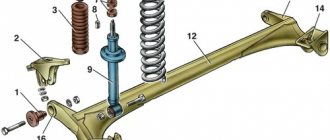
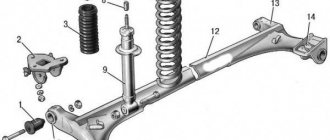
Being an integral element of the platform, the suspension of the Lada Largus has a reinforced design due to the rather massive bodies, both station wagon and van. Actually, both the front suspension subframe and the rear beam with separate localization of shock absorbers and springs are reinforced.
Lada Largus is essentially a replication of the original car model called Dacia Logan, which came out of the assembly line of Renault's Romanian subsidiary in 2006. And since 2012, after adaptation to the national characteristics of the Russian market, this super-compact model, intended for developing countries, received a rebranded version of Auto VAZ under the name Lada Largus FL.
The original, and subsequently the replication of this model, are based on the Renault family platform, namely the B0, which, according to some experts, was borrowed from Nissan.
Functional load of Lada Largus suspensions
- Comfort during movement is achieved through the interaction of mechanisms focused on smoothness, muffling unevenness and eliminating unwanted vibrations.
- Handling is characterized by an adequate response to all steering commands from the driver. Moreover, accuracy and convenience of maneuvers become important aspects when increasing or switching speed.
- The suspensions of the Lada Largus contain actively moving parts, so the safety of the entire vehicle largely depends on them.
Front suspension
One of the main tasks of this element of the chassis is to ensure smooth movement. When the front wheel encounters an uneven road, the body continues its movement along the previously traversed trajectory, “damping” all vibrations.
Its design is much more complex than the rear variation, since it provides the ability to change the position of the front wheels, thereby providing effective control of movement in all directions. This is justified by a number of design features that are subject to additional loads.
It is worth noting that the front part of the Lada Largus, like any other car, is heavier than the rear, because the weighty units of the power and chassis are concentrated there. Undoubtedly, this causes a large load, which contributes to its rapid wear. Thus, the condition of the front suspension is directly related to the safety of driving the car.
Rear suspension
As a rule, the rear suspension of the Lada Largus is much simpler than the front: the wheels of the same name are not required to change the angle of rotation, and their orientation is focused only on vertical movement. But, despite this, the condition of this unit is also related to the safety of movement and the corresponding level of comfort.
In relation to it, semi-dependent and dependent varieties are considered. In the first case, the suspension consists of two levers fixed between the body and the wheels, which provides optimal kinematics. The dependent suspension is connected by a rear axle beam, which is attached to the body by trailing arms.
conclusions
Largus can rightfully be called a reliable car. The parts of its chassis have a long service life and do not cause unpleasant surprises. Overall, this is a decent car for every day and for all occasions. Despite the fact that after restyling it increased in price, it still has no analogues.
In the comments, be sure to write what your opinion is about this car and share your experience of owning it.
Detailed review of the new car Lada Largus Cross FL
Malfunctions and ways to eliminate them
During its operation, the suspension can cause not only all sorts of sounds in the form of knocks and squeaks, but also direct problems with the steering. If this part behaves suspiciously, it should be immediately fully diagnosed.
Noise and knocking while driving
The main reasons for the suspension failure of the Lada Largus are related to uneven roads. For example, a knocking sound in the front suspension of a Lada Largus begins after the car falls into a hole or hits a bump.
In addition, the inexperience of the car owner is not the last circumstance that leads to repair of the chassis. Having noticed a pothole belatedly, the brake pedal is pressed, which only increases the load several times and aggravates the situation.
The problem may be faulty shock absorbers, worn ball joints, loose fastening bolts, or lack of lubrication. If worn parts need to be replaced, this should be done immediately. When a malfunction of the suspension is associated with the fixing force or lack of lubricant, tightening them and appropriate lubrication will correct the situation.
If there is noise or knocking in the rear suspension, in addition to rubber seals and torque rods, attention should be paid to the condition of the exhaust pipe. A detailed analysis of the entire mechanism allows you to accurately determine the cause of the breakdown and eliminate it in a timely manner.
