 28 — stabilizer bar; 29 — front suspension lever.
The front suspension is independent with telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers, coil conical springs, lower wishbones with braces and a stabilizer bar.
The basis of the suspension is a telescopic hydraulic shock absorber strut. Its lower part is connected to the steering knuckle with two bolts. The top bolt that goes through the hole in the strut bracket has an eccentric collar and an eccentric washer. By turning this bolt, the camber angle of the front wheel is adjusted. The telescopic strut is equipped with a helical conical spring, a polyurethane foam compression stroke buffer, as well as an upper strut support assembly with a bearing.
The upper support is secured with three self-locking nuts to the body mudguard cup. Its design differs significantly from the design of the supports used on VAZ-2108-2110 vehicles. Now, instead of a pressed-in thrust bearing, a steel bushing is installed, vulcanized to the rubber mass of the support, which eliminates backlash and extraneous sounds.
The thrust ball bearing used in automobiles has a larger diameter and a different design and is located between the upper support and the spring. Under the weight of the front of the car, the bearing is in a compressed position, which eliminates all gaps and knocks. The contact area of the balls with the raceways has increased significantly, and consequently, the durability of the bearing has increased.
In the new design, when the wheels turn, the strut housing rotates along with the spring. In this case, the shock absorber rod remains motionless and the connection between the rod and the shock absorber guide bushing wears less. A telescopic hydraulic shock absorber is installed in the strut housing.
The lower part of the steering knuckle is connected to the lower suspension arm through a ball joint. The support is attached to the steering knuckle with two bolts (the holes in the steering knuckle are not through). When unscrewing these bolts, be careful: with significant force they often break, so before disassembling, tap their heads in the axial direction.
Braking and traction forces when the car is moving are perceived by longitudinal braces connected through silent blocks to the lower arms and brackets installed on the lower cross member of the radiator frame. At the connection points (at both ends of the brace) washers are installed to adjust the longitudinal inclination of the wheel turning axis.
The steering knuckle is equipped with a double-row angular contact ball bearing of a closed type, which is secured in the knuckle with two retaining rings. The wheel hub is installed in the inner rings of the bearing with interference fit. The bearing is tightened with a nut on the shank of the outer wheel drive joint housing. The bearing is not adjustable in operation. The wheel hub nuts are the same, with right-hand threads.
The anti-roll bar is a spring steel bar. In its middle part there is a bend above the pipe of the additional muffler of the exhaust gas system.
Both ends of the stabilizer bar are connected to the lower suspension arms through struts with rubber and rubber-metal hinges. The rod in its middle part is attached to the body with brackets through rubber pads.
When not to panic
- If you got behind the wheel, decided to start the engine after a long period of inactivity, pressed the brake and started the engine, and at that moment the pedal “went away,” then there is no need to look for a malfunction: the phenomenon is normal. The fact is that when the car starts, the hydraulic vacuum booster begins to work: the process involves installing the mechanisms of the unit into the working position. It’s just that there is a difference between the force transmitted to the pedal when the engine is turned off and when the engine is running.
- If the brake fails after completing repair work to replace the pads, it also does not always indicate problems. In this case, the pedal begins to “go away” after bleeding the system, but then functions normally. This is due to the pistons of the working brake cylinders - they “search” for some time for the optimal gap between the disc and the pads.
Vibrations when starting off: possible faults and their elimination
When you start driving, when you depress the clutch pedal, engage first gear and release the pedal, vibrations appear when starting off. As a result, drivers are scratching their heads for a long time and cannot figure out what the essence of such a problem is. In fact, there are a large number of reasons for vibration when starting off. This may be related to the engine, transmission, and clutch. To properly fix the problem, you need to study this malfunction.
How to bleed brakes on VAZ cars
This is a procedure performed after repairs, replacement of individual system elements, or when replacing fluid. Pumping needs to be done by two people. But first, check the car's operating instructions, which should indicate the order of actions with the wheels. If there is no such point, start pumping from the rear right and left, then do the same with the front ones. You will also need to prepare:
- a thin hose or plastic tube with a diameter suitable for the bleeder fitting;
- a suitable small transparent container 0.5-1 l;
- key for unscrewing the fitting.
Next, place the car on an inspection hole so that you can get to each wheel from the inside. Have an assistant sit behind the wheel. Further actions:
- Fill the brake fluid reservoir to the maximum level.
