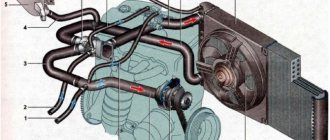
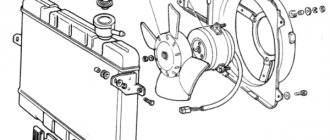
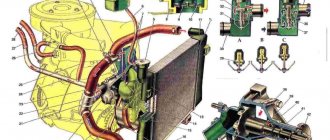
Lava Vesta. ENGINE COOLING FAN 21129 WITH M86 EURO-5 CONTROLLER
The controller controls the relay unit for turning on the electric fan of the engine cooling system. The electric fan turns on and off depending on the engine temperature.
The electric fan operates in two modes - at maximum speed and at reduced speed.
The reduced speed of the electric fan is activated when the coolant temperature is above 102 °C, as well as when there are DTOZh fault codes in the controller’s memory or when the air conditioner is running. In this case, the electric fan relay unit is controlled from the “X1.1/H2” contact of the controller.
The reduced speed of the electric fan turns off when the coolant temperature drops below 98 °C.
The maximum performance of the electric fan is switched on when the coolant temperature is above 103 °C, as well as when the refrigerant pressure in the line is high, both with the air conditioner running and the air conditioner not working. In this case, the electric fan relay unit is controlled from the “X1.1/H3” contact of the controller.
The maximum performance of the electric fan is switched off when the coolant temperature drops below 98 °C.
Rice. 1.4-01. Electric circuit of the fan of the engine cooling system of cars of the LADA VESTA family
Rice. 1.5-01. Engine crankcase ventilation system 21129: 1 — intake module; 2 — primary circuit hose; 3 — cylinder head cover; 4 — secondary circuit hose; 5 — inlet pipe hose; 6 - exhaust hose
Lava Vesta. ENGINE Crankcase VENTILATION SYSTEM 21129 WITH M86 EURO-5 CONTROLLER
The crankcase ventilation system (Fig. 1.5-01) ensures the removal of crankcase gases.
Crankcase gases flow through the exhaust hose into the oil separator located in the cylinder head cover on engine 21129.
The hoses of the first and second circuits are two hoses (one of small diameter, the other of large diameter), through which crankcase gases, having passed through the oil separator, are supplied to the combustion chamber.
The first circuit has a calibrated hole with a diameter of 1.7 mm. The calibration hole is located in the cylinder head cover tube. The primary circuit hose (small diameter hose) is connected to the cylinder head cover tube (oil separator fitting). The primary circuit hose goes from the oil separator to the intake module.
Engine cooling system design
The engine cooling system (ECS) consists of:
- cooling system pump (pump);
- engine radiator;
- air conditioner heater radiator;
- electric fan;
- expansion tank;
- thermostat;
- connecting hoses.
SOD uses a special liquid (antifreeze) based on a mixture of water and ethylene glycol. Mixing antifreeze of different brands is not recommended, and having different bases is unacceptable! When choosing antifreeze, you should pay attention not to its color, but to its chemical composition (type), recommended by the car manufacturer. In the event of an antifreeze leak, it is allowed to add distilled water, but after this it is necessary to restore the optimal concentration of antifreeze as quickly as possible. The density and concentration of antifreeze is presented in the table:
Removing and installing the expansion tank
To replace the expansion tank on a Lada Vesta, start with the actions that the manufacturer recommends before each repair: remove the negative terminal from the battery, stop the car. Next follow the instructions:
- Open the hood. Wait until the car has cooled down to avoid getting burned. To protect your hands during repairs, wear medium-thick gloves.
- Remove the steam hose from the “hero of the occasion” with your hands.
- Behind the part from below, unscrew the two bolts and one self-tapping screw that secure it in place.
- In place of the old part, put a new one, connect the hose, establish a strong connection, tightening it with a new clamp.
DSC_9596 (Copy)
Pull the hose off the radiator pipe and drain the liquid into a container.
To increase the intensity of liquid drainage, unscrew the cap of the expansion tank.
Next, you need to drain the fluid from the cylinder block.
Access to the drain hole in the cylinder block is blocked by the starter. In addition, the leaking liquid will inevitably get inside the starter, so the starter must be dismantled. To do this, disconnect the wire terminal from the negative terminal of the battery.
No. 2 Modification of the thermostat on the Lada Grant - replacement of the thermal insert
This method involves completely dismantling the flow regulator and disassembling it into its component elements. The detailed process is described above.
We troubleshoot the thermostat cavity, wipe it with a rag, and inspect it for cracks and other defects.
Removed spring from thermocouple
We replace the entire “core”. The following cores are suitable for the standard thermostat:
We replace the complete set, including the spring, and the modification of the Luzar thermostat on the Lada Grant is completed.