Departure of a vehicle from straight-line motion
Most often this is due to different tire pressures, incorrect wheel alignment or incorrect bearing clearance. These problems are resolved by checking and adjusting the characteristics to suit normal operation.
In some cases, even disassembling the suspension using specialized equipment is required. For example, if the front suspension arm of a Lada Largus is severely deformed, then the entire axle will need to be replaced.
It is worth noting that tire defects may not be immediately noticeable, so you should swap the wheels of the front of the car. If the direction of care changes, then the problem is in the condition of the rubber. When the loss of strength of one of the springs is to blame, it will immediately compress, affecting the visual tilt of the car body.
Vertical oscillation of the front wheels
This situation most often develops during braking or accelerating to maximum speed. The passenger car begins to tilt, and under the influence of road unevenness it makes oscillatory movements. This is justified by a possible imbalance of the wheels, settling of the suspension springs or failure of the shock absorbers.
In this case, the anti-roll bar may simply not work during acceleration and braking. Here you should check the condition of all parts and, if they are worn, replace them by securely tightening the fixing bolts.
Such vertical vibrations are unacceptable, since the chassis and steering perceive them as natural dynamic loads, which ultimately leads to loss of controllability.
Fuel system
The fuel tank of Largus is plastic, the filling volume is 50 liters.
There is no remote fuel filter like the Granta, Kalina, Priora, or classics. There is only a mesh on the fuel pump in the fuel tank. If you notice that the car’s throttle response has decreased, it has become worse at accelerating, then this is a reason to check the degree of contamination of the mesh and, if necessary, clean it.
I test drove the luxury Lada Largus Cross. I tell you in detail about my impressions
Due to the use of low-quality gasoline, it can clog very quickly. Otherwise, the Largus fuel system does not have any shortcomings or weaknesses. There is a full-size spare tire at the rear of the vehicle. This solution has pros and cons.
The advantage is that, being under the bottom, the spare wheel does not “eat up” the useful volume of the luggage compartment. Cons - the wheel rim becomes covered with heavy rust within just a few seasons. And the suspended structure in most cases turns sour within one winter. In this regard, the process of dismantling the spare tire can become very complicated.
Suspension on Lada Largus
It’s easy to understand how important suspension is in a modern car by taking an ordinary cart as an example. As a rule, driving on bumpy roads on it is not synonymous with comfort. In order to smooth out all the irregularities and dampen vibrations as much as possible, rear and front suspensions were invented. In addition, this system connects the wheels to the body.
The purpose of all pendants is the same. But the design features are different. For example, Lada Largus is a representative of the budget class on the B0 platform and has a simple suspension arrangement.
Stretcher
Largus became the first Lada car to feature a full-fledged subframe in its design. In previous reviews, I already wrote that the subframe is an important and necessary part of a car’s suspension. It promotes structural rigidity, evenly distributes the load from the suspension onto the supporting body, and prevents local overloads of the power elements of the body.
In addition, the subframe ensures the accuracy of the location of the suspension elements during their installation. Due to the presence of a subframe in Largus, only one parameter is adjusted at the wheel alignment post - wheel alignment.
The Lada Vesta has a composite subframe, the side members are separate. At Largus we have a non-separable one-piece subframe. The Lada Largus uses a rack-and-pinion steering system with a speed of 3.21 and a hydraulic booster.
The steering gear is mounted on a subframe and secured with two bolts. A version without hydraulic booster with a speed of 4.63 is also available. Electric power is not used on Largus. Taxiing at Largus is clear and informative. The steering rack lasts a long time and will not present any problems up to 200 thousand km. But the steering tips can begin to tap already up to 100 thousand kilometers.
Characteristics and design
The suspension on the Lada Largus has proven itself to be reliable, soft, energy-intensive and as simple as possible. Like many components, it migrated almost unchanged from Renault Logan. Manufacturers decided not to modernize this Logan part, which was recognized by car enthusiasts as indestructible on Russian roads.
