Print this article Font size 16
Regardless of the type of engine installed (carburetor or injector), on the VAZ 2109 we are dealing with a distributor-type ignition system. On the one hand, this is good, since replacement and repair of the unit is cheap. But the resource of parts leaves much to be desired.
Appearance of the device
Ignition coil malfunctions
The main types of ignition coil malfunctions include:
- A short circuit between the turns of any of the windings of the product.
- A break in the electrical circuit of the primary or secondary windings.
- Insulation breakdown of the secondary winding on the body of the device.
- There is a lubricant leak on the product cover.
- Defects on the device cover.
- Incorrect values of the measuring device when measuring the resistance value of the ignition coil of any winding.
With such above defects, the coil must be replaced. A qualitative check of the ignition coil is divided into several tests. These include:
- testing the product resistance in both circuits;
- testing the resistance of the device to the “mass” of the device.
To carry out the test, two conditions must be met: the external temperature must be in the range of 20-25 degrees Celsius and the presence of a measuring device - a megger. We connect the “crocodiles” of the device to the contacts of the product on the right and left and take measurements in the selected range. The winding resistance should be within the range of 0.4-0.5 Ohms. If the measurement value is different, the ignition coil must be replaced with an updated product.
To carry out the test, you need to connect the alligator clips to connector “B” and to the central contact. At the previously determined temperature value of the atmosphere, the measuring device in the given register should show 4.5-5.5 kOhm. If the measurement value of the “nine” ignition coil is different, then the device must be replaced with an updated product.
To test the resistance of the device to ground, one contact is attached to the body of the VAZ 2109 ignition coil, and the other to each output of the product in turn. When taking measurements, the megger must produce a value of at least 50 mOhm in the corresponding register. If the measurement indicator is different, the Lada coil of the ninth model must be replaced with an updated product.
Despite the fact that this “nine” ignition complex is not particularly difficult for a specialist, the principle of its operation is based on the fundamentals of electromagnetic induction and electrical phenomena. This makes it necessary to approach its diagnosis with a certain amount of knowledge in these areas.
In theory, everything turns out quite simply, but a number of car enthusiasts offer an alternative way to increase the functionality of the ignition coil by “nine”. They propose to replace the reel with a product with item number B-117, and replace the set of candles with a set of other products indexed in the number with the same name, but without the letter “P”. These experts assure the excellent reliability of this replacement and report that all the advantages of the contactless ignition system are preserved. The owners of the “nines” will have to make a decision!
Ignition coil
VAZ
2109
. system check
If suddenly the engine starts to stall, the power disappears, or the car won't start at all, the problem most likely lies with the ignition system. If we are talking about a VAZ 2109 carburetor engine, then the ignition system can be corrected even by a beginner. First, you should check the coil
ignition VAZ 2109, trampler, high-voltage wires, etc.
To check the ignition system, you need a multimeter, a Phillips and flathead screwdriver, and pliers with insulated handles. To set the ignition timing, you may need a 12V lamp with socket. To test for spark, you will need one accurately working spark plug, as it is strongly recommended not to test for spark from wire to ground.
When repairing the ignition system on a VAZ 2109, you can get a very unpleasant, but not fatal, electric shock from a high-voltage wire. To prevent this from happening, do not handle high-voltage wires with your bare hands while the ignition is on. For these purposes, it is best to use thick rubber gloves or insulated pliers.
Distributor slider VAZ 2109
Removal and installation
If the distributor fails, it can be repaired or replaced with a new one. It all depends on the specific failure.
