Hydraulic compensators of the Lada Vesta car are used to automatically adjust the valves. If they weren’t there, it would be necessary to adjust the valves every 10 thousand, like on a nine. Again, as in all previous VAZ engines, the knocking of hydraulic compensators when cold in a Lada Vesta car has not gone away. It is so accepted that all Vaz’s diseases are transmitted along the genetic hereditary line. On some cars, hydraulic lifters knock when cold and hot when the engine is warmed up. Lada Vesta did not leave either ordinary car enthusiasts or car critics indifferent. Usually a specific hydraulic compensator, or several at once, knocks in the engine. Some car owners, after a couple of thousand kilometers, began to worry about compensators.
Lada Vesta makes a knocking sound from the hydraulic compensators when it’s cold - when you start the car in the morning. Like any other sound (especially coming from the engine) in a car, knocking is very frightening - thoughts about major repairs begin to appear.
The dealer, while checking, warmed up the car for a couple of tens of minutes and, if the knocking did not stop, agreed to warranty repairs.
Many drivers had hydraulic lifters knocking only when cold, and the dealer refused to repair them under warranty. In order not to “kill” the engine of your favorite car, let's figure it out in order.
Problem
As sad as it is to realize, West owners are not spared this problem either. Many owners notice knocking noises under the hood of the Lada Vesta, and they come from the right side.
As a rule, you don’t have to search for long, since the situation is well known. It appears on sedans that were equipped with engine mounts from the VAZ 21129. As a result, a whole cacophony of sounds began to be heard from the engine compartment, including knocks, clicks, squeaks, etc. Moreover, these sounds are so loud that they can be heard even in the cabin.
The knock from the support is quite loud
And the best confirmation of this is numerous videos in which owners of the domestic model demonstrate trouble.
And in this video you can hear knocks directly inside the car.
In addition, some owners began to “dig deeper” and found out that a similar situation occurs not only on Vesta, but also on other models of the Renault-Nissan Alliance. In particular, on the Nissan Qashqai. This is also confirmed in the video.
As for the Lada X-Ray, the hatchback has not noticed such a problem, even though its engines are the same as those on the sedan. The whole point is that X-Ray is equipped with different supports for the power unit.
Catalog number and cost
The appearance of extraneous noise in the engine does not mean that a major overhaul of the power unit is necessary.
The cause may be faulty hydraulic compensators. If the car is not under warranty, the owner will have to replace this element.
Knock of hydraulic compensators on Vesta
You can prepare in advance and select an element in a spare parts store, indicating the article number. Catalog number – 21120-1007300-01. The price of one part is 250 rubles. The service center will inform you whether repair or replacement is needed and indicate the quantity that needs to be purchased.
Solution options
In fact, there are several of them.
Contacting the dealership
In the event of a visit to the dealer, there is, as a rule, no clear solution to the issue of knocking from under the hood of the Lada Vesta. It all depends on the specific salon. Some centers simply refuse to replace them, citing the fact that this is not a warranty case. Others sent information about the defect directly to AvtoVAZ, but this is a rather lengthy procedure, and therefore not everyone agrees to wait that long. And the answer is not always positive.
Many dealers refuse to replace the airbag under warranty.
But even if the dealer agrees to make a replacement, things don’t always go smoothly. The fact is that often a part is replaced with a similar one, although managers in the salon assure that it is already from a different batch. The result is the same - literally after a few thousand kilometers the sound returns.
However, some owners note that they had reinforced supports installed, after which the problem disappeared.
Independent actions
Do-it-yourself Lada Vesta engine mount replacement
Some car owners who have encountered a knocking noise from under the hood of their Lada Vesta decide to replace the support themselves, so as not to waste time traveling to the dealer and waiting for AvtoVAZ’s decision.
Sometimes you have to change the support yourself
The process itself is not too complicated and we will look at it in a separate article. However, in this case it all depends on the part purchased.
Sometimes the source of knocking under the hood of a Lada Vesta is not the support itself, but the bolt that secures it. Moreover, according to some owners, if you simply tighten it, the knock will soon be heard again. In this case, you have to add a grower.
