The task of the fuel system is high-quality, timely and complete supply of gasoline to the engine, as well as storage and purification of fuel.
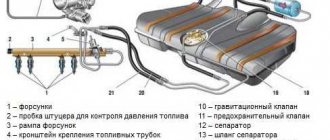
Structurally, the system consists of a fuel filter, injection system, fuel pump, tank and other elements connected by conductors.
In this case, the main function is performed by the fuel pump - it creates the necessary pressure in the fuel rail. If it decreases, serious malfunctions in engine operation are possible.
Checking the pressure in the fuel rail yourself
In order to perform the test, you will need a pressure gauge with a maximum value of 7-10 atmospheres. I do not recommend using a more powerful pressure gauge, since it will have a large error when measuring small pressure.
In addition to the pressure gauge, you must have a hose with an internal diameter of 9 mm, as well as tow (which is used for plumbing work). This will ensure a tight connection. Next, we strengthen all the joints with special clamps. If you don’t have the desire to “tinker,” you can buy a ready-made device for measuring pressure in the ramp.
Signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator
There are five main symptoms of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator (both types), which can be used to judge the complete or partial failure of this important unit. Moreover, the symptoms indicated below are typical for cars with both gasoline and diesel engines. However, it is worth mentioning that the listed situations may be signs of failure of other engine components (fuel pump, clogged fuel filter), so it is advisable to carry out comprehensive diagnostics in order to accurately determine its performance. So, the signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator are as follows:
- Difficulty starting the engine . This is usually expressed in a long rotation of the starter with the accelerator pedal depressed. Moreover, this sign is characteristic under any external weather conditions.
- The engine stalls at idle . To maintain its operation, the driver must constantly apply gas. Another option is that when the engine is idling, the speed is usually “floating”, unstable, until the engine stops completely.
- Loss of power and dynamics . Simply put, the car “does not pull,” especially when driving uphill and/or when loaded. The dynamic characteristics of the car are also lost, it accelerates poorly, that is, when trying to accelerate, a deep drop in revolutions occurs at their high values.
- Fuel is leaking from the fuel hoses (rail) . In this case, replacing hoses (clamps) and other nearby elements does not help.
- Excessive fuel consumption . Its value will depend on both the breakdown factors and the engine power.
Accordingly, if at least one of the above symptoms appears, it is necessary to perform additional diagnostics, including using an electronic error scanner available in the ECU memory.
Fuel pressure regulator error
Diagnostic errors of the fuel pressure regulator
In modern cars, a fuel pressure sensor is installed as a regulator. If it fails partially or completely, one or more errors associated with this unit are formed in the memory of the electronic engine control unit. At the same time, the engine malfunction light is activated on the dashboard.
When there is a DRT malfunction, the driver most often encounters errors numbered p2293 and p0089. The first is called “fuel pressure regulator - mechanical failure”. The second is “the fuel pressure regulator is faulty.” For some car owners, when the corresponding regulator fails, errors are formed in the ECU memory: p0087 “the pressure measured in the fuel rail is too low relative to the required one” or p0191 “fuel pressure regulator or pressure sensor.” The external signs of these errors are the same as the general signs of failure of the fuel pressure regulator.
, Scan Tool Pro Black Edition, will help you find out if there is such an error code in the ECU memory.
. This device is compatible with most all modern cars with an OBD-2 connector. It is enough to have a smartphone with an installed diagnostic application.
You can connect to the car control unit via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. Scan Tool Pro, having a 32-bit chip and easy to connect to, reads and stores all sensor data not only in the engine, but also in the gearbox, transmission, or auxiliary systems ABS, ESP, etc. It can also be used to monitor fuel pressure readings in real time, which it transmits to the vehicle’s ECM while performing a series of checks.
Step-by-step instructions - how to check the pressure in the fuel system
Important note! Before checking the pressure in the fuel system, make sure that it is intact and not depressurized, otherwise your measurements will not be accurate.