Note to the driver! Such modernization is possible only with thermostats manufactured by BEHR. Products from other companies are incompatible in terms of parameters. Many car owners do not know about these subtleties and end up in ridiculous situations.
As an alternative, use a core from Daewoo or Renault, catalog part number - Vernet 4898.92. The design of the part is somewhat different and requires adjustment. For standard thermostats from Luzar, such an upgrade is not possible.
Subject to the recommendations, fuel consumption will decrease by 1.0 - 1.5% minimum.
DSC_9622 (Copy)
Let's start the engine. With the engine running, vigorously compress all the hoses of the cooling system several times in turn - this will help the fluid fill the system and displace air from it. As the coolant level in the expansion tank drops, bring the level to normal and screw on the tank cap. When the engine warms up, the outlet (lower) radiator hose should be cold for some time, and then quickly heat up, which will indicate the beginning of fluid circulation in a large circle. After waiting for the cooling system fan to turn on, stop the engine. After the engine has cooled, check the coolant level again and, if necessary, replenish the system.
Analogues of parts for Lada Vesta and their advantages
- Luzar, produced in Ukraine. The advantages of luzer are that the heating system begins to heat up better and faster. And replacing the thermoelement becomes much easier, you only need to unscrew two bolts and the element on your hands, you don’t need to remove a lot of pipes.
- Pekar article 21900100000000000, manufacturer Russia. It does not have a thorough design, so it does not retain the heat of the engine well.
- The automagnet is designed with new valves that release antifreeze in doses. Almost never overheating.
- Pramo article number 2108210000000000000, although often used, has many negative reviews. Sudden opening of valves and others. Produced in Russia, China.
In order for the thermoelement to last a long time, it is necessary to use antifreeze recommended by the manufacturer. Replace breakdowns only with high-quality auto parts, only from the manufacturer of original parts. Don't buy fakes. Replace broken parts in a timely manner. When operating an engine with a broken spare part, the operating temperature of the engine differs sharply. That is, there are jumps from 79 to 95 degrees, and this can negatively affect the operation of the motor in the future and shorten its service life.
Operational problems
The main malfunctions identified during the operation of vehicles in this configuration include:
- problem with the cooling system due to insufficient thermostat reliability
- problem with the ignition system due to faulty ECM units
- problem with bending valves when the timing belt breaks
The knocking sound of hydraulic lifters, which disappears as it warms up and reaches operating temperature, is considered normal.
The most expensive repair is associated with engine overhaul when the timing belt breaks and the valves are bent. The modified design of the pistons, with a hole in the bottom, does not provide sufficient distance to prevent the open valves from hitting the bottom.
Maintenance 45,000 kilometers for Lada Vesta
In terms of the amount of work and materials, maintenance for 45,000 kilometers of Lada Vesta is the same as for 15,000 kilometers. However, if the owner of a Lada Vesta undergoes regular maintenance based on mileage, and not on time, for example, a year after the previous visit, then it will be necessary to change the brake fluid.
This maintenance also includes a large number of diagnostic work. Official service workers will be required to check the functionality of all systems and the tension of the generator belt. They also check the level of all fluids and the density of the electrolyte in the battery. In our example of the Lada Vesta sedan, it turned out that some battery banks had a low electrolyte density. It is worth noting that the Lada Vesta model comes from the factory with a battery from an unknown manufacturer. There is not a single badge stuck on its black body. This battery is less than a year old. Exactly the same amount for the Lada Vesta that we brought for service.
After lifting the Lada Vesta car on a lift, we were able to examine the condition of the Nokian Nordman 5 winter tires. We bought them immediately after purchasing the car and installed them. Accordingly, they have gone through one incomplete winter, and they are already missing half the number of thorns.
Tuning
Thanks to the standard design, the 21129 motor has a potential of 150 hp. The most popular modernization of internal combustion engines is in the following ways:
- tuning of the block and cylinder head - boring the cylinders up to 88 mm maximum, grinding the head channels, installing lightweight pistons;
- tuning of the intake tract – 54 mm damper instead of the standard one, filter with zero air resistance;
- tuning of the exhaust tract - spider at the exit;
- timing modernization - modification of 8.9 Stolnikov camshafts with mandatory phase adjustment.
VAZ engines are turbocharged with rotary compressors, superchargers or mechanical turbines. However, inertial mechanical pressurization is already present inside the standard receiver, so this option is not economically viable.
Thus, the Euro 5 standard has been achieved in the 21129 engine without increasing power and making special design changes to the basic version 21127. The M 86 control unit of the next firmware version is used. The valves are not protected from bending by the pistons, the overall user rating is +4.