The removal and installation procedure is as follows:
First you need to de-energize the car's electrical circuit by disconnecting the battery. Then you need to disconnect the wires from the switchgear. After this, also disconnect the vacuum tube going to the corrector. Next you need to find the cable holder that goes to the throttle actuator. This cable must be removed. Remove the bracket holding the wires, along with them and the pins. To do this you will need to unscrew the nut. Be careful. There is a washer under the nut, you can't lose it. After this, you need to mark the switchgear housing and the drive of the auxiliary elements. If you do not put a mark, then after further securing the mechanism in place you will have to reinstall and adjust the ignition. On the distributor body there is a socket to which the high-voltage wire harness is connected. The fasteners need to be compressed; to do this, remove the wires using a screwdriver. Then remove the rubber plug that is located in the clutch housing. Rotate the crankshaft by hand until the piston of the 1st cylinder reaches TDC. The mark on the flywheel in the hole should correspond to the center line on the housing scale. You can then unscrew the nuts that secure the manifold and remove it. As for further installation, it is carried out in the reverse order. When reinstalling the device, make sure that the valve shaft rotates so that the outer contact of the slide is opposite the terminal corresponding to cylinder 1 of the internal combustion engine. The terminal itself is located on the lid. During installation, combine the risks as we reported above. If you have difficulty installing the ignition, use this article.
Sorry, there are no surveys available at this time.
Purpose of distributor VAZ 2109
In any ignition system, contactless or contact, there are two circuits. high voltage and low voltage. Distributor, ignition distributor. It is a device that deals with both high voltage wiring and low voltage wiring. His main task. distribute high voltage between the spark plugs at the right time and in a certain order.
The distributor works as follows. High voltage is created in the ignition coil due to electromagnetic induction. It is connected via a high-voltage wire to the central contact of the distributor cap. The contact is in constant interaction with the slider, which distributes the current to four contacts corresponding to the spark plug in the cylinder. The slider constantly rotates and alternately closes the central contact with the spark plug contacts. Current is supplied to the spark plugs through high-voltage wires in the order determined by the cylinder sequence. 1-3-4-2. The slider is driven by a drive shaft, which is connected to the camshaft.
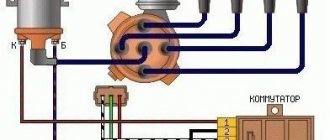
Sensor-distributor 40.3706
1 – coupling; 2 – body; 3 – vacuum regulator; 4 – vacuum regulator rod; 5, 7 – covers of the vacuum regulator; 6, 12 – springs; 8 – fitting for supplying vacuum; 9 – diaphragm; 10 – centrifugal regulator; 11 – contactless sensor; 13 – driven plate of the centrifugal regulator with screen; 14 – roller; 15 – weights; 16 – oil seal; 17 – cover; 18 – rotor; 19 – protective screen; 20 – holder of the front roller bearing assembled with the sensor support plate; 21 – washer for fastening wires; 22 – sensor support plate with bearing.
Features of the operation of different ignition systems
Ignition on the VAZ 2109 is necessary to ignite the air-fuel mixture when starting the engine. If the ignition does not work correctly, the engine will start and run intermittently, and its power during start-up and acceleration will noticeably decrease. In addition, fuel consumption will be noticeably increased. The conclusion from this is that the correct operation of the ignition system should be constantly monitored.
It’s worth mentioning right away the differences in the ignition design of “nines” with different types of fuel supply. Their SZ is similar, but they differ in the elements of electric charge distribution.
- In “nines” equipped with a carburetor, there is a coil and a distributor.
- For systems with an injector, an ignition distribution module consisting of several coils and an electronic controller is installed.
The second difference is how the system works. In cars with an injector it is not required, but in VAZs with a carburetor you have to do it manually.
In nines, two types of ignition systems are used:
- contact;
- contactless with transistors.
The first is installed in carburetor “nines”, and the second in injection ones. Thanks to the use of contactless ignition, the system has the following advantages:
- Working with a Hall sensor, which makes the system more stable and increases its overall efficiency.
- The absence of contact with the working parts and elements of the system increases the service life of the elements and makes maintenance of the circuit components easier.
- Excellent spark distribution between spark plugs.
- Generating a powerful spark, which prevents system failures.
- Fuel economy.
- Works even with low battery charge.
Over time, the contact type SZ has practically ceased to be used, so from now on we will focus on the contactless analogue.
