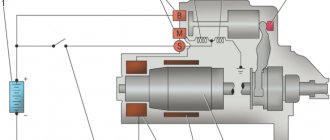
The car starter is an electric motor that is powered by the battery. The starter's job is to engage the flywheel of the internal combustion engine to turn the crankshaft and then start the engine. During engagement with the flywheel (braking torque), the car starter takes on an electric current of about 350 A.
This device is designed for short-term operation; prolonged rotation of the starter significantly reduces its service life. Note that a fully serviceable engine starts from the starter almost immediately, without the need to rotate the crankshaft for a long time. In the cold season, up to 2 attempts to start the internal combustion engine from the starter are allowed.
Checking the serviceability of the starter - video with example
Many motorists have encountered a situation where the car refuses to start and the starter is to blame. Most often, when the starter breaks down, it is necessary to continue driving, so motorists are looking for ways that will allow the car to start and drive the distance to the nearest car service center. In domestic and most imported cars, you can easily deal with the problem directly. Knowing how to directly close the starter can quickly but temporarily solve the problem and continue driving.
Often the reason why a car engine fails to start is the starter, so you always need to know how to start the car bypassing this device. Since closing the starter directly is the best option, you need to know all the intricacies of the procedure and perform it carefully and accurately. Using just a few tools, you can start your car in a couple of minutes, which is especially important in cold seasons.
Brushes and winding
Inside the starter housing there are 4 steel cores (shoes) with a winding that is connected into a circuit.
Healthy! Some cars do not use cores with windings, but magnets, which is much more convenient.
The current to the winding comes from the central input, and the output is output to two copper-graphite positive brushes that go to the commutator. Also connected to it are negative brushes that come from the starter mass. All brushes are constantly pressed using small springs. But, since graphite is not the most durable material, these elements tend to wear out quite quickly. When brush wear reaches a critical level, the solenoid relay stops receiving current.
In the event of such a breakdown, the starter will not make any extraneous sounds. To repair, you will need to disassemble it and evaluate the condition of the brushes. If everything is in order with them, then we look at the windings. If they burn out, the layer of varnish that is applied to them will also burn out. Also, instead of copper color, the windings will be black. An unpleasant burning smell also indicates a problem. In this case, the best thing would be to replace the entire assembly, although you can get by with new windings.
Repair of a collapsible solenoid relay
The manufacturer equips starters with a non-separable or collapsible retractor device. If a non-separable relay breaks down, it must be replaced, but a dismountable relay can be repaired. The described method allows you to check the solenoid relay of all VAZ models: 2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106, 2107, 2108, 2109, 21099, 2110, 2111, 2112, 2113, 2114, Niva, Lada Priora, Kalina, Granta, Vesta and most foreign cars. Disassembly and repair of the relay is carried out in the following order:
- Unscrew the nuts securing the housing cover.
- If necessary, the ends of the windings are additionally soldered.
- After removing the cover, inspect the power contacts:
- If they burn, the damaged part is cleaned with sandpaper;
- When worn out, replace.
- The device is assembled in the reverse order and tested for functionality.
- The repaired relay is installed back on the starter.
Car starter: main purpose
Sooner or later, every car owner, regardless of its make and model, has to face the problem that his vehicle refuses to start. The first thing, naturally, is to check the fuel level, battery charge, and electronics. If all this does not cause any complaints and doubts about serviceability, then most likely the problem is in the starter. After all, successful engine starting depends on it.
Currently, as a rule, relays 35.3708 with an end-mounted collector are installed on cars of this model.
However, on some copies of the VAZ 2106, starters made in Germany or Belarus may be installed, since they can be interchanged with starter 35.3708.
At an earlier time, approximately in the 70-80s, the ST-221 starter was also installed.
