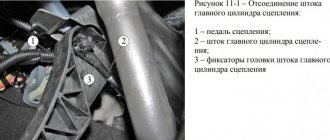
In my article today I want to talk about the brake pedal , namely what it should ideally be, tight or, on the contrary, soft, how to find this golden mean?
By and large, the brake pedal can have several positions and states.
The first state is the one provided by the manufacturer, when when you press the brake pedal there are no dips or jerks, and no special effort is required. There are also two other unpleasant pedal conditions that can cause driver anxiety.
This refers to the state of the pedal when it is excessively tight or, on the contrary, very soft. Both one and the second phenomenon are equally unacceptable and indicate malfunctions and the need for urgent repairs of the brake system.
A stiff brake pedal can become stiff for several reasons, and they may not necessarily be associated with the traditional “sores” that are typical for all brake models. However, I still propose to consider the most common of them, and I will also try to give practical advice on how to eliminate them.
Most problems that cause the brake pedal to become soft are related to either the vacuum booster or the brake master cylinder.
Reasons why the brake pedal becomes hard:
1. Clogged air filter of the vacuum booster. Treated by replacing the air filter;
2. Sticking of the valve body in the vacuum booster. The vacuum booster needs to be replaced;
3. The vacuum booster diaphragm is damaged. Solved by replacing the vacuum booster;
4. Faulty vacuum booster tip. The tip should be replaced;
5. Sticking or failure of the check valve in the vacuum booster. To eliminate, it is necessary to replace the check valve;
6. The check valve of the vacuum booster is faulty or the seal is broken, resulting in fuel entering the chamber of the vacuum booster. The vacuum booster with check valve should be replaced;
7. Damage to the hose that connects the vacuum booster and the intake manifold, or the hose fastening on the fitting is loose. It can be treated by replacing the hose, or, if possible, by tightening the fastening clamp. The condition of the hose should be regularly monitored, this is especially true in the cold season. As long as the hose is cold, it retains the necessary rigidity - the brakes function normally. However, after several tens of minutes of motor operation, the hose heats up and becomes more elastic. If, for example, during inspection you do not find delamination, the capacity of the hose will decrease, which in turn can cause problems with the brake pedal.
8. The sealing rings in the working wheel cylinders are swollen; this often occurs as a result of fuel and lubricants getting on their surface, or as a result of using low-quality brake fluid. To correct this situation, it is necessary to repair the working brake cylinders and replace the brake fluid
Here are several ways to independently check the performance of the vacuum booster.
First of all, start the engine to allow a vacuum to occur in the system. After this, press the brake pedal; if the pedal is hard, this is a clear sign of a faulty hose or amplifier. Then turn off the engine and wait 5-7 minutes, do not press the brakes.
It is necessary to specify the malfunction; to do this, press the pedal. If it is still hard, most likely the fault lies in the vacuum booster valve.
There is also another test. When the engine is not running, it is necessary to depress the brake pedal several times in order to remove the vacuum in the brake system. After this, without releasing the pedal, you need to start the engine; if the pedal begins to move down a little, the amplifier is in order.
Cause of soft brakes
A soft brake pedal, as a rule, simultaneously indicates several breakdowns in the brake system. More precisely, there are many reasons why the brake pedal can become soft. Sometimes this phenomenon is also called brake pedal failure.
The most common reasons why brakes may become soft are:
Air brake system. Troubleshooting occurs by bleeding the brakes and removing air from the brake system.
Airing can occur for the following reasons:
1. Low level of brake fluid in the expansion tank, depressurization of the brake system;
The brake pedal has become hard: the reason
So, during operation, you can discover that the brake pedal has become hard, medium or too soft. The reasons for a tight pedal, that is, when the brake pedal on a car is too hard, can be either a design feature of a particular car or a malfunction. In other words, a hard brake pedal may be normal for certain car models. If the brakes become hard for another reason, repairs are necessary.
To transfer pressure, brake fluid is poured into the system. The fluid is supplied through steel pipes and rubber hoses from the master cylinder to the brake wheel cylinders. The working cylinders use their piston to transmit pressure to the brake calipers, pressing the brake pads against the brake disc or drum.