- Clean the fitting, put a spanner on it and insert a tube, one end of which is lowered into a container containing brake fluid.
- Have an assistant press the pedal several times and keep it pressed.
- Unscrew the fitting and, holding it with a key, watch the nature of the liquid pouring out. If there are bubbles, tighten the fitting and instruct an assistant to repeat the operation.
- Pumping should be carried out until bubbles stop coming out.
How to bleed the brakes without an assistant is shown in the video below.
If air comes out despite repeating the procedure many times, the reason should be sought in depressurization of the system.
Ball joints
Experienced car enthusiasts recommend carefully checking the entire chassis.
For inspection, the car is jacked up, and the ball joint is installed so that the wheel hangs in the air. Then, with the palm of one hand, take the wheel by the upper part, and with the other hand, by the lower part. You need to wobble the wheel with your hands. If the wobble is present and felt, then the ball joint must be replaced. This should eliminate vibrations and knocking.
The brake failed at full speed: what to do?
First, try pressing the pedal sharply several times: perhaps its functionality will be partially restored. Next, assess the situation and identify a place where you can gradually turn. Then tighten the handbrake (don't do it too hard) and start shifting (if you have a manual transmission) to a lower gear. At the same time, when the lever is in “neutral”, press the accelerator (perform “re-throw”) to “prepare” the gearbox gears for emergency operation. As a last resort, choose the lesser of two “evils” - it is better to run into some obstacle near the road (roadside bushes are a good option) than to collide with a car.
Emergency situation
Brake failure while driving can be very dangerous. In this case, the main thing is not to panic. You need to smoothly tighten the handbrake, then, if the car has a manual transmission, gradually shift to lower gears.
During switching, be sure to re-throttle to equalize the rotation speed of the primary and secondary shafts. If possible, it is better to drive into a roadside obstacle than into an oncoming car.
Results
To avoid the situation described above, you need to periodically diagnose the condition of the brake system: add fluid, change it, install new pads, check the brake discs, monitor the condition of all components: the hydraulic vacuum booster, the working and master brake cylinders. If you suspect that they are malfunctioning, immediately carry out repairs or contact a service center.
The sensations that the driver experiences when the brake pedal “falls” during braking cannot be called pleasant, even if this does not cause any serious consequences. The reasons why the brake pedal fails usually lie in a violation of the tightness of the brake system circuits. However, we will consider their possible options in more detail, and also find out what needs to be done if the brake pedal fails, depending on the circumstances under which this happens.
Violation of tightness
What happens when there is a brake fluid leak?
Unlike liquid, air tends to compress, which leads to failure of the brake pedal when braking.
If the brake system leaks, the following occurs. The driver presses the pedal, the brake fluid begins to flow out under pressure. After the pedal is released, air enters the system under vacuum. Unlike liquid, air tends to compress, which leads to failure of the brake pedal when braking. The most common culprits for leaks are brake wheel cylinders and frayed brake lines. Cylinders begin to leak due to wear on the sealing rings, as well as scratches on the surface of the cylinder pistons. The tubes fray due to vibration. To prevent this from happening, when assembling the brake system, the pipes are secured with special clamps, and the main pipes are placed in plastic gutters. But negligence during repairs and corrosion cause the walls of the tubes to become thin, and subsequently cracks appear in them. Moreover, in order for the brake pedal to slowly sink when pressed, it only takes a few drops of brake fluid to leak - air will already enter the system. This often confuses the car owner: “how is it that the brake pedal sinks, but the fluid does not drain?” The loss of a few drops of liquid will practically not lead to a decrease in its level in the tank, and the leak is sometimes difficult to detect due to its insignificance, especially in wet weather. A leak can also occur through the main brake cylinder, but it can only be detected by disconnecting the latter from the vacuum brake booster. It happens that it is filled to half with brake fluid .
Emergency cases - the brake pedal “falls to the floor” when pressed sharply
Large losses of brake fluid lead to the fact that the brake pedal can fall “to the floor,” that is, all the way. This happens when brake hoses and tubes break. You can avoid such a nuisance; you just need to periodically (at least once every six months) inspect the pipelines. If cracks appear on the outer shell of the brake hoses, they must be replaced without putting them off “for later.” Moreover, when purchasing new hoses, pay attention to the year of their manufacture - the manufacturer must affix the appropriate mark. If the product was released more than two years ago, do not buy it. Rubber has a certain shelf life, after which it partially loses its properties, and the “new” hose may fail you in the coming frosts. The brake pedal can suddenly “fail” also in the case when there is critical wear of the brake parts - discs, drums, pads. In this case, the piston of the working cylinder is simply pushed out.