- First of all, open the hood and turn off the ignition.
- Then we find the fuel rail of the injectors.
- We unscrew the plug of the fuel pressure fitting and, using the spool, unscrew the nipple.
- Prepare some kind of rag or utensil for residual fuel that may splash (Be careful with your eyes!).
- Connect the hose of our device to the fitting and secure it using the same clamp.
How does the fuel pressure regulator work?
Structurally, the old-style valve (installed on gasoline cars) has its own body, inside which there is a valve, a membrane and a spring. The housing has three fuel outlets. Through two of them, gasoline passes through the pressure regulator, and the third outlet is directly connected to the intake manifold. At low (including idle) engine speeds, the fuel pressure in the system is low and it all goes into the engine. As the speed increases, the corresponding pressure increases in the manifold, that is, at the third terminal of the RTD, a vacuum (vacuum) is created, which, at a certain value, overcomes the resistance force of its spring. This creates the movement of the membrane and the opening of the valve. Accordingly, excess fuel gains access to the second outlet of the regulator and goes back into the fuel tank through the return hose. Due to the described algorithm, the fuel pressure regulator is often called a check valve.
As for the fuel pressure sensor, it is a little more complicated. So, it consists of two parts - mechanical and electrical. The first part is a metal membrane that bends under the influence of force caused by pressure in the fuel system. The thickness of the membrane depends on the pressure for which the fuel system is designed. The electrical part of the sensor consists of four strain gauges connected according to a “Winston bridge” circuit. Voltage is applied to them, and the more the membrane bends, the greater the output voltage from them will be. And this signal is sent to the ECU. As a result, the electronic control unit sends the appropriate command to the pump so that it supplies only the amount of fuel required at the moment.
Diesel engines have a slightly different fuel pressure regulator design. In particular, they consist of a solenoid (coil) and a rod, which rests against the ball to shut off the reverse flow. This was done for the reason that the diesel engine vibrates very strongly during its operation, which affects the wear of the classic (gasoline) fuel regulator, that is, partial and even complete compensation of hydraulic vibrations occurs. However, its installation location is similar - in the engine fuel rail. Another option is on the fuel pump housing.
What pressure should the fuel system have?
- When the ignition is turned on, the pressure in the system should be ~ 3 atm no less.
- At idle, the device should show ~ 2.5 atm.
- When the fuel pressure regulator tube is removed, the pressure gauge should show ~ 3.3 atm.
- With a pinched drain tube in a working ramp there will be ~ 7 atm.
- Podgazovka should increase the pressure to 3 atmospheres, then decrease to 2.5 atm.
- After the fuel enters the system, turn off the ignition and watch what the pressure gauge shows. In a working rail, the pressure should drop to 0.7 bar, and then stabilize at this mark.
- If the pressure instantly drops to zero, the fuel pressure regulator (FPR) is most likely faulty. The RTD will need to be removed and replaced, or the check valve of the fuel pump motor will have to be replaced.
- Increase the rpm to 3000 and watch the pressure gauge needle; if it goes down, you definitely have a problem with the fuel pump.
- If the fuel pump does not create the required pressure for a long time, the mesh or fuel filter of the fuel pump is most likely clogged.
- If none of the above options are confirmed, a more detailed diagnosis is most likely required, which includes checking: TPS, IAC, mass air flow sensor, as well as compression in the engine cylinders.
Source:
Regulator location
It is located in the side and at the top of the ramp; you can see its location in more detail in the photo below. The regulator is indicated by two arrows: the red arrow shows its approximate location, and the blue arrow shows the regulator itself. It is easy to find and quite simple and quick to change.
Where is the fuel pressure regulator on the VAZ 2115
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0087 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light) illumination. It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
- The Check Engine Light comes on and there may be more than one code present, such as a lean or rich code coming from the oxygen sensor.