Using Lubricant
As practice and numerous attempts to solve the problem have shown, getting rid of the knocking noise under the hood of the Lada Vesta is quite simple. It is necessary to lubricate the support itself with silicone grease - directly in those areas where the rubber of the support comes into contact with the metal. Some people use WD-40 liquid for this, but it is not recommended to use it, as it washes out too quickly - it lasts literally for a day.
After this manipulation, the knocking stops, which is recorded on video.
Source
Design and function of hydraulic compensators
Many car enthusiasts do not know whether the Vesta has hydraulic compensators. Lada Vesta is equipped with a 16-valve engine 21129 with a volume of 1.6 and 1.8 liters. Both power units have camshafts - intake with 8 hydraulic pushers and exhaust also with 8 elements.
The function of hydraulic compensators is to automatically adjust the gap between the valve and the camshaft of the car. The fundamental difference from previous generations of VAZ engines is that it was necessary to adjust the thermal gap every 10-15 thousand kilometers.
AVTOVAZ recommendations for determining the causes of engine knocking
One of the reasons why customers contact the LADA dealership is the appearance of knocking noises in the engine. To determine the causes of extraneous noise, recommendations were sent to PSSS specialists (since there are relatively frequent complaints about piston knocking, further emphasis is placed on the pistons).
1.
Open the hood of the car, ask the client to demonstrate a non-functional knock. If there is engine knocking, go to step 2.
2.
Using a stethoscope, localize the location of the knock by sequentially listening to the lower and upper parts of the cylinder block in the area of all cylinders. Ideally, this is how you can identify a “knocking” cylinder. Regardless of the success of localizing the knock, proceed to step 3.
3.
Make a high-quality video recording with the sound of knocking, for example, on a smartphone. In the video, first remove the car (so that the model is clear), then its registration plate, then remove the running engine (the mode in which it knocks) with the hood raised. Video duration is from 15 to 30 seconds.
4.
Assess how the knocking noise changes when the “knocking” cylinder is turned off (by turning off the spark plug of a given cylinder). If it was not possible to localize the knocking in step 2, then turn off all cylinders one by one.
5.
Describe the diagnostic work and send a video file with a recording of the non-functional knock to the factory. Wait for further instructions from the specialists of PJSC AVTOVAZ.
6
. After receiving instructions from the specialists of PJSC AVTOVAZ to disassemble the engine, remove it from the car and disassemble it, remove the pistons.
7.
Take photos of the pistons and cylinders using the procedure below:
A)
Gently wipe the surface of the cylinders and pistons from liquid oil, DO NOT TOUCH hard carbon deposits and varnish.
b)
Using a dark colored marker (or felt-tip pen), mark the piston/cylinder number, front/rear part of the cylinder, loaded/unloaded side of the piston/cylinder. Examples of markings are shown in all photos below. Mark the cylinder number on the top of the piston with a sharp metal object. The loaded side is the release side, indicated by stripes. The unloaded side is the inlet side for 16 cells. ICE and spark plug side for 8 cells. ICE is indicated by dots. The points between the cylinders indicate the direction towards the front of the engine. An example of a marked cylinder block is shown below.
V
) Clean (if necessary) the lens of your camera or smartphone.
G)
Focus the camera and take a photo according to the sample photo. If necessary, take as many photos as required for a sharp shot.
In the photo below, the pistons are separated from the connecting rods and are standing on a table.
If the pistons are assembled with connecting rods, then place them on the table surface and photograph from above.
An example of correct cylinder block markings
: stripes – loaded side; dots – unloaded side; arrows or ticks indicate the direction to the front of the engine; number of stripes and dots – cylinder number.
Photo of the 2nd cylinder, loaded side.
The two red stripes at the top of the photo mark the loaded side (black arrow).
The two red dots at the bottom of the photo mark the unloaded side (yellow arrow).
The red tick on the right marks the rear of the engine (blue arrow).
The red tick on the left marks the front of the engine (green arrow).
Photo of the 2nd cylinder, unloaded side.
Photo of the 2nd cylinder, front side.