Replacing DTOZH
Sensor catalog number – 21120385101005
The issue of replacing the sensor should be raised if there are significant problems indicating its malfunction. Replacing the sensor is carried out in several simple steps:
- First thing you need to do is drain the coolant
- disconnect the block with wires from the sensor
- unscrew the sensor using a 19 mm wrench
Installing the sensor is done in the reverse order and does not pose any special problems. However, in some cases, after installing a new sensor, a small leak may form, which will require replacing the copper nut or applying a temperature-resistant sealant to the sensor threads.
Coolant temperature sensor malfunctions
Sometimes, before it completely fails, the sensor gives incorrect readings - such a malfunction can also lead to the fact that you do not detect a serious breakdown in a timely manner (depressurization of the cooling system, failure of the cooling fan or pump, etc.). A faulty coolant temperature sensor has the following symptoms:
- The thermometer needle located on the dashboard does not rise when the engine is hot or goes off scale when the engine is cold.
- The non-standard position of the thermometer needle raises suspicion. There are two options here: either the coolant is really at that temperature, or the DTOZH is really “lying.”
- The on-board computer issues the corresponding error codes.
If you do not respond to a sensor breakdown in a timely manner, you may miss more serious engine breakdowns.
Motor VAZ 21179
This engine option was the first in the line with a volume of 1.8 liters. produced since 2022. Externally similar to competitors, but inside there are a lot of design features characteristic of the 179 model. Vesta with a 1.8 liter engine installed 21179. is much more dynamic and powerful than his less productive colleagues.
Characteristics of 21179 engine:
Power - 122 horsepower, spins up to 6050 rpm. The most powerful of our line. Volume - 1.8 l. It is assembled using a selective conveyor method. Drive and timing type - a German device from INA is installed for tensioning a toothed belt. The belt will need to be replaced after about 90 thousand km. Torque characteristics - 170/3750. Motor weight - 110.1 kg. Higher than competitors, but the difference is not noticeable. Block material is cast iron. Electronic ignition system controlled by a processor. The fuel used is similar to the previous version, AI-95 gasoline. Using a 179 engine, the car will accelerate to 100 km/h in 12 seconds. Fuel consumption: in the city - 10 l, mixed type of movement - 8 l, on the highway - 7 l. Toxicity - Euro5. No different from others, despite significantly different parameters. The running life is set at 300 thousand km, which significantly exceeds that of the 129 model.
As advantages of the engine, we note the following: - The 179 engine is installed on the long-awaited Lada Vesta Cross by many car enthusiasts. The power and driving characteristics are enough to not have any problems driving; — fast and confident driving and start from traffic lights;
— design feature for changing gas distribution phases; — lightweight and enlarged intake (31 mm) and exhaust (28 mm) valves were used; — standard AMT VAZ transmission is used. Some of the components were not made in Russia, but were manufactured by leading automakers. For example, the valves are made by Mahle, and the oxygen sensor is made by Bosch.
The disadvantages of the engine are higher fuel and oil consumption compared to the other two power plants. Valve bending (like other options in the line), resulting in a high noise level when operating in any gear. The last circumstance is typical for engines installed in Lada Vesta.
Purpose, principle of operation
The main purpose of the cooling system is to maintain a constant temperature so that the engine does not overheat.
An important role is played by the operation of the Lada Vesta 21129 engine thermostat. It is designed to switch from a small to a large circuit. When the thermostat is turned on, a large circuit is connected, where the liquid is cooled due to the counter flow of air passing through the heat exchanger.
A significant role is played by the electric fan installed behind the Vesta radiator. It is controlled by a signal from a sensor that is installed on the motor. When the set temperature is exceeded, a signal is given to turn it on.
The signal is given regardless of the position or presence of the key in the Lada ignition switch. An expansion tank is designed to compensate for the expansion of liquid in the Vesta cooling system. When both circuits operate correctly, the operating temperature of the Lada Vesta engine is maintained.
Interior ventilation diagram
Air ducts run from the stove body, which direct air flows to the windows, into the interior and legs. The central deflectors can adjust air flow in different directions, and its strength is controlled using a horizontal wheel underneath them.
AVTOVAZ has implemented airflow for the Vesta driver’s legs in a new way. The air duct nozzle is located not on the side, but above the foot of the right foot. Some owners of the new sedan believe that this design is not very successful, because It warms the toes worse than the foot itself. For the front passenger, the air duct exits closer to the wall of the engine shield and a similar situation will not arise.
Worth o. On versions of the car with air conditioning, a small air duct fits into the glove compartment, which can cool, for example, a water bottle.