FAQ
Let's touch on several interesting questions that both novice drivers and very experienced car enthusiasts may ask. So:
- What is the current of the starter solenoid relay? Answer : Much depends on the model of starter and relay, but in most devices a current of 15-20 Amps passes through the control contact. In some cases this current is greater, but also remember that the strength of the current depends on whether the contacts are clean;
- How to disassemble the starter solenoid relay? Answer : This question was addressed above. In this case, you can get to the “filling” of a non-separable relay, although you cannot do without special tools and damage to the integrity of the case.
We have already described the relay repair process above. Even an inexperienced car enthusiast will not have any particular difficulties with this. The problem can only arise during the search for relay parts. However, many parts for repairs can be found from the already mentioned Danish ]Cargo[/anchor]. Most of the goods offered by the company are produced in the countries of Southeast Asia, but their quality is quite high.
Diagnostics of wiring and contacts
If the starter does not turn, then the reason may relate to the vehicle's electrical wiring or bad contacts. Often the problem appears along the voltage path from the (+) terminal to the solenoid relay. To start the starter, 200 Amperes are needed, but if the reason is in the contacts, then it is not a fact that exactly this amount of current will reach. In such a situation, the solenoid relay will work, since it only needs 10 Amps, but the voltage is not enough to spin up the starter.
In such a case, you can hear several clicks, and sometimes entire series. First, you should carefully check the car's wiring. If oxidation is detected on the contacts, they must be cleaned in order to be able to transmit current in full.
Basic faults
The solenoid relay, although its structure is quite simple, can suffer from many external and internal influences. The first and most obvious: destruction of the materials from which the relay consists. The second and even more common problem: relay failure due to burning of contact plates (often called nickels). Third: winding combustion (also a very common problem). Why does the starter solenoid relay light up? The most common cause of malfunctions of this nature lies in the electrochemical processes observed in the relay when water enters.
Signs of malfunctions of the unit's solenoid relay in the car include the following:
Troubleshooting wires
Some drivers, in search of a malfunction, are in a hurry to remove the starter, but such hasty actions should not be taken, since often the problem of the engine not starting is due to wires, poor contacts or their absence. Here are the most typical defects:
If there is a bad ground on the engine, a sign of a defect will be a slight click on the first attempt to start, then all the instruments may go out, and with the next turns of the key any signs of “life” will disappear altogether (but not necessarily). Checking the presence of mass is quite simple, but the check needs to be done by two people:
You should also ensure the reliability of all fasteners on the starter; to do this, perform the following steps:
If the BP wire is connected using a connector, bend the tongue of the “chip”; here the connection should be tight.
When, after cleaning all contact parts, the engine starts, it means that the malfunction has been eliminated, and there is no need to find out what caused the defect. If nothing has changed for the better, then you should definitely check the starter; to do this, the unit will have to be dismantled.
Starter solenoid relay diagram
Solenoid relay circuit
In addition to the previous point, we present to your attention a diagram of the starter retractor relay . With its help, it will be easier for you to understand the principle of operation of the device.
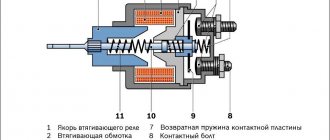
The solenoid coil of the relay is always connected to the negative side through the starter. And the holding winding goes directly to the battery. When the relay core presses the working plate against the bolts, and “plus” is supplied to the starter from the battery, then a similar “plus” is supplied to the “minus” output of the retractor winding. Because of this, it turns off, and the current continues to flow only through the holding winding . It is weaker than the retractor, but has sufficient strength to constantly hold the core inside the housing, which ensures continuous operation of the motor. The use of two windings allows you to significantly save battery energy when starting the engine.
How does the starter start the engine?
Let's take a closer look at the principle of operation of the starter. After closing the contacts, the current flows to the winding of the traction relay. At this time, the anchor moves and extends the bendix. The gear of the latter is connected to the flywheel ring. When the armature reaches its final position, the contacts close, allowing current to flow to the starter motor winding. The device begins to rotate and the car starts.