Photo of 2nd cylinder, rear side
Photo of the 2nd piston, loaded side (two black stripes on the skirt at the top right)
Photo of the 2nd piston, unloaded side (two black dots on the skirt at the top right)
Photo of the 2nd piston, back side (two black dots on the skirt at the top left)
Photo of the 2nd piston, front side (two black stripes on the skirt at the top left)
Photo of the 2nd piston, top view (the number “2” means the second cylinder)
Photo of the 2nd piston, bottom view.
8
. Measure the diameters of each cylinder in a section perpendicular to the axis of the crankshaft, in zones 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 and 100 mm from the mating plane of the block with the cylinder head (see photo below) with an accuracy of 0.001÷0.005 mm (the specified measurements are for installed piston groups from Federal Mogul).
9
. Measure the diameters of the skirts of each piston at a distance of 10 mm from the lower edge of the skirt (see photo below) with an accuracy of 0.001÷0.002 mm. Record it in the protocol. The pistons of the VAZ-21179 1.8 l engine - 16 cl (only these) have a special window on a graphite coating at a distance of 10 mm from the lower edge of the skirt. If the measuring instrument allows you to take measurements in a window without affecting the graphite, then be sure to indicate “measurement for metal” in the protocol.
10
. Send photographs and measurement reports of pistons and cylinders to the factory. Wait for further instructions from the specialists of PJSC AVTOVAZ.
Let us remind you that we previously published a collection of Technological Instructions (for Lada Vesta, XRAY, Granta/Kalina, Largus), which will help you service your car with your own hands.
Source
Knock - connecting rod bearing - Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas, article, page 1
Knock - connecting rod bearing
The knocking sound of the connecting rod bearings (dull knocks) is heard throughout the entire height of the block and disappears when the fuel supply is reduced. It appears as a result of wear of the crankshaft bearings and connecting rod journals.
The knock of the connecting rod bearings is sharper than the knock of the main bearings. It is heard when the engine is idling with the gear shift lever in neutral and intensifies with increasing crankshaft speed. The knocking of connecting rod bearings can be easily determined by disconnecting the spark plugs one by one by removing the tips with high-voltage wires from them.
The knock of connecting rod bearings is somewhat different than that of main bearings. It is usually rhythmic, mid-tone and the zone 2 listening is slightly higher than the main bearings. The knocking noise of connecting rod bearings increases significantly with increasing load. It can also be eliminated by replacing the liners at a service station.
The knock of connecting rod bearings is sharper than that of main bearings. It can be heard at idle and depends on the engine speed. To determine which bearing is faulty, you need to turn off one of the cylinders in turn, removing the high voltage wire from the spark plug. The reasons that cause knocking of connecting rod bearings are similar to those stated above.
Typically, connecting rod bearing knocks have a metallic tone that is harsher than main bearing knocks. The knocking sound is heard when the engine is idling and when the gearshift lever is in neutral position and intensifies with increasing engine speed. The knocking of connecting rod bearings can be easily determined by turning off the spark plugs one by one.
Usually the knock of the connecting rod bearings is sharper than the knock of the main bearings. It can be heard when the engine is idling when the throttle is opened sharply.
When fuel burns in engines with a high compression ratio, knocking noises reminiscent of connecting rod bearings are observed.
A dull knock that increases with a sharp increase in crankshaft speed is a sign of wear on the main or connecting rod bearings. The knock of the connecting rod bearings is somewhat less powerful than the main ones, and is heard through the wall of the cylinder block in the areas corresponding to the upper and lower positions of the crankshaft cranks.
This knocking indicates an increased clearance in the bearing and is detected when there is a sharp change in the engine crankshaft speed.
The knock of the connecting rod bearing, usually less powerful than the knock of the main bearing, is heard through the block wall in the area corresponding to the upper and lower positions of the piston pin. The appearance of a knock in the connecting rod bearings also indicates an unacceptable increase in the gap between them and the shaft journals. The knock of the piston pin is heard in the upper half of the cylinder and through the cylinder head.