The list of main reasons why the brake pedal is hard to press or the brake pedal is not pressed includes problems with the vacuum booster. The following problems should be noted:
- Malfunction of the vacuum brake booster limit switch. Replacing the end switch solves the problem;
- The vacuum booster also has a special check valve. If the valve sticks or does not work, the specified element must be replaced;
- The VUT may also have a dirty air filter, which prevents dirt from entering the system. If the filter is clogged, in a similar situation the brake pedal is also pressed hard;
- The amplifier also has a special check valve. If the VUT valve is stuck, this element must be replaced;
- Often the reason why the brake pedal becomes hard after several presses or the brake pedal is hard after parking is the brake booster diaphragm. The VUT diaphragm breaks or cracks, and the entire amplifier must be replaced;
- At the same time, we note that fuel may enter the booster chamber (often due to a broken check valve), which will also immediately affect the operation of the brake pedal;
- One common cause of a hard brake pedal that won't press down is the hose connecting the intake manifold to the booster. The specified hose wears out and becomes deformed, that is, over time it may require replacement. It also happens that it loosens on the fitting. In this case, a tight fit can solve the problem;
- The list ends with the use of dirty brake fluid that has lost its properties, the ingress of third-party fluids into the brake cylinders, as well as swelling of the sealing rings. To fix the problem, the cuffs and seals need to be replaced (repair of brake cylinders), and the brake fluid must also be replaced. In some cases, entire brake cylinders need to be replaced.
Mono: how to change car brake fluid for one person without assistance
There is only one way to solve the question of how to replace brake fluid for one person. His goal is to update the composition in the tank and lines without using the help of a partner. The features of this method are similar to bleeding the brakes:
- To speed up the process, it is recommended to immediately remove the working emulsion from the expansion tank using a bulb or a syringe with a tube attached.
- The preparatory stage consists of purchasing 1 liter of brake fluid and a 1 meter long tube, suitable in diameter to the outlet fittings on the brake cylinders. You will also need a cut-off bottle with a certain amount of working fluid so that air does not pass through the fitting into the system.
- During the process of replacement/pumping, the composition gradually leaves the tank. The level must be replenished regularly, otherwise the system will become airy.
Process technology
The essence of the replacement is the flow of the working fluid under the influence of gravity. After all, the tank is at the highest point. In fact, the operation is no more difficult than checking the injectors of a diesel or gasoline engine. As a result, the set of actions is as follows:
- Empty the expansion tank and fill it with new fluid up to the MAX limit mark.
- Clean all 4 drain fittings and install tubes on them. Place the latter in plastic containers with “brake fluid”.
- Unscrew all the drain fitting nuts one by one:
- right rear;
- left rear;
- right front;
- left front.
- While watching how the composition drains, do not forget to add a new drug to the tank.
- When the volume of liquid poured from the left front wheel reaches approximately 200 ml, tighten the fittings on it and on all other cylinders in the reverse order:
- front left;
- front right;
- rear left;
- rear right.
- Restore the fluid level in the tank.
- Clean the fitting and put a tube on it, lowered into the brake fluid.
- Create pressure in the retarding system.
- Unscrew the union nut and wait until the liquid pressure decreases to low.
- Close the fitting.
- Repeat until liquid comes out without bubbles.
Leveling up
The method is relevant if there is no air in the deceleration system. If there are air bubbles in the unit, the emulsion will not drain under the influence of gravity. Excessive pressure is required to bleed it off - just like in production. In this case, replacing the composition comes down to bleeding the brakes:
Excessive pressure in the system can be created in several ways:
- Find an assistant or pump the brake pedal yourself and press it with a gas stop from the hood/trunk installed between it and the seat.
- Insert the syringe with the emulsion into the lid of the tank and seal it. Having opened the fitting, press the syringe pusher.
- Install the car nipple into the cover. Seal with sealant or superglue. Remove the nipple and install the tube. Install the opposite end of the hose onto the quick-release tip of the pump. Take excess pressure from the spare tire. You can do it even simpler - apply pressure from the compressor to the spool.
If the brake pedal is pressed hard: diagnostics
As you can see, a tight brake pedal is often due to problems with the vacuum booster. At the same time, its operation can be quickly checked on the spot.
To diagnose VUT, you can use two methods. In the first case, you need to start the engine for the vacuum booster to start working. Normally, the pedal is soft; after two or three strong presses on the brake, the engine speed will briefly increase.