Kalina, 1117-1119
A more modern VAZ model, Lada Kalina, is equipped with an ignition module marked: 2112-3705010-12. It has the following characteristics:
Load voltage 1MΩ +25pF>24kV
Spark charge duration 1.14-1.5 ms
Operating temperature range from -40 to +140 degrees C
Rated supply voltage 12V.
Ignition coil malfunctions
The main types of ignition coil malfunctions include:
- A short circuit between the turns of any of the windings of the product.
- A break in the electrical circuit of the primary or secondary windings.
- Insulation breakdown of the secondary winding on the body of the device.
- There is a lubricant leak on the product cover.
- Defects on the device cover.
- Incorrect values of the measuring device when measuring the resistance value of the ignition coil of any winding.
With such above defects, the coil must be replaced. A qualitative check of the ignition coil is divided into several tests. These include:
- testing the product resistance in both circuits;
- testing the resistance of the device to the “mass” of the device.
To carry out the test, two conditions must be met: the external temperature must be in the range of 20-25 degrees Celsius and the presence of a measuring device - a megger. We connect the “crocodiles” of the device to the contacts of the product on the right and left and take measurements in the selected range. The winding resistance should be within the range of 0.4-0.5 Ohms. If the measurement value is different, the ignition coil must be replaced with an updated product. To carry out the test, you need to connect the alligator clips to connector “B” and to the central contact. At the previously determined temperature value of the atmosphere, the measuring device in the given register should show 4.5-5.5 kOhm. If the measurement value of the “nine” ignition coil is different, then the device must be replaced with an updated product. To test the resistance of the device to ground, one contact is attached to the body of the VAZ 2109 ignition coil, and the other to each output of the product in turn. When taking measurements, the megger must produce a value of at least 50 mOhm in the corresponding register. If the measurement indicator is different, the Lada coil of the ninth model must be replaced with an updated product.
Despite the fact that this “nine” ignition complex is not particularly difficult for a specialist, the principle of its operation is based on the fundamentals of electromagnetic induction and electrical phenomena. This makes it necessary to approach its diagnosis with a certain amount of knowledge in these areas. In theory, everything turns out quite simply, but a number of car enthusiasts offer an alternative way to increase the functionality of the ignition coil by “nine”. They propose to replace the reel with a product with item number B-117, and replace the set of candles with a set of other products indexed in the number with the same name, but without the letter “P”. These experts assure the excellent reliability of this replacement and report that all the advantages of the contactless ignition system are preserved. The owners of the “nines” will have to make a decision!
When should you change the ignition coil? • The coil must be replaced if various types of defects appear on the ignition coil itself, namely on its plastic part: 1. Cracks. 2. Skolov. 3. And also signs of overheating. 4. And traces of oil leaks.
Checking the coil for VAZ 2101-2110
First, let's look at the sequence of checks on VAZ cars. Moreover, checking the carburetor for VAZ-2101 and VAZ-2110 is no different, the only difference is in the readings.
Next is the verification process itself:
It is better to test the coil when it is removed from the car. Before starting removal, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery. From the coil we disconnect the wires from the side terminals, as well as the central wire. It is better to mark the wires from the side terminals so that they are not confused during installation. Loosen the coil fastening and remove it
Before checking with a multimeter, we clean it from dust and dirt, especially paying attention to the terminals. Then we inspect it for external damage.
