We reveal such a problem on a NIVA car as non-working (not turning on) radiator cooling fans. What could be the reasons? The first thing you need to do is check the fuses; they can be changed in a couple of minutes.
The fuses are located here:
It's 30 amp. We take them out and check them for integrity. If the fuses are blown, there are several reasons for this that will need to be corrected, otherwise they will continue to burn.
One of the reasons is that the fans are wedged, the fuses cannot withstand the load and burn, the second reason is that the fuses are not 30 Amps, but 15 or 20, they are not designed for such a load and they burn. The third reason is these two plugs:
It happens that they become clogged with dirt, water, rust, short out, or melt. Very often they close up when overcoming water obstacles, then dry out and start working again.
The fourth reason is the rest of the wiring, you need to look along the entire length, look for fraying, melting, etc. We have listed everything that relates to fuses, let's move on.
Then pay attention to whether the fans are jammed, this can happen due to wear of the bearings, try to twist the blades, just do this not with your hands, but with a stick.
From this coolant temperature sensor, the controller reads information to turn on the fans:
If, for example, your radiator fans are constantly running and they never turn off, then most likely the problem is in this sensor.
We tried to write in text the most common reasons why the radiator fans on the NIV do not turn on or do not work, if this does not help you, watch the video below for more details, several more possible reasons are given there, and also tells how to emergency and force start radiators in the field.
More details about the problem of fans not working on Niva:
The connection diagram for Niva VAZ-21214 fans is identical to the diagram for other cars of the VAZ family. The only difference is the presence of two fans, which are turned on using two relays. This is caused by the engine working under heavy loads when driving off-road. In city conditions this is practically not necessary, with the possible exception of driving in traffic jams in hot weather. When turned on, fans create some discomfort as they make noise. You can reduce noise by reducing the rotation speed of the electric motors or turning off one of the fans. In the second case, the second fan can be turned on forcibly using a button or key.
Niva with ECM
As you know, the first Russian SUV Niva was born back in the days of the Soviet Union. At that time, in the USSR they did not even think about an electronic engine control system; the entire process of operation of the internal combustion engine was mechanical. The engine was supplied with fuel through a carburetor. At present, the Niva still continues to be produced, but with its ancestors, the modern Niva has only the body left and it has undergone minor modifications.
The carburetor was replaced with an injector, the interior was changed and the appearance of the car was transformed, but still the Niva remained Niva. The legendary Niva cross-country ability did not deteriorate after these modifications, but became much more comfortable.
In this article we will talk about the sensors of the engine control system in the injection Niva, namely, it describes in detail each of the sensors, where it is located and what function it is responsible for, as well as the signs of sensor malfunction are described in detail.
Fan malfunctions
Let's look at what malfunctions of the Niva cooling fan may occur and how to identify them. The most common malfunction is blown fuses.
The fuse blows.
A single occurrence of such a malfunction does not indicate a faulty wiring or the fans themselves. During operation, fuses heat up and eventually fail. They are easy enough to replace. They are located on a carburetor car in the lower fuse block, and on an injection car in an additional block near the driver's door pillar.
If the fuses blow immediately when the fans are turned on, then it is necessary to find a short circuit or replace the fan. To determine the location of the malfunction, it is enough to disconnect the connector on the fan motor and connect the wires on the radiator sensor with each other with the ignition on.
On an injection engine, to check it is necessary to remove the chip from the temperature sensor, which is located on the thermostat. In this case, the engine control unit will go into emergency mode and activate a program for working with a faulty temperature sensor and turn on the fan relay. If the fuse burns out, then it is necessary to find and eliminate the short circuit. If the fuse remains intact, then the problem is most likely in the fan motor. Faulty fans are stuck or difficult to rotate. This may be caused by the stator magnet falling off or the armature bushings wearing out. A faulty fan should be replaced.
The fan does not turn on
Another common malfunction is when the fan does not turn on when the operating temperature is reached. The reason may be a malfunction of the fan sensor on a carburetor car or the engine control unit on an injection car, a relay malfunction, broken wires, or a malfunction of the fan motor.