- The vehicle may misfire due to lean fuel, rough driving, or lack of power when accelerating. This may be more obvious at higher RPMs when more fuel is required. There may also be a too lean error code sent by the oxygen sensor.
- A faulty sensor can cause the PCM/ECM to command more fuel, resulting in rich fuel, which in turn results in poor fuel economy. There may be a fault code from the oxygen sensor indicating that the fuel mixture is too rich.
Location of the regulator in the fuel tank
The RTD is placed directly in the fuel tank in systems that do not have a return line. The advantage of such a system is the absence of an additional pipeline. The required volume of fuel is supplied directly from the tank, that is, excess fuel does not accumulate in the engine compartment, and accordingly, there is no need to send it back to the tank. Thanks to this design, the fuel does not overheat and evaporates less, which is an additional advantage.
Messages 16
1 Topic by denisby4kov.77 2015-06-22 23:57:56
- denisby4kov.77
- New member
- Inactive
- Registration: 2015-06-22
- Messages: 6 Thanks : 0
Topic: no pressure in the fuel rail (filter, pump and regulator replaced)
Hello. Such a problem - I was driving and began to tune the engine. I got to the garage and that was it. It starts, just under the throttle it stalls. I made a mistake on the fuel pump, I bought a pump motor and a filter. everything has been replaced. the problem has not gone away. I suspect a pressure regulator. purchased and replaced. the same. on the fuel rail there is a fitting for a pressure meter - so, I press the nipple on the fitting, three drops splash from there and that’s it. I suspect the injectors. who can tell me what?
2 Reply from 7491cm3x 2015-06-23 04:45:36
- 7491cm3x
- Connoisseur
- Inactive
- From: Norilsk
- Registration: 2015-01-29
- Messages: 467 Thanks : 119
- Car: VAZ 2112 1.5l 16v
Re: no pressure in the fuel rail (filter, pump and regulator replaced)
Connect the pressure gauge, turn the ignition key and measure the pressure. I don’t remember how much there should be, but Google will help. If below normal, look for a leak. If the injectors are pouring so much pressure that the pressure drops below normal, you will hardly start the engine, because the spark plugs will be flooded to the brim. Is there a smell of gasoline anywhere? Has the fuel filter been changed recently? Mesh in the tank?
3 Reply from denisby4kov.77 2015-06-23 07:59:06
- denisby4kov.77
- New member
- Inactive
- Registration: 2015-06-22
- Messages: 6 Thanks : 0
Re: no pressure in the fuel rail (filter, pump and regulator replaced)
The fuel pump, mesh and filter are new + pressure regulator. After turning off the ignition, the sound is like a Kamaz is leaking excess air. from under the hood
conclusions
After reading this article, you can easily take measurements in the fuel rail and compare the results with standard indicators of serviceability in the fuel system.
The article will describe a testing technique that does not require special devices.
From the tool you will need:
- Any mechanical pressure gauge with a maximum reading from 6 to 10 atmospheres (0.6-1.0 MPa)
- 8 or 9 mm fuel or oxygen hose
- Cap for unscrewing nipples on the wheel
- Two clamps
- Pliers
1. We took a regular gas pressure gauge with a scale of up to 1.0 MPa. It has a threaded connection and screws perfectly onto a 9 mm oxygen hose. You can use a mechanical one to check tire pressure. They are usually inserted into the fuel hoses by 8 mm.
2. Screw it into the hose and tighten it with a clamp:
3. Unscrew the plastic cap from the fuel rail. It should unscrew by hand, but if it hasn’t been touched for a long time, you may need pliers:
4. If the car has just been turned off, then the gas in the ramp is under pressure. First, it is recommended to release the pressure by pressing on the spool and placing a rag or a plastic “bottle” with the neck cut off. It is more convenient to bleed using a wheel cap.