If there are any, further checking is pointless; it is better to replace it immediately; Checking the primary winding. To do this, switch the multimeter to ohmmeter mode and connect its probes to the side terminals. Different types of coils were used on different VAZ models, so you need to know which resistance readings are correct for them. So, for the B-117A model, used on classical models (VAZ-2101-2107), the resistance of the primary winding is 3.07-3.5 Ohms. And on classic models with a contactless system, coils marked 27.3705 are used; this parameter is 0.4-0.5 Ohm. On VAZ-2108-21099 cars, as well as VAZ-2110 carburetor, models with numbers are used - 3122.3705 and 8352.12. For the first of them, the resistance of the primary winding is considered normal in the range of 0.39-0.47 Ohms, and for the second - 0.37-047 Ohms; Next, the secondary winding is checked. To do this, switch the multimeter to the kOhm measurement mode, leave one of its probes on the side terminal, and connect the second to the central terminal. For a working B-117A coil, the resistance of the secondary winding should be 7.4-9.2 kOhm. For model 27.3705 this parameter should be around 5.0 kOhm, for 3122.3705 - 0.4 kOhm, and for 8352.12 - 1.0 kOhm; The last thing to check is the insulation resistance. To measure this parameter, switch the multimeter to measurement mode in MOhm. To measure, we connect one probe to the coil body, and connect the second to each terminal in turn. When measuring this parameter on all specified models, the multimeter should show at least 50 MOhm; If any of the parameters does not match the specified values, then the coil is faulty and must be replaced.
Recent comments
- Mechanik on Carburetor starting device 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex Check the fuel level in the carburetor float chamber. Plus check if the fuel pump is pumping.
- Boris on Carburetor starter 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex After gas does not work on gasoline. The engine starts for 2-3 seconds and stalls. Half a minute later the same thing.
- Boris on Carburetor starter 2108, 21081, 21083 Solex engine starts but stalls after 2-3 seconds. after 0.5 minutes the same thing
- Andrey on Replacing thresholds on a VAZ 2108 Thank you, useful article. I also have to change the threshold on the eighth road.
THE MOST KNOWN PROBLEMS WITH IGNITION COIL BREAKAGE:
- Winding damage. This factor leads to breakdown of the insulating layer, resulting in a short circuit.
- Open circuits and overload. The reason is a malfunction of the spark plugs or due to defects in high-voltage wires.
In general, ignition coils fail quite rarely, but sometimes such troubles do happen. Typically, the insulating layer of the coil can be damaged as a result of an instantaneous voltage increase of up to 35,000 V. As a result, the secondary voltage drops and misfires occur under load. As a result, the coil cannot produce the voltage needed to start the engine running.
Reasons for failure of ignition coils:
— Spark plugs are of low quality. Always monitor the quality of the spark plugs installed on your car and do not install cheap fakes - if you skimp on this, you can end up getting stuck for a much tidy sum. The reason is reverse gases and insulator breakdown, which adversely affect the condition of the rubber tip of the ignition coil.
— Overheating of the ignition coils. Structurally, the coils are designed to work at any temperature conditions of the engine, but as practice has shown, if your engine is hotter than it should be (lean mixture, faulty cooling system), the coils “die” more actively. We do not want to say that any heating is fraught with danger to the coil, but there is a certain resource for heating-cooling cycles. This also affects the rubber tip and the electronics of the reel.
What are the risks of driving with a non-working coil:
— Melting of the catalytic converter in the exhaust system.
— If you drive with a faulty coil, the engine mounts may wear out over time due to excessive vibrations.
— High fuel consumption associated with a drop in engine power and efficiency.
How to check a non-working coil yourself:
— The easiest way is to alternately disconnect the connectors (chips) from each coil in turn during “triplication”, so when you disconnect a chip from a working coil, you will hear a dip in revolutions and unstable operation on the remaining cylinders, and when disconnected from a non-working coil, the engine will run Will not change. It is this coil that needs to be changed.
— If it is possible to remove the coils, then a good way to determine this is to measure the resistance of the primary and secondary windings (between the contacts, between the contacts and the output to the spark plug), record and compare the readings on all coils, usually the resistance of faulty coils is strikingly different
In addition, pay attention to the condition of the spark plug electrodes; on a faulty coil, the spark plugs are usually wet and with black soot
- In some cases, the car’s self-diagnosis can “tell” which cylinder is not igniting (only if the check engine light is on). Look for trouble codes for your car.
How professionals determine a faulty ignition coil:
There are motor testers (scanners) that allow you to analyze the operation of electronic components of cars, including coils. The author of the article came across three different methods for professionally identifying a faulty coil: alternately turning off the cylinders (turning off the injectors), alternately turning off the control voltage, and analyzing the curves of an oscilloscope connected to the coils.
