The situation when the battery is discharged overnight so that the engine is difficult to start is familiar to many. The reason is the high leakage current of the car battery. During idle time, the battery self-discharges and parasitic currents in the vehicle circuit consume energy. An article about how to identify hidden consumers and eliminate current leakage, identify acceptable energy consumption in a car during idle time and not drain the battery
Leakage from battery when ignition is off
If the ignition is turned off, the engine does not work and the battery does not recharge. All energy accumulated during movement is spent on powering consumers - heating windows, operating the media center, lighting. The more consumers that are not turned off, the faster the battery discharges. Therefore, all devices must be turned off during long periods of inactivity.
However, if the circuit of a TV, sound system, or air conditioner is incorrectly assembled, there may be a leakage current. Often the mistake that leads to a drop in battery voltage is putting these devices into sleep mode rather than turning them off completely. Checking for leaks with a multimeter will reveal the problem.
Oxidized wiring contacts lead to the occurrence of parasitic currents. The reason is resistance, which contributes to heating of the wires. In this case, stray currents are not the main thing - you can get a fire. Worn electrical wiring with twists and poor insulation has the same consequences.
However, the battery itself loses capacity over time and the rate of self-discharge increases. If there is no large current leakage, but the battery is discharged, then you need to check its suitability.
Finding the root problem
One of the key factors causing the problem is any electronic device or support for the operation of additional equipment.
These devices are being used more and more often in cars. During the search, devices installed independently of each other must be taken into account. The factory circuitry in the machine is well protected and a short circuit will only occur if there are significant defects. For example, if the protective cover is accidentally damaged. Sometimes the car owner misplaces the wires, placing them in the wrong position, which seemed most suitable to him. This usually causes a short circuit.
Failure results in loss of current in the battery . Wiring installed by the vehicle owner may be dangerously close to the engine. During operation, the motor becomes hot and the wire insulation may melt. The cord rubs against the edges of metal elements, especially in places where the door closes. As a result, the insulation is broken and a short circuit occurs in the electrical network.
After measuring the current consumption, it is necessary to begin a visual inspection of all equipment if the rate of loss of electricity in the machine does not correspond to the readings of the multimeter. It is necessary to take into account individual parts and assemblies that are subject to any mechanical stress. If it is difficult to identify breakdowns, you should move on to in-depth diagnostics.
What is the normal leakage current of a car battery?
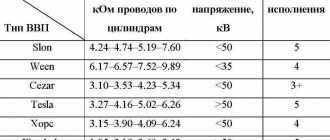
Why is battery leakage current allowed, and why is the norm determined? What should be the leakage current of a VAZ car of old models and a modern AUDI? It depends on the equipment. Both cars have a clock, a security alarm, but the AUDI has an ECU that cannot be turned off, an audio system.
The clock consumes 1mA, the alarm system consumes 20 mA, the audio system consumes 3 mA - and the norm for current leakage in a VAZ car will be 24-30 mA. For AUDI, the norm will be 50-80 mA, but there the generator is more powerful and the battery is capacious. The standard current drain from the battery depends on its equipment.
What should you keep in mind?
When carrying out preventive maintenance on the battery, we recommend checking the leakage current of the car battery. On a modern car, the norm is a value of 15─75 mA with the on-board network consumers turned off.
If the leakage current value significantly exceeds the norm, then at a minimum you should consult an automobile electrician. If you have a tester and the skills to handle it, then you can find the problematic device or faulty wiring yourself. We also recommend reading about how to check battery capacity.
How to check a battery for current leakage with a multimeter
Taking the leakage current in your own car as the norm, you can measure the total parasitic currents with a multimeter. Exceeding the norm can occur due to a short circuit in the network or too powerful additional consumers. Sometimes the cause of current leakage from the battery is a malfunction of the generator or starter. Only through consistent testing of the network for current leakage can the true cause of the drain in the vehicle battery capacity be established.
How to measure battery leakage current
To diagnose current leakage, you will need a multimeter tester - it can work as a voltmeter, ohmmeter and ammeter with wires and alligator clips. You will need an open-end wrench, gloves and a notepad for notes.
The car should be prepared:
- turn off all electronics, including the DVR and amplifiers;
- disconnect hidden consumers in the glove compartment and under the hood;
- open the hood, secure it and loosen the negative terminal on the battery;
- close the doors, but open the windows so that you can enter the cabin if the central locking works.
Procedure for measuring battery leakage current
- set the multimeter to measure amperes in the 10 A position;
- make an open circuit, connect an ammeter into the open only on the negative pole;
- take leak readings.
When the indicators correspond to the norm - 20-80 mA, the diagnosis is considered complete.
Find and fix the leak
In search of a violation accompanied by current leakage, you will have to examine the circuits of all consumers. You need to start with installed freelance equipment. This is where problems are often found. Reasons: additional wiring was installed in an inappropriate and inconvenient location. They can heat up and chafe.
The problem areas are considered to be alarms and doors. The limit switches on the door closing and opening circuit may be faulty. The alarm after switching on after 5 minutes should reduce current consumption. No - a reason for examination.
If the causes of the leak have not been established, the generator needs to be checked. If the power unit does not recharge the battery, this is determined as follows:
- Measure the voltage at the battery terminals in the absence of consumers - when fully charged, 12.6-12.9 V.
- Start the engine, turn on consumers - heating, headlights, heater, measure at the battery terminals - from 12.8 to 14.3 V.
The voltage at the terminals is less - the generator does not recharge the battery.
Watch the video on how to check your battery for current leakage.
