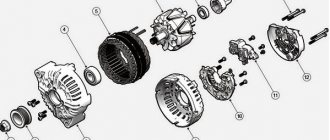
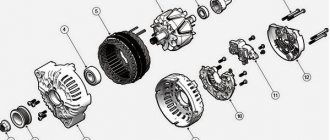
The appearance of third-party sounds in the operation of the power unit is caused by a violation of the gaps in the gas distribution mechanism (GRM). Most motorists rush to adjust the valves, but this does not always help.
The valve knock on the Grant may become quieter, but will not disappear altogether. Often the reason lies in worn hydraulic compensators. Unprofessional intervention in repairs can only harm the operation of the unit, so use the services of certified workshops.
Why does the engine start knocking?
First of all, you need to understand that both the engine itself and the attachments can knock. For example, the owner may hear noise and knocking from the pump, generator, power steering pump, etc. If we talk about the engine itself, knocking noises can appear as a result of wear or damage to the connecting rod bearings, pistons, in case of problems with the timing belt, etc.
So, if knocking suddenly appears in the engine, the main reasons may be:
- decrease in engine oil level or loss of its properties;
- the engine began to overheat for one reason or another;
- the power unit is worn out, there are problems with the CPG and the crankshaft;
It is also important to consider whether the engine knocks only when it is cold and/or when it is hot. It is also important to determine whether such a knock is intermittent or constant.
The fact is that the power unit does not always knock constantly.
Often knocking noises are heard only when cold, but disappear after warming up. Note that in this case, on some internal combustion engines, the knocking of the pistons in the cylinders is heard when cold. The reason is that the cylinder liners are worn out, which leads to the formation of a gap between the piston and the cylinder wall.
However, given that the pistons are aluminum, they expand after warming up. It is not difficult to guess that after expansion the gap becomes smaller and the knocking in the engine disappears when it is hot. Also, on a cold engine, the timing chain may make noise.
The fact is that the oil pressure after starting the internal combustion engine is insufficient. If a hydraulic timing chain tensioner is designed, the tension is simply not enough and noise appears, which will disappear with warming up.
Hydraulic compensators often knock when cold, and this is considered normal. If the knocking sound of the hydraulic compensators does not disappear after warming up, and changing the oil and flushing the lubrication system does not help, then the hydraulic compensators need to be changed.
Now let's move on to the problem of engine knocking after reaching operating temperatures. Let us immediately note that if the engine knocks “when hot,” the problems may be more serious compared to the noise of an unheated internal combustion engine.
First of all, the crankshaft or CPG parts may be knocking. This indicates a lot of wear. In a nutshell, while the engine is cold, the oil is less fluid and not as diluted. In fact, the lubricant fills the gaps that have increased due to wear.
As a result, there is no knocking in the mating pairs after starting a cold engine. However, as the power plant warms up, the oil becomes liquid and knocking begins to appear, quite clearly.
More precisely, a knocking sound in the engine when hot indicates that the gap is increased in the area of the main bearings (between the main bearings and the crankshaft journals). Also, the clearances can be increased in the connecting rod bearings, although in practice in this case a metallic knock is more often heard in the engine, regardless of whether the engine is cold or warm.
Knocking when hot can also occur when the piston pin cracks, or if cracks have formed on the piston skirt. One way or another, a knocking sound in the engine after warming up requires stopping operation and immediate diagnosis.
Another common problem is engine knocking at idle, that is, when the engine (regardless of the degree of warming up) is idling. If you raise the speed, the knocks and noises disappear or become less intense.
Let us immediately note that knocking at idle can indicate either that a part is touching another due to vibrations (for example, covers, casings, etc. may be knocking), as well as backlash in various pulleys, gears and drives.
As you can see, there are many reasons for engine knocking, for this reason it is important to localize the source as accurately as possible. Now let's look at the most common problems and look at the most common sources of engine noise in more detail.
ENGINE KNOCKING IN FRONT WHEEL VAZ CARS
In front-wheel drive VAZ cars, the engines may have different digital indices, since the engines are installed on different car models. But basically all power units have the same circuit diagram, but they may differ:
- 8-valve or 16-valve cylinder head;
- Piston diameter;
- Carburetor or injection fuel system;
- Minor design features (different sensors, collector configuration, etc.).
In particular, the VAZ 2114 car is equipped with an 8-valve 4-cylinder engine with a volume of 1.5 liters of the VAZ 2111 model, with a fuel supply system of the “injector” type (distributed injection). Exactly the same internal combustion engine (ICE) is equipped with the VAZ 2115 and VAZ 2113.
Various knocking noises can occur in an internal combustion engine, and it is not necessarily the valves that are knocking. Knocks can occur:
- In the piston group,
- In the crank mechanism;
- In the gas distribution system;
- In attachments (water pump, generator, etc.).
Why does the engine knock, what could be causing the knocking:
- insufficient amount of oil in the oil system crankcase;
- wear of parts due to long-term use;
- manufacturing defects;
- engine overheating;
- operation of the motor at constant maximum loads.