Professional diagnosticians NEVER DISCONNECT THE COILS MANUALLY, as this can lead to failure of the engine ECU.
What to do with a non-working coil???
The most reasonable way is to replace it, all imported ignition coils are non-separable and filled with polymer to prevent moisture from entering, even if you can replace/repair microelectronic parts, it is no longer possible to assemble the coil without oxygen getting inside. Replacing the ignition coil - only in this case can you ensure long-term operation of your car!
If the manufacturer of your car has provided for the supply of a separate rubber tip from the ignition coil, you can order and replace the old tip with a new one, but this will not guarantee you that the electronic part that worked under increased load has survived in the old coil.
Examination
If you notice signs of a problem with the ignition coil, or have to deal with a situation where the engine “died,” be sure to check the condition of this element.
As you test, you will be able to determine what caused the coil to fail and how the problems can be corrected.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Z5cUQhKBZm0
Ignition coil
How to check the device? The instructions are not complicated, even a beginner can handle it.
First, let's check the condition of the unit, and then check for correctness of the resistance of the coil itself.
- If the engine cannot be started, make sure that the coil itself is producing a spark at all. To do this, the central wire is removed from the distributor and a spare spark plug is connected to it.
- Now take the spark plug with pliers and place the metal casing on the breaker or motor.
- If a spark does not appear when the engine starter is turned, there is a malfunction in the ignition system.
- So check the power to the coil, or rather its presence. For this you will need a multimeter. One terminal is connected to contact B on the coil, and the second goes to ground. Turn on the ignition. If there is no voltage, the culprit is the ignition switch.
- You can start the engine in emergency mode. To do this, the plus from the battery is thrown onto contact B of the coil.
If there is voltage but there is no spark, check whether the primary winding is intact. To do this, the side low-voltage wires are disconnected from the coil and resistance measurements are taken with a multimeter. Then the secondary winding is checked.
ignition coil
We will tell you about this procedure in more detail.
Multimeter for testing
Checking coil resistance
- Unplug your car. To do this, simply disconnect the negative terminal from the battery.
- Disconnect all wires and leads going to and from the coil.
- Be sure to arm yourself with the necessary tools and a tester. A universal multimeter or ohmmeter will work fine.
- Take measurements on the primary winding. To do this, the tester probes must be connected to the low-voltage terminals located at the edges of the coil. Before doing this, do not forget to clean the terminals from accumulated dirt and traces of oxidation. Surely they formed during the operation of the car.
- Record the data.
- Now the resistance of the secondary winding is checked. To do this, you need to transfer one ohmmeter probe to terminal B of the coil, and the second to the high voltage.
- Note your results.
- The last stage of the test involves measuring the insulation resistance to ground. To do this, you need to connect one terminal of your tester to ground (this is the ignition coil housing), and connect the second one in turn to all three terminals - a pair of low-voltage terminals and one high-voltage one located in the middle of the device. If the coil is working properly, then in all three measurement cases you will get a resistance of at least 50 ohms.
- Check the table against the previously recorded data.
[media= https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2F4BDExybgs]
| Coil type | Winding | Resistance indicators |
| 3122.3705 | Primary winding | 0.43 ohms +/- 0.04 ohms |
| 8352.12 | 0.42 ohm +/- 0.05 ohm | |
| 3122.3705 | Secondary winding | 4.08 ohms +/- 0.40 ohms |
| 8352.12 | 5.00 ohms +/- 1.00 ohms |
We measure the resistance of the ignition coil
Repair
In fact, the only way to repair a faulty ignition coil on a carburetor or injection VAZ 2109 is to replace the device.
Here you just need to choose which element will replace your old coil.
- MZATE-2. This is a standard coil, which all VAZ 2109s were equipped with from the factory. It costs about 600 rubles and serves well;
- An excellent alternative option, characterized by reliability, durability and operational efficiency. But it costs about 1800-2000 rubles;
- Valeo. Something between the factory and Bosch version, which has good characteristics and positive reviews. Today such a reel costs an average of 1,500 rubles.