Circuit breakers
The signaling and “music” stand apart. Whether you need to “dig” further is up to you to decide. If your qualifications and experience do not allow you to eliminate the current leak on your own, it is better to go to a service center. Now even a dishonest serviceman will not be able to fool you, because you already know the cause of the leak.
- Electrical leakage in a car is a common fault.
p, blockquote 1,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 2,0,0,0,0 —>
It is found even in new cars, in which, being packed with electronic devices, it is extremely difficult to detect and eliminate leaks.
p, blockquote 3,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 4,0,0,0,0 —>
Normal battery leakage current
Current leakage refers to the presence of current flowing from the power bus to ground or to a common wire. It is known that the starting circuit of the ignition switch is powered by bus 15. Bus 30 powers the entire vehicle network from the positive terminal of the battery. Switching off the ignition does not interfere with the energy consumption of other devices. Checking the battery for current leakage is carried out by measuring with a multimeter and visually examining the condition of the wires.
Therefore, with a large leakage current, consumers from bus 30 are examined one by one:
- Car radio – on a working radio the leakage is 10 mA.
- Car alarm - the security device consumes up to 200 mA of current, depending on the brand. There is feedback, a transceiver, GSM, but modern systems minimize the permissible battery leakage current.
- The engine control unit is powered by bus 30, its leakage is a few milliamps.
- Climate control, ABS, body control and other control systems together allow a leakage current of 10 mA.
- A faulty generator will completely discharge the battery in 30 minutes; in a normal situation, the leakage is a few mA.
- Wet and dirty contacts create electrolysis currents and parasitic currents. With normal maintenance of wires and contacts, the leakage current is about 5 mA.
- Self-discharge of a battery is also a leakage current. Internal self-discharge is caused by the quality of the electrolyte, sulfation, destruction of the plates, and it can exceed all other losses.
The leakage current rate is calculated taking into account all consumers, depending on the type of car brand.
What does the generator have to do with it?
The generator is responsible for replenishing the battery charge and normally must keep the current at the same level and can itself create problems. Firstly, if there is insufficient power or a technical breakdown, due to insufficient tension of the drive belt, the generator cannot produce the required voltage. Its malfunction affects the stability of the on-board electrical system. Secondly, the excess voltage created by the generator can accelerate the wear and tear of other electrical equipment, including the battery.
If the diode bridge of the generator breaks down and its windings short-circuit, it itself can turn from a source of electricity into a consumer and contributes to even greater leaks and after the battery gives up all its charge, the car will lose its functionality.
Electrical equipment is one of the basic systems of a car, the serviceability and stable operation of which largely determines the convenience and safety of all systems.
Leaks in the on-board electrical system of cars are one of the most common problems. They cannot be ignored, because over time this can lead to serious damage.
Carry out diagnostics of electrical equipment on your car in a timely manner.
High battery leakage current - problems
A large leakage current, at which it is imperative to find the problem point, is considered to be 0.5 A. A loss of half an ampere in ten hours will absorb 5 A/h, and a car left for 4 days will be discharged to zero. Therefore, when parked for a long time, the car is left with an open circuit.
If there is a problem unit in the car in which a leakage current is created, heating will definitely begin in the transistor or microcircuit. The block will fail. If current leaks through the conductor, a fire will not occur, but the insulation may be damaged. This will lead to a short circuit, intense heating at the contact point and a fire.
How to find current leakage on a battery without a device? In the dark, stop the car, open the hood, close the door, but do not activate the security system. Remove the wire from the positive terminal and wait 5 minutes. Reconnect the battery terminal. If there is a strong spark, there is a leak. A small spark is a natural process. Next, you should measure the indicators and determine the problem area.
An absolutely accurate sign of current leakage without measurement - after a week of parking, a fresh battery is completely discharged.
Battery leakage current
How to determine a specific source of energy consumption?
Perhaps the contacts on the battery have just oxidized - clean them well:
- We leave our car with the ammeter connected.
- Open the fuse box and begin to remove the fuses one by one.
- At the same time, we look at the ammeter readings (by pulling out the fuse, you have broken the circuit, thereby closing the source of energy consumption).
- We go through all the fuses until we find the most consumed one, after removing which, the ammeter readings show acceptable numbers (no more than 0.20-0.40 mA per hour).
- Having found the right fuse, we look at what it is responsible for. Next, we begin to work with the direct source of energy consumption.
After checking all the fuses and not finding the problem, then perhaps the source lies in the relay block. Either the relay is stuck, or the wires are worn out and shorted (we check all rivets and washers with insulation for resistance). In this situation, the relay unit must be replaced.
If after all the checks of the fuses and relays nothing is found, then the current consumption lies in a circuit not equipped with a fuse: Starter, alternator, etc. Most likely the diode bridge is broken (see 3 weak diodes going to excitation).
A couple of tips from experienced car enthusiasts
Tip 1.
It is not necessary to measure leakage using the “negative” terminal; you can test the on-board network using the “positive” terminal.
The algorithm of actions is approximately the same - the terminal block is disconnected from the “positive” terminal of the battery.
Probes are connected to them and measurements are taken. But if when measuring on the “negative” terminal the polarity of the device connection is not important, then when checking on the “plus” it is important to connect the device correctly - the “negative” probe of the device is connected only to the terminal block with a wire, and the “positive” probe to the battery terminal.
It is important here not to confuse the polarity, otherwise you can damage the device.
Tip 2.
Before taking measurements, it is better to open the car windows, and you should not leave the keys in the ignition.
The fact is that when the terminal block is disconnected from the battery, the central locking may be activated, as a result of which the car will close.
Open windows and keys in your pocket will avoid such troubles as a locked car with the keys inside.