Knocking in the VAZ 2114 engine has a different character; determining the cause is sometimes difficult even for technicians who have some experience in repairs. But there are characteristic sounds that are identified quite easily:
- a sharp “dry” metallic sound, clearly audible when you sharply press the gas pedal. This is how the crankpins (bearings) of the crankshaft knock. This is a serious knock, at a minimum, it requires crankshaft grinding;
- the sound is medium in tone; when the speed increases, it seems that something is rolling around inside the internal combustion engine. This is how the pistons usually knock;
- single clicking sound. As the speed increases, it seems to merge, and is similar to the sound of a working sewing machine. This is how parts of the gas distribution mechanism (camshaft, pusher) usually knock.
How do valves knock, how to determine it? The valve knock is usually quite sharp, clicking, and high-pitched. He can knock not just one, but several at once. To understand the cause of various noises in the gas distribution mechanism (GRM), you need to have at least a little idea of its structure. The VAZ 2114 timing belt consists of the following elements:
- camshaft.
- timing gear.
- Timing belt.
- Pushers.
- Adjusting washers.
- Inlet and exhaust valves.
Basically the scheme works as follows:
- From the rotating crankshaft, movement is transmitted through the timing belt to the camshaft gear;
- The gear is rigidly fixed to the camshaft (fixed with a key and secured with a bolt), so the shaft is also driven;
- The camshaft cams press on the adjusting washer located in the outer part of the bottom of the pusher.
- The pusher presses the valve, the valve opens and closes when the crankshaft moves, the working mixture is filled into the internal combustion engine cylinders, and the working cycle is completed.
The cause of the knock can be any link in the gas distribution mechanism. But there are the most common reasons:
- Large gap between the camshaft cam and the pusher;
- Wear of camshaft bearings;
- Wear of the seat in the cylinder head (cylinder head) under the camshaft;
- Worn uneven surface of the adjusting washer;
- Breaking of the seat for the pusher in the cylinder head.
The main sources of extraneous sounds in the engine
You must understand that not every extraneous sound is a signal of engine malfunction. This primarily concerns knocking noises in the outer parts of the engine. But everyone has a reason that must be found. For example, the flagellum that holds together the bundle of electrical wires has broken. The wires fell apart and when the engine was running, some of them began to muffledly hit some surface. Will this lead to serious consequences? At first, no. If measures are not taken, then after a long time the insulation on the wire will wear out and a short circuit may occur, which, through the combustion of a fuse, will de-energize some part of the on-board network. Parts that have loose fastening bolts often knock. This is also an unpleasant, but not critical situation. It is enough to take the keys and tighten the loose threaded connections yourself.
Types of extraneous noise in the power unit
Here are the most common extraneous sounds in the engine that should alert the car owner:
Air leak into carburetor
Hissing . This specific sound under the hood of the car while the engine is running may indicate air leaks in depressurized vacuum systems or in the cooling system. The consequences can be severe. In the first case, the brake system may fail, in the second, the engine may overheat due to an antifreeze leak. Therefore, you urgently need to go to a car service center to diagnose and eliminate the cause of the hissing sound.
A squealing or sharp whistling sound most likely indicates a weakened drive belt of some component: timing belt, generator, water pump, air conditioning compressor. The belt begins to slip in the drive pulleys and at the same time emit a characteristic squeal. If timely measures are not taken, the belt may break with unpleasant consequences.
Engine Listening Zones
Knocks of different tones inside the engine in the area of the crankshaft, pistons, and valves give rise to diagnosing the operation of the engine as a whole to identify the cause of extraneous sounds. Unusual knocking inside the engine is a cause for the most serious concern. Their appearance may signal the possible high costs of eliminating them. If the liner rattles, you will need to disassemble the engine with grooving or even replacing the crankshaft. A knocking sound appeared in the middle of the block - the connecting rod and piston group was worn out. You will need to completely disassemble the engine, bore the cylinder block, change pistons, rings, pins. If the sound is clearly audible in the upper part, then perhaps the valves need to be adjusted, or perhaps the piston reaches the cylinder head due to a large gap in the connecting rod bearings.
Reasons for the appearance of extraneous sounds in the engine
The reasons and circumstances under which knocking appeared are different. Extraneous noise can be clearly heard both outside the engine and inside it. Internal ones are more dangerous than external ones. The cylinder block contains the crankshaft, pistons, connecting rods, and parts of the gas distribution mechanism. If the knocking comes from this group of mechanisms, then this is always associated with partial or complete disassembly of the engine to eliminate the malfunction. Often the sounds are sharp in nature, which intensifies when the throttle is opened smoothly. If the sounds are loud, with a “light tinkling” of iron and appear with a rapid increase in the speed of rotation of the flywheel, then this indicates detonation - a violation of the fuel ignition regime.