The coil is the most important element of the ignition system; if it fails, you can forget about traveling about your business.
How to check an ignition coil: 3 proven methods
Loading …
Coil resistance measurement
It is important to note that this procedure cannot be performed without an ohmmeter or tester. The procedure is as follows:
- the car is de-energized (by disconnecting the negative cable from the battery);
- completely remove all wires from the coil;
- measurements are taken on the primary winding (the probes are applied to two low-voltage terminals, installed as we remember - along the edges);
- to avoid distortion of readings, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the outputs from dirt and oxides;
- It is better to write down the results.
Next, measure the resistance on the secondary winding with a tester. Here one probe is combined with the “B” contact, and the second with a high-voltage cable.
And finally, all that remains is to find out what the ground resistance is. To do this, one wire of the multimeter is applied to it, and with the second you need to touch three contacts in turn:
- two low-voltage;
- one high-voltage one (it is in the center of the coil).
If nothing happened to it, then in all three cases the tested resistance level will be within 50 Ohms.
Depending on the type of coil, the normal readings in Ohms will be as follows:
- at primary – 0.43 +/- 0.04;
- on the secondary – 4.08 +/- 0.40.
If nothing happened to the distributor, you will need to inspect the switch module - this can be done using a light bulb.
It will not be possible to check it qualitatively, since a special stand is used for this in car repair shops. But a light bulb (12-volt) will confirm that the impulse controlling the spark is being received.
To do this, remove the wire from the “K” connector from the coil itself and connect the lamp itself into the circuit in series (at break). When the starter starts working, it should blink - this indicates that the switch is working. Otherwise, it will need to be replaced with a functional one.
It is also worth understanding that the coil itself cannot be repaired.
Source
Checking the ignition coil on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
If such malfunctions occur in the operation of the engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars such as the disappearance of a spark or a weak spark, unstable idling, inability to adjust idle speed, difficult starting or impossibility of starting the engine, failures and jerks when starting and in motion, etc., It makes sense to check the functionality of the ignition coil.
Required Tools
- 8 mm spanner or open-end wrench
— a tester (multimeter or similar device) with an ohmmeter mode (preferably also a megohmmeter)
Preparatory work
You can check the ignition coil on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars without removing it from the car.
- remove the negative terminal from the battery
- disconnect the high-voltage wire from the ignition coil
- disconnect the wires leading to the two terminals of the coil
To do this, use an 8 mm wrench to unscrew the nuts securing the wires to terminals “K” and “B”. We disconnect the wires, remembering their position, so as not to confuse them when installing them back.
— Check the serviceability of the primary winding of the ignition coil
Checking the primary winding of the ignition coil of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 To do this, connect one tester probe to terminal “B” and the second probe to terminal “K” - the terminal of the primary winding. We turn on the device in ohmmeter mode. The resistance of a serviceable primary winding of the ignition coil should be close to zero (0.4 - 0.5 Ohm). If it is lower, then there is a short circuit, if higher, there is a “break” in the winding.
— Check the serviceability of the secondary (high-voltage) winding of the ignition coil
Checking the secondary winding of the ignition coil of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 To do this, connect one tester probe to terminal “B” of the ignition coil, and the second probe to the terminal for the high-voltage wire. We measure resistance. For a working secondary winding it should be 4.5 - 5.5 kOhm.
— Check the insulation resistance to ground
For such a test, it is necessary that the multimeter has a megohmmeter mode (or a separate megohmmeter is needed) and can measure significant resistance.
To do this, we attach one tester probe to terminal “B” of the ignition coil, and press the second probe to its body. The insulation resistance must be very high - 50 mOhm or higher.
If at least one of the three checks shows a malfunction, the ignition coil should be replaced.