Front suspension device
The main structural details are the following elements:
- stretcher;
- levers;
- spherical bearing;
- silent blocks;
- repeated fist;
- hub;
- shock absorber with spring;
- anti-roll bar.
Experienced car enthusiasts will immediately understand that structurally this is an ordinary MacPherson, but there are some dissimilar parts. Unlike other models of the Volzhsky Automobile Plant (with the exception of the Vesta family), the Lada Largus suspension is equipped with a subframe to which an anti-roll bar with silent blocks is attached.
The front suspension of the Largus is independent, and the subframe serves to increase rigidity.
Also, in previous AvtoVAZ models, the ball joint is changed separately from the lever. Largus uses the Logan suspension platform, so here the ball joints are changed only together with the lower arm. At the same time, we must pay tribute: the suspension design is reliable and durable.
The next difference between Largus is the mounting of the anti-roll bar. Here it is not rigidly attached to the strut with the shock absorber; it is attached directly to the lower arm. In this design there are no so-called tips, which are located on the rod connecting the strut and stabilizer. They usually wear out over time and become a source of suspension noise.
If you do not take into account the ball joint, which is assembled with the lower arm, the Largus front suspension is simple, and most importantly, repairable. Basically, problems begin to arise with fairly active mileage (more than 100,000 km). Due to the simplicity of the device and the small number of elements, even beginners can diagnose a fault.
Largus rear suspension diagram
Rear suspension features
The basis of the entire structure is a semi-independent beam. Inside it there is a stabilizer bar, which is rigidly fixed to the lower arms. The latter, in turn, (namely, the amplifiers) are supported by shock-absorbing springs.
The main feature of the Largus rear suspension is that the spring and shock absorber are not a single module, but are located separately from each other.
Structurally, the Largus rear suspension consists of a beam, shock absorbers, springs and silent blocks (not counting fasteners and other connecting elements). There are usually no special problems with the rear suspension, even with high mileage. The system, both front and rear, is reliable and easy to repair, and spare parts are always available.
Steering
Two types of steering gear are used: with power steering and without power steering. In both cases, the steering rack lasts up to 200 thousand km.
Steering ends may begin to knock at 100 thousand km.
Read reviews about the work of Largus State Police.
Restoration of suspension elements of Lada Largus
Repair work mainly involves the removal and replacement of worn parts. To carry them out you will definitely need the following set of tools:
- jack (if there is no lift);
- set of socket heads and wrenches;
- screwdrivers;
- hammer, mounting blade, etc.
Suspension repairs at the rear and front differ slightly. In addition, the front suspension is structurally more complex. Therefore, most of the work on replacing failed parts is considered from the front.
Replacing the anti-roll bar
Elements crack, tear, and wear out as they wear out, causing play to appear at the joints. Therefore, in the case of Largus suspension stabilizer struts, it is necessary to replace worn rubber-metal parts. Replacing the Lada Largus stabilizer is as follows.
- Raise the front of the car (or use a lift).
- Unscrew the stabilizer mount to the arms (you should first clean the screw from dirt so you can use a spanner).
- When unscrewing the fastener (nut), use a wrench to hold the screw, preventing it from turning.
- Remove the lower rubber bushing.
- Pull out the screw along with the bushing and the plastic washer located below.
The fasteners of the stabilizer and suspension arm are removed in the same way. New parts are installed in the reverse order of removal. When tightening the fasteners, do not overtighten. To replace the rod pads, you need to unscrew the bolt securing the bracket and subframe using a spanner. Next, you should dismantle the pillow and install a new part in its place in the reverse order. The suspension bar cushion on the other side is changed in the same way.
To dismantle the rod itself, you need to unscrew the fastenings on the lever side and remove the brackets. If, upon inspection, signs of wear are found in the places where the cushions are attached, it is better to change the bar.
Replacing levers
On Lada Largus cars it is not necessary to change them so often. This is usually done when changing ball joints or silent blocks. To work, you also need to hang the entire front part - if you lift only one side, the stabilizer will not allow you to remove the lever.