5. Unscrew the nipple with the cap. It is similar to a wheel nipple:
6. We put a hose with a pressure gauge on the threaded part and tighten the connection with a clamp:
7. Start the car and first of all make sure that there are no gasoline leaks from the connections. Then we look at the pressure gauge readings.
8. For fuel systems with “return” (a pressure regulator is installed on the fuel rail, from which a tube goes back to the tank), a pressure of 2.7 atm is considered normal (when re-gasping it should jump up to 3 atmospheres). However, a pressure of 2.5 atm is also acceptable. If the pressure is less, then the fuel system is faulty. Pressure pulsation (0.2 atm) indicates a clogged coarse mesh (located in the tank with the fuel pump).
9. Next, we check the pressure regulator. To check, disconnect the hose going from the regulator to the intake manifold. The fuel pressure should increase to 3.2 atm (at 2.7 initial). Up to 3.0 atm is also acceptable. If the pressure has not changed or changed only slightly (0.1-0.2 atm), then you need to check the fuel pump.
10. The maximum pressure developed by the pump is checked. To do this, use pliers to pinch the return fuel line (coming from the regulator). Different pumps show different pressures, but a new one should have at least 6 atm. A pressure of 5 atm indicates severe wear, but will still serve. If the pressure is less than 4.0 atm, the pump is faulty or the pipeline with the fine filter is clogged. If the fuel pump is working properly, and the pressure in the rail drops after the “return” is restored to less than 2.5 atm, and/or does not change when the regulator hose is disconnected, then the regulator is faulty. If, when the return line is pinched, the pressure rises slightly, and engine performance deteriorates significantly, then there is a high probability of injector leakage.
11. To eliminate the influence of the injectors, it is better to measure the pressure on the supply line itself by disconnecting it from the ramp and inserting it into a hose with a pressure gauge. If the pressure has risen to 5-6 atm, and with the “return” compressed it is significantly less, then the injectors are allowed to pass through. It is necessary to remove the ramp and check the condition of each individually.
12. You can check for clogging of the pipeline as follows. Remove the rear seat and unscrew the hatch. We see the fuel pump assembly underneath it. If the pipeline has quick-release connections, then we buy such a connection in the store (50 rubles).
13. If the pipeline is installed on threaded connections, you will have to buy the entire tube and cut off the tip:
14. Connect it to the pump outlet, and put a hose with a pressure gauge on the other end. Let's check the pressure again. If the pressure gauge readings increase to the normal 6 atm (after pumping gasoline several times by turning the key), then change the fine fuel filter and bleed (or flush the entire system).
15. Replacing the fuel filter is shown here:. The only difference is that after removing the filter, we direct the fuel supply hose into a plastic bottle (preferably transparent) and turn on the ignition with the key (the fuel pump turns on and fuel spills into the bottle). We inspect the condition of the fuel in the bottle. Then we install a new filter, remove the hose from the ramp and direct it into the bottle. We turn on the ignition several times and spill gasoline. We inspect the fuel in the tank again. If dirt is found after the filter, then washing the injectors is also required. We assemble the entire system and measure the pressure readings again. If the readings have not changed, then check the correct clamping of the “return” (you can try connecting a pressure gauge to the output of the regulator). If this does not help, then perhaps the blockage is serious and requires blowing with air under high pressure. It would be a good idea to check the entire pipeline from the tank for mechanical damage (dents, kinks).
16. Fuel systems without a return line are diagnosed in almost the same way. The main difference is that here the fuel regulator is located on the pump body. The fuel goes from the pump to the fine filter, and then goes to the regulator. Near the body, the fuel pipe bifurcates. One tip goes to the regulator, and the second goes to the fuel rail.
17. The main difference in the readings is the normal pressure at the ramp is 3.8 atm. When over-gassing it should jump up to 4 atmospheres. If the pressure is less, immediately check the pump. We connect a pressure gauge to the pump outlet and check the pressure. The pressure should also be at least 6 atm for a new one.