Notes and additions
— Ignition coils installed on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars can be of two types: dry with a closed magnetic circuit (3122.3705) and oil-filled with an open magnetic circuit (8352.12, 027.3705, 27.3705, 27.3707-01, ATE1721). The winding resistances for them are slightly different. Coil 3122.3705 – primary winding 0.43±0.04 Ohm, secondary 4.08±0.4 kOhm. Coils 8352.15, etc. – primary winding 0.42±0.05 Ohm, secondary 5±1 kOhm. Measurements were carried out at +25 degrees.
Twokarburators VK - More information on the topic in our VKontakte group, on Facebook Twokarburators FS, in Odnoklassniki - Twokarburators OK and in Yandex Zen - Twokarburators DZ
— The procedure for connecting high-voltage wires to the distributor cover on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Malfunctions of the contactless ignition system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Malfunctions of the distributor of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Checking high-voltage wires on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Setting the ignition timing on the engines of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Comparative test repair
— Checking the ignition coil of the ignition system of carburetor engines of VAZ 2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106, 2107 cars
How to check the ignition module?
We have already learned what the ignition module is and what are the signs of its malfunction (unstable idling, failures during acceleration, engine twinkling).
In this article we will talk about how to check the ignition module with your own hands.
From personal experience: on the Internet, while reading various forums on this topic, I came across a post that broken high-voltage wires do not affect the ignition module in any way. In fact, faulty high-voltage wires can lead to the fact that a spark, in search of the shortest direction, can be sent to a nearby relay, which contributes to module burnout.
Let's move on directly to checking the ignition module. To correctly and accurately check the ignition module, you need a device such as an oscilloscope. But, as a rule, the average driver does not have anything like this, except for the usual warning light and tester, so our task is to use only these devices that are available to everyone.
Checking the ignition module
Before checking the module itself, we need to check the block of wires coming to it.
To do this, first of all, disconnect the wiring block, take the tester and connect one tester probe to the block at pin A, connect the other probe to engine ground. Turn on the ignition and look at the tester readings: the voltage should be around 12V. If there is no voltage, then you need to check the fuse. going to the ignition module. The next step is to take a 12V test light and connect it to contacts A and B. Turn on the starter and look: the light should blink, if it doesn’t blink, then there is an open circuit on contact A. We perform this operation in the same way with contact B. There are several ways to check the ignition module , and we will look at some of them.
1. The first and easiest way to check a module is to replace the module with a known working one. Everything is simple here: we take the module from the donor’s car and change it. But there are certain disadvantages:
- The donor car may not be available, buying a new module does not suit our task;
- Not every car will have an ignition module: “of course!” - you say, - “from SAMAR this will do.” But not everything is so simple: as a rule, the first Samaras with a 1.5 liter engine are equipped with an ignition module. New Samaras with 1.5 and 1.6 liter engines are often equipped with ignition coils. Let me remind you that the ignition module consists of a switch and an ignition coil. In new Samaras the switch is located in the ECU. Therefore, the module is eliminated as unnecessary, leaving only the coil. Take this fact into account and look for a new donor;
- It is imperative to make sure that the high-voltage wires are in good condition: how to check the high-voltage wires?
Otherwise, there is a high probability that the ignition module will burn out.
2. The next method is the method of moving the module. To do this, we move the block of wires, knock and move the module itself. If, at the moment of our influence on the module, the operation of the engine changes noticeably, then the matter is most likely in poor contact. This malfunction is not catastrophic, so you can try to repair the module yourself: Repairing the ignition module. If the module cannot be repaired, then it must be replaced (Replacing the ignition module).
3. To check we need a tester. Using a tester in ohmmeter mode, we measure the resistance at the paired high-voltage terminals of the ignition module 1 and 4 of the cylinder; and between cylinders 2 and 3. The resistance should be the same but vary around 5.4 kOhm.
labavto.com
One of the reasons for problems with a spark in the internal combustion engine on a VAZ 2109 is a malfunction of the ignition coil (IC). To accurately diagnose a malfunction, you need to know the design of the unit, be able to check it and, if necessary, install a new product.