Video: Mercedes 126, found the cause of the knocking in the engine
Knocks from detonation
If the knocking is strong with a ringing “metallic” tint and occurs when the gas pedal is sharply pressed, or under load, then this is the result of detonation - explosive combustion of fuel in the cylinders. Moreover, detonation occurs differently in different types of engines. Gasoline engines have the expression “knocking fingers.” This is not entirely correct. In fact, during abnormal fuel combustion, the piston skirt knocks when it passes top dead center. Gasoline detonation is the result of refueling with poor fuel with a low octane rating, incorrect valve timing adjustment, and prolonged engine operation in an overheated state. To eliminate detonation, it is enough to cool the engine, adjust the fuel injection and ignition systems, and fill the tank with gasoline in accordance with the technical regulations of the car.
Diesels also have fuel detonation, but their reason for its formation is different. This is an early injection of diesel fuel or a lean fuel mixture, which arises from improper operation of the pressure valve in the high-pressure fuel pump (HPF). Moreover, the sound will be loud, ringing, similar to the blows of a piston on the surface of the cylinder head. In such cases, they say that the diesel engine operates “hard”. This impression arises because the compression ratio of diesel engines is much higher than that of gasoline engines, so in normal operating condition the distance between the piston and the block head is microscopic. You can get rid of detonation by restoring the operation of the pressure valve on a special stand in a service station.
Even in diesel engines, at idle speed, the knocking of the plungers is clearly audible. This is a design feature of almost all engines of this type. These sounds do not pose any threat. Diesel engines have been used with them for more than one year. In engines with gasoline injection, an experienced ear hears the “clicks” of fuel injectors, which are also inherent in most engines of this type. They do not pose any serious threat to the engine, and in no way affect its performance characteristics.
Valve mechanism knocks
If the valve bushings and hydraulic compensators are worn out, the gaps between the ends of the valves and pushers have increased - ringing, clear sounds will be clearly audible in the area of the cylinder head. It's not difficult to get rid of this. It is necessary to change worn parts and dirty engine oil. Rinse and clean all channels and valve mechanism parts from dirty deposits and adjust the thermal clearances in the valves. This work is specific, requiring special equipment, cleaning agents, and tools. Therefore, it is performed at technical inspection stations. First of all, this applies to cars of domestic and foreign production that are under warranty.
Grant engine mounting pads
To replace the power unit suspension mounts on a Lada Granta VAZ 2190, you will need: a TORX E14 socket, 17" wrenches (socket and socket), 19" wrenches, a jack or a similar lifting mechanism. The power unit (engine and gearbox) is mounted on two rubber cushions on the right and left, fixed through brackets on the engine and gearbox housing, and one rear cushion (also rubber), fixed through a bracket on the gearbox housing. 1. Hang the front part of the car on supports or lift the Lada Granta VAZ 2190 on a lift. 2. Remove the engine protection (see “Removing and installing the engine protection”).
3. Before removing the rear engine mount, place a jack under the gearbox housing.
4. To replace the rear support cushion, unscrew the left one.
5. and the right nuts securing the pillow to the body.
6. Remove the three bolts securing the rear support bracket to the gearbox housing.
7. and remove the bracket together with the pillow.
NOTE: It is necessary to remove the rear cushion together with the bracket because the bolt securing the engine support cushion to the bracket is difficult to access on the car.
8. Clamp the bracket in a vice, remove the bolt securing the pillow to the bracket.
9. and remove the rear engine mount cushion.
10. Install the rear engine support cushion on the Lada Granta VAZ 2190 car in the reverse order of removal, orienting it during installation so that the protrusion on the bracket is installed between two protrusions on the inner race of the support cushion.
11. and the longer arm (shown by the arrow) of its outer race was directed towards the right side of the car.
12. Before removing the left engine mount cushion, install a jack under the gearbox housing.
13. Remove the two bolts securing the left engine mount to the bracket.
14. Remove the bolt and unscrew the two nuts securing the engine mount to the body side member.
15. and remove the left engine mount.
Please note that the cushion of the left support, although similar in appearance to the cushion of the right support, differs from it in the design of its attachment to the bracket. The holes in the inner race of the left engine mount are threaded, and the same holes in the race of the right engine mount are smooth.
16. Install the left engine mount cushion on the Lada Granta VAZ 2190 in the reverse order of removal.
17. Before removing the right support cushion, install a jack under the engine.
18. Remove the bolt and unscrew the two nuts securing the right engine mount cushion to the body side member.
Sound diagnostics
If a problem arises that the engine is knocking, as already said, it is first of all important to determine the nature of the knock, as well as the location of its occurrence. Some of the reasons can be diagnosed without disassembling the power plant
Some of the reasons can be diagnosed without disassembling the power plant.
Thus, a special device - a technical phonendoscope - will allow you to more accurately determine the location of the noise.
Using it, the engine is listened to and it is determined in which mechanism or system malfunctions have occurred.
You can also use more advanced equipment, for example, a motor tester.
A simple procedure will allow you to determine the destruction of the connecting rod liner.
It is done like this: with the engine running, when a loud knocking noise appears, the high voltage wire is removed from the spark plug one by one on each cylinder.
If the fault lies in the connecting rod bearing, then disconnecting the wire on the cylinder that has the problem will significantly reduce the knocking noise.
If noise occurs, when there is a suspicion of destruction of the bearing of any attachment, you can determine which equipment has problems by disconnecting their drive from the on-board network.