An experienced driver can distinguish a knock when the main bearings are worn from a knock when the connecting rods wear. It is usually rhythmic, sonorous, metallic, and mid-tone. The knocking noise of connecting rod bearings increases significantly with increasing load, and disappears when the ignition is turned off. Eliminate the knocking of connecting rod bearings by replacing the bearings.
The knock of the connecting rod bearings is sharper than the knock of the main bearings. It is heard when the engine is idling with the gear shift lever in neutral and intensifies with increasing crankshaft speed. The knocking of connecting rod bearings can be easily determined by disconnecting the spark plugs one by one by removing the tips with high-voltage wires from them.
The knock of connecting rod bearings is somewhat different than that of main bearings. It is usually rhythmic, mid-tone and the zone 2 listening is slightly higher than the main bearings. The knocking noise of connecting rod bearings increases significantly with increasing load. It can also be eliminated by replacing the liners at a service station.
Pages: 1 2
www.ngpedia.ru
For what reasons do hydraulic compensators knock on Lada Vesta: fault diagnosis
Sounds and background
Poor maintenance of the engine oil system can cause knocking of hydraulic compensators in Lada West even at low mileage. Unsuitable oil viscosity or untimely replacement of it are direct preconditions for the appearance of clattering noise from “hydrikis” in the near future.
Not all owners correctly recognize a specific engine knock when they hear it for the first time. Meanwhile, the hydraulic modules rattle identically to a running diesel engine. To be more precise, the sound is similar to the acoustic design of a functioning injection pump of a diesel or gasoline engine with direct injection.
Simply recording the presence of a knock will not help identify the cause of the problem. It is necessary to find out how hydraulic modules behave:
- Hot.
- To the cold.
- At different speeds.
It will become clear later that these circumstances are important in determining a strategy for eliminating tapping.
Knocks when cold
A sudden clattering noise should not always be regarded as a breakdown. This fully applies to the case when the sound appears briefly when starting a cold engine - literally for 1-2 seconds. Such a reaction only indicates the bleeding of oil from the hydraulic tappets due to long-term parking, but does not in any way indicate problems with the oil supply to the hydraulic compensator unit during operation of the power plant.
Longer tapping when cold is unacceptable. The prerequisites for violation of the operating mode are identical to the reasons for the clattering of hydraulic compensators on the Lada Priora, of which there are several:
- Insufficient pressure in the oil system (oil pressure lamp is on).
- Excessive contamination with wear products or mediocre quality of the oil composition.
- Oil of inappropriate viscosity: it is impossible either to push the fluid through small channels or to maintain the specified pressure.
- Coked holes in the oil system lead to knocking from the hydraulic compensators of the Lada Vesta engine due to a decrease in pressure inside them.
- Hydraulic pusher wedge due to carbon deposits.
- Wear of the plunger pair, leading to oil emulsion leaks.
Tapping on hot
Vest owners sometimes notice that when the engine is cold, it whispers, and as it warms up, a clattering sound occurs from the hydraulics. Such a symptom can appear for any of the above “cold” reasons. However, more often the knocking of hydraulic compensators on a hot engine has its own prerequisites:
- Incorrect oil level. Engines equipped with hydraulic compensator devices are quite sensitive to foaming of the oil composition, which occurs when the lubricant is overfilled. Underfilling is also fraught - the oil pump will pick up air.
- The increase in landing areas for hydraulic pushers is the result of overheating of the cylinder head.
Rough operation of the engine at idle
The engine shakes (the gear shift lever shakes). Consequence of wear of the cylinder-piston group (pressure difference in the cylinders).
There may be malfunctions of the power supply system and (or) the engine ECU.
It can be eliminated by flushing the injector (cleaning the injectors), replacing high-voltage wires, spark plugs, ignition coils, or checking and adjusting the electronic engine control system (ESC) (you need computer diagnostics of the engine, determination of fault codes, and from them identification of a faulty engine ESC module (sensor) (in such cases, “CHECK” usually lights up).
If the power supply and (or) ignition system and ESU (electronic control system) of the engine are in order, then
Costly repairs can be avoided by timely replacement of engine rings. In this case, it is possible that the block is bored or the engine block is lined (in case of uneven critical wear of the cylinder).