To remove it, you will need to unscrew the attachment of the rod to the lever and remove the motor protective shield. Next, the bolt securing the ball joint and steering knuckle is unscrewed. This bolt needs to be pulled out if you can’t knock it out with a hammer. Use a flat-head screwdriver or pry bar to loosen the connection between the ball joint and the steering knuckle.
The next step is to press the lever down. The ball end will disengage with the steering knuckle. Use a socket to unscrew the bolt securing the bracket to the subframe, after which it can be removed.
Front suspension
See also Rear suspension device
The front suspension is independent with telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers and coil springs.
The front suspension consists of stamped lower wishbones and an anti-roll bar mounted on the front suspension subframe.
The front suspension subframe is stamped-welded, box-section, secured in the front part with two bolts to the side members of the engine compartment, in the rear part with two bolts to the power elements of the front panel.
Front suspension: 1 — front suspension arm; 2 — subframe; 3 — bolts securing the suspension arm to the subframe; 4 — anti-roll bar; 5 — bracket for fastening the stabilizer bar; 6 — shock absorber strut and shock absorber spring; 7 — steering knuckle; 8 — bolt securing the anti-roll bar; 9 — coupling bolt connecting the steering knuckle and the ball joint pin; 10 — ball joint; 11- rear silent block of the lever (front silent block is not visible);
General view of the MacPherson front suspension assembly: 1 – suspension subframe; 2 – right and left front suspension arms; 3 – steering knuckle with hub and bearing; 4 – shock absorber; 5 – anti-roll bar
Subframe: 1 – places where the subframe is attached to the front part of the body; 2 – places for attaching the front suspension arm to the subframe; 3 – rear mounting points for the subframe and anti-roll bar; 4 – bracket for fastening the rubber suspension cushion of the exhaust system; 5 – bracket for securing the rear support of the power unit.
Front suspension lever: 1 – lever; 2 – ball joint; 3 – ball joint boot; 4 – silent blocks of the suspension arm (front and rear)
Anti-roll bar: 1 – nut; 2 – lower rubber bushing; 3 – rubber-metal bushing; 4 – plastic washer; 5 – upper rubber bushing; 6 – screw; 7 – anti-roll bar; 8 – rod fastening bracket; 9 – stabilizer rubber cushion
Front suspension shock absorber : 1 – shock absorber strut; 2 – shock absorber spring; 3 – compression buffer with boot; 4 – nut for attaching the shock absorber to the body; 5 – support washer; 6 – nut for fastening the upper support; 7 – upper shock absorber support; 8 – upper support bearing; 9 – upper thrust spring cup
About modern car suspensions
The suspension connects the body to the wheels, absorbs the forces acting on a moving car, and dampens vibrations. Suspension settings directly affect the car's handling.
The suspension design is divided into four groups of parts. Conventionally, because in various schemes some elements can perform the functions of two groups, and sometimes even three.
The first group is elastic parts that absorb the effects of forces transmitted from contact with the road surface (springs, springs, torsion bars or hydraulic pneumatic elements). The second group is guide rods that transmit lateral and longitudinal forces and their moments, as well as connecting the body with other suspension elements, transmission and wheels. The third group is elements that dampen vibrations (shock absorbers or shock absorber struts). The fourth is the suspension fastening elements.
There are also dependent, independent and semi-independent suspensions.
Actually, the car inherited the first versions of the suspension design from the cart. The oldest of them is the spring; it was used by the Romans back in the first century BC. It is still widely used today on commercial vehicles and SUVs. In the production of modern springs, advanced materials are used, for example, instead of metal it can be reinforced plastic.
On front-wheel drive vehicles, McPherson struts are most often used in the front suspension design. This is actually a shock absorber and spring assembly. It is attached from below to the steering knuckle, from above to the roof splash guard. This scheme also includes one or two wishbones. The main advantages of the McPherson suspension are its compactness and ease of installation, which is important both for manufacturability and ease of repair. On some cars, McPherson struts are also used in the rear suspension.