If after this the extraneous noise disappears, the faulty equipment is replaced or sent for repair.
Knocks at the top of the engine.
They are diagnosed sequentially. First, the condition of the cylinder head elements and their fastening is checked.
Then the valves are adjusted or the hydraulic compensators are washed. At the same time, the level and condition of the oil are checked.
Then the head is removed from the engine and a full range of restoration work is carried out.
Middle and lower part of the engine.
An accurate determination of the sources of knocking in the lower part of the engine is possible only after disassembling the engine.
Since severe wear of the cylinder-piston group also causes unwanted sound, therefore, if a knock occurs in the middle part, the condition of this group can be assessed by measuring compression.
If the knock is caused by detonation, its presence can be determined by the behavior of the power plant.
If it continues to work for some time after a forced stop, there is detonation in the cylinders.
Diesel power plants.
Diagnostics in these engines is carried out identically to those described, but their fuel system can be diagnosed only after removing its elements and only on special stands.
What to do if valves are knocking
Extraneous noise in the engine appears most often on cars that the owners do not take care of, and if they do, it is from time to time, and the breaks in these cases are usually very long. An illustration of this can be an analysis of the reasons why valves knock.
The most common reason is increased clearance between the arms and the camshaft cams. And this reason can be eliminated simply by adjusting the valves. And, again, an elementary thing that every driver should know - the valves must be adjusted every fifteen thousand kilometers. This is a mandatory rule.
Careless drivers have had cases when they remembered the valves after 70 thousand miles, and then the car mechanic could not do anything with them, they could not be adjusted.
Car owners often worry about valve knocking on a cold engine. That is, when the engine is cold, there is a clear knocking sound, but as the engine warms up, these sounds disappear. Experienced automobile mechanics explain this by saying that on a car with a fairly high mileage, parts wear out, and this especially happens with parts of the power plant. Small gaps appear between them, which generally do not affect the operation of the systems for the worse, but manifest themselves in a cold state. It is because of these resulting gaps that such annoying sounds appear for drivers. When heated, the metal expands, the gaps disappear, and along with this the unpleasant sound disappears.
However, this does not mean that one should be indifferent to extraneous noise in the engine when it is cold, especially if the owner monitors the timeliness of all adjustments. After all, on a cold engine, at idle speed, the main or connecting rod bearings of the crankshaft can make noise, and this is already very serious. You should definitely contact a specialist for diagnosis.
Every driver heard the valves knocking when hot. Especially with a sharp increase in speed. The most common reason for this is low-quality gasoline. But there may be other reasons, for example, a knock sensor has failed. Or the oil pressure has dropped.
In addition to increasing the clearance, the causes of noise produced by valves can be:
- wear of the camshaft cams - in this case it is necessary to replace the entire camshaft;
- valve spring failure - if this is detected, a new spring must be installed;
- the guide bushing may need to be adjusted or replaced;
- Valve knocking can be caused by completely different reasons, for example, a poorly tensioned timing belt or poor flow of oil through the camshaft to the fingers due to clogged channels in the valve.
It is very difficult for an inexperienced person to determine by ear that the valves on a VAZ 2114 are knocking. Nevertheless, experts recommend some folk remedies, recalling that the camshaft rotates twice as slow as the crankshaft and, accordingly, the sound of the valves should not be frequent. For better sound perception, they suggest placing an empty metal mug to your ear and placing it on the hood. In this case, the sound becomes clear and easy to hear.
An attentive and experienced driver always listens to the sounds of his car. If an unfamiliar knock, noise, or clanging appears in the engine, he will immediately try to determine the cause and nature of this phenomenon. If there is something knocking under the hood, this is a signal of one or another malfunction of the car, which can come out - in the literal sense of the word.
Inability to gain power
Situations are also possible when the engine makes “heavy” sounds, which is accompanied by the inability to gain full power. And there are reasons for this.
If you purchased Granta new, then the problem may be its newness.
Until a break-in period of 6-7 thousand kilometers is completed, maximum power cannot be gained. Moreover, it is not recommended to increase the crankshaft speed above the 3 thousand mark for the first 2000 thousand kilometers.
Low pressure in the fuel system
If at high speeds it seems to you that the engine:
- does not develop enough power,
- It's like he's hitting a wall
- or when accelerating, “they throw extra weight into tow”
Airbag malfunctions
You can tell that the airbags have become unusable by the amount of engine vibration. If it operates in normal mode, and the body begins to rattle, transmitting vibration to the steering rack, pedal block, and instrument panel, you can be sure that the reason for this is the wear of the pillows.
The greatest vibration is usually observed when the engine starts, as well as when it is turned off. When the rubber cushions are completely worn out, a knocking noise may appear caused by the contact of the engine elements and its supports.
To be more convincing, start the engine, open the hood and visually inspect the engine mounts and the cushions themselves. Place your palm on the motor and feel how much it vibrates.
The causes of failure of engine mounts can be:
- deformation due to spent life, mechanical or temperature effects;
- loss of elasticity due to “aging” of rubber and temperature changes;
- delamination or cracking caused by exposure to chemically active liquids.