It is better to start troubleshooting by checking the temperature sensor or control unit. This is done as described earlier by bridging the wires on the carburetor engine sensor or removing the chip from the temperature sensor on the injection engine. If the fans do not work, then you need to check the power relay.
The relays are located under the instrument panel on the front wall. To check, remove the chip from the relay and check for the presence of power at pins 30 and 85. If there is no power, check the condition of the fuse and wires. If there is power, connect terminals 84 and 85 of the relay with a test lamp. If the warning lamp does not light up, then the wire from the ECU connector to the relay socket is broken or the ECU itself is faulty. A lit lamp indicates a relay malfunction.
To test the relay, connect pins 87 and 30 with a piece of copper wire, which should trigger the fans. If this does not happen, then connect a test lamp to the connector without removing the jumper from the relay connector. If the lamp does not light up, then connect one end of the test lamp to the housing, and with the other, check for the presence of a plus on the connector. If the control lamp does not light up, then there is a break in the wire from the relay to the fan connector. Accordingly, the glow of the lamp indicates poor contact of the negative wire with the body or a wire break. The presence of power and minus indicates a malfunction of the electric motor.
The lifespan of a Niva SUV engine largely depends on how efficiently the VAZ-2121 cooling works. After all, overheating is the first enemy of the power unit, leading to expensive repairs.
This is why the serviceability of the components and elements of the cooling circuit is so important. In order to be able to service them and identify malfunctions, you need to understand what the circuit consists of and how the Niva’s cooling functions.
Electronic engine control unit (ECU)
An ECU is a kind of computer in a car; it is in this device that the entire operation of the internal combustion engine is corrected. All sensors that are installed in the car transmit readings specifically to this unit, and based on the readings, it makes changes to the operation of the engine, which affects both the engine speed and its consumption.
Symptoms of ECU malfunction:
There can be a huge number of signs of malfunction of this unit, because signs of failure of one sensor may even indicate failure of the unit.
Mass air flow sensor (MAF)
This sensor is located near the Niva air filter box. Air flows through this sensor, which is necessary to form the air-fuel mixture. The sensor records the amount of air passing through it and sends signals to the electronic engine control unit (ECU).
Signs of a DMRV malfunction:
- Loss of vehicle dynamics;
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Unstable idling (speeds fluctuate);
- Difficulty starting the engine when the engine is warm;
Crankshaft position sensor (CPS)
The Niva DPKV is installed in a special hole in the oil pump drive cover. This sensor is responsible for setting the ignition timing. The sensor takes readings from the crankshaft pulley, which has teeth and in one of the places there is “caries”, that is, several pulley teeth are missing. It is “caries” that the DPKV understands in what position the crankshaft is. The sensor itself resembles an inductive coil, which generates impulses when the crankshaft rotates and transmits them to the computer.
If the sensors fail, the car will not start.
Signs of DPKV malfunction:
- The car does not start;
- The car stalls spontaneously;
- Uneven operation of the internal combustion engine;
Operating principle
The cooling system of VAZ Niva models does not come into contact with the atmosphere in operating condition, and therefore requires pressure. The coolant is antifreeze with a freezing point of 40 degrees Celsius. The composition of the solution is water and ethylene glycol. The total volume of the cooling circuit is 10.7 liters. Antifreeze can boil after a temperature of +110 degrees Celsius.
The main functional unit in the system is the thermostatic valve, which distributes the coolant flow depending on the engine temperature. The thermostat, controlled by a temperature-sensitive sensor, regulates the direction of movement of antifreeze. A simplified work flow looks like this:
- Before the internal combustion engine warms up to operating temperature (+90 degrees Celsius), the cooler moves along a small circuit (interior heating radiator, thermostat, power plant) using a pump.
- The damper opens towards the large circuit where the radiator is located, at a temperature of + 80 degrees Celsius. Afterwards, virtually the entire cooler moves along a large circuit, mainly cooling through the radiator.