Also on modern passenger cars, the double wishbone front suspension design is widespread. Springs, torsion bars, pneumatic elements or hydropneumatic devices are used as elastic parts in this scheme.
Multi-link suspension is the name given to a design that includes four or more levers and is used on both the front and rear axles. This suspension allows for better handling and was initially used primarily on premium cars. Now it can be found on cars in the mass segment. The main disadvantage of this design is the high cost and complexity of repairs, since many parts and fasteners have to be replaced.
On cars in the mass segment, a torsion beam is most often used in the rear suspension design; it is also called a torsion beam. This type of suspension is semi-independent, since the wheels can turn at a small angle as a result of elastic deformation of both the beam itself and the fastening elements. Its main advantages are compactness, low cost, and manufacturability. But there are also serious drawbacks. The main one is that during long-term operation, fatigue cracks may appear in the beam, which are difficult to diagnose.
Recently, premium segment cars have increasingly used air suspension with integrated control. They allow you to provide constant ground clearance regardless of the vehicle load, as well as change the ground clearance depending on the vehicle speed and road conditions. This scheme is most relevant for crossovers and SUVs. In this design, pnsvmoelmsnts or hydropneumatic devices are used. The suspension is operated using microprocessors. The main disadvantages of this scheme are high cost and complexity, both in production and repair.
Active suspensions have recently become widespread on premium segment cars, in which the stiffness of the elements and ground clearance are adjusted using electric drives. Some sports cars even have active anti-roll bars. In the future, the suspension will be even more integrated into the overall complex of active safety features for the car.
Video
Ways to increase the clearance of Largus
The domestic station wagon is very popular due to its unpretentiousness and reliability. One of the important indicators is solid ground clearance. Transporting goods with these vehicles is a common occurrence. And this inevitably leads to an increase in the load on the suspension, namely on the shock-absorbing struts, which sag due to weight, resulting in a decrease in ground clearance.
We must not forget the quality of Russian roads. It is sometimes impossible to move through potholes and potholes without damaging the suspension. In any case, the amount of ground clearance in this regard is crucial. Because of these factors, many Largus owners try to increase the ground clearance with their own hands. Today there are several ways to do this inexpensively and quickly.
Increasing ground clearance with your own hands
In order to increase ground clearance (suspension lift), car owners use several basic techniques:
- installation of wheels or tires with a larger radius;
- installation of special spacers for shock-absorbing struts;
- replacing the springs with stiffer ones, as well as installing extended shock absorbers.
Some people use air suspension for these purposes. From the point of view of rationalism (and Largus is mainly used by people who prefer the practicality of a station wagon), this is unjustified. Firstly, the equipment is expensive, and secondly, not every car owner can install air suspension with his own hands. Plus, the compressor and receiver will take up useful space in the trunk, which is again impractical.
This type of suspension tuning is not popular.
Installation of wheels with a larger radius
Largus comes standard with 15R wheels. Many motorists choose the 16 or 17 radius option instead of the one proposed by the factory. Additionally, this makes the car's exterior more attractive. However, this option also has a significant drawback, namely the unstable position of the car when driving, as well as malfunctions in the ABS system and some related sensors.
Installation of spacers
The most budget option (and popular) is to install special spacers, which are sold at any auto parts store. The only thing that is required from the car owner is the removal of the suspension struts. The parts themselves are unified and suitable for many VAZ cars. Spacers are installed between the rack and the body bowls (as an option - between the beam and the rack).
Replacing strut parts
One of the best methods for increasing ground clearance is to install stiffer springs and longer shock absorbers. As a rule, such racks are approximately 20 mm longer than standard devices. In combination with reinforced springs, they are able to significantly increase ground clearance, and the car does not sag all the way when transporting the maximum permissible weight of cargo. The only drawback is the higher price of such kits.
Repairing the suspension yourself and increasing the ground clearance on the Lada Largus is easy to do if you have at least minimal car repair skills. If you have never done this before, it is still recommended to carefully study the instructions. And if you are unsure of your own abilities, it is better to turn to qualified car service specialists.
Source