The Bendix returns to its original position as soon as the flywheel begins to rotate at a higher speed than the starter shaft. And the supply of electrical energy to the device stops when the key returns to the first position. A gear starter is also installed on the VAZ 2107, in this case the current flow pattern is slightly different; it reaches the armature through a gear drive. Thanks to this, power is significantly increased. This is not the only difference that the gear mechanism has, but we won’t talk about that now.
This is interesting: How to remove a dent on a car with your own hands
Electrical reason
If, when starting the engine, you can hear the starter spinning, but the engine does not engage, then the problems may be localized in the solenoid relay. It is installed on the starter housing and has terminals for connecting the positive wire from the battery and the control contact of the ignition switch. The pull-in relay is a coil with two windings. The first winding here is retracting, the second is holding
The functions of these two windings are different. The effort also varies. The pull-in coil of the relay is necessary to extend the bendix and close the contacts to supply voltage to the brushes of the electric motor. In turn, the retaining winding creates enough force so that the bendix can obtain reliable engagement with the flywheel crown. If the starter just turns at idle, then the retractor winding works fine. You need to look for the problem elsewhere.
If there is an interturn short circuit in the holding winding of the retractor relay, then the bendix is not locked in the position of engagement with the ring, and the gear is thrown back. The torque is not transmitted to the engine, and it does not start - the VAZ starter spins at idle.
Repair involves restoring or replacing the entire solenoid relay. Another excellent solution is to replace the starter entirely with an original device. But this is not a solution for everyone, so experts can advise repairing the unit - disassembling the retractor, making defects, replacing or restoring worn parts
Malfunctions and their features
During operation of the power unit starting device, the entire load is transferred to its solenoid relay. Therefore, to the question: why does the starter click, we can answer that the relay begins to function, making characteristic sounds. This indicates a malfunction, since the starter does not work at this moment and does not turn the crankshaft of the car engine. The occurrence of such symptoms is typical for the following situations:
- short circuit or burning of the turns of the rotor or stator windings;
- deterioration of the bushings, which caused the motor shaft to jam;
- breakdown of the rotor to ground.
Without removing the device from the car and completely disassembling it, it will not be possible to detect such malfunctions.
The traction clicks due to the fact that its core moves between the retracting and fixing windings, and if the voltage on the latter is insufficient, it cannot hold on and returns to its original position. The presence of clicks is evidence of unsuccessful attempts by the core to stay in the required position. It will not be possible to start the engine and start moving, because the starter stops turning, and the retractor relay clicks, which does not allow the bendix and flywheel to engage.
Note that if it was not possible to start the vehicle engine the first time, this is not at all evidence of a faulty starter. It is likely that most systems have not yet started working; to do this, you need to turn the ignition key again.
In addition to the solenoid relay, burnt contacts (this is accompanied by a characteristic burning smell and, in some cases, smoke), lack of ground, disruption of the integrity of the electrical network, or a discharged power source can cause problems with the engine starting system. Elimination of these faults is carried out on an individual basis.
Operating principle of the solenoid relay
Before moving directly to the malfunctions and methods for eliminating them, it will be useful for car owners to know the device of the starter retractor relay and how it works. It is immediately worth noting that the mechanism is a classic electromagnet , consisting of two windings (holding and retracting), a circuit for connecting it to the starter, as well as a core with a return spring.
When the ignition key is turned, voltage from the battery is supplied to the coils of the solenoid relay. This creates an electromagnetic field that moves the core located in its body. That, in turn, compresses the return spring. As a result of this, the opposite end of the “fork” moves towards the flywheel. In this case, the gear connected to the bendix is squeezed out until it engages with the flywheel ring. As a result of engagement, the contacts of the built-in starter circuit are closed. Next, the retracting winding is turned off, and the core remains in a fixed position with the help of a working holding winding.
Scheme of operation of the solenoid relay
After the ignition key turns off the engine, voltage to the solenoid relay stops supplying. The anchor returns to its original position. The fork and bendix, which are mechanically connected to it, disengage with the flywheel. Thus, a malfunction of the starter solenoid relay is a critical failure due to which it is impossible to start the engine.