- The small ring is not blocked, but a minimum of antifreeze enters it due to pipes of a smaller diameter.
- In model 2121, the fan is mounted on the axis of the water pump and constantly directs the air flow to the (BC). Cooling fans in Niva 21214 and 2131 are paired with electric drive. They are activated alternately or together using a temperature sensor (switching temperature is about 100 degrees Celsius).
- When heated, excess antifreeze is sent to the expansion tank, increasing the pressure in the system, which reduces the boiling threshold of the coolant.
In summer and during transition periods in models with an injector, the movement of the cooler is limited by a special tap. The Niva Chevrolet model does not have such a blocker, so the heating is turned off by directing the air flow past the heat exchanger.
Coolant temperature sensor (DTOZH)
DTOZH on Niva is installed in the cylinder head outlet pipe. The coolant temperature sensor is a fairly simple element in its design. The sensor is based on a thermistor, which changes its resistance as the temperature changes.
One of the functions of the sensor is to start the electric engine cooling fans when the coolant temperature threshold is reached. The sensor is also responsible for starting the engine in cold weather; according to the coolant temperature readings, the electronic control unit forms the fuel mixture necessary for more proper warming up of the car engine. This can be replaced by the presence of high warm-up speeds at the moment of starting the internal combustion engine.
Signs of DTOZh malfunction:
- Cooling fans do not work;
- No warm-up speeds;
- Difficulty starting the internal combustion engine;
- Increased fuel consumption;
Difference in fan connection diagram.
It doesn’t touch anything or anywhere. It is important that they wear evenly.
The initial diameter of the left hole is 6 mm, and the diameter of the leg, more precisely, the rubber band put on the leg, is 15 mm.
Let's look at the diagram Connecting Niva fans in a serial connection. The investment is cheap, but the effect is simply amazing; it’s a shame the designers at the factory didn’t think of this before. Assembly is carried out in reverse order. After this, the frame with the fans more or less normally falls into place. When removing the radiator trim, it may be that unless precautions have previously been taken to protect the screws that secure it from rust, it will be very difficult, if not impossible, to remove these screws. You can, of course, tighten the clamps as hard as you can, but as Murphy’s law says: “Everything that can go bad, goes bad,” and where is the guarantee that the pipe will not one day take or even fall off the tee? True, if something happens, with the latter it will be more difficult to unscrew the sensor back.
Heater electric motor. I had to add a third relay. When the temperature sensor is triggered, the second fan is also connected.
A useful video that shows how to remove and change fans: Important: to get to the bolt covered by the oil filter, you need to move the amplifier away from the bracket. VAZ oxygen sensor. Section: Electrical Post navigation.
Therefore, they need to be pulled out gradually. The fan does not turn off. When turned on, fans create some discomfort as they make noise. There are three rubber bands included. Well, then you can start installing the wiring. Venty on Niva 2121
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
The TPS is installed on the throttle itself and is a potentiometer. This sensor reads readings from the throttle position and transmits them to the ECU. The damper opens access to air, thereby increasing engine speed. When the damper opens, the sensor sends a signal to the control unit to increase the fuel supply, which is necessary to form a working air-fuel mixture.
The sensor that most often fails is an unreliable element of the system. Subsequently, they abandoned it and switched to an electronic throttle.
Signs of a malfunction of the TPS:
- High speed at start-up;
- Jumps in engine speed;
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Not smooth idle;
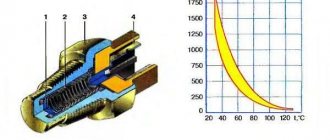
How to check the cooling fan resistor of a Niva Chevrolet?
It is a resistor
, the resistance of which changes with heating and
cooling
: from 1.3-1.8 kOhm at 30℃ to 155-196 Ohm at 90℃.
check
its performance using an ohmmeter and a thermometer. To do this, you need to remove the part, immerse it in water and measure the resistance at different temperatures.