Electrics and body
The generator bearings have insufficient life. They can begin to hum by 80,000 km. Power windows often squeak and raise the windows slowly due to glass jamming in the seals. Electric window motors often fail. You can also note the leakage of the rear lights of sedans: not only water, but also insects penetrate inside.
The paint on the body can be easily damaged by stones flying from under the wheels of other cars. The resulting paint chips “bloom” quite quickly. The paint layer is so thin that it is sometimes rubbed off by the door seals. The seat adjustment knob often breaks off.
All of the listed problems with Grants are a consequence of either an outdated design or a budgetary approach to production. It is obvious that Grant has exhausted its possibilities for modernization. We need a new platform and a new level of security. Lada Granta is the last car in production today that does not have a front subframe - an important element that serves to reduce noise and vibration, as well as increase the passive safety of the car.
It’s always worth telling how your Granta never broke down (or broke down every thousand kilometers) in the comments below.
Source
Knocking or detonation. Signs and differences
Detonation in the engine of any technical vehicle, including the Lada Granta Sedan/Liftback, is similar to a small explosion with a shock wave. It is at the moment of explosion that the valve(s) knock.
The clattering noise is not always associated with faulty valves. It is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis followed by replacement of worn elements.
- vibration increases as engine speed increases;
- black smoke from the vehicle exhaust system;
- a sharp decrease in engine power;
- frequent increase in operating temperature to a critical level.
If the knocking noise occurs when the engine is “hot,” then the reason is insufficient engine oil level.
Checking hydraulic compensators of Lada Granta Sedan / Liftback
At home, identifying the source is extremely difficult, sometimes impossible. Work of this complexity is carried out in certified service stations using acoustic equipment.
Related link:
Adsorber Lada Granta: signs of malfunction, solutions, replacement
After the technician identifies the defective pushers, they must be removed, washed thoroughly, and reinstalled. If the hydraulic lifters are also knocking, then replace the elements with new ones.
Causes
When the power unit operates correctly, the sequence of the fuel combustion process is maintained. It starts from the spark plugs, and then fills the entire chamber equidistantly.
Detonation combustion occurs in a completely different way. The entire volume of the fuel-air mixture explodes simultaneously, sharply, provoking a significant increase in the pressure and temperature of the cylinders themselves. Under such conditions, chemically active compounds are formed in places of the highest concentration of unburned fuel.
When critical values are reached, chemical chain reactions occur that promote explosive ignition. The resulting wave moves quite quickly, strongly impacts the walls of the chamber and the surfaces of the cylinders, and at the same time new points of spontaneous combustion are organized. The result is numerous oscillatory phenomena that provoke vibrations of the power unit.
It can occur for various reasons, the most common are:
Fuel composition. If air and fuel are in a 9-0 ratio, which violates the average, then in the event of penetration into a chamber with elevated temperature and pressure, various oxidative reactions are formed in remote areas, which are the primary source of the process of self-ignition, that is, detonation. The magnitude of the ignition timing. An increase in this indicator provokes a shift in the maximum pressure peak, which becomes a factor in the occurrence of detonation processes. Octane number of the fuel mixture. The lower this indicator, the greater the likelihood of detonation. A decrease in this criterion leads to an increase in the chemical activity of the fuel to the oxidation process. Therefore, car owners using 76-octane gasoline notice the knocking of the piston pins much more often than drivers who fill the tank with 92-octane gasoline. Compression ratio. An indicator characterizing the ratio of the volume of one cylinder to the total volume of the combustion chamber. Its increase leads to the fact that pressure and temperature invariably begin to increase, which means that the risk of detonation increases. Therefore, if a power unit with a sufficiently high compression ratio is installed, then the car owner is recommended to use high-leaded gasoline. Glow ignition, which causes spontaneous combustion of the fuel mixture in the cylinders. Occurs due to the presence of burning soot or high temperature in the chamber
It is equally important to choose the type of spark plug correctly. There are “cold”, “warm” and “medium” candles, characterized by different heat indicators
This is necessary so as not to cause a fire if the insulator of the central electrode of the spark plug overheats. Increased load on the motor. If the driver tries to start every time, for example, from third gear, then at some point he will invariably hear the fingers of his engine knocking.
Refueling with low-quality fuel
Many systems and devices of the power unit can contribute to the fact that a gasoline engine operates like a diesel engine. However, there is one external reason that contributes to the appearance of unusual sounds. This is low-quality fuel.
The main property of gasoline, which characterizes its resistance to detonation (explosive pre-ignition), is the octane number. If the engine is designed for AI-95 gasoline, and at the gas station you were filled with low-octane fuel, troubles are inevitable.
- Under certain loads, fuel detonation occurs, accompanied by detonation knocks reminiscent of the ringing of piston pins and, remotely, the sound of a running diesel engine.
- To increase the octane number, octane-increasing additives are added to low-grade gasoline, which are deposited in the nozzles of the working injectors on an injection engine. The supply of fuel to different cylinders becomes uneven, which leads to harsh engine operation. In advanced cases, the injectors become completely clogged, as a result of which the engine begins to “trouble.”