Detailed diagnostics: structural component of knocking
Guided only by a thermal sign, it will not be possible to find out exactly why the hydraulic compensators are knocking. An additional set of tests is required. Its essence is to analyze changes in the acoustic design of the Vesta engine, changing the speed and taking into account the temperature of the coolant.
Operating with revolutions
The testing stages boil down to analyzing the operation of the motor in various modes:
- A knocking sound when cold or hot, which disappears at high speeds, indicates wear of the ball valve of the hydraulic module or its clogging with wear products. Option No. 1 - change the oil and oil filter to ones known to be suitable for the 129 engine. As a last resort, replace substandard hydraulic compensators.
- A clattering sound exclusively on a hot engine, which goes away with increasing speed, indicates a critical condition of the plunger pair. It can only be eliminated by replacing the compensator assembly.
- Tapping noises are heard only at high speeds, regardless of engine temperature, and at idle the engine operates smoothly - check the oil level. It is advisable to fill slightly above the average dipstick level, without exceeding the MAX mark. A damaged oil pickup has a similar effect.
Consequences of ignoring a fault
The main prerequisite for troubleshooting is intrusive extraneous noise. Few people know what the real danger of tapping is. Excessive clearances in the timing belt affect the operating mode of the cams: the resulting shock loads significantly reduce the service life of the crankshaft.
What does the color of the exhaust smoke indicate?
The color of smoke from the exhaust pipe can be white, black, and other shades (depending on the additives in the fuel and the type of fuel itself). In this case, color serves as an important diagnostic sign and directly indicates malfunctions that have arisen in the engine. White smoke on a warm engine is 100% wear of the valve stem seals (determined by oil deposits on the spark plugs and (or) oil consumption) and (or) valve guides, and white smoke is also a sign of wear of the oil scraper rings of the engine piston group (checked by measuring engine compression) .
You can avoid costly repairs by promptly replacing oil seals, valve guides, and engine rings.
How to eliminate the knocking of hydraulic compensators on Lada Vesta using auxiliary means
The manufacturer sets the service life of hydraulic compensator mechanisms for the entire period of operation of the motor. There are no routine maintenance activities for these units. By filling in high-quality lubricating fluid and knowing how often to change the engine oil, problems with hydraulic tappets can be avoided.
Use proven lubricant
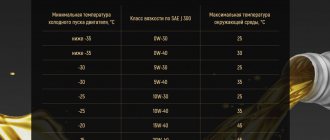
At the first appearance of knocking, attempts are often made to change the oil composition. Well, the action is justified both when recording the fact immediately after replacing the emulsion, and as an early prevention of coking of the hydraulic pushers. It is important not to deviate from the factory viscosity standards:
But this is not enough. A good product will be one that, according to reviews, is problem-free for the VAZ 21129. Since the development is still young and little technical information has been collected on oils, you can use the database for 126 and 127 sixteen valves. For example, Shell Helix Ultra 5W-40 was not suitable for them. Among the optimal lubricants were the following:
- Liqui Moly Optimal Synth.
- Mobile Ultra.
- Total Quartz Energy 9000.
- Wagner Windigo.
Additives
Additional auto chemicals are not used as the main solution to the problem. Its task is to delay repairs by several thousand km. Accordingly, it is advisable to use this method only in case of wear or damage to the expansion joints. Liqui Moly Hydro-Stossel-Additiv and XADO products can be considered as additives.
The engine knocks while driving: what should the driver do?
When you experience engine knocking, the first thing you need to do is check the engine oil level. The appearance of a knock may well be due to a drop in pressure in the lubrication system. If everything is in order with the level, then at the initial stage it will be necessary to more accurately localize the fault, eliminating possible knocking noises from fuel equipment, drives, attachment pulleys, etc. Next, it is necessary to determine the nature of the knock, and also confirm or refute the fact that it intensifies under load. If, as the load on the internal combustion engine increases, the engine knocks more strongly, then most likely the problems have arisen in the crankshaft and the CPG.