Clutch vibration when starting viburnum
- To the beginning of the forum
- Forum Rules
- Old design
- FAQ
- Search
- Users
There is a misalignment in the basket, so it starts to wobble, the clutch disc slides unevenly over the flywheel and the basket, I changed the basket and it went away..
that is, all front-wheel drive vehicles vibrate when starting off
There's a misalignment in the basket and that's why it's crashing
but usually another 30 thousand is like
At the bottom the moment is different from the carb.
At the bottom the moment is different from the carb. It would be nice to enrich the bottom a little, but how can you do it?
on carb 21083 max torque at 3500 on eng 2111 max torque on shelf 2900 - 3200
who should add what to whom?
It twitched and shook when moving. I rebuilt the carb normally, it starts normally. There were thoughts about the clutch, however. So, it’s not always the clutch’s fault.
Transmission vibrations and jerking due to the carb cannot be confused.
Transmission vibrations and jerking due to the carb cannot be confused.
Information on icons and features
You can not
start topics You
cannot
reply to messages You
cannot
edit your messages You
cannot
delete your messages You
cannot
vote in polls You
can
attach files You
can
download files
Pedal dips associated with recent repairs
If the brake pedal sinks in when the engine is off, this is a sign of a serious problem.
Sometimes it happens that the driver has just bled the brakes, but the pedal still falls through. This means that there is still air in the brake system. It happens that when pumping together, the one holding the pedal releases it too early, without waiting for the partner to close the bleeding fitting. After repairing the caliper or replacing the brake pads, the brake pedal fails the first time you press it. Afterwards it works fine. This happens due to the fact that the pistons of the working cylinders are installed “in place” - so that the gaps between the pads and discs (or drums) become minimal. The return movement of the pistons is blocked, depending on the design, in various ways. After installing the parts in the working position, the brake pedal begins to work normally. When the brake pedal fails after repair, the brake fluid level remains normal if it has not previously dropped below the minimum level. After a long period of inactivity, the brake pedal fails after starting the engine due to the fact that the vacuum booster starts working . At the same time, the mechanisms are also installed in the working position. In general, the failure of the brake pedal when the engine is running is a normal phenomenon; it is simply felt as a result of a large difference in the force required to press the “silent” or running engine. But if the brake pedal falls down when the engine is off, this is a sign of a serious malfunction. It is quite possible that the brake system does not work at all - perhaps due to a complete lack of fluid in the circuits.
Steering Troubleshooting
If the type of mechanism is a screw-nut, then during long-term operation the wear of the rubbing parts increases the gap between the worm and the driven gear. It can be eliminated by tightening the adjusting bolt in the steering gear housing cover and using high-quality lubricant. The main thing is not to overtighten the bolt while tightening. Otherwise, rotation of the steering wheel will be difficult and wear of parts will only increase.
If the type of mechanism is rack-and-pinion, then severe wear increases the gap between the rack and pinion. The malfunction can also be eliminated by tightening the adjusting bolt. However, there are mechanisms where there is no gap adjustment. They are replaced assembled, or disassembled and polished on machines. Poor fastening of the steering linkage supports is caused by poor tightening of the bolts. This is also a breakdown of the bracket or, in rare cases, the spar. Eliminated by tightening the bolts and welding broken parts. What to do if vibration occurs when starting off (VAZ 2101-2109)? Let's take a look below.
Broken master cylinder
Master brake cylinder
Repairing the master brake cylinder is a thankless task; it is best to replace it with a new one.
The brake master cylinder has a design similar to that of the pump. And like any other pump, the piston seals or the piston itself can wear out. In this case, the sealing rings installed on the vacuum booster side may be in good condition. As a result, although the liquid from the cylinder will not flow out, a violation of the internal seals will lead to the fact that the cylinder rod (piston) will move when the pedal is pressed, but will not create pressure in the circuits. Depending on the degree of wear, the brake pedal will either periodically sag when pressed sharply, or slowly go down with constant pressure on it. In the case of this reason, the brake pedal fails even when pressed smoothly, but the fluid does not leave the system. Repairing a cylinder is a thankless task; it is best to replace it with a new one.