- The additives contained in “bodied” gasoline cover the electrodes of the spark plugs with a layer of red soot, and due to misfires, the engine again “troubles.”
Tip: try to refuel at chain gas stations located in large populated areas or along busy highways. If you run out of fuel, fill up the minimum amount of gasoline at the first gas station you come across in order to get to the nearest verified gas station.
Causes of engine knocking
The knock itself is formed when one element of the power plant hits another.
At the same time, the noise in the engine varies, it occurs under certain conditions and disappears when they change.
In most cases, knocking is a signal of problems with certain mechanisms - the timing belt, crank mechanism, cylinder-piston group, but they also appear in other components of the unit.
Criteria for the nature of the knock.
Extraneous noise generated in the power plant can be divided into several criteria:
- The power of sound;
- Cause-and-effect relationships;
- Sound (metallic knocking, etc.);
- Cyclicality.
Let's look at each of the criteria.
The knocking sound in the engine may be weak and barely audible - in this case, the car can continue to be used, but it will not hurt to carry out diagnostic work.
There is an average knock that can be heard clearly, but it is not difficult to drown it out, for example, with loud music.
A car with such knocking noises can be used for a short period of time, enough to be able to get to a garage or service center.
Distinct loud sounds coming from inside the power unit indicate significant problems in its operation.
With such sounds, the engine is turned off and the car is delivered to the garage or service only by a tow truck or in tow, since serious problems may arise with the engine.
Cause-and-effect relationships in the occurrence of knocking occur after non-professionals intervene in the power unit.
That is, whether, on the contrary, failure to perform technical work or repairs will lead to engine malfunctions.
Sources of knocking (metallic) in the engine:
- Oil that is not recommended for use on this engine or counterfeit products;
- Poor quality or defective parts that were installed during repairs can also cause knocking in the engine.
- Severe wear of the components will naturally lead to the appearance of extraneous noise.
Types of sound and how they differ.
Based on the sound, engine knocking is divided into loud and dull.
A loud knock, also called metallic, occurs when parts made of hard metals collide with each other, and there is no oil layer between the parts.
A dull knock in the engine occurs when parts strike, one of which is made of soft metal, and there is an oil layer between the parts.
By the cyclical nature of the knocks, you can roughly determine which mechanism requires intervention.
Thus, a knock in the engine occurs in proportion to the rotation of the crankshaft, indicating possible problems with the cylinder-piston group, gas distribution or crank mechanisms.
The source of spontaneous knocking that occurs haphazardly may be located in the engine attachment.
For example, a knocking sound can be made by a loose generator, and the noise will arise due to the vibration of the power unit.
What does impact intensity mean?
If a clear knocking sound in an internal combustion engine appears unexpectedly and does not disappear over time, this means that the working parts are rapidly deteriorating due to the operation of the machine under high load conditions. The result of destruction is exceeding the cyclic fatigue limit of the metal.
If the knocking began with barely noticeable manifestations and, over time, began to gradually intensify to an impossible rumble, this indicates gradual abrasion and wear of metal surfaces.
Important: The intensity of the increase in the sound of impacts depends on the modes in which the vehicle operates: the load on the power unit, the crankshaft speed. When the permissible loads on an internal combustion engine are exceeded, the wear of parts of the cylinder-piston group and the crank mechanism increases. The main sign of defects that have appeared in these groups of elements is an increase in the intensity of extraneous sounds, turning into real noise, with increasing loads.
The intensity of non-standard engine sounds also depends on the quality of lubrication of friction units. List of working pairs in which parts interact closely:
- pistons with piston pins;
- camshaft with cylinder head;
- valve bushings;
- cylinders with pistons, etc.
Valve knocking - reasons
The number one reason can be called a violation of the gaps between the cams and the camshaft levers. This happens in the following way: the gap between the above parts increases, after which the cam begins to hit the rocker, as a result, strange sounds begin to appear in the engine compartment, similar to the clatter of metal on metal. The larger the gap, the stronger the clatter and subsequent wear. If you leave everything as it is and do nothing, then eventually the engine will completely fail, stop starting and at least “require” major repairs. The size of the gap between the valves is clearly regulated by the manufacturer of the power unit, therefore, at the slightest deviation, it is necessary to adjust the valves taking into account the parameters set by the manufacturer.
The second, no less common reason for knocking is that the valve clearance is too small. Over time, the clamped valves stop closing altogether, which leads to engine overheating, a drop in the compression ratio, and, as a result, excessive fuel consumption. In order to prevent such a turn of events, it is recommended to adjust the valves after 10-15 thousand km. mileage
Valve knocking may occur due to engine detonation. As you know, detonation is a kind of explosion, the result of which is a wave capable of shaking all parts and components of the internal combustion engine, including valves. As a result, it turns out that due to detonation, a metallic clatter of the valves may appear, although the reason will not be in the valves. Signs of detonation: black smoke from the exhaust, strong vibration, loss of engine power.
A common phenomenon is when valves knock “hot,” meaning when valves click after the engine has warmed up. In this case, the reason may be increased speed at low oil pressure; this may again occur due to increased clearances or excessive wear of parts.