Features of checking the performance of elements of the starting system of a car engine
After visual inspection of the condition of the starting system parts, they begin to dismantle the starter to test its components:
- It is possible to determine how worn out the brush assembly is only after disassembling the starter housing. Despite the long service life of the brushes, they still wear out. At the same time, their development on some starter models does not allow the traction relay to be activated. In this case, the clicks it makes will not be heard.
- Burning of the windings on the coils can be easily determined both visually and by the presence of a burning smell. Since it makes no sense to restore their functionality, you will have to replace the starter.
- It is possible to perform a traction stress test without its housing. To do this, you need to close the two large terminals on the relay using a screwdriver, being careful not to catch the housing elements. The presence of problems with the retractor will be signaled by the beginning of shaft rotation. Note that one of the unpleasant consequences of this is the burning of the relay contact groups. Since they contain a special protective coating to prevent damage, it is not recommended to clean carbon deposits from them. In this case, only a complete replacement of the traction rod is indicated.
In addition to the procedures described above, it is necessary to pay attention to the ignition switch by checking the voltage in it. Often contact is lost in this node due to the coating of the wires with an oxide film and the formation of corrosion areas. To do this, it is enough to clean them, solder them, or replace them.
Where to start if the starter on a VAZ does not turn - and what needs to be checked first
Before disassembling the starter, it is necessary to check the serviceability of the wiring and some components. Perhaps the problem lies with them.
First of all, check if the battery is charged.
Then, using a tester, check whether voltage is supplied to the auxiliary relay terminal.
It is also necessary to check whether power is supplied from the ignition switch. To do this, remove the connector from the relay, connect the tester and turn the key to start. When you turn the key to this position, power should appear at the connector.
If no malfunctions were identified during this check, and the starter on the VAZ-2110 still does not turn, then it is necessary to remove it and determine the cause of the malfunction.
The VAZ 2105 starter clicks reasons
- To the beginning of the forum
- Forum Rules
- Old design
- FAQ
- Search
- Users
Hello, dear ones!
Recently a problem appeared - I didn’t turn the starter! There is a click - but it doesn’t turn! I replaced the starter relay and it started starting with half a turn! I drove like this for a week. Then, when I started starting the starter, it turned very poorly, it felt like the battery was dead, but it was fine. After ten seconds the car started. Last night the starter again did not turn at all, only a click and silence! I tried a new relay, but the starter was silent! The wires to the starter are intact, I didn’t find any breaks! Please tell me how to treat this! Thank you! PS The starter does not turn on a cold or hot engine! With a push it starts from half a meter!
Then, when I started starting the starter, it turned very poorly, it felt like the battery was dead, but it was fine.
The wires to the starter are intact, I didn’t find any breaks!
Found the reason! It turned out that the wire leading from the retractor to the starter had burnt out!
First of all, hello everyone! Not long ago I joined the classics, having bought a ’99 7 from a friend. The car is in good condition - it was used only in the summer, in the winter it was parked in a heated garage. There is no rot, but the right driver's door was in an accident. New summer tires (we still have to buy winter ones), battery, seats in the cabin. After the purchase, I changed the engine oil and antifreeze, and the generator did not charge, so I had to change that too. Well, and the wheel alignment, of course.
So I learned to drive this car for about a month and was happy with everything except the madly clicking turn signal/hazard light relay (2-4 times per second
) and the fact that the car did not start the first time.
However, this morning, as usual, after turning the starter for the first time, starting up and immediately stalling, the second time the starter stopped turning. When you turn the key, something clicks, but the starter does not turn. Since I'm no stranger to fixing cars, and also because I had to run to work, I took a minibus. But there is a desire to get involved and figure out what’s going on.
In the Behind the Wheel program “Repairing VAZ-2107, -21047” it is written that you need to tighten the wire ends, crimp the terminals, replace the faulty starting relay or starter. I'm wondering how much of this is true and what's the best place to start.