Another test involves pressing the brake several times with the engine off. Normally, the pedal should be soft for 2-3 presses, then it becomes hard. After this, you should press the brake and start the engine without releasing the pedal. The pedal should go down after the engine starts. If this does not happen, then you also need to look for a problem with the VUT.
Methods for checking a vacuum booster
There are several ways to check the vacuum booster. First you need to start the engine. A vacuum will be created in the system. Next they press the brakes. If the brake pedal is hard, then there is a fault in the hose or booster. You need to turn off the engine and wait 5 minutes, but do not apply the brakes.
To specify the malfunction, you need to press the pedal. If it continues to be hard, then in most cases there is a problem with the vacuum booster valve.
There is another way. The engine must be turned off. To relieve the vacuum in the brake system, press the brake pedal several times. Then the engine is started, but the brake pedal is not released. If the pedal goes down, then there is no problem with the amplifier.
Soft brake pedal: reasons
Having figured out why the brake pedal can be hard, you should pay attention to an equally common problem when the brake pedal has become soft. In such a situation, the brakes may be weak and perform poorly, which is no less dangerous than a hard pedal.
In extreme cases, the brake pedal may not rise after being pressed or may sink to the floor when braking. Naturally, in the case of a “cotton” pedal, owners are interested in what is the cause of the malfunction, why the pedal is soft after bleeding the brakes, and also how to make the brake pedal harder.
If bleeding has already been carried out, there is a high probability that mistakes were made, undetected breakdowns, brake fluid leaks, etc. occurred. For example, drivers often encounter a problem when, after replacing the brake pads, the pedal is soft, the brake pedal falls off after replacing the brake fluid, after bleeding the brake pedal fails, but the fluid does not drain, etc.
- One way or another, the main reason is depressurization of the brake system. Pipes fray and crack, problems with brake cylinders are possible, dirty brake fluid damages the cylinder mirror. Jamming of the TC pistons should not be ruled out.
At the same time, it is necessary to inspect the locations of all connections, fittings and other elements, since even a few drops of brake fluid leakage have no effect on the level in the reservoir, but air still enters the system, which is the cause of the soft pedal.
It should also be taken into account that if certain elements of the brake system have been changed (discs, pads, drums, working cylinders, etc.), in this case the braking efficiency will be slightly reduced until the parts are broken in. In this case, over several tens of km. The pedal may also feel softer than usual, or the brake pedal may alternate between being soft and stiff.
If the brake fluid is dirty, old and has lost its properties, it may boil due to heat. This leads to the brake pedal sinking or becoming too soft (“cotton”). This situation is dangerous because the problem may have a so-called “floating” nature. If such symptoms appear, you need to start with a complete replacement of the brake fluid.
Is it possible to add brake fluid from another manufacturer or brand to the reservoir?
Going to buy 1 liter of TJ – it would seem that there’s nothing special about it. I came to the store, ordered, paid and went to the garage with a satisfied look. This was the case before, when out of all the auto chemical enterprises there was only one in the news - the Dzerzhinsky plant. Now you can not only easily confuse diesel and gasoline oil, but also the composition of the braking system. After all, in the market, even experts sometimes get their eyes wide open. Here you have Rosdot, and Sintec, and a bunch of other similar names.
What will an unscrupulous driver do? He’ll take any one and go with the idea of quickly resolving the issue. Motorists are rushing to warn against such indifference. The mixing operation is, of course, permissible, and the manufacturer even indicates with what compounds his product can be used. The question is whether it is possible to add brake fluid of another brand when the consumer is not aware of the origin of the emulsion already filled.
Undoubtedly, the code for the current composition can be found in the instruction manual. What if it is lost, or the car is bought secondhand? In general, if the situation is unclear, it is recommended to completely change the working fluid. What you definitely shouldn’t do is pour in TF with a low boiling point. Dangerous.
#1 Gladiator
Our locomotive fly forward!
Good afternoon. Now that I have time, I want to work on the brakes.
There is a pressing problem - low braking (slowdown) efficiency and a soft brake pedal.
Those. There seem to be brakes, but for a critical situation they are clearly too weak - I may not have time to stop. Those. I press the pedal (at least to the floor) and it slows down slowly. There is not even any talk about use.