Engine tuning
Initially, engine 21127 had already received factory tuning, but there were still opportunities to further increase power:
- In addition to the standard receiver, a damper with a diameter of 54 mm is mounted to achieve a performance of about 110 liters. With.;
- another 10 l. With. will be added by replacing the exhaust catifold with a “spider”;
- The Stolnikov camshaft modification 8.9 will provide power in the upper speed range.
Tuning 21127
Complex tuning is possible by installing a Stolnikov 9.15 camshaft with a phase shift of 316 degrees, replacing injectors with Bosch 431 360 (more efficient compared to standard ones) and milling the valve seat stages. In this case, the internal combustion engine will receive about 150 hp. With.
Thus, motor 21127 is an industrially tuned version of the previous internal combustion engine 21126. The characteristics are improved only by modifying the intake air system (damper inside the receiver plus DBP, DTV).
Fan drive types
Creating an intense air flow requires significant fan drive power. The energy for this can be taken from the engine in various ways.
Continuous rotation from pulley
In the simplest early designs, the fan impeller was simply slipped onto the water pump drive belt pulley. Performance was ensured by the impressive circumference of the blades, which were simply bent metal plates. There were no noise requirements; the nearby ancient engine muffled all sounds.
The rotation speed was directly proportional to the crankshaft speed. A certain element of temperature control was present, since with an increase in the load on the engine, and therefore its rotation speed, the fan also began to force air through the radiator more intensely. Deflectors were rarely installed; everything was compensated for by oversized radiators and a large volume of cooling water. However, the concept of overheating was well known to drivers of that time, being the price to pay for simplicity and lack of forethought.
Viscous couplings
Primitive systems had several disadvantages:
- poor cooling at low speeds due to the low speed of the direct drive;
- with an increase in the size of the impeller and a change in the gear ratio to increase airflow at idle speed, the engine began to overcool with increasing speed, and fuel consumption for the stupid rotation of the propeller reached a significant value;
- While the engine was warming up, the fan continued to persistently cool the engine compartment, performing exactly the opposite task.
It was clear that further increases in engine efficiency and power would require fan speed control. The problem was solved to some extent by a mechanism known in technology as a viscous coupling. But here it must be arranged in a special way.
The fan clutch, if we imagine it in a simplified way and without taking into account the various design options, consists of two discs with notches, between which there is a so-called non-Newtonian fluid, that is, silicone oil that changes viscosity depending on the speed of the relative movement of its layers. Up to a serious connection between the disks through the viscous gel into which it will turn. All that remains is to place a temperature-sensitive valve there, which will supply this liquid into the gap as the engine temperature rises. A very successful design, unfortunately, is not always reliable and durable. But often used.
The rotor was attached to a pulley rotating from the crankshaft, and an impeller was put on the stator. At high temperatures and high speeds, the fan produced maximum performance, which is what was required. Without taking up extra energy when airflow is not needed.
Magnetic coupling
In order not to suffer with chemicals in the coupling, which are not always stable and durable, a more understandable solution from an electrical engineering point of view is often used. An electromagnetic clutch consists of friction discs that touch and transmit rotation under the influence of a current supplied to an electromagnet. The current came from a control relay that closed through a temperature sensor, usually installed on the radiator. As soon as insufficient airflow was determined, that is, the liquid in the radiator overheated, the contacts closed, the clutch was activated, and the impeller was spun by the same belt through the pulleys. The method is often used on heavy trucks with powerful fans.
Direct electric drive
Most often in passenger cars, a fan with an impeller mounted directly on the electric motor shaft is used. Power for this motor is provided in the same way as in the described case with an electric coupling, only here a V-belt drive with pulleys is not required. When necessary, the electric motor creates airflow, turning off at normal temperature. The method was implemented with the advent of compact and powerful electric motors.
A convenient quality of such a drive is the ability to operate when the engine is stopped. Modern cooling systems are heavily loaded, and if the airflow suddenly stops and the pump does not work, local overheating is possible in places with maximum temperatures. Or gasoline boiling in the fuel system. The fan can run for a while after stopping, preventing problems.
Purpose, principle of operation
Cooling system The main purpose of the cooling system is to maintain a constant temperature so that the engine does not overheat.
An important role is played by the operation of the Lada Vesta 21129 engine thermostat. It is designed to switch from a small to a large circuit. When the thermostat is turned on, a large circuit is connected, where the liquid is cooled due to the counter flow of air passing through the heat exchanger.
A significant role is played by the electric fan installed behind the Vesta radiator. It is controlled by a signal from a sensor that is installed on the motor. When the set temperature is exceeded, a signal is given to turn it on.
The signal is given regardless of the position or presence of the key in the Lada ignition switch. An expansion tank is designed to compensate for the expansion of liquid in the Vesta cooling system. When both circuits operate correctly, the operating temperature of the Lada Vesta engine is maintained.