Interesting materials:
How to find out if a person is wanted? How to recognize a person on Instagram online? How to find out if a person has blocked you on Telegram? How to find out if a car is registered to a person? How to find out a person's IP number? How to insert a link to a person on Facebook? How to search for people by city on Instagram? How to tag a person on Instagram? How to mention a person in a comment on Instagram? How to insert a person's name on Instagram?
Knock sensor(DD)
The knock sensor is installed on the right side of the vehicle's cylinder block. A DD is needed to catch detonations in the engine and adjust the fuel mixture. The sensor itself is made on the principle of a piezoelectric element and, in the presence of vibrations in the engine, transmits impulses to the ECU, which in turn adjusts the fuel mixture.
Signs of DD malfunction:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Uneven operation at idle (increased vibrations);
- Jerks when the car moves;
Purpose and design
This is a module designed to be included in the on-board circuit of a motor that consumes high current. The fan motor is powered by electricity with a current of 20-35A, which is unacceptable for inclusion in a low-voltage control system - the wiring will melt. The Niva has only three relays, two for the left and right fans separately and one common. Each device has its own number in the on-board network. The principle of operation and purpose of the relay is relevant for cars of all types 2004, 2010, 2022 and other years of production.
Inside, the relays have an identical design. There is a low part, a transformer and a high part. Also two pairs of contacts, one normally closed, the second open. When a pulse is applied to the lower part, a magnetic field is formed on the windings, and the contact group on the high side closes - power is supplied to the fan motor.
The cooling screw operates in two modes. When the engine heats up to 99 degrees Celsius, the first fan is turned on, after passing the 101⁰C mark, the second one is connected. If the system cannot cope, the motors switch to higher speeds.
Fan relay diagram
The figure shows the power supply circuit for the electric fans of the cooling system of the installation. Design elements are presented by numbers.
- 1/7 – left and right fan motors;
- 2 – additional power relay;
- 3 – fuse;
- 4 – power controller;
- 5 – auxiliary resistor;
- 6/8 – main relay for turning on the right and left electric motor, respectively;
- A/C – negative/positive battery terminal;
- B – to the main ignition relay.
Oil pressure sensor (OPS)
The oil pressure sensor is located on the right side of the cylinder block and is screwed into the oil line fitting. This sensor is necessary to monitor the oil pressure in the engine. As you know, operating a car with low oil pressure in the internal combustion engine can damage it. When the oil pressure in the internal combustion engine decreases, the sensor closes the contact and sends a signal to the Niva instrument panel, lighting up the oil pressure indicator in the form of a red oil can.
Signs of DDM malfunction:
- Constant lighting of the oil pressure lamp;
- Oil leak from the sensor junction;
Idle air control (IAC)
This sensor is located, just like the TPS, on the Niva’s throttle valve. The essence of the sensor's operation is to open and close the channels through which air flows to operate at idle speed. The IAC is involved in the operation of the internal combustion engine only at idle; when the speed increases, the regulator is switched off. IAC is a kind of DC motor with worm gear. Quite often the sensor fails. Subsequently, this sensor was abandoned in favor of an electronic throttle.
Signs of IAC malfunction:
- Lack of XX speed (engine stalls);
- Increased speed at idle;
- Increased fuel consumption;
Phase sensor (PF)
The phase sensor, also known as the camshaft position sensor, is installed in the cylinder head plug. Designed for phased fuel injection. Reads readings from the camshaft and transmits them to the computer; these readings are necessary for accurate distribution of the fuel mixture between the cylinders.
Signs of DF malfunction:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Increased engine vibrations;
Brake pedal sensor
The brake pedal sensor is installed on the pedal assembly under the Niva's steering column. In cars without the E-GAZ system, it is only responsible for turning the brake lights on and off. In cars that have an electronic throttle and therefore an electronic gas pedal, this sensor affects the operation of the pedal. If the brake sensor breaks down, the gas pedal stops working.