By analogy with a bicycle - there are those in which you press on the pedal and the rear wheel is blocked until the black stripe on the asphalt, and on the other - you press - but you won’t stop quickly, there is no effective deceleration (that’s how it is for me).
1. The brakes are bled. True, the sorcerer did not stick a screwdriver into it, but he loaded the trunk with 100 kg.
2. The front cylinders were sour. I treated it a little with castor oil. When driving without braking, they do not jam, the discs are cold. When driving around the city, they work. After the trip, the discs are warm (the front right and rear left are hotter than the front left and rear right). The rear right disc is the coldest. When braking, the car does not go anywhere. There is no vibration.
3. GTZ costs Pilenga. The vacuum rod was not adjusted. If you stand at a traffic light and keep your foot on the brake, the pedal does not go down, i.e. The GTZ doesn't seem to let it through.
4. When the car is not started, it is impossible to pump up the brake pedal. Previously, after several pumping motions, its stroke became less and less and the pedal became stuck. Now this is not the case. True, if you start the engine with the pedal pressed, it goes down a little. Well, when pumping up the pedal, it hisses a little - it wheezes. True, when running, the engine speed does not change when swinging.
5. The brake hoses are new (Lukas), the brake fluid is fresh, there are no leaks anywhere.
Why is the brake pedal higher than the gas pedal?
Drivers often wonder why on many models all the pedals in the car are not on the same plane. As a rule, on a car with an automatic transmission, the brake pedal is noticeably higher than the gas pedal. On cars with manual transmission, the clutch and gas are also often lower than the brake.
Let us note that there is a lot of debate on this matter and there are a number of conjectures and assumptions. Some car enthusiasts claim that this is inconvenient, others complain that if the pedals were in the same plane, it would be easier to control the car, etc.
Let’s also add that some owners believe that the brake pedal is placed higher in order to increase its travel, and also taking into account the need for more force (lever).
Let's sum it up
Taking into account the above, it becomes clear that any deviations from the norm in the operation of the brake system (either a soft brake pedal, a hard brake pedal, or a combination of problems) require immediate diagnosis. After identifying the malfunction, it is necessary to properly eliminate the problem.
You also need to promptly change the fluid, bleed the brakes, inspect the brake hoses for defects and leaks, install new brake pads, discs or drums in a timely manner, lubricate the brake caliper guides, etc. This approach will allow you to safely operate the car and achieve high-quality performance of the braking system in any conditions.
The brake pedal falls to the floor, the brakes disappear unexpectedly, after replacing the brake fluid, pads, brake discs: the main causes of the malfunction.
Reasons why the engine may stall when you press the brake. The power unit stalls during sudden braking, when the clutch and brake are depressed, etc.
What is engine braking? How to perform this technique correctly. Pros and cons, sleep recommendations. Engine braking on cars with automatic transmission.
How to brake correctly in a car with a manual transmission: types of standard braking on a manual transmission, emergency and emergency braking, tips.
The clutch pedal has fallen: why does this happen? The main reasons why the clutch pedal fails, what should the driver do if the clutch fails.
Driving a vehicle always involves various risks. A high-quality braking system can avoid most of them. Thus, if you find a hard or soft brake pedal, you need to immediately address this problem. If such problems arise, you should not delay; it is better to conduct a thorough diagnosis to find out what exactly is the cause of the problem.
Brake operation when the engine is off
The pressure on the pedal is related to the vacuum booster. And the VU itself can only work with the engine turned on. When parked for a long time, the pressure in the vacuum chamber becomes atmospheric - the amplifier does not work. When you press the pedal, the force is transmitted directly from the levers to the master cylinder. The resistance on the pedal increases by 3-5 times.
A hard brake pedal after parking is normal.
If you start the engine while holding down the pedal, it should fall slightly. You can go safely.
Monitoring the technical condition of a car is a conscious need for any driver who wants to ensure the safety of himself and others.
Should I be concerned if the brake pedal is stiff or soft after bleeding?
The manufacturer has ensured that the brake pedal is pressed as easily and conveniently as possible. It is important that there is no need to exert significant effort while pressing, and various dips and jerks are unacceptable. Regardless of whether the brake pedal is soft and does not stop well, or there is a problem of some other kind, it is important not to leave things to chance. In general, if the brake pedal fails, then you urgently need to go to a service station or top up the brake fluid yourself. Most likely there is a leak in the brake system.