18. If the pressure is working, then check if the fuel filter is clogged. To do this, we restore the fuel line from the pump and connect to the tube suitable for the regulator. The easiest way to do this is to cut off the old tip from the fuel filter, install one end of it in a clip, and put a hose with a pressure gauge on the other. If the pressure is identical to the pump pressure, then the filter is clean. If a significant drop is visible, the filter must be replaced.
In this article we will consider the faulty state of the injector control system
and as an example, consider the fuel supply system.
How the fuel system works
Fuel is supplied to the ramp under excess pressure (6 atmospheres), which is created by the fuel pump.
Using the pressure regulator on the nozzle, a constant pressure drop of 3 atmospheres is maintained. At constant pressure and a linear characteristic of the injectors, the amount of fuel injected is determined by the duration of the injector control pulse. This is a theory. On a real engine, the pressure drop can be from 2.8 to 3.2 atmospheres. This is an acceptable range within which no deviations in engine operation are observed. Why is pressure variation possible? It is determined by the spread in the characteristics of pressure regulators.
How to check the fuel system?
Let's connect the pressure gauge to the fuel rail.
With the fuel pump turned on and the engine not running, the pressure should be 2.8-3.2 atmospheres. If the engine is idling, the pressure should drop to 2.2-2.5 atmospheres. When over-gassing, the pressure gauge needle should deviate into the zone of 2.8-3.2 atmospheres. Now let's check the operation of the injectors. With the engine not running, we will create the required pressure in the ramp (2.8-3.2 atmospheres), after which we will apply a series of test pulses to the first injector, monitoring the change in pressure. The above procedure must be carried out for all injectors. The pressure drop should be the same in all cases. If the results of checking the fuel pressure correspond to those described above, the fuel supply system is working properly.
What will happen if the fuel pressure in the rail is low?
(less than 2 atm.) or increased (more than 4 atm.)? The amount of fuel injected will change in proportion to the pressure deviation from the norm. In other words, the air-fuel mixture will become lean or rich.
It will be especially painful in engine control systems without oxygen sensor feedback, since the controller does not know about the malfunction and continues to calculate the fuel supply for a normal fuel pressure value. In control systems with an oxygen sensor, the controller can compensate for changes in the composition of the air-fuel mixture, but only within reasonable limits.
If the fuel pressure is incorrect, problems arise with starting the engine, dips appear when the vehicle moves, and fuel consumption increases.
Troubleshooting the fuel system
Let us recall the composition of the fuel supply system.
It includes: a fuel tank with a submersible fuel pump installed in it, a fuel filter, fuel lines (supply and drain lines), an injector ramp and a pressure regulator. Failure of any of these components may cause incorrect fuel pressure. Let's try to list the most common malfunctions for each component of the fuel supply system. Gas tank.
Through special pipelines, the gas tank communicates with the atmosphere, which prevents its deformation (flattening). If the connection with the atmosphere is broken, a vacuum is created inside the gas tank. In this case, the pressure in the fuel rail may be low.
Gasoline pump.
There may be several malfunctions:
- the fuel pump does not develop the required pressure, resulting in low fuel pressure;
- the check valve of the fuel pump does not hold pressure, as a result - a rapid drop in pressure after turning off the ignition;
- contamination of the fuel pump mesh filter, as a result - reduced pump performance, which affects the dynamic operating conditions of the engine.
Fuel filter.
A dirty fuel filter can lead to low fuel pressure due to reduced fuel line capacity. If the fuel filter is damaged (torn), dirt can enter the injectors with all the ensuing consequences.
Fuel lines.
Fuel lines may be pinched. If this happens to the supply line, then the fuel pressure will be reduced, if it happens to the drain line, it will be increased. In addition, the use of low-quality gasoline with a high tar content can lead to a decrease in the capacity of fuel lines.
Fuel pressure control.
There are regulators with a stuck diaphragm in the open or closed position. In the first case, the fuel pressure in the system will be reduced, in the second - increased.