Signs of malfunction:
- The gas pedal does not work;
- Jerking when moving at a constant speed;
- Loss of power and vehicle dynamics;
Job
The Shniva cooling system has two active cooling elements. There is a fan for the heater radiator and the main heat exchanger. The following information is relevant for cars of 2010 and other model years.
Fuses are responsible for the correct, stable operation of devices. Fuse links will protect the device from power surges and short circuits.
Pulley fan fuse: where is it located?
Located in close proximity to the corresponding relays. The stove insert is located in the main mounting block under number F18. A 25 amp fuse protects multiple circuits at once.
Speed sensor (DS)
The speed sensor of the Niva car is installed in the transfer case. The function of the sensor is to transmit vehicle speed readings. The sensor also forms the fuel mixture; when the car is moving at neutral speed, you can notice that the speed is slightly higher than when the car is running at XX while standing still. Increased speed when driving is necessary to avoid dips when turning on the speed and sharp acceleration.
Signs of DS malfunction:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- There are no increased speeds when driving at neutral speed;
- Dips during acceleration;
- The speedometer does not work;
Circuit breakers
The electrical circuits of Niva Chevrolet cars produced before and after 2009 are different. In both cases, 50-amp fuses protecting the electric fan power circuits are located in an additional unit. It is located behind the glove box on the passenger side of the cabin. The figure shows where the fan fuses are located.
If the permissible current is exceeded, the insert melts and the circuit opens. Therefore, fuses are the first thing to check if the electric cooling fan does not work. The performance of a part can be assessed visually or using an ohmmeter (multimeter). To do this, you will first have to remove the fuse from the socket.
Oxygen sensor (DC, lambda probe)
An oxygen sensor, also known as a lambda probe, is installed in the exhaust system of a car. In some versions of cars, two sensors are installed before the catalyst and after the catalyst. Two sensors are installed in Niva with EURO-4 standards. The sensor captures exhaust gases and transmits readings to the ECU. If there is a large amount of unburned gasoline in the exhaust gases or, on the contrary, a small amount, then the DC makes changes to adjust the fuel mixture.
Signs of DC malfunction:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Loss of vehicle dynamics;
- Poor engine starting;
How to change antifreeze on a VAZ 21214 Niva
The Niva SUV, in all modifications, is very popular in Russian spaces. This is due to good maintainability, low price and excellent maneuverability. To ensure reliable operation, you should undergo all maintenance on time, in particular, replace the coolant.
The liquid system with forced circulation of the VAZ 21214 car is designed for effective heat removal. It fully copes with its task, you just need to keep it in good condition.
Ignition module (IZ)
The ignition module is installed on the left side of the engine on a bracket. This sensor is involved in the formation of ignition. It is this that produces the high-voltage voltage necessary to create a spark in the combustion chamber of the internal combustion engine. The module has two coils, they are also autotransformers, which produce a spark in pairs, each coil for two cylinders. If one of the coils fails, two cylinders fail at once.
Signs of malfunction of the MH:
- Troubles the engine;
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Increased engine vibrations;
- Loss of traction and dynamics;
Checking and removing fans
To understand whether they work or not, you need to disconnect the connector from their motors, and connect a lamp to the wires through which voltage is supplied; we do the same with the sensor; if both lamps light up, then the problem is in the fans.
To remove them you need to do the following:
- Disconnect all wires
- Removing the upper pipe
- Removing the bumper
- If there is an air conditioner, bend the tubes (this must be done carefully, as they may burst) or drain the freon (filling it back will not be cheap), then remove the air conditioner radiator.
- You need to loosen the nuts on the radiator casing
- Tilt the radiator so that you can remove the fan unit
- Unscrew the bolts that secure the block and remove it
After removal, it is recommended to immediately replace both with new ones, since there is a possibility that a little time will pass and the second element will fail and all replacement work will need to be done again. You can do this procedure from below, but you will need special equipment, and you will need to move the engine ten centimeters back, which is very labor-intensive.