If the knocking frequency is two times different from the crankshaft rotation speed, then problems with the timing belt are likely. This is because the crankshaft rotates twice as fast as the camshaft. Warming up the engine in such a case can lead to increased knocking, since with increasing temperature the valve clearances increase. As for the load on the internal combustion engine, the knock of the gas distribution mechanism usually does not depend on the operating mode of the engine. An exception may be hydraulic compensators, which knock more intensely under load.
When knocking occurs on a cold or hot engine, that is, depending on the temperature, you need to additionally take into account the possible expansion of worn parts as they warm up and a decrease in clearances (the knocking weakens). At the same time, the dilution of the heated oil can lead to increased knocking. The first case is typical for CPG, the second affects the bearings of the crank mechanism.
Based on the conclusions drawn about the nature of the knock, you can decide whether to go to the service center on your own or call a tow truck. Finally, we would like to add that increased knocking under load and its rapid progression when driving is a clear sign that it is better to refuse independent movement. In this case, the engine should be turned off to prevent further destruction of the power unit.
Oil filter
If it is clogged, then this is one of the reasons why the hydraulic compensators knock when cold. Extraneous sounds stop as the engine warms up. Then some of the lubricating fluid passes through the filter. However, in most cases, a miracle does not happen. The driver will hear a knock even when the engine is hot.
To get rid of this problem, you just need to replace the filter.
More experienced car enthusiasts constantly keep a “logbook”, where they write down the mileage when changing the oil, as well as the operation time. This helps a lot to complete it on time.
Comments • 12
The piston is recessed to prevent the valve from contacting the piston during normal operation. If the belt breaks, it will still bend.
@ Alexey Lyutych I do not dispute that I assembled the engine myself on many of my cars, but I agree that the factory grooves on the previous pistons are notched, so that when the engine is running they do not touch the valve. I replaced the piston from the factory by the Federal Piston Magnate, with STK deep grooves so that if the belt breaks, the pistons do not touch the valves
@cool friends I don’t want to argue, it’s long and tedious. Study the principle of engine operation and why excavations are being carried out, inform the car. After this, all questions will disappear.
The piston is at top dead center and I have turned the camshaft. The valve did not touch the piston. How can valves bend if the belt breaks?
@ Alexey Lyutych Have you seen this in practice?
@ cool friends the valve is still bent. The notches were made for a different purpose. It folds not only on 8-valve engines.
Because the robot has a pallet printed on it, and the fur has aluminum on it. Something wise! The grooved piston may have been installed for a long time. For this reason, many people have had to repair their engine.
Hi, could you tell me what size pistons you installed?
Something has overtaken the engine a little, Kent has 330 miles and is running fine so far.
@cool friends I understand, but with a stamped tray it doesn’t get warm in hot weather? Oil is 3 liters, and on Vesta 4 liters.
The engine was fine! But due to the fact that the first piston was hitting hot at idle, but when removing the head it was noticeable that the fourth one was also hitting, and because of this they began to beat
The only indicator of problems with the autoplay valve system is noise. It may sound cold or hot, at idle or at high speeds, or even completely distort engine noise throughout the entire operating cycle. The sixteen-valve VAZ 21129 engine is not immune from the manifestation of such symptoms in the early stages of operation. You can and should fight them, but first you need to know why they arise.
Adjusting the VAZ 2106 carburetor float and other repairs
The main malfunctions not only of this type of device, but of all carburetors in general are associated with frequent clogging of channels that have a rather small diameter. Here, as a rule, the calibrated holes and jets of the VAZ 2106 carburetor suffer from such a “disease”. In this case, there is a disruption in the idle speed, and this will also have the most negative impact on the functioning of the throttle valve and its other devices. A similar malfunction can be eliminated by washing and further purging all clogged channels.
If they are also found to be leaking, then such parts should be urgently replaced. This failure may be caused by the following reasons:
- any fastening connections have become loose;
- the integrity of the sealing rings or rubber gaskets is damaged;
- as a result of strong overtightening of screws, nuts and their fastenings, the carburetor covers were damaged or the diaphragm of the accelerator pump, starting device or throttle valve of the float chamber was deformed;
- Also, the possibility of natural wear of some elements of this part, such as a needle valve, etc., cannot be ruled out.