Chassis
Owners who have had the opportunity to travel not only behind the wheel of products of the domestic automobile industry, note that the Granta’s handling is far from ideal: the car does not hold a straight line well, behaves unstably when cornering and when braking. The main reason is the lack of a subframe.
As for the reliability and service life of suspension elements, shock absorber struts sometimes start knocking before the first maintenance. With a mileage of 80,000 km, the front fastenings of the front suspension arm braces may crack and fail. Ball joints rarely run more than 60,000 km. The remaining parts of the front suspension have an acceptable service life.
The rear suspension design is simple and reliable. Except that the service life of the wheel bearings is short - sometimes they have to be replaced at 40,000 km. The steering rack often begins to tap at 50,000 km. Adjusting the rack and pinion mechanism does not always help. The resource of the front brake mechanisms is also insufficient. It has been noted that the pads wear out quickly, and the discs are not durable. Sometimes discs, having survived three sets of pads, ask for replacement at 75,000 km. The rear brake mechanisms have their own problems: the handbrake cables become sour, the brake cylinders leak. And all this, as a rule, with mileages up to 100,000 km.
Knocking noise at high speeds.
The reason why a knocking sound appears in the engine at high speeds is detonation. Detonation is the process of combustion of the fuel mixture in the cylinder earlier than expected. As is laid down in the operating principles of any automobile internal combustion engine, all work is based on 4 strokes. Ignition of the fuel must occur strictly at a certain point in time. Sometimes, ignition occurs ahead of time, that is, before a spark appears on the spark plug. At this moment, detonation occurs and, as a result, the engine knocks at high speeds under load.
Detonation can occur for several reasons
- low octane fuel
- early ignition
- unsuitable spark plugs
- heavy carbon deposits in the cylinders
Detansion is the main enemy of an engine, and especially an engine with a turbine.
How to determine detonation?
If you have a knocking sound in the engine that is expressed by a loud and ringing sound when you gain speed, then this is detonation. It appears when the engine is spinning up, and under heavy loads on it. Cases when detonation occurs:
- During acceleration (at high speeds)
- When climbing uphill or when driving with a heavy load
- When the gear is too high for the current speed
Transmission
The manual transmission has been modernized more than once. It now has a cable drive, thanks to which the gears are engaged with less effort, and the accuracy of the selection mechanism has increased. This box has the factory index VAZ-2181. But the sound when its gears operate is still too loud. The problem with the second gear synchronizer has not been completely resolved. Poor engagement and rapid wear of the synchronizer, despite numerous upgrades, still occur. As well as oil leaks through the seals. The reason is the low quality of the seals themselves and the insufficient accuracy of the positioning of the seal relative to the shaft. All this fully applies to the VAZ-2182 robotic gearbox, because it was created on the basis of a mechanical one.
In the case of gearbox 2181, the clutch mechanism rarely lasts more than 100,000 km, especially if the car is used in a big city and often sits idle in traffic jams. In robotic gearboxes, the clutch lives even less.
The only truly reliable transmission in the line is a 4-speed automatic from the Japanese company Jatco.
Valves knock “cold” and/or “hot”
As mentioned above, the causes of valve knocking, first of all, include violation of thermal clearances. This gap may be too large or too small. A common situation is when valves knock on a cold engine, but as the engine warms up, the extra sounds disappear. Auto mechanics with extensive experience explain this phenomenon simply.
In a car engine with high mileage, the parts are already worn out, resulting in increased gaps between them. At the same time, the gaps remain within normal limits, that is, such an increase does not affect the proper operation of the systems and the engine itself. The only nuance can be considered an increase in valve noise on a cold engine. After the engine heats up, the metal expands, conditionally “selecting” excess gaps, and the engine begins to operate normally.
Another common situation is that the valve mechanism on a new or recently repaired engine is knocking. In such a situation, you need to check the quality of the adjustments. As already mentioned, the valves may become stuck and require readjustment. Another reason for knocking when cold is wear of the pusher. The formation of dirt and deposits in the pusher area, engine oil leakage and other deviations cause a decrease in the efficiency of lubricant supply. As a result, after starting a cold engine and until a certain warm-up, a ringing metallic sound is clearly heard. In this case, the valves “clatter” a lot.
For a more accurate determination, you can use a simple and accessible method. It is necessary to prepare an empty metal can or mug, which is applied to the surface of the hood and a knock is heard through it. The sound is heard more clearly, which allows you to more accurately determine the malfunction. Let us add that some car enthusiasts confuse the knocking of valves on a cold engine with the knocking of the timing chain. In this case, you need to carefully diagnose the malfunction, that is, check the condition and degree of tension of the chain.
Let's move on to diagnosing and finding out the causes of valve knocking, which cannot be eliminated by standard adjustments.