Injectors.
The following types of faults are typical:
- the injector does not open, resulting in a lean air-fuel mixture;
- the injector is constantly open, resulting in an enriched air-fuel mixture;
- the injector works, but its characteristic has “floated away”, as a result - the air-fuel mixture is incorrect.
On-board diagnostics to identify faults
A malfunction of the fuel system leads to a deviation in pressure in the fuel rail.
As a result, the amount of fuel supplied to the cylinders differs from the calculated one, and the air-fuel mixture becomes depleted or enriched. In engine management systems with an oxygen sensor, the controller monitors the current composition of the air-fuel mixture. If the air-fuel mixture deviates significantly from the desired value, the controller perceives this condition as a malfunction, and one of two fault codes is recorded in the controller’s memory:
- P0171 - fuel system too lean;
- P0172 - fuel system too rich.
Increased or decreased pressure in the fuel rail
is just one of the reasons why codes P0171, P0172 can be recorded in the controller’s memory. The cause of a significant depletion or enrichment of the air-fuel mixture may be faulty mass air flow sensors, oxygen sensors, or injectors. Air leaks lead to an over-lean air-fuel mixture.
The fuel pressure value may be outside the permissible range, but the on-board diagnostics does not record anything. It’s a very real situation - on-board diagnostics are not omnipotent.
The vehicle's fuel system is designed to store, clean, supply fuel to the engine, create a fuel-air mixture and deliver it directly to the engine cylinders for combustion. Since the most important component in this process is the fuel-air mixture, the vehicle’s fuel system also includes an air purification system, which is supplied to the injectors through the intake pipe.
Measuring pressure in the VAZ fuel rail
Tips that may be useful when measuring blood pressure
- When purchasing a measuring device, you should not take a pressure gauge with a large upper pressure limit (there are pressure gauges designed for 16, 25 kg/cm² and higher). In this case, the accuracy of the device readings will be insufficient, with a large error.
- When relieving pressure in the ramp, you need to stock up on rags and also cover the generator with a rag. so that gasoline does not get on it.
- When tightening the pressure gauge fitting, it is advisable to wrap a little tow on the threaded connection, which is used when carrying out plumbing work. The tow will create a tight connection and prevent gasoline from leaking while the engine is running.
Fuel rail removal procedure:
- The first step is to relieve the pressure in the pipeline.
- Then you need to remove the receiver.
- Disconnect the wires from the injectors.
- Using a 17-mm open-end wrench, unscrew the ramp fitting. In this case, you need to keep the end of the fuel line hose from twisting.
- We take the hose tip away from the fuel rail fitting and use a screwdriver to remove the O-rings from the ends of the tubes. We check the rings - damaged ones need to be replaced.
- Using a 5mm hex wrench, unscrew the 2 bolts securing the fuel rail to the intake manifold.
- Remove the fuel rail from the car.
Disassembling the fuel rail:
- Using a screwdriver, remove the lock.
- Remove the nozzle from the ramp.
- In the same way, remove the remaining 3 injectors.
- We check the O-rings at the junction of the injectors with the fuel rail and with the intake manifold. Damaged rings must be replaced.
- If necessary, use the cap from the wheel nipple to unscrew the spool of the diagnostic fitting.
Assembly and installation of the fuel rail:
- Before assembly, coat the O-rings with a thin layer of oil.
- We assemble and install the fuel rail in place in the reverse order.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Similar articles
How to replace the rear engine mount on a VAZ 2114
How to replace the front engine mount on a VAZ 2114
Signs indicating fuel system malfunctions:
- The engine is running rough or there are some interruptions in its operation.
- Idle speed floats, engine stalls at idle.
- Excessive fuel consumption occurs.
- CO in the exhaust is higher than normal.
If the car has similar indicators, the ECU at this moment works well, the problem is most likely in the fuel rail. To make sure that this is so, you need to check the pressure in the rail.