Both a tight pedal and too easy its movement are an alarming symptom that can indicate a number of serious problems.
The brake pedal fails (the brakes are too soft)
It is worth noting that if you feel weak braking when pressing the brake of a VAZ 2109 or any other model, you need to think about the fact that these may be features of a particular vehicle. Perhaps you just moved from another car, so you feel some discomfort while driving a new car.
On the other hand, such a symptom can also occur when air enters the system. It should be noted that in the event of depressurization of the system, the pipeline may completely burst and completely fail. This can be corrected by bleeding the brakes. At the same time, you should diagnose the cylinders, check the level of the brake fluid, as well as its quality (often air gets into the brake system simply because there is too little fluid) and perform a full check of the vehicle (the latter will help determine the presence of hidden problems) ;
If the pedal becomes soft after replacing the brake fluid, then, as a rule, the problem lies in the use of a low-quality mixture. Alternatively, it is possible that air got into the system during replacement - this is also worth paying attention to.
It is also quite common for the pedal to feel soft after bleeding the brakes. First of all, you should bleed the master cylinder. As a rule, this solves a similar problem. Alternatively, there may be problems with the anti-lock braking system (if equipped). In any case, if the brakes are soft after bleeding, you should approach this task responsibly. Perhaps you should contact specialists who can quickly and effectively fix the problem.
Video about the operating principle of the brake master cylinder:
Causes of a hard brake pedal
If the brake pedal is either soft or hard, or the pressure is too tight, there are also several possibilities for the problem. The main reasons here include:
- clogging of the air filter of the vacuum booster. Basically, here you need to replace the filter itself;
- increased sizes of sealing rings in wheel cylinders.
Typically, in this case, the pedal became hard after changing the brake fluid.
You should not use low-quality death; it is better to buy the liquid recommended by the manufacturer. As a result, such a problem will not occur; - presence of mechanical damage on the diaphragm. The element should also be replaced;
- problems with the functioning of the tip in the amplifier. It is necessary to replace it with a working part;
- check valve stuck. These components cannot be repaired, so they should be replaced;
- Vacuum booster valve sticking. You just need to replace this element;
- presence on the hose between the intake manifold and the deformation amplifier or loosening of the fastening. First, try tightening the fastening clamp. If this does not help, you need to change the hose.
We discussed why a soft or hard brake pedal effect occurs. Regardless of the cause of this problem, malfunctions of the braking system are quite serious, so you should take a very responsible approach to diagnosis and repair. If you cannot fix the problem yourself, you should immediately contact a professional - in no case is it recommended to get behind the wheel of a car in which the brakes do not work correctly.
Malfunctions of the "vacuum"
A vacuum brake booster (VUT), or simply a “vacuum booster,” creates in the vehicle’s vehicle the pressure necessary for their proper operation.
If the amplifier is not working well, the pedal simply won't push through. Since the vacuum booster is a rather complex part consisting of many components, a malfunction of any of them can lead to this situation. And since a breakdown of an amplifier component, as a rule, requires its replacement, correct diagnostics will help save the car owner not only time, but also money.
If the filter element of the “vacuum tank” is clogged, it is enough to replace it so that the amplifier begins to function normally again. This also applies to a damaged vacuum booster diaphragm, and problems with the tip or check valve. It is enough to replace one damaged component, and the vehicle will act like new again. It is important to accurately diagnose what exactly needs to be changed.
Sometimes no major replacements are required at all. For example, in a situation where the vehicle is depressurized. The seal can be broken in two cases: either the hose between the “vacuum reservoir” and the intake manifold is damaged, or the clamps are loose. And if in the first case replacing the hose is still necessary, then in the second it is enough to tighten the clamps. This can also be done at a car service center, but the car owner is quite capable of dealing with such a problem on his own.
But it happens that the unsuitability of only one component completely renders the VUT unusable. This most likely occurs in a situation where vehicle malfunctions are ignored for a long time. As a result, a badly damaged valve moves to such a position that it disables the entire “vacuum tank”. An example is damage when a valve jams in the amplifier, and the latter has to be completely replaced. This is one of the most expensive types of vehicle repair.
We recommend: How to replace valve stem seals without removing the cylinder head?