In some cases, when adjusting the valves does not help, it is necessary to remove the camshaft and check it for play. At the same time, the rockers should be inspected for severe wear at the ends of the valves. If such a development is detected, then it can be removed, after which it is necessary to check the marks and installation of the valves
During the inspection, equal attention is paid to both the intake and exhaust valves. The knocking of valves “when hot” after the engine reaches operating temperatures, in addition to the broken clearance, can occur at idle or when the engine speed increases
This often occurs due to a decrease in oil pressure in the lubrication system. In this case, you should check the suitability and condition of the lubricant in the engine (viscosity, degree of contamination, etc.), after which you will need to additionally measure the engine oil pressure. Also, we should not forget about the natural wear of parts or the occurrence of breakdowns, which naturally causes an increase in noise after the internal combustion engine warms up. When determining the causes of timing knock, you must always remember the phenomenon of engine detonation. If the process of fuel combustion in the cylinders becomes explosive, then the shock wave hits the cylinder walls and other elements of the CPG strongly. Such impacts can cause valve knocking, although the valve mechanism itself is serviceable and normally adjusted.
Reviews
| № | Positive |
| 1. | Vasily: I drove a little more than 50,000 km, there is no knock in the gas distribution mechanism. I regularly fill up with high-octane fuel and fill in Shell 10W-40 semi-synthetic oil. |
| 2. | Konstantin: in two years of active operation of the machine, the valve knocked once. As the service station worker found out, the reason was that the fastening nut was not tightened sufficiently. Half an hour later I was driving the car again. |
| 3. | Vladlen: I recently noticed dark-colored exhaust gases coming from a car, I thought there was a problem with the gas distribution mechanism. During the diagnostics, it turned out that there was a violation in the enrichment of the mixture in the system, as a result of which carbon deposits formed. |
| 4. | Ignat: I heard a lot of complaints about the gas distribution mechanism, I didn’t have any breakdowns in a year and a half of using the car. Perhaps the reason is constant maintenance, careful handling, refueling with high-quality oils and fuel. |
| 5. | Ivan: in two years of using the car, I cleaned the gas distribution mechanism once for preventive purposes. The machine works stably, there are no complaints. |
| Negative | |
| 1. | Vitaly: after 55,000 km, the valves began to knock, I took the car to the service center, and it turned out that the leg was deformed. Replaced with new ones, they gave a guarantee. Dissatisfied with the quality of workmanship. |
| 2. | Kirill: at the first convenient opportunity, re-tighten the valve mechanism on the Lada Granta. Lots of defects, poor quality fitting, loose knots. |
| 3. | Slavik: in the third year of operation of the machine, I replaced the valve mechanism with a new one. The old one has fallen into disrepair. |
Conclusion
The average service life of the gas distribution mechanism of the Lada Granta does not exceed 50 - 60 thousand km. In order not to reduce the resource, periodically carry out preventative maintenance on your car, replace worn parts with new ones.
Refilling with high-quality motor oils and high-octane fuel will only increase the life of the valve mechanism.
Often, the cause of premature wear of timing elements is an aggressive driving style. Increased load and high temperatures contribute to premature wear of components.
Engine knocking when cold
If you hear a dull knock when starting the engine, the cause is the crankshaft. It is in the first minutes that the sound is heard as clearly as possible, since the oil has not yet warmed up and, accordingly, has not lubricated this part. Over time, the sound disappears, but it can still be heard at idle. The knock, as was said, is dull, but its sonority can increase with increasing speed.
The main reason is severe wear of the shaft bearings, which leads to a large gap. The situation is further worsened by the use of low-quality oil with various impurities. The only way you can diagnose whether the crankshaft is the cause is at a specialized car service center by disassembling the engine. Repairs can be done by boring the crankshaft, but in particularly advanced cases, drivers will have to fork out money for a new part.
Also, another reason for knocking when cold is a malfunction of the camshaft. If the camshaft is heavily worn, of course, you will clearly hear sounds even after the car has warmed up. Also, the knocking frequency of this element is half the speed of the motor itself. This fact will additionally help with diagnosis. The reasons are similar to those described above: oil starvation, use of counterfeit products and increased wear of bearings.
Knocking from the camshaft is especially dangerous in cars equipped with hydraulic compensators. The problem is that they will compensate for the gap created between the pushrod and the camshaft, causing the valves to be misaligned. The result will be a drop in compression, a decrease in power and increased fuel consumption. To check the camshaft, you will have to disassemble the engine. If you do not have such skills, contact a car service.
Often the source of noise is the timing chain. In systems with hydraulic tension, oil may not flow immediately, which leads to knocking. The hydraulic compensators themselves can also “click.” In this case, they must be replaced immediately.
Third-party sounds on startup
Engine knocking during startup most often occurs due to malfunctions in the lubrication system.
Poor performance of the oil pump, insufficient amount of oil and clogging of the channels with pollutants leads to the fact that the oil does not have time to reach all the rubbing surfaces in time, which is why grinding and knocking noises are heard.
Due to problems with the lubrication system, oil does not flow into the hydraulic compensators, without which they begin to knock.
If noises appear during startup, it is advisable to stop the engine and check the oil level. If necessary, bring the level to the desired value.
If this does not help, you can change the oil and pre-flush the system.
Next, if the knocking noise persists during startup, you need to check the condition of the oil pump.