Coil design features
This unit is designed to convert low on-board voltage (12 V) into high voltage (15-30 thousand V), which is supplied to the spark plugs to ignite the fuel assemblies in the engine cylinders. The impulse is transmitted through high voltage wires.
Both engines with injector and carburetor engines have an ignition system with a distributor (distributor). The scheme of work is not complicated. The distributor receives low-voltage current, which is then transmitted to the short circuit. The received pulse is converted into high-voltage current. Then the distributor distributes it in a certain order to the candles.
The main elements of the coil are the primary and secondary windings, wound on an external magnetic circuit. The first one has a small number of turns of copper wire - from 100 to 150, but it has a large cross-section. The second has a much larger number of turns - from 15,000 to 30,000, the wires are also made of copper, but with a smaller cross-section. There is a primary winding on top, and a secondary winding inside it.
In the secondary winding, a high-voltage current arises due to the action of electromagnetic induction and the accumulation of charge in the primary winding, which arise after cutting off the current in the primary. The high-voltage current is supplied to the central terminal of the short circuit, and then the distributor distributes it to the spark plugs.
Signs and causes of malfunctions
Most often, the spark disappears unexpectedly, but attentive drivers with experience can predict the disappearance of the spark by the following signs:
- 500 km before the end of the short circuit service life, the car can sometimes be difficult to start, only after a few minutes of warming up. Some drivers associate this with idling.
- When starting a cold engine and pressing the accelerator pedal, the engine begins to actively rev. This lasts a few seconds and after further pressing the accelerator, the engine runs normally.
- Dips or jerks at start.
- Unstable idling, unstable engine operation at low speeds.
- When you press the accelerator hard, instead of increasing speed, dips appear.
- Weak spark or its complete disappearance.
Typical short circuit faults:
- there are oil stains on the cover;
- short circuit between the turns of any of the windings;
- breakdown of insulation of the secondary winding to the housing (ground) short circuit;
- break in the electrical circuit of the windings;
- mechanical damage or defects on the body or cover of the short circuit;
- The readings on the measuring tester do not meet the requirements.
Device Features
The ignition coil serves to produce a spark coming from the spark plug electrodes. To put it briefly and simply, this is a small transformer that operates in pulse mode and converts 12 volts from the car into 20-30 thousand volts at the output. High-voltage wires are used to transmit the impulse, which also sometimes cause coil malfunctions.
The distributor-type ignition system works simply - the distributor (distributor) receives a low-voltage pulse from the car's network, transmits it to the coil, and it, in turn, transforms the pulse into a high-voltage pulse. Next, the distributor distributes sparks among the cylinders depending on the order of their operation.
Structurally, the VAZ 2109 coil consists of a pair of windings - secondary and primary.
- The primary winding has fewer turns, but wires with a larger cross-section;
- The secondary winding of a coil with a large number of turns, but a smaller wire cross-section.
Windings
Signs of breakdown
Often the spark at the carburetor disappears unexpectedly when the driver is not prepared for such a turn of events. But if you have enough experience and pay close attention to the behavior of your car, you can detect signs of a malfunction before the spark disappears and the engine does not start.
So, why does the spark disappear, what are the reasons and what signs may indicate a failure of the ignition coil?
- Approximately 500 kilometers before the coil’s life is over, on a cold engine the device normally starts working only after a couple of minutes of warming up. The engine starts with difficulty, but some people think that the problem is in the idle system. At the same time, the engine begins to behave unstably at low speeds. This phenomenon occurs within 10-30 seconds, so you don’t always have time to pay attention to it.
- Another short-term symptom is the engine actively shaking when starting a cold engine and holding down the gas pedal. This will happen literally for 3-5 seconds, and after pressing the pedal again, everything will return to normal.
- When accelerating or changing gears at the gearbox, the engine may produce jerks, vibrations, and the dynamics deteriorate for a short time. The downside is that such a symptom may appear for a few moments, but disappears just as quickly.
- The most obvious sign is the complete failure of the engine to try to start. The spark disappears, and therefore the chances of starting are zero.