Brake pedal does not return
This kind of malfunction does not happen very often - the pedal does not return to its original position after being pressed. This can happen due to improper adjustment of the brake light switch or due to a broken vacuum booster follower valve. It turns out that the valve, being pressed to the seat when the pedal is already released, prevents air from entering the cavity of the booster in front of the main brake cylinder. Therefore, the same air continues to press on the amplifier diaphragm from the pedal side, which prevents its return. If by adjusting the free play of the pedal it is not possible to achieve its normal operation, most likely you will have to change the vacuum booster itself, or try to repair it.
The braking system in any vehicle plays the most important role as its failure can lead to serious consequences. Some drivers encounter a problem when the brake pedal fails. If a person is faced with such a situation, then it is necessary to resolve it as quickly as possible.
The principle of operation of the braking system
The first step is to understand the general principle of operation of the braking system. This will help you understand the reasons why the brake pedal sometimes fails and the fluid does not drain. In most cases, the mechanism in question is hydraulic, where a special substance is used.
Not long ago, the more popular mechanical braking system was one that used cables instead of fluid. However, engineers of automobile companies have long moved away from this principle, replacing it with a hydraulic one. This is due to the fact that the mechanical engineering industry is constantly developing along with the capacity of the units.
Thus, the moment came when mechanical brakes stopped coping with their task.
It is worth noting that there is another principle of the systems under consideration, namely pneumatic. This is the most reliable system installed on large trucks. It could also be installed on ordinary passenger cars, since it is superior in quality to hydraulic ones. However, due to the heavy and bulky design this is not possible .
Any hydraulic system consists of several elements that form it. This includes:
- brake discs and pads;
- hydraulic line;
- master cylinder:
- four working cylinders located on each wheel;
- compensator.
Causes and solution to the problem
When the driver understands how the brake system works, he can deal with its malfunction. If the brake pedal fails, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics as soon as possible and identify the cause. First of all, it is recommended to check the level of brake fluid, which is stored in a special reservoir.
This tank has two manufacturer's marks . One displays the minimum permissible liquid level, and the second the maximum. Although this substance is incompressible, its amount can still decrease over time. This is due to the fact that brake pads can gradually wear out during operation. Because of this, the working cylinder needs to travel a longer distance to act on the wheel, and this requires more fluid.
Thus, air begins to leak into the free space of the tank, and, as a result, airing occurs. The brake pedal begins to sink and stops working as it should.
There is another reason why airing can occur. In this case, the fluid level may be completely normal. This is due to situations where the driver brakes too often at high speeds or drives at low speeds with the pedal constantly pressed. For example, this happens during a systematic descent from a steep slope. This problem is also facilitated by high air temperature, which heats the liquid even more.
This problem can be solved with the help of brake discs that are equipped with a cooling system. Specialized brake fluid designed to work in high temperature conditions can also help.
It is recommended to regularly service the vehicle and check the condition of the entire system. This way you can protect yourself from unpleasant situations on the road that can lead to serious consequences.
Malfunction after replacing pads
Quite often, drivers are faced with a situation where new brake discs, pads or drums have just been installed, and the problem of a failing pedal appears immediately. The first thing to note is that after such events, during the first days, the braking system may not work entirely correctly. This is a normal procedure that occurs quite often. In this regard, after replacing brake system elements, it is recommended to use the car as carefully as possible.
This problem is due to the fact that the brake pads and discs cannot work properly right away. They need some time during which they need to get used to properly. This procedure must be completely completed within 200-400 kilometers. If this does not happen, then most likely the problem is in the details themselves.
During the first time after replacing the pads, when you press the pedal, the car may not respond immediately, twitch and vibrate.
It is recommended to prepare for this in advance and not accelerate to high speeds to avoid consequences.
Vacuum booster
The last popular reason for problems with a car's brake system is problems with the vacuum booster. However, in this case, the pedal does not fall, but is pressed quite tightly, which greatly affects the effectiveness of the brake.
The vacuum booster is another element of most brake mechanisms, which are designed to make pressing the pedal more comfortable. This happens more easily and requires much less effort from the driver. However, the VU diaphragm may become unusable, which will cause difficulties in the operation of the entire system.
This problem can only occur when the engine is running. When the car is turned off, the pedal will be pressed normally. This feature allows for easy initial diagnosis. If the engine does not work and the pedal works correctly, but problems begin when the engine is running, then this is due to the diaphragm. To find a solution, you need to contact the service center.