In this case, the way out will again be to replace the old spare part with a new one.
If the car behaves strangely on the road, does not gain enough power, drives poorly or may even stall, while gasoline consumption increases, then, most likely, it is necessary to adjust the float of the VAZ 2106 carburetor. After all, the reasons for such behavior can be an excessive fuel level , entering the float chamber, which leads to the throwing of candles, and its elementary shortage. In such a situation, not only the float, but also the needle valve should be correctly adjusted, and then trips will bring only the most positive emotions.
To solve the problem of how to adjust the idle speed on a VAZ 2106, you need to stock up on a set of driver’s tools, although one screwdriver is enough for this technological operation. On the Internet you can watch the “VAZ 2106 idling” video clip about carrying out adjustment work to stabilize the idling speed of the vehicle.
To adjust the idle speed of the “six” carburetor, a number of preparatory conditions must be observed. These include:
The operation is carried out only on the motor that has reached operating temperature (about 90 degrees Celsius).
The clearances of the timing valves and ignition contacts (with a contact system) must correspond to the required dimensions.
When adjusting the idle speed of a VAZ 2106 carburetor on a cold engine, the required result cannot be achieved. If there is no idle speed, it will appear only if the correct adjustment conditions are met.
If the VAZ of the “sixth model” stalls at idle, then to find out how to adjust the idle speed, you need to use the following algorithm:
The process of adjusting the idle speed on a VAZ 2106 car is carried out using two screws for adjustment, the first is the quality screw, the second is the quantity of the mixture.
In accordance with the factory parameters, the quantitative adjusting screw is locked with a sealed limiter sleeve. To carry out adjustments and when there is no idle speed on the VAZ 2106, the seal is removed and adjustment work is carried out.
Using a high-quality screw, we achieve a value of 900 rpm, checking the value with the tachometer readings.
Using the quantity screw, we use a gas meter to set the carbon monoxide value in the range of 0.6-1.3 percent. The circular movement of the adjusting screw changes the number of rotations of the crankshaft of the power unit.
In this situation, we re-fix the required crankshaft speed parameters with the first screw. If everything is done correctly, then when you sharply press and lower the accelerator pedal, the rotation value should remain stable.
If all operations are performed correctly, there should be a smooth increase in engine speed and the unit should operate stably.
Sources
- https://carnovato.ru/vaz-2106-karbjurator-regulirovka-poplavka/
- https://vz06-up.ru/dvg/holostoj-hod-vaz-2106.html
Replacing elements
Specialized websites will provide assistance when changing compensators. Many resources post videos explaining why the hydraulic compensators on the Vesta are knocking.
Replacing hydraulic compensators on Vesta
Only an experienced auto mechanic can replace hydraulic compensators. This work requires dismantling many components of the Lada Vesta engine. It is rational to carry out repairs together with the replacement of other worn timing elements - belt, pump, rollers, having purchased the necessary spare parts in advance.
The work is performed in the following sequence:
- The car is installed on a level surface.
- The battery terminals are disconnected.
- The plastic engine cover is removed.
- The intake manifold is dismantled and the 4 holes are tightly closed with a rag.
- The crankcase ventilation hoses are removed.
- The valve cover is removed.
- The hydraulic compensator clearance is tested with a feeler gauge to identify elements that require replacement.
- The timing belt and rollers are removed.
- The camshaft gears are removed.
- The bolts holding the main bearing beds are unscrewed.
- The camshaft housing plate is removed.
- The shafts are removed.
- The body plate is cleaned of carbon deposits and old sealing agent.
- Compensators to be replaced are removed.
- New elements are cleaned of technological lubricant and installed in the cylinder head cups.
Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
When installing the housing plate, sealant is applied to the degreased surface of the part. The bolts are tightened in the prescribed order with the recommended tightening torque.
If there is a knocking sound from the hydraulic compensator, there is no point in waiting for the situation to worsen. The problem needs to be solved. This will avoid costly timing belt repairs.